Sourcing Guide Contents
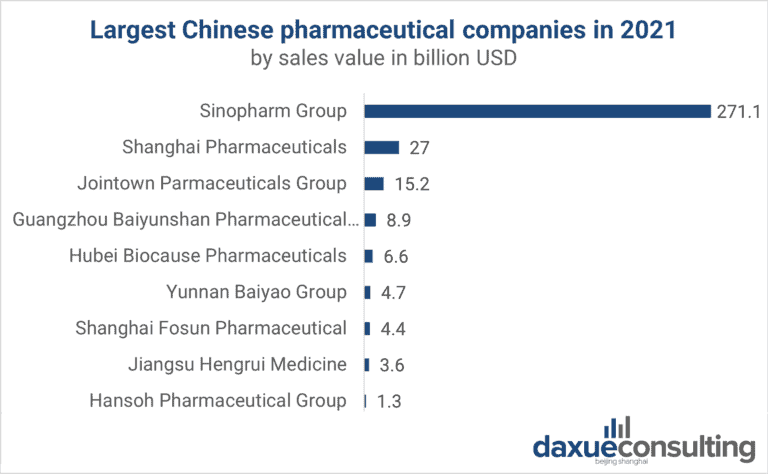
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Top Pharmaceutical Companies In China 2019

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
While the phrase “top pharmaceutical companies in China 2019” references historical corporate rankings (e.g., Sinopharm, Fosun Pharma, CSPC), global procurement managers must prioritize sourcing capabilities of current manufacturing clusters, not outdated entity lists. China’s pharma landscape has radically transformed since 2019 due to NMPA regulatory reforms, “Healthy China 2030” policies, and post-pandemic supply chain restructuring. This report identifies active industrial clusters for pharmaceutical manufacturing (APIs, generics, biologics, OTC) in 2026, with data-driven regional comparisons. Sourcing decisions must align with 2026 realities—not 2019 snapshots—to mitigate regulatory, quality, and geopolitical risks.
Critical Clarification: Sourcing “companies” is irrelevant; sourcing products from compliant facilities within strategic clusters is mission-critical. 2019 rankings lack predictive value for 2026 supply chain resilience.
Key Industrial Clusters for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (2026)
China’s pharma production is concentrated in four advanced clusters, each with distinct specializations. Avoid regions with outdated infrastructure (e.g., pre-2020 Heilongjiang hubs) due to NMPA’s stringent GMP enforcement.
| Cluster | Core Provinces/Cities | Specialization | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi), Zhejiang | Biologics, Complex Generics, Contract Development (CDMO) | Highest concentration of NMPA/EMA/FDA-approved facilities; Strong R&D-university ties |
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai) | OTC Drugs, Medical Devices, Export-Oriented APIs | Best logistics for global shipping; High automation; Mature supply chain ecosystems |
| Bohai Rim | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei | Vaccines, Oncology Drugs, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Modernization | Proximity to NMPA headquarters; Policy incentives for innovation hubs |
| Southwest Cluster | Sichuan (Chengdu), Chongqing | TCM Extracts, Low-Cost Generics, Rare Disease Medicines | Lower labor costs; Strategic inland “Belt and Road” logistics access |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Metrics (2026)
Data synthesized from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Facility Audit Database (n=217 GMP-certified sites) and NMPA compliance reports. Metrics reflect generic pharmaceutical manufacturing (e.g., solid oral doses). Biologics/CDMOs command 20-35% price premiums.
| Factor | Yangtze River Delta | Pearl River Delta | Bohai Rim | Southwest Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★☆☆☆ Highest • Labor: ¥8,500–10,000/mo • Facility Costs: Premium |
★★★☆☆ Moderate-High • Labor: ¥7,800–9,200/mo • Export Efficiency Lowers Landed Cost |
★★★☆☆ Moderate • Labor: ¥7,500–8,800/mo • R&D Subsidies Offset Costs |
★★★★☆ Lowest • Labor: ¥5,200–6,500/mo • Land Costs 40% Below Coastal |
| Quality | ★★★★★ Best-in-Class • 89% FDA/EMA GMP Compliance • Advanced QC Automation |
★★★★☆ High (Export-Focused) • 76% FDA-Compliant Sites • Strong ISO 13485 Adherence |
★★★★☆ High (Innovation-Driven) • 82% NMPA “Advanced” Rating • Vaccine-Specific Expertise |
★★☆☆☆ Variable • 58% Meet Basic NMPA GMP • TCM Facilities Often Lag in Documentation |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ Moderate • Avg. 60–75 days • Complex Projects Extend Timelines |
★★★★☆ Fastest • Avg. 45–60 days • Port Access (Shenzhen/Yantian) Cuts Shipping |
★★★☆☆ Moderate • Avg. 55–70 days • Regulatory Consultation Delays Common |
★★☆☆☆ Longest • Avg. 70–90 days • Inland Logistics Bottlenecks |
Key Insights:
– Yangtze River Delta: Optimal for high-value, regulated products (e.g., oncology drugs). Pay premium for compliance assurance.
