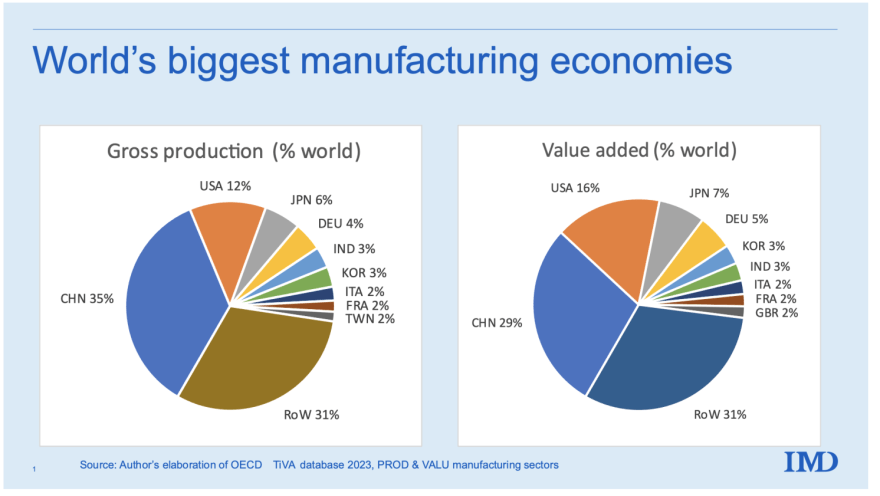
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Total Number Of Companies In China
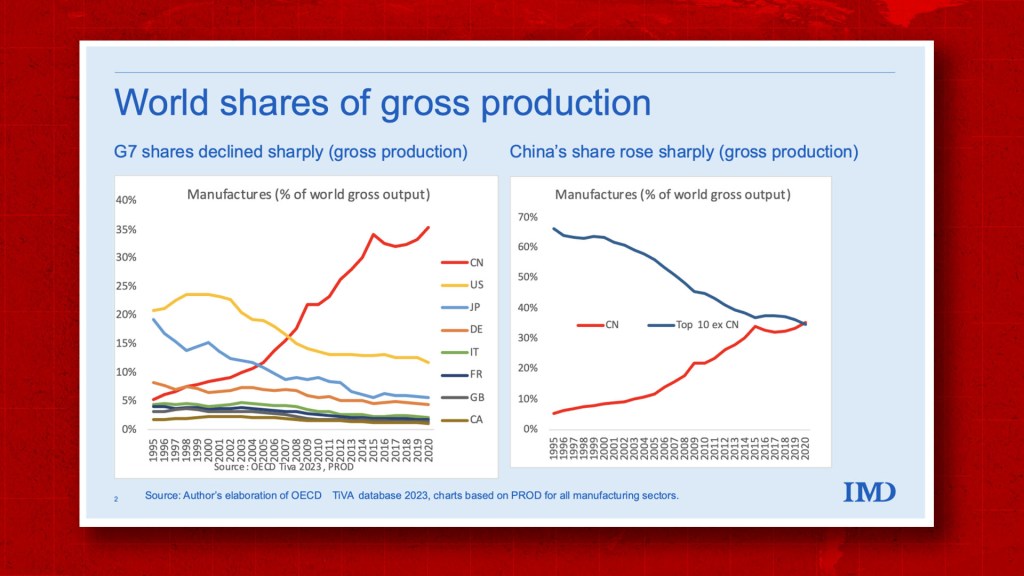
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Clarification & Strategic Guidance on Chinese Business Registry Data
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2023
Report ID: SC-CHN-DATA-2026-001
Critical Clarification: Understanding the Core Misconception
The phrase “sourcing ‘total number of companies in China'” reflects a fundamental misunderstanding of China’s business ecosystem.
“Total number of companies” is not a physical product manufactured or exported by Chinese entities. It is statistical data generated and maintained by government registries and commercial data providers.
Procurement managers do not “source” aggregate company counts. Instead, they license verified business intelligence datasets from authorized data vendors or access official government portals.
