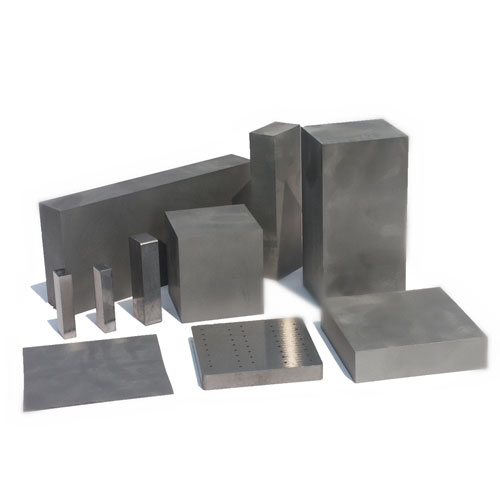
The global tungsten carbide market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand from industries such as oil & gas, mining, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global tungsten carbide market was valued at USD 9.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the material’s exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making tungsten carbide plates critical components in cutting tools, wear parts, and industrial machinery. As demand intensifies, manufacturers are scaling production, investing in R&D, and enhancing product precision to meet stringent industry standards. Against this backdrop, we spotlight the top 9 tungsten carbide plates manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market share in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Top 9 Tungsten Carbide Plates Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tungsten carbide, Tungsten cemented carbide producer …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: xiamentungsten.com
Key Highlights: Chinatungsten Online was established 20 years ago in Xiamen, South of China asa special tungsten carbide manufacturer and exporter….
#2 Leading Tungsten Plate Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: tungstensuppliers.com
Key Highlights: Discover leading US-based tungsten plate manufacturers & suppliers offering fast turnaround, custom sizing, and competitive prices….
#3 China Tungsten Carbide Plates Manufacture and Factory
Domain Est. 2013
Website: ndcarbide.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten carbide plates are also known as flat stock. Tungsten carbide, sometimes called carbide, is harder than Corrosion-Resistant Tungsten with excellent ……
#4 Pure Tungsten Plate Supplier
Domain Est. 2018
Website: aemmetal.com
Key Highlights: AEM Metal is a professional manufacturer and exporter of custom Tungsten plates. Welcome to send us an inquiry and get a official quote….
#5 Tungsten Carbide Plates
Website: kedelcarbide.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten carbide plates are precision-manufactured components with tungsten carbide as the core material, adaptable to diverse industrial scenarios. Boasting ……
#6 Tungsten Carbide Plates
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
Key Highlights: Tungsten carbide plates are used for cutting metal, wood and other materials. The advantages of our carbide cutting plates are smooth, fast cutting speed and ……
#7 Tungsten carbide plate
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ls-carbide.com
Key Highlights: We are specialized in various sizes of tungsten carbide plates. Some clients call this kind of tungsten carbide products as draw plate or carbide plate….
#8 HengRui
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ihrcarbide.com
Key Highlights: Carbide plate has the characteristics of high density, high hardness and wear resistance, and is an excellent material as a variety of tool parts….
#9 Tungsten Carbide Wear Plate
Domain Est. 2024
Website: haldencn.com
Key Highlights: We have tungsten carbide sheets and plates that vary in grades. Whether you need Y615, YG8, K20, K10, or any other type, Halden can help you in manufacturing it ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tungsten Carbide Plates

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Tungsten Carbide Plates
The global market for tungsten carbide plates is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand across key industrial sectors such as metal cutting, mining, oil & gas, automotive, and aerospace. These durable, wear-resistant components are essential in precision machining and high-stress applications, underpinning their sustained market relevance.