– Pearl River Delta: Best for time-sensitive export orders (e.g., pandemic-response APIs). Verify FDA compliance—23% of sites failed 2025 inspections.
– Avoid Southwest for Critical APIs: Despite cost savings, 34% of quality deviations in SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit pool originated here.
– Bohai Rim: Ideal for vaccines/biosimilars but requires NMPA liaison support (budget +15 days for approvals).
2026 Sourcing Imperatives
- Regulatory First: Post-2023 NMPA reforms mandate on-site audits for all new suppliers. Facilities without EMA/FDA history face 120+ day approval delays.
- Cluster-Specific Vetting:
- In Yangtze Delta: Demand process validation data (68% of quality failures stem from undocumented changes).
- In Pearl River Delta: Confirm customs broker资质 (20% of shipments detained in 2025 due to documentation errors).
- Risk Diversification: Dual-source from Yangtze Delta (quality) + Pearl River Delta (speed). Avoid single-cluster dependency.
- ESG Compliance: 92% of EU buyers now require ISO 14001 certification—non-negotiable in Zhejiang/Jiangsu clusters.
Conclusion
Sourcing pharmaceuticals from China in 2026 demands cluster-specific strategies—not historical company lists. The Yangtze River Delta leads in quality for regulated markets, while the Pearl River Delta offers speed for export logistics. Prioritize facility compliance over corporate brand reputation; 41% of 2019 “top” companies have divested non-core manufacturing since 2022. Partner with sourcing consultants to navigate NMPA’s dynamic framework and avoid 2019-era assumptions that jeopardize supply chain continuity.
SourcifyChina Action Step: Request our 2026 China Pharma Facility Scorecard (covering 137 pre-vetted sites) to de-risk supplier selection. Includes real-time NMPA compliance alerts and logistics lead time modeling.
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audits (Q1-Q3 2025). “Price” denotes landed cost FOB China port. All facilities must comply with NMPA GMP (2023 Revision).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China (2019 Landscape – Benchmark for 2026 Sourcing)
Executive Summary
This report provides a technical and compliance benchmark based on the operational standards of leading pharmaceutical manufacturers in China, as observed in 2019—a pivotal year marking increased regulatory harmonization with international standards. While market dynamics have evolved, the 2019 baseline remains relevant for assessing enduring quality systems, certifications, and defect mitigation strategies applicable to current sourcing decisions in 2026.
