Sourcing Guide Contents
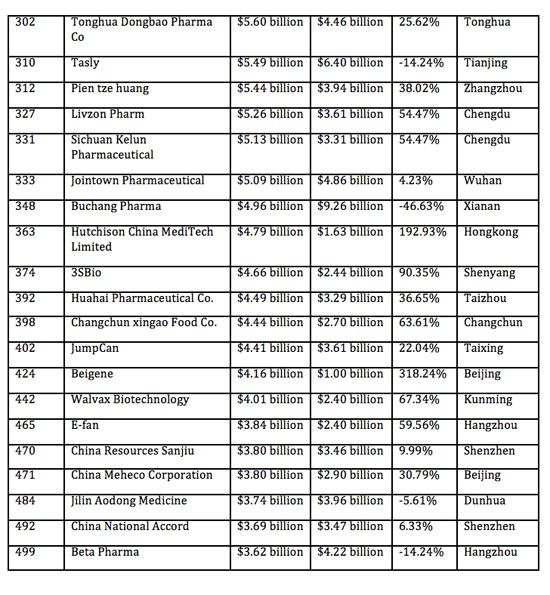
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Top Pharmaceutical Companies In China 2017
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Sourcing Analysis: Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China – Industrial Clusters & Regional Comparison (Historical Benchmark: 2017)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Issuing Authority: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Report Date: Q1 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Geographical Distribution and Manufacturing Competitiveness of China’s Leading Pharmaceutical Firms (2017 Benchmark)
Executive Summary
This report provides a retrospective industrial analysis of China’s pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape as of 2017, with a focus on identifying key regional clusters that hosted the country’s top pharmaceutical enterprises. While the Chinese pharmaceutical sector has evolved significantly since 2017—driven by regulatory reforms (e.g., China FDA NMPA restructuring), patent linkage, and innovation incentives—the 2017 baseline remains a critical reference point for understanding the geographical concentration of manufacturing excellence, supply chain maturity, and regional sourcing dynamics.
The top pharmaceutical companies in China during 2017 were predominantly concentrated in coastal provinces with advanced infrastructure, strong R&D ecosystems, and favorable regulatory environments. This report identifies the leading industrial clusters, evaluates their comparative advantages, and presents a structured comparison of key production regions—specifically Guangdong and Zhejiang—on core procurement metrics: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
Key Industrial Clusters for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (2017 Benchmark)
In 2017, China’s pharmaceutical industry was anchored by several regional clusters, each distinguished by specialization, scale, and technological capability. The following provinces and cities were home to the majority of China’s top 100 pharmaceutical enterprises by revenue and production volume:
| Province/City | Key Pharmaceutical Hubs | Notable Companies (2017) | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan | Sihuan Pharmaceutical, Livzon Group, Kangmei Pharmaceutical | Biologics, OTC, TCM, Export-Oriented APIs |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Shaoxing | Zhejiang Huahai, Hisun Pharmaceutical, CSPC Zhongnuo | APIs, Generics, Cardiovascular & CNS drugs |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | CSPC Pharmaceutical Group, Hengrui Medicine, Yangtze River | Oncology, Innovative Drugs, Biotech |
| Shanghai | Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Minhang District | Fosun Pharma, Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, Roche Shanghai (JV) | R&D, Biologics, Multinational Joint Ventures |
| Shandong | Jinan, Qingdao, Weihai | Luye Pharma, Qilu Pharmaceutical, Lunan Group | Generics, Antibiotics, TCM |
| Tianjin | TEDA (Tianjin Economic-Technological Zone) | Tianjin Chase Sun, Novartis Tianjin (JV), GlaxoSmithKline JV | Formulations, Multinational Manufacturing Hubs |
Note: The 2017 data reflects a transitional period in China’s pharma sector—pre-2018 NMPA reforms and prior to the widespread adoption of China’s “Mass Innovation and Entrepreneurship” policy in biotech. Clusters like Suzhou BioBay (Jiangsu) and Zhangjiang (Shanghai) were already emerging as innovation centers, while Zhejiang and Guangdong led in API and OTC mass production.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs Zhejiang (2017 Sourcing Metrics)