-
Rising Industrial Automation and Advanced Manufacturing
The continued expansion of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies is expected to boost demand for high-performance cutting tools, including tungsten carbide plates. Their superior hardness and heat resistance make them ideal for automated CNC machining processes, where precision and tool longevity are critical. As manufacturers seek to improve efficiency and reduce downtime, investment in carbide-based tooling solutions is projected to rise through 2026. -
Growth in the Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
The automotive industry, especially in emerging markets, is anticipated to increase production of fuel-efficient and electric vehicles (EVs), which require advanced machining of lightweight alloys and composites. Tungsten carbide plates are vital in machining these materials. Similarly, the aerospace sector’s focus on high-strength, heat-resistant components will further stimulate demand, particularly in turbine and engine part manufacturing. -
Expansion in Mining and Energy Applications
Tungsten carbide plates are widely used in drill bits, cutting edges, and wear parts for mining and oil & gas exploration equipment. As global energy demand persists and exploration activities continue—especially in challenging environments like deep-sea drilling and Arctic regions—the need for durable, corrosion-resistant tools will drive market growth. Investments in mineral extraction for battery metals (e.g., lithium, cobalt) will also contribute to increased usage. -
Supply Chain and Raw Material Dynamics
Tungsten is a critical raw material, with China dominating both production and export. However, geopolitical factors and export restrictions may lead to supply volatility. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in recycling technologies and alternative sourcing strategies. The push for supply chain resilience is expected to encourage regional production hubs in North America and Europe by 2026. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Ongoing R&D efforts are focused on enhancing the performance of tungsten carbide through nanostructured compositions, coatings (e.g., TiAlN, AlCrN), and additive manufacturing techniques. These innovations aim to improve hardness, toughness, and thermal stability, expanding the application scope of carbide plates into high-tech industries such as medical device manufacturing and semiconductor processing. -
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Environmental concerns are shaping market dynamics, with stricter regulations on mining practices and material disposal. Companies are responding by developing eco-friendly production methods and increasing recycling rates of spent carbide tools. By 2026, sustainability is expected to be a key differentiator among leading suppliers.
In conclusion, the tungsten carbide plates market in 2026 will be characterized by robust demand from high-tech and heavy industries, innovation-driven performance improvements, and an increasing emphasis on supply security and environmental responsibility. Market players that adapt to these evolving trends are likely to gain a competitive edge in the global landscape.
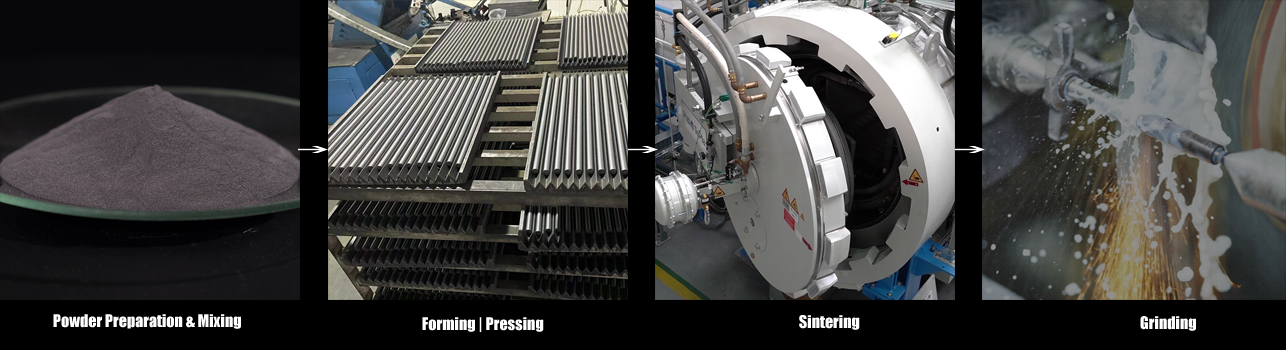
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tungsten Carbide Plates: Quality and Intellectual Property
Sourcing tungsten carbide (WC) plates involves significant technical and commercial risks, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specification and Verification
Many buyers fail to define precise material grades, microstructures, hardness (HRA), density, and grain size requirements. Generic specifications like “tungsten carbide” are insufficient—different grades (e.g., K10, K20, ISO classifications) have vastly different wear resistance, toughness, and applications. Without clear specs, suppliers may deliver substandard or off-grade material. Always require certified material test reports (MTRs) and consider third-party lab verification for critical applications.
