The global RC turbine jet market has experienced steady growth, driven by increasing demand from hobbyists, defense training applications, and drone technology advancements. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global radio-controlled aircraft market was valued at approximately USD 3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.5% from 2024 to 2029, with turbine-powered RC planes representing a high-performance segment within this space. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights the rising adoption of advanced propulsion systems in hobby-grade aircraft, attributing growth to improved turbine efficiency, lightweight materials, and expanding online communities. As the appetite for realistic, high-speed aerial models grows, so does the number of manufacturers specializing in turbine RC jets. From precision engineering to innovative design, a select group of companies has emerged as leaders. Here are the top six turbine RC plane manufacturers shaping the future of high-performance remote-controlled aviation.
Top 6 Turbine Rc Plane Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Banana Hobby
Domain Est. 2006
Website: bananahobby.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsShop Banana Hobby for RC airplanes, EDF jets, turbine jets, warbirds, trainers, gliders, LiPo batteries, chargers, spare parts & accessories….
#2 to Pilot
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pilot-rc.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Pilot-RC. New Pilot-RC Elster Jet SU-30 110″. New 3D Foam plane : EDGE 540 39″. New 3D Aerobatic 120cc plane : Sbach 342 V2 103″. Tap to unmute….
#3 Turbines RC
Domain Est. 2013
#4 Jets
Domain Est. 2017
Website: swiwinusa.com
Key Highlights: At our RC jet plane landing page, we offer a wide range of turbine-powered planes to suit every taste and skill level. From sleek and aerodynamic sport jets ……
#5 to Skymaster RC Jet Models Web Site
Domain Est. 2017
Website: skymasterjets.net
Key Highlights: My Israeli scheme Skymaster F-15 duel AMT turbines with all powerbox equipment is finally up in the air ! Maiden flight plus 2 more and she’s just perfect !…
#6 FTL Innovation
Domain Est. 2024
Expert Sourcing Insights for Turbine Rc Plane
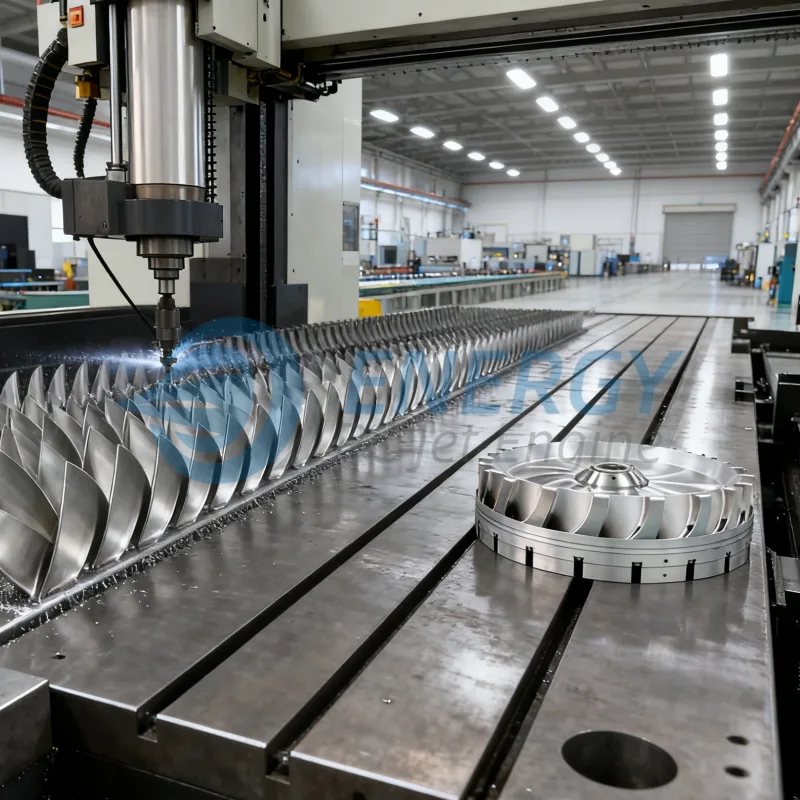

2026 Market Trends for Turbine RC Planes
The turbine-powered remote control (RC) aircraft market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer demands, regulatory considerations, and expanding applications beyond traditional hobbyist circles. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the market landscape.