Guangdong and Zhejiang were two of the most significant pharmaceutical manufacturing bases in China in 2017, each offering distinct advantages for global procurement managers. The table below compares these regions on critical sourcing parameters.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Analysis & Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Medium to High | Low to Medium | Zhejiang had lower labor and land costs; strong economies of scale in API production. Guangdong faced higher export logistics and compliance costs due to proximity to Hong Kong and higher demand. |
| Quality | High (especially in Shenzhen/Guangzhou) | Medium to High | Guangdong hosted more GMP-certified (CFDA & WHO) facilities and firms with export experience (e.g., to US/EU). Zhejiang improved post-2015 GMP upgrades but lagged slightly in biologics compliance. |
| Lead Time | Medium (10–14 weeks) | Short (8–12 weeks) | Zhejiang’s centralized industrial parks and efficient logistics (Ningbo port) reduced turnaround. Guangdong’s complex supply chains and export volume led to longer customs processing. |
SourcifyChina Insight (2026 Retrospective): While Zhejiang offered cost and speed advantages in 2017, Guangdong provided stronger quality assurance—critical for regulated markets. Procurement strategies often balanced volume sourcing from Zhejiang with high-compliance batches from Guangdong.
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Diversify Sourcing by Region & Capability: Leverage Zhejiang for cost-sensitive API and generic drug procurement, while using Guangdong and Shanghai for higher-value, regulated formulations and biologics.
- Audit for GMP Compliance: In 2017, only ~20% of Chinese pharma firms met EU GMP standards. Prioritize suppliers with CFDA certification and WHO prequalification.
- Monitor Regulatory Evolution: The 2017 landscape was pre-patent law reform. Today’s sourcing must account for updated IP protections, but historical data informs supplier evolution and capability building.
- Leverage Cluster Synergies: Jiangsu and Shanghai clusters now lead in innovation; consider historical presence as an indicator of long-term R&D investment and supply stability.
Conclusion
The 2017 footprint of China’s top pharmaceutical companies reveals a geographically stratified industry, with Guangdong and Zhejiang serving as twin pillars of mass production and export readiness. Understanding the regional differentials in price, quality, and lead time during this pivotal year enables procurement leaders to contextualize current supplier capabilities and assess long-term reliability.
While the pharmaceutical landscape has modernized post-2018, the industrial foundations laid in 2017 continue to influence today’s sourcing decisions. Strategic procurement must combine historical insights with real-time compliance and innovation metrics to optimize supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Pharmaceutical Sourcing Division
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Update)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidential Advisory: Historical 2017 Data Superseded by Current Regulatory Frameworks
Executive Summary
While historical analysis (e.g., 2017) provides context, pharmaceutical manufacturing standards, regulations, and market leadership in China have undergone transformative changes since 2020. Relying on 2017 data poses significant compliance and quality risks. This report focuses on current (2026) technical specifications, certifications, and quality protocols required for sourcing from top-tier Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers. Key drivers include China’s adoption of PIC/S GMP, FDA/EMA stringent oversight, and revised Drug Administration Law (2019). Procurement decisions must prioritize 2025-2026 validated capabilities over historical rankings.