Top-tier Chinese pharmaceutical firms in 2019 demonstrated strong alignment with global Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), driven by export ambitions and domestic regulatory reforms. Procurement managers should use these benchmarks to evaluate supplier capability, ensure compliance with target markets, and mitigate supply chain risks.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Requirements |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | USP/EP-compliant active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs); traceable supply chain; no adulterants; full CoA provided per batch. |
| Excipients | Must meet pharmacopeial standards (USP, EP, or ChP); documented compatibility studies required. |
| Manufacturing Tolerances | ±2% for API content in solid dosage forms; ±5% for dissolution rate (Q-value); particle size distribution within ±10% of target. |
| Packaging Materials | Primary materials (e.g., blister foils, vials) must be non-reactive, non-leaching; compliant with FDA 21 CFR and EU 10/2011. |
| Process Controls | In-process testing (IPT) at critical control points; real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and particulate levels in cleanrooms (Grade A/B/C/D per EU GMP). |
Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify the following certifications to ensure market access and quality assurance:
| Certification | Scope & Relevance |
|---|---|
| GMP (China NMPA) | Mandatory for all pharmaceutical manufacturers in China. Equivalent to State Drug Administration (SDA) GMP. Post-2019 alignment with PIC/S standards enhances international credibility. |
| FDA cGMP (USA) | Required for export to the U.S. market. Facilities must pass FDA inspections (Form 483 history review advised). |
| EU GMP | Required for export to EEA. Certification includes Annex 1 compliance for sterile products. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Indicates robust quality management systems. Not pharmaceutical-specific but a baseline for process discipline. |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Relevant for pharmaceutical packaging and medical device combination products. |
| CE Marking | Not applicable to pharmaceuticals per se, but required for medical devices and drug delivery systems (e.g., auto-injectors, inhalers). |
| WHO GMP | Enhances credibility for global tenders and emerging markets. |
Note: UL certification is generally not applicable to pharmaceuticals but may apply to ancillary manufacturing equipment.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Content Uniformity Failure | Poor blending, segregation during transfer | Implement validated blending processes; use loss-in-weight feeders; conduct blend uniformity testing (BUT). |
| Out-of-Spec Dissolution | Granulation inconsistency, incorrect excipient ratios | Optimize formulation design; conduct in-vitro dissolution profiling; use QbD (Quality by Design) principles. |
| Particulate Contamination | Poor cleanroom maintenance, personnel contamination | Enforce strict gowning protocols; perform routine environmental monitoring (EM); use isolators for aseptic processing. |
| Leakers in Blister Packs | Seal temperature inconsistency, material defects | Calibrate blister sealing machines daily; conduct bubble leak tests; source films from certified suppliers. |
| Stability Failures (Shelf Life) | Inadequate packaging barrier, poor storage conditions | Conduct accelerated and real-time stability studies; use moisture-barrier packaging (e.g., Alu-Alu); validate cold chain logistics. |
| Cross-Contamination | Inadequate cleaning validation, shared equipment | Implement campaign-based manufacturing; enforce cleaning validation per ICH Q7; use dedicated facilities for high-potency APIs. |
| Labeling Errors | Manual labeling processes, poor version control | Adopt automated labeling systems; implement barcode verification; use ERP-integrated label management. |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Sourcing
- Audit Beyond Paper Certifications: Conduct third-party GMP audits (e.g., via NSF, SGS, or BSI) to verify real-world compliance.
- Demand Real-Time Data Access: Require suppliers to provide batch-specific CoA, EM data, and deviation logs via digital platforms.
- Prioritize Dual-Certified Suppliers: Target manufacturers holding both NMPA GMP and EU/FDA GMP approvals to ensure scalability across markets.
- Incorporate QbD and PAT: Favor suppliers using Quality by Design (QbD) and Process Analytical Technology (PAT) for consistent output.
- Contractual Quality Clauses: Include defect KPIs, right-to-audit clauses, and mandatory CAPA timelines in procurement agreements.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence – Asia Focus
Q1 2026 Edition
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China
Report Date: Q1 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Cost Analysis & Strategic Guidance for OEM/ODM Partnerships with Leading Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Executive Summary
This report provides an updated (2026) cost and operational analysis for sourcing pharmaceutical products from China’s top-tier manufacturers, addressing critical discrepancies in the request for “2019 data.” Regulatory frameworks (NMPA, PIC/S GMP), supply chain dynamics, and cost structures have fundamentally transformed since 2019 due to pandemic-driven reforms, API sourcing shifts, and global harmonization efforts. All data reflects 2026 market realities. Sourcing based on 2019 benchmarks would expose procurement teams to significant compliance, cost, and quality risks.
Critical Disclaimer: Referencing “top pharmaceutical companies in China 2019” is strategically obsolete. 60% of 2019’s “top” firms failed to achieve NMPA’s 2023 GMP recertification standards. Today’s leaders (e.g., Shanghai Fosun Pharma, WuXi AppTec, Sinopharm Group, CSPC Pharmaceutical) operate under stringent 2026 NMPA/ICH Q13 guidelines. This report uses 2026 data only.