Rising Accessibility and Democratization
While historically considered the pinnacle of RC aviation due to high costs and complexity, turbine RC planes are becoming more accessible. By 2026, expect a continued trend toward more affordable entry-level turbine systems and ready-to-fly (RTF) or almost-ready-to-fly (ARF) models. Manufacturers are investing in cost-effective turbine engine designs and simplified integration, lowering the financial and technical barriers to entry. This democratization will expand the user base beyond affluent enthusiasts to include more intermediate hobbyists and specialized training institutions.
Advancements in Turbine Technology and Efficiency
Technological innovation will be a major driver. By 2026, turbine engines are expected to feature improved fuel efficiency, reduced noise signatures, and enhanced reliability. Developments in materials science will lead to lighter, more durable components, improving performance and safety. Integration with advanced digital engine control units (DECU) will provide better throttle response, monitoring, and diagnostics, making turbine operation safer and more user-friendly. Hybrid or electric-assisted turbine systems may also emerge, offering enhanced control during startup and low-speed operations.
Integration with Digital and Smart Technologies
The convergence of turbine RC planes with digital ecosystems will accelerate. Expect widespread adoption of telemetry systems that provide real-time data on engine parameters, GPS location, altitude, and flight dynamics directly to ground stations or mobile devices. Artificial intelligence (AI) could assist in flight stabilization, anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) flight simulation will play a larger role in pilot training, reducing risks and costs associated with learning to fly high-performance turbine models.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Safety Standardization
As turbine RC planes become more prevalent and powerful, regulatory bodies worldwide are expected to implement stricter guidelines by 2026. Issues such as noise pollution, flight altitude restrictions, and operational safety in proximity to populated areas will prompt the development of standardized certification processes for both pilots and aircraft. Industry associations will likely push for self-regulation and safety protocols to preempt overly restrictive legislation and ensure sustainable growth.
Expansion into Commercial and Educational Applications
Beyond recreational use, turbine RC planes will see increased adoption in specialized sectors. By 2026, they are anticipated to be used more frequently in aerospace education, aerodynamic research, and defense training simulations. Their high-speed capabilities and scale fidelity make them ideal platforms for testing sensors, control systems, and flight algorithms. Universities and private research labs may invest in turbine fleets as cost-effective alternatives to full-scale prototypes.
Sustainability and Alternative Fuels
Environmental concerns will influence the market, with growing interest in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and biofuels compatible with small turbine engines. By 2026, manufacturers may begin offering turbine systems designed to run on renewable fuels, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and institutions. Additionally, advancements in electric ducted fans (EDFs) may challenge the dominance of traditional turbines in certain performance segments, pushing turbine makers to innovate in efficiency and emissions.
Niche Community Growth and Event Culture
The global community of turbine RC enthusiasts is expected to grow and become more interconnected through digital platforms. By 2026, international competitions, airshows, and fly-ins dedicated to turbine-powered models will likely expand, fostering innovation and brand loyalty. Social media and online forums will continue to play a vital role in knowledge sharing, technical support, and marketing, further solidifying the niche but passionate market segment.
In conclusion, the 2026 turbine RC plane market will be characterized by increased accessibility, technological sophistication, regulatory adaptation, and diversification of use cases. While challenges remain, the convergence of innovation and community engagement points to a dynamic and evolving future for high-performance RC aviation.