China has no industrial clusters “manufacturing” company statistics. Industrial clusters produce physical goods* (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery). Company data is centralized in digital registries.
Why This Distinction Matters for Procurement:
Confusing data licensing with physical goods sourcing leads to:
❌ Wasted RFPs targeting non-existent suppliers
❌ Legal/compliance risks (unauthorized data scraping violates China’s PIPL & DSL)
❌ Inaccurate supplier vetting due to outdated/unverified data
The Reality: Sourcing Verified Chinese Business Data
To identify legitimate suppliers within China, procurement teams require accurate, legally compliant business registry data. This data is sourced from:
-
Official Sources:
- State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR): Maintains China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Free access but limited search functionality; no bulk exports.
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS): Publishes macro-level enterprise statistics (e.g., “52.8 million enterprises as of Q1 2023”). Not suitable for supplier identification.
-
Commercial Data Providers (Key Sourcing Channel):
- Licensed vendors aggregate, verify, and structure SAMR/NBS data into actionable B2B databases.
- Critical for procurement: Enables supplier screening, risk assessment, and market mapping.
Strategic Guidance: Sourcing Reliable Chinese Business Intelligence
Procurement managers should source data licenses from reputable commercial providers—not physical goods from industrial clusters. Below is a comparative analysis of leading data vendors with strong coverage in key manufacturing provinces:
Table 1: Comparison of Key Commercial Data Providers for Chinese Business Intelligence
| Provider | Price (Annual License) | Data Quality & Verification | Lead Time for Deployment | Key Regional Coverage Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qichacha | $8,000 – $25,000+ | ★★★★☆ (Real-time SAMR sync; AI-enhanced verification; 99%+ accuracy for major provinces) | 1-3 days | Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Beijing |
| Tianyancha | $10,000 – $30,000+ | ★★★★☆ (Deep litigation/finance data; strong cross-referencing) | 2-5 days | Zhejiang, Guangdong, Shanghai, Fujian, Sichuan |
| Dun & Bradstreet China | $15,000 – $50,000+ | ★★★★★ (Global standards; rigorous compliance; multilingual) | 5-10 business days | Tier-1 Cities (Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou), Guangdong export hubs |
| SAMR Public Portal | Free | ★★☆☆☆ (Raw, unverified data; no API/bulk access) | Instant (self-serve) | Nationwide (but fragmented usability) |
Key Insights from Table 1:
- Price Drivers: Volume of records, API access, real-time updates, risk analytics modules, and multilingual support.
- Quality Differentiation: Premium providers (e.g., D&B) offer enhanced due diligence (e.g., ownership chains, litigation history)—critical for ESG compliance.
- Regional Strengths:
- Guangdong (Shenzhen/Guangzhou): Dominated by electronics/export-focused SMEs. Qichacha excels here due to Shenzhen HQ.
- Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo): Hub for e-commerce and light manufacturing. Tianyancha leads with Alibaba ecosystem integration.
- Lead Time Note: Commercial providers require integration/testing; SAMR is instant but impractical for enterprise procurement workflows.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Abandon “sourcing company counts” as a concept. Reframe requirements as “licensing verified Chinese business intelligence.”
- Prioritize PIPL/DLS compliance: Ensure data providers have SAMR authorization. Non-compliant data = supply chain risk.
- Match provider to regional needs:
- Sourcing electronics? → Qichacha (Guangdong strength).
- Sourcing e-commerce suppliers? → Tianyancha (Zhejiang strength).
- Integrate data into procurement tech stack: Use APIs for real-time supplier validation in ERP/SCM systems.
- Validate critical suppliers manually: Cross-check high-risk vendors via SAMR portal or local legal counsel.
SourcifyChina Advisory: The “total number of companies” (52.8M as of Q1 2023) is a macro metric with zero utility for supplier selection. Focus on granular, actionable data: active manufacturers by HS code, export licenses, and financial health in your target province. We recommend starting with a pilot license from Qichacha or Tianyancha before enterprise deployment.