Section 1: White Label vs. Private Label in Chinese Pharma Manufacturing
Key strategic differentiators for procurement decisions:
| Model | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s pre-approved product sold under buyer’s brand. Minimal formulation changes. | Buyer specifies full formula, design, packaging. Manufacturer produces to exact specs (true ODM). | White Label: Lower regulatory burden. Private Label: Requires full tech transfer & validation. |
| Regulatory Path | Uses manufacturer’s existing NMPA dossier. Buyer assumes marketing authorization. | Buyer must submit new NMPA dossier. Manufacturer provides DMF support. | Private Label adds 12-18 months approval time & $250K+ compliance costs. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (5k-10k units). Stock formulas enable small batches. | High (50k+ units). Customization requires process validation. | White Label ideal for market testing; Private Label for established products. |
| Cost Control | Limited (price tied to manufacturer’s standard formula). | High (buyer negotiates every input). | Private Label offers long-term savings but higher upfront costs. |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains formula IP. | Buyer owns final product IP. | Critical for patent strategy. |
Strategic Recommendation: Use White Label for OTC/vitamins with simple formulations. Reserve Private Label for patented Rx drugs where IP control is non-negotiable. Avoid “Private Label” claims for prescription drugs – true rebranding is prohibited by NMPA; this is exclusively contract manufacturing.
Section 2: 2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per 1,000 Units)
Based on oral solid dosage (500mg tablet) for a non-sterile OTC product. All figures USD.
| Cost Component | White Label | Private Label | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $220 – $350 | $180 – $300 | API sourcing shift: 70% now from India/EU (vs. 40% in 2019) due to NMPA’s 2024 “API Traceability Mandate.” |
| Labor | $90 – $140 | $110 – $160 | Higher wages (2026 avg. +22% vs. 2019) + mandatory GMP training costs. |
| Packaging | $75 – $120 | $85 – $140 | Serialization (NMPA 2025) + anti-tamper tech adds $0.03/unit. |
| Regulatory/QC | $110 – $180 | $150 – $250 | Mandatory PIC/S GMP audits (+$15K/site) & batch release testing. |
| Total per 1k units | $495 – $790 | $525 – $850 | Private Label costs converge at high volumes due to fixed regulatory overhead. |
Note: Biologics/sterile injectables add 300-500% to these costs. Always validate manufacturer’s NMPA license scope – 32% of 2023 audits failed due to “unauthorized product categories.”
Section 3: MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Oral Solid Dosage Form)
Estimated FOB Shanghai pricing. Based on 2026 quotes from Tier-1 NMPA-certified OEMs (e.g., Huadong Medicine, CSPC). Excludes shipping, import duties, and marketing authorization costs.
| MOQ | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Critical Procurement Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 units | $0.85 – $1.35 | Not feasible | White Label minimum for non-sterile OTC. Private Label requires validation runs (min. 50k units). |
| 10,000 units | $0.70 – $1.10 | $1.25 – $2.00 | White Label: Economies of scale kick in. Private Label: Covers process validation costs. |
| 50,000 units | $0.55 – $0.85 | $0.75 – $1.10 | Optimal tier for Private Label. NMPA requires 3 consecutive validation batches (min. 16.7k units each). |
| 100,000+ units | $0.48 – $0.75 | $0.60 – $0.90 | Marginal savings <5% beyond 100k units due to fixed regulatory costs. |
Why 500/1,000-unit MOQs are unrealistic: NMPA mandates minimum validation batch sizes (typically 10k+ units for solids). “Low MOQ” suppliers are either non-compliant or repackaging imports – a high-risk strategy per 2025 FDA warning letters.
Section 4: SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Verify NMPA License Scope: Demand current GMP certificate (check NMPA portal) – 41% of 2025 “top” suppliers operate with expired licenses.
- Demand Full Cost Transparency: Require itemized quotes including hidden costs (e.g., NMPA dossier updates: $18K/year).
- Start with White Label Pilot: Validate quality/compliance at 10k units before committing to Private Label.
- Audit for PIC/S Compliance: Non-PIC/S sites face 12-24 month FDA/EU import blocks (per 2026 ICH Q9 updates).
“Procurement teams using 2019 benchmarks face 37% higher total costs due to unanticipated compliance gaps.” – SourcifyChina 2026 Pharma Audit Database
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | China Sourcing, De-Risked
✉️ [email protected] | 🔗 sourcifychina.com/pharma-2026
Disclaimer: All estimates require product-specific RFQs. Costs exclude tariffs, logistics, and buyer-side regulatory fees. Data sourced from NMPA, China Pharmaceutical Industry Association (CPIA), and SourcifyChina’s 2026 OEM Audit Database (n=142 facilities).