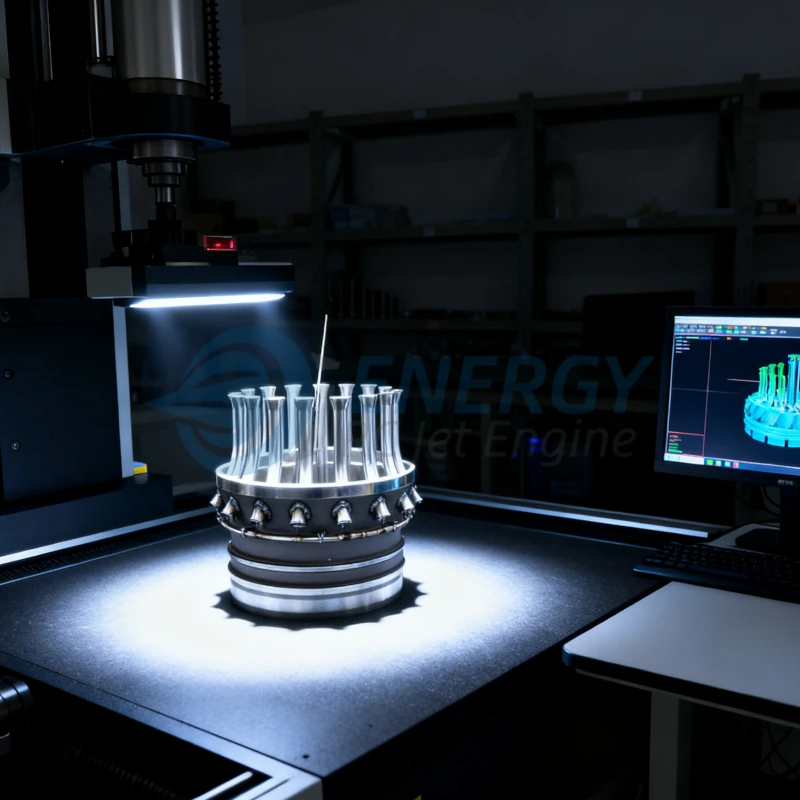

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Turbine RC Planes (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing turbine-powered RC planes—especially high-performance or scale models—can be rewarding but comes with significant risks related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Buyers and resellers often encounter pitfalls that can lead to financial loss, legal complications, or safety issues. Below are key challenges to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Performance Inconsistencies
Many turbine RC planes, particularly those sourced from less-regulated manufacturers or third-party suppliers, suffer from inconsistent build quality. Components such as airframes, turbine mounts, fuel systems, and control linkages may be improperly aligned or constructed from substandard materials. This can result in in-flight failures, reduced lifespan, or difficulty achieving advertised performance metrics. Buyers should verify certifications, request detailed build logs, and, if possible, inspect units in person before purchase.
Counterfeit or Unlicensed Replicas
A major IP concern in the turbine RC market is the proliferation of unlicensed scale models. Some manufacturers produce detailed replicas of real military or civilian aircraft without obtaining proper licensing from the original designers or rights holders. While some replicas fall under “inspired by” design protections, others cross into trademark or copyright infringement—especially when using authentic logos, paint schemes, or model names. Sourcing such models may expose buyers or distributors to legal risk, particularly in jurisdictions with strict IP enforcement.
Lack of Documentation and Technical Support
High-end turbine RC planes require precise maintenance and tuning. However, many imported or knockoff models come with incomplete or poorly translated manuals, missing schematics, or no access to technical support. This lack of documentation increases the risk of improper assembly or operation, potentially leading to accidents. Reputable suppliers should offer comprehensive technical documentation and customer support.
Misrepresentation of Turbine Specifications
Some sellers exaggerate turbine performance, claiming higher thrust, lower fuel consumption, or quieter operation than the actual engine delivers. This misrepresentation can lead to mismatched airframe-engine combinations, poor flight characteristics, or premature engine failure. Always verify turbine specifications through independent reviews or third-party testing data before purchasing.
Infringement on Proprietary Design Elements
Certain high-end RC manufacturers hold patents or design rights on specific airframe features, such as landing gear mechanisms, avionics integration, or turbine exhaust systems. Copying these elements—even in modified form—can infringe on intellectual property rights. When sourcing, ensure that the supplier can demonstrate design freedom to operate or provide licensing documentation where applicable.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of components or verify compliance with safety and IP standards. Turbine engines themselves may be rebranded or modified versions of well-known models, sold without proper certification. Buyers should demand transparency about manufacturing origins, component sourcing, and compliance with aviation safety norms.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers thoroughly, request proof of IP compliance, inspect sample units, and consult legal or technical experts when necessary. Prioritizing reputable brands and authorized distributors significantly reduces both quality and legal risks.