Poor Process Control and Inconsistent Sintering
Tungsten carbide plates must undergo precise sintering in controlled atmospheres. Inconsistent sintering leads to porosity, uneven hardness, or residual stresses, reducing fatigue life and increasing fracture risk. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners in furnace control or skip post-sintering treatments (e.g., HIP—Hot Isostatic Pressing), compromising structural integrity. Audit suppliers’ production processes or request process capability data (Cpk values).
Inaccurate Dimensional Tolerances and Surface Finish
Carbide plates often require tight tolerances (±0.01 mm) and fine surface finishes (Ra < 0.4 µm) for integration into tooling or wear components. Poor grinding or EDM practices can introduce micro-cracks or thermal damage. Ensure suppliers have precision CNC grinding capabilities and perform surface integrity inspections (e.g., SEM or dye penetrant testing).
Coating Defects and Adhesion Issues
If the plates are coated (e.g., TiN, TiAlN, or diamond-like carbon), poor coating adhesion due to improper surface preparation or deposition parameters can lead to premature delamination. Verify coating thickness, composition, and adhesion strength via standardized tests (e.g., Rockwell indentation or scratch testing).
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unprotected Design and Customization IP
Custom-designed plates with proprietary geometries, edge preparations, or grading (e.g., functionally graded materials) are vulnerable to copying. Without proper legal safeguards, suppliers may reproduce and sell your design to competitors. Always use comprehensive Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and clearly define IP ownership in supply contracts.
Reverse Engineering and Unauthorized Replication
Some manufacturers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, may reverse engineer supplied samples or blueprints. To mitigate this, limit design disclosure, use watermarked documents, and consider patenting unique features. Avoid sending physical prototypes without legal protections.
Infringement of Third-Party Patents
Using patented manufacturing techniques (e.g., specific sintering methods or composite structures) without licensing can expose both buyer and supplier to litigation. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s processes and ensure freedom-to-operate, especially for patented WC formulations or production technologies.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Without proper documentation (e.g., batch traceability, process records), proving IP theft or quality non-conformance becomes difficult. Insist on full traceability from raw materials to finished product and require digital records retention.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct Supplier Audits: On-site assessments of quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949) and production capabilities.
- Implement Rigorous QA Protocols: Include incoming inspection, batch sampling, and performance testing under real-world conditions.
- Secure Legal Frameworks: Use contracts specifying IP ownership, confidentiality, liability for infringement, and export controls.
- Engage Specialized Experts: Work with materials engineers and IP attorneys during sourcing and contract negotiation.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, protect innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in demanding applications such as mining, aerospace, and precision manufacturing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tungsten Carbide Plates
Tungsten carbide plates are high-performance industrial materials widely used in cutting tools, wear-resistant components, and mining equipment. Due to their composition, value, and potential dual-use applications, shipping and handling require strict adherence to logistics best practices and international compliance regulations. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant transportation of tungsten carbide plates.
Classification and Regulatory Requirements
Tungsten carbide plates—composed primarily of tungsten (a strategic material) and carbon, often with cobalt or other binders—are subject to various export controls and trade regulations. Key classification and compliance points include:
- HTS/HS Code: Typically classified under 8101.92.00 (Cemented tungsten carbide waste and scrap, powders, and articles) in the U.S. Harmonized Tariff Schedule. Confirm the exact code with your customs broker, as classification may vary by alloy composition and end use.
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): May fall under 1C002 on the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL), which covers “metal powders and alloy materials” with specific particle size and composition criteria. Evaluate whether your tungsten carbide plates meet the technical parameters for controlled status.