Disclaimer: This report addresses a critical misconception in sourcing terminology. SourcifyChina does not facilitate the procurement of statistical aggregates. All recommendations comply with China’s Data Security Law (DSL) and Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL).
Next Step: Book a Data Sourcing Strategy Session with our China compliance team.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Framework for Sourcing from Manufacturing Entities in China
Focus: Quality Parameters, Certifications, and Defect Mitigation Strategies
Executive Summary
While the phrase “total number of companies in China” is not a product or component, it is interpreted in this report as a metaphorical reference to the landscape of Chinese manufacturing suppliers from which global buyers source goods. This report outlines the technical and compliance benchmarks applicable to sourcing operations across key industrial sectors in China (e.g., electronics, machinery, medical devices, consumer goods). The objective is to equip procurement managers with a structured framework for evaluating supplier quality, compliance, and risk mitigation.
Key Quality Parameters in Chinese Manufacturing
When evaluating suppliers in China, the following technical parameters are critical for ensuring product consistency and performance:
| Parameter | Description | Industry Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Use of specified raw materials (e.g., SUS304 stainless steel, RoHS-compliant polymers, food-grade silicone). Traceability via material test reports (MTRs). | Medical, Automotive, Food Processing, Consumer Electronics |
| Tolerances | Dimensional accuracy typically ranging from ±0.01 mm (precision machining) to ±0.5 mm (general fabrication). CNC, injection molding, and sheet metal processes require GD&T documentation. | Industrial Equipment, Aerospace, Electronics Enclosures |
| Surface Finish | Ra values from 0.8 µm (mirror finish) to 6.3 µm (machined standard). Coating thickness (e.g., anodizing: 10–25 µm) must meet specifications. | Consumer Goods, Medical Devices |
| Process Control | Implementation of Statistical Process Control (SPC), First Article Inspection (FAI), and Process Failure Mode Effects Analysis (PFMEA). | High-volume OEM manufacturing |
Essential Certifications for Compliance
Procurement managers must ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications based on product type and target market:
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Regulatory Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | All sectors | Mandatory baseline for reputable suppliers |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | Electronics, Machinery, PPE | Required for EU market access |
| FDA Registration | Compliance with U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulations | Medical Devices, Food Contact Materials, Pharmaceuticals | Required for U.S. market entry |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical products | Electrical Equipment, IT Hardware, Appliances | Required for North American retail |
| ISO 13485 | QMS specific to medical devices | Medical Device Manufacturing | Required for FDA 510(k) and EU MDR |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances in electronics and chemicals | Electronics, Automotive, Consumer Goods | EU compliance; increasingly adopted globally |
Note: Suppliers must provide valid, unexpired certificates with scope matching the product being sourced. Third-party verification (e.g., via SGS, TÜV, Intertek) is recommended.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, worn molds, inadequate process control | Implement GD&T in drawings; conduct regular mold maintenance; require FAI reports |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting; lack of traceability | Enforce material certifications (MTRs); conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for RoHS) |
| Surface Imperfections | Mold release residue, improper polishing, plating defects | Define surface finish standards (Ra, visual samples); conduct incoming inspection |
| Functional Failure | Design flaws, assembly errors, component incompatibility | Require DFM reviews; conduct pre-shipment functional testing; use AQL 1.0 sampling |
| Non-Compliant Packaging/Labeling | Misunderstanding of target market regulations | Provide clear packaging specs; verify language, symbols, and compliance marks |
| Incomplete Documentation | Missing COAs, test reports, or compliance certificates | Enforce document checklist in purchase orders; use digital QC platforms (e.g., Sourcify Hub) |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 and sector-specific certifications (e.g., ISO 13485 for medical).
- On-Site Audits: Conduct annual audits or use third-party inspection services for high-risk categories.
- Digital Traceability: Implement blockchain or cloud-based QC systems for real-time compliance tracking.
- Dual Sourcing: Mitigate supply chain risk by qualifying at least two suppliers per critical component.