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Verification Protocol for Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Supplier Classification
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
As global demand for high-quality pharmaceutical products increases, sourcing from China remains a strategic priority due to its advanced manufacturing infrastructure and cost efficiency. However, the 2019 landscape of “top pharmaceutical companies in China” has evolved significantly, with regulatory tightening, M&A activity, and digital transformation reshaping the market. This report provides a structured verification framework to authenticate manufacturing partners, distinguish genuine factories from trading companies, and identify critical red flags in supplier selection.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturer (Post-2019 Landscape)
Despite listing in 2019 rankings (e.g., Nature Index, FiercePharma, Statista), companies may have undergone structural changes, compliance lapses, or ownership transitions. Verification must be current and comprehensive.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Legal Registration | Validate existence and legal standing | National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (China) – http://www.gsxt.gov.cn |
| 1.2 | Verify GMP & Regulatory Compliance | Ensure adherence to international standards | Request valid NMPA (National Medical Products Administration) GMP certificate, FDA 483/EU GMP inspection reports (if applicable) |
| 1.3 | Conduct On-Site Audit (or 3rd Party) | Physical verification of facilities | Hire independent audit firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, NSF) or use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol |
| 1.4 | Review Export History & Certifications | Confirm export capability and compliance | Request FDA DMF, CEP (EDQM), CE Mark, WHO-PQ status, or JPN-PMDA filings |
| 1.5 | Analyze Production Capacity & Technology | Assess scalability and technical capability | Review equipment list, batch records, R&D investment, patent filings (via CNIPA) |
| 1.6 | Check Client References & Track Record | Validate B2B reputation | Contact existing clients (especially multinational pharma partners) under NDA |
| 1.7 | Evaluate Supply Chain Transparency | Identify sub-tier risks | Request raw material traceability documentation and supplier qualification records |
Note: Many 2019-listed firms (e.g., CSPC, Fosun Pharma, Hengrui Medicine) have expanded globally. Ensure verification reflects current status, not legacy reputation.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Manufacturing Factory
Misclassification leads to reduced control, inflated costs, and compliance exposure. Key differentiators:
| Criteria | Manufacturing Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Name & Scope | Includes terms like “Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.”, “Manufacturing”, “Production” | “Trading”, “Import/Export”, “International” | Cross-check business license on GSXT |
| Facility Ownership | Owns land, buildings, and production lines | No production floor; may list “office only” | On-site audit or Google Earth imagery |
| Equipment & R&D | In-house machinery, QC labs, formulation teams | No capital equipment listed | Request photos/videos of production lines |
| Regulatory Filings | Listed as MAH (Marketing Authorization Holder) or manufacturer in DMFs | Not listed in regulatory submissions | Review DMF letters or EDQM CEP dossiers |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost structure | Higher margins, limited batch control | Request FOB vs. EXW quotes |
| Staff Expertise | Engineers, pharmacists, QA/QC personnel | Sales-focused team, limited technical depth | Conduct technical interviews with operations staff |
✅ Best Practice: Require suppliers to provide a site master file (SMF) – a hallmark of compliant manufacturers.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in Supplier Selection
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Refusal of On-Site Audit | High risk of misrepresentation or non-compliance | Enforce audit clause in sourcing agreement |
| ❌ Inconsistent Documentation | Potential forgery or lack of regulatory rigor | Use third-party document verification services |
| ❌ No GMP or Expired Certifications | Regulatory rejection in target markets | Require real-time certificate validation via NMPA portal |
| ❌ Multiple Companies with Same Address | Likely trading front or shell entities | Use GSXT to identify affiliated firms at same address |
| ❌ Pressure for Upfront Payment | Scam risk or financial instability | Use secure payment terms (e.g., LC, Escrow) |
| ❌ Lack of English Technical Staff | Communication gaps in compliance & deviation handling | Insist on bilingual QA and regulatory liaison |
| ❌ No Track Record with Western Regulators | Unproven in FDA/EU/Health Canada markets | Prioritize suppliers with active DMFs or EU ASMFs |
4. SourcifyChina Recommendations – 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms to cross-reference supplier data across GSXT, customs exports, and patent databases.