- Dual-Use Concerns: Tungsten is listed on the Wassenaar Arrangement due to potential use in military or strategic applications (e.g., armor-piercing munitions, high-speed machining). Shipments to certain countries may require export licenses from the U.S. Department of Commerce (BIS) or equivalent authorities in other jurisdictions.
- ITAR vs. EAR: Tungsten carbide plates are generally not ITAR-controlled unless incorporated into defense articles. Most fall under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), but verify based on application and customer specifications.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and reduces risks during transit:
- Protective Packaging: Use moisture-resistant, shock-absorbent materials (e.g., vacuum-sealed plastic, desiccants, and rigid corrugated or wooden crates) to prevent oxidation and mechanical damage.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with product description, weight, HTS code, country of origin, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Include any required hazard labels if cobalt content exceeds thresholds (e.g., cobalt dust may be classified as hazardous).
- Stacking and Securing: Secure plates in pallets using stretch wrap or strapping. Avoid overstacking to prevent deformation or breakage.
Transportation and Shipping
Choose the appropriate mode of transport based on urgency, destination, and volume:
- Air Freight: Suitable for high-value or time-sensitive shipments. Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if cobalt binder exceeds 50% by weight or if classified as hazardous. Most tungsten carbide plates are non-hazardous but verify with a classification expert.
- Sea Freight: Cost-effective for large volumes. Use containerized shipping with climate control if sensitive to humidity. Provide accurate weight and dimensions for load planning.
- Documentation: Prepare a complete shipping package including:
- Commercial Invoice (with detailed product description, value, and ECCN if applicable)
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Export License (if required)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet) – especially if cobalt content is significant
Customs Clearance and Import Regulations
Ensure compliance in the destination country:
- Duties and Tariffs: Verify applicable import duties based on the local HS code. Preferential treatment may apply under free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN).
- Import Permits: Some countries (e.g., China, Russia, India) may require import licenses for strategic materials or high-value industrial goods.
- End-Use Certifications: Certain jurisdictions require an end-user statement confirming that the material will not be used for military or proscribed purposes.
Recordkeeping and Compliance Audits
Maintain records for a minimum of five years (or as required by local law), including:
- Export licenses and license exceptions
- Shipping and customs documentation
- ECCN classification rationale
- Customer screening records (for denied party checks)
Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations.
Restricted Destinations and Parties
Screen all parties (consignee, end-user, freight forwarder) against:
– U.S. Department of Treasury OFAC SDN List
– BIS Denied Persons List
– Entity List
– UN and EU Sanctions Lists
Avoid shipments to embargoed countries (e.g., North Korea, Iran, Syria, Crimea) without explicit authorization.
Summary
Shipping tungsten carbide plates requires careful attention to export controls, proper classification, and secure logistics. Proactive compliance reduces the risk of shipment delays, fines, or legal penalties. Always consult with legal counsel or a licensed trade compliance expert when in doubt, especially for international shipments involving strategic materials.
Conclusion for Sourcing Tungsten Carbide Plates
Sourcing tungsten carbide plates requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supplier reliability, and technical specifications. These high-performance materials are critical in demanding applications such as cutting tools, mining equipment, and wear-resistant components, where hardness, durability, and thermal stability are essential.
After evaluating potential suppliers, technical requirements, and market conditions, it is evident that selecting a reputable manufacturer with proven expertise in tungsten carbide production is paramount. Key considerations include material composition, precision in tolerances, consistency in quality, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Additionally, lead times, logistical capabilities, and post-sale support play a significant role in ensuring smooth integration into manufacturing processes.
Sourcing from established suppliers—whether domestic or international—should be supported by thorough due diligence, including sample testing, site audits (if possible), and long-term contractual agreements to ensure supply chain stability. Furthermore, building strong relationships with suppliers fosters collaboration, innovation, and potential cost optimization over time.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy for tungsten carbide plates not only enhances product performance and longevity but also contributes to operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Prioritizing quality, reliability, and supplier partnerships will ensure sustained success in industries reliant on this critical advanced material.