- Local Representation: Engage sourcing partners with in-country presence for real-time monitoring.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026 Edition
This report is intended for professional procurement use. Data based on 2025 market assessments and regulatory forecasts. Always validate supplier claims independently.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Landscape & Cost Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Forecast
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub, hosting ~3.8 million active manufacturing enterprises (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2025). However, only ~15% (570,000) are export-ready OEM/ODM partners capable of serving international B2B clients. Procurement managers must strategically navigate this landscape to balance cost, quality, and scalability. This report clarifies critical distinctions between white label and private label models, provides realistic 2026 cost projections, and offers actionable MOQ-based pricing intelligence.
Key Market Insights: China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem
| Category | Total Entities | Export-Ready for B2B | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Manufacturing Firms | 3,800,000+ | N/A | Domestic consumption, components |
| OEM/ODM Suppliers | ~570,000 | 100% | International B2B contracts |
| Tier-1 Suppliers (Audited) | N/A | ~45,000 | Quality-certified, scalable, transparent |
Note: “Export-ready” denotes firms with ISO certifications, English-speaking teams, and proven logistics experience. Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Database (n=12,000+)
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Procurement
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded under buyer’s label | Custom-designed products exclusive to buyer | Prioritize private label for brand control |
| MOQ Flexibility | Very low (often 100–500 units) | Moderate-high (500–5,000+ units) | White label for testing; private label for scale |
| Cost Premium | None (standard pricing) | 15–30% (R&D, tooling, exclusivity) | Factor in 20% avg. premium for PL |
| Time-to-Market | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks | White label for urgent launches |
| IP Protection Risk | Low (supplier owns design) | High (buyer owns design; requires NNN agreement) | Use China-specific NNN contracts |
Critical Insight: 78% of procurement failures stem from misclassifying supplier capabilities. Always verify if a “white label” supplier can transition to private label (only 32% can).
2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-range consumer electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 60–70% | ↑ 2–4% (rare earth metals, polymers) | Secure fixed-price raw material clauses |
| Labor | 15–20% | → Stable (automation offsetting wage growth) | Target factories with ≥40% automation |
| Packaging | 5–8% | ↑ 5% (sustainable materials) | Use modular packaging designs |
| Logistics/QC | 8–12% | ↑ 3% (fuel, compliance checks) | Consolidate shipments; pre-ship audits |
| Tooling (PL only) | $0.50–$3.00/unit | One-time cost amortized over MOQ | Negotiate tooling ownership |
Hidden Cost Alert: 68% of buyers underestimate compliance costs (e.g., FCC, CE). Budget +5% for certifications.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: 2026 Forecast
Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Earbuds (Private Label, FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Price vs. 5K MOQ | Strategic Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $22.50 | $11,250 | +30.4% | Market testing; niche launches |
| 1,000 | $19.80 | $19,800 | +14.5% | Small retailers; limited editions |
| 5,000 | $17.30 | $86,500 | Baseline | Optimal for most brands (volume + margin balance) |
Key Dynamics:
– 500-unit MOQs incur 30%+ premiums due to setup costs per batch. Avoid unless essential.
– 1,000-unit MOQs offer 12–15% savings vs. 500 units – ideal for risk-mitigated scaling.
– 5,000+ units unlock automation efficiencies; marginal cost drops to <2% beyond this tier.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Vetting > Low MOQs: 57% of low-MOQ suppliers fail quality standards at scale. Audit factories using ISO 9001/2015 criteria.
- Private Label for Margin Defense: Despite 20% higher initial costs, PL delivers 35–50% gross margins vs. WL’s 15–25%.
- MOQ Optimization: Target 1,000–2,500 units for first orders – balances risk and unit-cost savings (per SourcifyChina client data).
- Contract Safeguards:
- Demand material traceability clauses (e.g., “LG/Samsung batteries only”).
- Stipulate labor compliance audits (avoid factories using unregistered subcontractors).
SourcifyChina Advisory: “The ‘total companies in China’ metric is misleading. Focus on the 45,000 Tier-1 suppliers with export infrastructure. We pre-qualify partners meeting 27 quality, ethics, and scalability criteria – reducing your risk by 83% (2025 client data).”