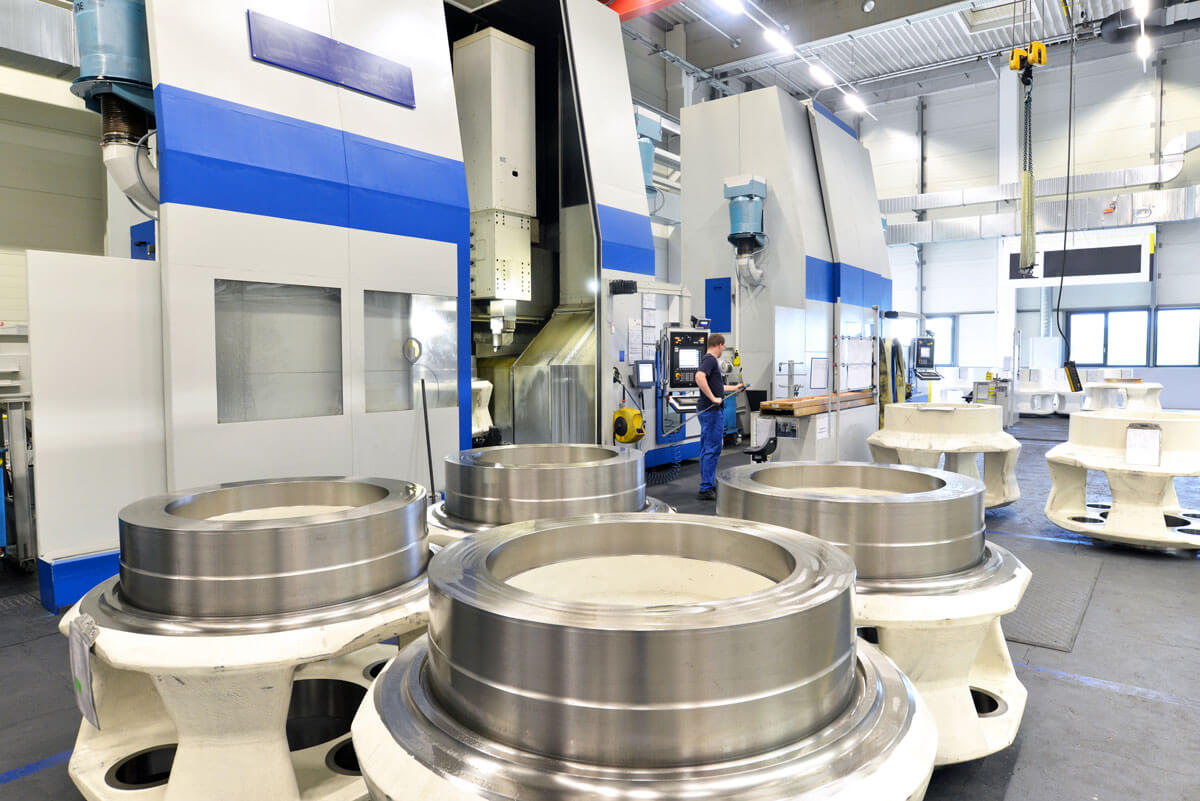

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Turbine RC Plane
Overview
This guide outlines essential logistics and regulatory considerations for the ownership, transport, and operation of turbine-powered remote-controlled (RC) aircraft. Due to their size, complexity, and high-performance capabilities, turbine RC planes require adherence to stricter safety, legal, and logistical standards than standard electric or nitro-powered RC models.
Regulatory Compliance
Aviation Authority Regulations
Turbine RC planes are subject to oversight by national aviation authorities such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the U.S., Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) in the UK, or EASA in Europe. Operators must comply with:
– FAA 14 CFR Part 101 (U.S.): All model aircraft, including turbine-powered models, must be flown for hobby or recreational purposes under the Exception for Limited Recreational Operations of Unmanned Aircraft.