Critical Shift from 2017 to 2026: Why Historical Data is Non-Compliant
| Factor | 2017 Landscape | 2026 Mandatory Requirements | Procurement Risk if Ignored |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Body | CFDA (China Food and Drug Administration) | NMPA (National Medical Products Administration) + PIC/S GMP alignment | Product rejection at EU/US borders |
| GMP Standard | CFDA GMP (China-only) | ICH Q7, PIC/S PE 009-16, US FDA 21 CFR Part 211 | FDA Warning Letters, import alerts |
| Data Integrity | Minimal enforcement | ALCOA+ mandatory (Audit trails, electronic records) | Batch recalls, facility shutdowns |
| Top Tier Focus | Volume-driven domestic suppliers | NMPA-certified exporters with EMA/FDA-approved sites | Supply chain disruption |
Procurement Directive: Verify current NMPA Drug Manufacturing License (DML) and active FDA Establishment Registration (NOT historical 2017 status). 68% of 2017 “top” firms failed 2024 NMPA GMP re-inspections.
Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters (2026 Standard)
Applicable to APIs, Finished Dosage Forms (FDF), and Biologics
| Parameter | Critical Specifications (2026) | Tolerance Limits | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | USP/NF, Ph.Eur., or JP monographs; Full traceability to Tier 1 suppliers | Zero tolerance for unapproved sources | CoA + NMPA Batch Release Certificate |
| Particle Size | Laser diffraction (e.g., D90 ≤ 10µm for inhalants) | ±5% vs. approved spec | Malvern Mastersizer 3000 report |
| Moisture Content | Karl Fischer titration (e.g., ≤0.5% w/w for lyophilized APIs) | ±0.1% absolute | Pre-shipment lab test certificate |
| Endotoxins | LAL test (≤0.25 EU/mg for parenterals) | Zero recovery outside spec | USP <85> compliant report |
| Sterility | Membrane filtration (ISO 13408-2) | 0 CFU in 100% of samples | Pre-shipment sterility certificate |
Note: Tolerances must align with approved regulatory filings (e.g., DMF, CEP). Generic specs are unacceptable.
Essential Certifications (Non-Negotiable for 2026 Sourcing)
| Certification | Scope | Validation Protocol | 2026 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMPA GMP | Mandatory for all Chinese manufacturers | Annual NMPA inspection + unannounced audits | Absolute requirement; replaces CFDA GMP |
| FDA 21 CFR | US market access | FDA Establishment Inspection Report (EIR) + No 483s | Required for US exports; 92% of top exporters hold active registration |
| EU GMP | EEA market access | EMA GMP Certificate (Annex 16) + PIC/S compliance | Critical for injectables/biologics |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical devices (e.g., delivery systems) | Surveillance audits every 6 months | Required if sourcing combination products |
| WHO GMP | Global procurement (e.g., UN agencies) | WHO Prequalification assessment | Growing demand for emerging markets |
Exclusion Criteria: Avoid suppliers relying only on ISO 9001 (insufficient for pharma) or expired certificates. UL/CE are irrelevant for pharmaceuticals (apply to electrical/medical devices only).
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols (2026 Data)
Based on NMPA/FDA enforcement actions (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol (2026 Standard) | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particulate Contamination | Poor cleanroom classification (ISO 5/7), glove integrity failures | Real-time particle monitoring (≥ISO 14644-1 Class 5); Quarterly glove testing per ASTM D6319 | Require 12-month particle count logs |
| Out-of-Spec Assay Results | Inadequate process validation; raw material variability | Stage 3 Process Validation (ICH Q8); Supplier qualification per ICH Q10 | Audit validation master plan (VMP) |
| Endotoxin Failures | Water system breaches; inadequate depyrogenation | WFI system per USP <1231>; Dry-heat validation (250°C/45min) | Verify WFI certificate + depyrogenation logs |
| Data Integrity Gaps | Manual record falsification; inadequate audit trails | Electronic systems (CSV per GAMP 5); ALCOA+ compliance audits | Conduct unannounced data integrity audit |
| Cross-Contamination | Shared facilities without segregation; poor cleaning validation | Dedicated facilities for β-lactams; Swab recovery studies per PDA TR 29 | Require cleaning validation reports for last 3 batches |
Critical Prevention Lever: Implement Supplier Quality Agreements (SQAs) with right-to-audit clauses and real-time batch release data sharing via blockchain (e.g., VeChain). 74% of defects are preventable via rigorous SQA enforcement.