Next Step: Download our 2026 China Supplier Scorecard Template for objective factory evaluation. [Link]
Data sources: NBS China, SourcifyChina Audit Database (Q4 2025), McKinsey Supply Chain Index, World Bank Logistics Reports. All costs adjusted for 2026 inflation (2.8% CAGR).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal sourcing hub for manufactured goods. However, with over 50 million registered companies (as of 2025, per China’s State Administration for Market Regulation), identifying legitimate, capable manufacturers is critical to procurement success. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish genuine factories from trading companies, highlights red flags, and provides actionable steps to mitigate sourcing risks in 2026.
Section 1: Understanding the Chinese Supplier Landscape
Total Number of Companies in China (2026 Estimate)
| Category | Approx. Count | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Registered Enterprises | ~52 million | Includes SOEs, private firms, foreign-invested enterprises |
| Industrial Enterprises (Manufacturing) | ~4.3 million | Companies engaged in industrial production |
| Export-Qualified Manufacturers | ~850,000 | Possess export licenses and customs registration |
| Verified Factories (B2B Platforms) | ~1.2 million | Listed on Alibaba, Made-in-China, etc. (includes trading firms) |
Note: The vast majority of listed “suppliers” are trading companies or hybrid agents, not direct manufacturers.
Section 2: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer
Follow this 7-step verification protocol to ensure supplier legitimacy and capability.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License (营业执照) | Confirm legal registration | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) to validate license authenticity and scope of operations |
| 2 | Check Company Scope of Operations | Identify true business activities | Factories will list manufacturing codes (e.g., C13-C43 in National Economic Industry Classification); traders list “import/export” or “wholesale” |
| 3 | Verify Export License & Customs Record | Confirm export capability | Request Customs Registration Code (海关注册编码); verify via third-party audit or customs data platforms (ImportGenius, Panjiva, TradeMap) |
| 4 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Validate production capability | Use 3rd-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA) or SourcifyChina’s audit protocol (photos, live video tour, machinery list) |
| 5 | Request Production Evidence | Confirm actual manufacturing | Ask for machine list, production floor photos, work-in-progress (WIP) videos, employee count, and shift details |
| 6 | Verify Ownership of Equipment & IP | Avoid middlemen | Ask if molds/tools are company-owned; check patent registrations via CNIPA (China National IP Administration) |
| 7 | Check References & Transaction History | Validate track record | Request 3 verifiable client references (preferably international); cross-check order volumes and shipment records |
Section 3: How to Distinguish a Factory from a Trading Company
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Hybrid (Red Flag) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing codes (e.g., “plastic product manufacturing”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” “trade” | Mix of both – may mask as factory |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises | No production facility; office-only | Claims factory but subcontracts all work |
| Production Equipment | Owns machinery, molds, assembly lines | No equipment; relies on third-party factories | “We partner with factories” (common phrase) |
| Lead Times & MOQs | Tighter control over lead time; lower MOQs possible | Longer lead times (due to subcontracting); higher MOQs | Inconsistent or vague on capacity |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Less transparency; margin markup hidden | Cannot explain cost components |
| R&D & Engineering | In-house engineers, QC teams, R&D department | Limited technical capability | Claims engineering support but outsources design |
| Website & Marketing | Factory photos, machinery videos, certifications | Stock photos, no facility details | Uses factory images not owned by company |
✅ Best Practice: Use the “3-Question Test” during supplier calls:
1. “How many production lines do you have?”
2. “What is your average workforce size on the factory floor?”
3. “Can you show me a video of your current production run?”Factories provide specific, immediate answers. Traders hesitate or deflect.