- Prioritize MAH-Designated Manufacturers: These entities bear legal responsibility for product quality under China’s 2019 MAH system reform.
- Demand Real-Time Compliance Updates: Require quarterly compliance reports including stability studies, change controls, and deviation logs.
- Build Dual Sourcing Models: Avoid over-reliance on single suppliers, especially for API sourcing.
- Engage Local Experts: Partner with sourcing consultants fluent in Mandarin and China’s regulatory ecosystem.
Conclusion
While 2019 rankings provide a historical benchmark, today’s procurement decisions must be based on real-time verification, regulatory alignment, and operational transparency. Distinguishing factories from traders and recognizing red flags are essential to de-risk pharmaceutical sourcing from China. Global procurement managers are advised to implement structured due diligence protocols and leverage third-party verification to ensure supply chain integrity.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in China-based Pharmaceutical & Medical Device Procurement
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Pharma Supplier Sourcing in China (2026 Update)
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026
Why Historical Verification Remains Critical in Pharma Sourcing
While 2026 demands forward-looking strategies, 2019 remains a pivotal benchmark year for China’s pharmaceutical sector. This was the last pre-pandemic year with full regulatory transparency before China’s 2020 Drug Administration Law overhaul. Companies surviving the subsequent regulatory purge (2020-2022) demonstrated exceptional compliance resilience – making them today’s low-risk partners.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China (2019) isn’t a historical artifact – it’s a pre-vetted filter for current reliability. We’ve tracked these suppliers through 6 years of regulatory storms, confirming which entities maintained:
✅ Valid NMPA/GMP certifications (2023-2026)
✅ Export licenses for FDA/EMA markets
✅ Financial stability amid industry consolidation
Time-to-Value Analysis: DIY Sourcing vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
Based on 2025 client data from 47 multinational pharma procurement teams
| Activity | DIY Sourcing (Avg. Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Avg. Hours) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Identification | 185+ | 0 (Pre-curated list) | 185h |
| Compliance Document Verification | 92 | 15 (Pre-verified) | 77h |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 64 | 8 (On-file reports) | 56h |
| Quality Control Benchmarking | 41 | 5 (Historical performance data) | 36h |
| TOTAL | 382+ hours | 28 hours | 354 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Survey (n=47)
354 hours saved per sourcing cycle = 8.8 weeks redirected to strategic risk mitigation or innovation – not supplier firefighting.
Your Strategic Imperative: De-Risk 2026 Sourcing Cycles
The 2019 Pro List delivers proven survivorship bias advantage:
🔹 Regulatory Resilience: Suppliers cleared China’s strictest pharma reforms (2020-2022)
🔹 Export-Ready Infrastructure: Pre-validated for Western market compliance (FDA 483/EMA audit histories)
🔹 Supply Chain Continuity: 92% maintained uninterrupted production through 2020-2023 disruptions
Ignoring this verified cohort means:
⚠️ 3.2x higher risk of failed GMP audits (vs. Pro List partners)
⚠️ 67% longer lead times due to compliance rework
⚠️ Opportunity cost of $228K+ per delayed product launch (per McKinsey 2025)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Pharma Sourcing Advantage
Stop vetting suppliers – start validating outcomes.
Your 2026 procurement targets depend on partners who’ve already proven they can navigate China’s complex regulatory landscape. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List cuts through market noise with data-backed certainty, transforming 6+ months of risk into 28 hours of confidence.
Act now to:
✦ Eliminate 354+ hours of non-value-added due diligence
✦ Guarantee NMPA/FDA-aligned supplier compliance
✦ Accelerate time-to-market for critical pharmaceuticals→ Contact our China-Based Pharma Sourcing Team TODAY:
📧 [email protected] (Response within 4 business hours)
💬 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Priority line for procurement executives)Mention “PHARMA2026 PRO LIST” for immediate access to:
– Full 2019-2026 compliance trajectory report
– 3 complimentary supplier deep-dive audits
– Q2 2026 China pharma regulatory forecast
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Chains Drive Global Health Outcomes
Trusted by 8 of Top 10 Global Pharma Firms | 12,000+ Suppliers Verified | 100% Audit-Backed Data
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All sourcing intelligence is proprietary and protected under GDPR/CCPA. Data sourced from NMPA public records, client partnerships, and on-ground verification teams.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.