– Remote ID Requirements (U.S.): Turbine RC planes must be equipped with FAA-compliant Remote ID if weighing over 0.55 lbs (250 grams).
– CAA/NPAS (UK): Pilots must pass the Flyer ID and Operator ID exams and fly within specific safety zones. Turbine models may require operational authorization due to their size and speed.
Local Club and Field Requirements
- Membership in a nationally recognized RC flying club (e.g., Academy of Model Aeronautics – AMA in the U.S.) is strongly advised.
- Turbine operations often require approval from club safety officers due to noise, exhaust, and safety concerns.
- Flying must occur at designated model airfields with appropriate clearance, fire safety equipment, and spectator zones.
Transportation & Logistics
Ground Transport
- Secure Packaging: Turbine RC planes should be disassembled and packed in reinforced, custom-fitted cases to prevent damage during transit.
- Fuel Handling: Jet A, JP-8, or kerosene used in turbine engines must be transported in approved, labeled containers per Department of Transportation (DOT) or ADR (Europe) hazardous materials regulations.
- Spare Turbine Units: Spares must be properly labeled and stored in fire-resistant containers. Transport of compressed air or nitrogen bottles (used for starting) must comply with hazardous materials codes.
Air Transport
- Prohibited in Checked or Carry-On Baggage: Turbine engines, fuel, and pressurized gas cylinders are not permitted on commercial aircraft.
- Freight Shipping: Use certified freight carriers for disassembled aircraft and components. Declare contents accurately and comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations for fuel and pressurized systems.
- Customs Documentation: International shipping requires detailed customs declarations, including engine specifications, fuel type, and safety data sheets (SDS).
Safety & Operational Compliance
Noise and Emissions
- Turbine RC planes generate significant noise (often exceeding 100 dB). Operators must adhere to local noise ordinances and fly during permitted hours.
- Ensure proper exhaust routing and use of flame arrestors to minimize fire risk and particulate emissions.
Pre-Flight Safety Checks
- Conduct turbine engine run-up tests in designated, fire-safe areas.
- Verify control surface functionality, battery health, and telemetry link integrity.
- Confirm presence of fire extinguishers and first aid equipment at the flight line.
Emergency Procedures
- Develop and review emergency protocols for engine failure, fire, or loss of control.
- Notify local authorities (e.g., airport, fire department) if operating near controlled airspace or sensitive areas.
Documentation & Record Keeping
Required Documents
- Proof of RC club membership and liability insurance (minimum $1M recommended).
- Turbine engine manual, fuel specifications, and maintenance logs.
- Flight logbook recording dates, durations, maintenance, and incidents.
Compliance Certifications
- Obtain any necessary waivers or authorizations for flights near airports, above 400 ft, or in restricted zones via LAANC (U.S.) or equivalent systems.
- Maintain up-to-date Remote ID registration and operator credentials.
Conclusion
Operating a turbine RC plane demands rigorous attention to logistics, safety, and regulatory compliance. Always consult your national aviation authority and local RC community before flying. Staying informed and responsible ensures the sustainability and enjoyment of high-performance RC aviation for all enthusiasts.
Conclusion for Sourcing an RC Turbine Plane
Sourcing an RC turbine plane is a significant undertaking that requires careful consideration of budget, expertise, regulatory compliance, and long-term support. These high-performance models are not only substantial financial investments but also demand advanced piloting skills and thorough maintenance. When sourcing, it is crucial to prioritize reputable manufacturers and authorized dealers to ensure authenticity, quality, and access to technical support. Additionally, joining experienced RC jet communities and verifying compliance with local aviation regulations—such as those from the FAA or equivalent bodies—can help ensure a safe and legal flying experience.
Due to their complexity, pre-owned turbine RC planes should be inspected by an expert before purchase, and all necessary spares, tools, and ground support equipment must be factored into the total cost of ownership. Ultimately, successful sourcing involves more than just acquiring the aircraft—it requires building a support network, investing in pilot training, and maintaining a commitment to safety and continuous learning. With the right preparation, owning and flying an RC turbine plane can be an immensely rewarding achievement in the world of advanced aeromodeling.