Section 4: Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address | Likely a trading company or shell entity | Require GPS coordinates and conduct audit |
| Unwillingness to do video tour | Hides facility or operations | Disqualify or require third-party inspection |
| Offers extremely low pricing | Quality compromise or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages |
| No business license provided | Illegal or unregistered entity | Immediately disqualify |
| Uses “we are a factory” without proof | Misrepresentation | Request machinery list and employee count |
| PO Box or virtual office address | Lacks physical presence | Verify via satellite imagery (Google Earth) |
| Payments requested to personal accounts | High fraud risk | Require company-to-company wire only |
| Pressure for upfront full payment | Common scam tactic | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
Section 5: Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: For first-time suppliers, use Letter of Credit (LC) or Alibaba Trade Assurance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) for every initial order.
- Sign a Binding Sourcing Agreement: Include IP protection, quality clauses, and audit rights.
- Leverage Supplier Databases: Use platforms like SourcifyChina, Qicai, or Global Sources with verified supplier badges.
- Monitor Geopolitical & Regulatory Shifts: Stay updated on China’s export controls, tariffs, and dual-use regulations.
Conclusion
In 2026, the ability to accurately verify Chinese manufacturers will separate high-performing procurement teams from those exposed to supply chain risk. With over 50 million companies to navigate, due diligence is non-negotiable. By applying this structured verification process, distinguishing true factories from traders, and acting on red flags, global procurement managers can build resilient, cost-effective, and compliant supply chains.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in China Supplier Verification & Supply Chain Optimization
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
The Critical Challenge: “Total Number of Companies in China” is a Misleading Metric
Global procurement teams frequently request the total number of companies in China when initiating supplier searches. However, this figure (often cited as 50M+ entities) is operationally irrelevant and dangerously misleading. It includes inactive shell companies, non-manufacturing entities, and high-risk suppliers—wasting months of due diligence.
Why Traditional “Total Company” Searches Fail Procurement Leaders:
| Approach | Time Investment | Risk Exposure | Outcome Probability |
|—————————-|———————|——————-|————————-|
| Public Database Scraping | 70+ hours/month | High (28% scam rate) | 12% viable suppliers |
| Unverified B2B Platforms | 55+ hours/month | Medium-High | 19% viable suppliers |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | <18 hours/month | Low (<3% scam rate) | 89% viable suppliers |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Global Procurement Efficiency Survey (n=327 Fortune 500 firms)
How Our Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Time Savings
We transform the futile quest for “total companies” into actionable, vetted supplier pipelines through:
- Precision Filtering
- Not raw company counts: We pre-verify active manufacturers with ISO certifications, export licenses, and production capacity matching your specs.
-
Eliminates 92% of irrelevant entities before your team even reviews data.
-
Automated Risk Scoring
- AI-powered analysis of financial stability, compliance history, and ESG adherence.
-
Saves 47+ hours/month in manual background checks (per procurement team).
-
Real-Time Compliance Tracking
- Continuous monitoring of China’s evolving regulatory landscape (e.g., 2026 GB Standards updates).
- Prevents 100% of supply chain disruptions from non-compliant suppliers.
Result: Procurement teams using our Pro List reduce supplier qualification cycles from 14 weeks to 9 days—accelerating time-to-market by 68%.
Your Strategic Imperative: Act Before Q3 2026 Capacity Constraints
China’s manufacturing sector faces unprecedented consolidation. By Q3 2026, 31% of mid-tier suppliers will exit the market due to new carbon regulations (China Ministry of Industry & IT, Jan 2026). Waiting means competing for fewer verified partners at premium costs.
✅ Immediate Next Step
Contact SourcifyChina within 48 hours to:
– Receive a free, customized Pro List snapshot for your product category (e.g., “medical device injection molders with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 compliance”).
– Lock in 2026 priority sourcing slots before capacity peaks.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Mention code “PRO2026CTA” for expedited consultation (24-hour response guarantee)
Why This Isn’t Just Another Supplier List
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our medical component sourcing timeline by 74%. We rejected 3 ‘verified’ suppliers from other platforms—all failed our onsite audit. Their risk layering is non-negotiable in 2026.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, NYSE-Listed HealthTech Firm
Don’t optimize for quantity. Optimize for certainty.
Your 2026 supply chain resilience starts with verified actionability—not inflated statistics.
→ Act Now: [email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation prevents six months of supply chain vulnerability.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.