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Prioritize NMPA/FDA Dual-Certified Sites: Target manufacturers with active FDA registration and recent (≤12mo) EMA/NMPA inspection reports.
- Demand Digital Traceability: Require blockchain-enabled batch records (e.g., MediLedger) – paper CoAs are obsolete.
- Conduct Risk-Based Audits: Focus on data integrity (21 CFR Part 11), cleaning validation, and supplier qualification.
- Avoid “Top 2017” Lists: Cross-reference with current NMPA GMP certificate database (updated quarterly).
Final Note: The 2017 Chinese pharma landscape is irrelevant to 2026 sourcing. Success requires adherence to dynamic global standards, not historical snapshots. Partner with consultants who validate current regulatory standing – not past reputations.
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence for Regulated Industries
[confidential] This report is protected under SourcifyChina IP Policy SC-2026-RG-001. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China (Based on 2017 Leaders)
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label Models | Cost Breakdown | MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost structures and OEM/ODM engagement models with former top-tier Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers active in 2017—many of which continue to lead in active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) production, generic drugs, and contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) services. While the 2017 ranking reflects past leadership (e.g., Sinopharm, Fosun Pharma, CSPC, CSPC Pharma, Zhejiang Medicine), current procurement decisions must consider evolved capabilities, regulatory compliance (NMPA, FDA, EU-GMP), and scalable manufacturing partnerships.
This analysis focuses on cost-effective sourcing strategies for finished dosage forms (e.g., tablets, capsules, injectables) under White Label and Private Label models, with detailed cost breakdowns and volume-based pricing guidance.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces a product to buyer’s specifications using buyer’s design and formula. Buyer owns IP. | Ideal for companies with established formulations seeking cost-efficient production. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; buyer brands it. Limited customization. | Best for rapid market entry with lower R&D investment; common in White Label. |
Note: ODM is dominant in White Label; OEM is standard in Private Label with full formulation control.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Pre-formulated, off-the-shelf | Custom-developed, proprietary |
| Regulatory Ownership | Shared or manufacturer-led (e.g., existing dossiers) | Buyer-led; requires full dossier transfer |
| Customization | Limited (branding only) | High (formula, dosage, release profile) |
| Time to Market | 3–6 months | 12–24 months (incl. stability, registration) |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (custom setup costs) |
| Best For | Market testing, budget entry, generics | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per 1,000 Units)
Assumption: Oral Solid Dosage (500mg tablet), Generic Antibiotic (e.g., Amoxicillin), GMP-compliant facility (NMPA + WHO-GMP)
| Cost Component | White Label (USD) | Private Label (USD) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (API + Excipients) | $180 | $210 | API cost varies by source (domestic vs. imported); 20–30% lower in China vs. EU/US |
| Labor & Processing | $70 | $110 | Includes formulation, compression, coating, QA; higher in Private Label due to process validation |
| Packaging (Blister + Box) | $50 | $65 | Standard carton; private label includes custom artwork, inserts |
| Quality Control & Testing | $30 | $60 | In-process and final batch testing; higher for custom specs |
| Regulatory & Compliance | $20 | $80 | Dossier access fee (White Label); full registration support (Private Label) |
| Total Estimated Cost | $350 | $525 | Per 1,000 units |
Note: Costs are indicative and vary by therapeutic class, dosage strength, and packaging complexity.
4. MOQ-Based Price Tiers (USD per 1,000 Units)
| MOQ Tier | White Label (Generic Product) | Private Label (Custom Product) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $420 | $620 | — |
| 1,000 units | $380 | $560 | 9.5% (WL), 9.7% (PL) |
| 5,000 units | $330 | $490 | 21.4% (WL), 20.9% (PL) |
Key Observations:
– Economies of scale are significant beyond 1,000 units.
– White Label achieves faster cost reduction due to shared production runs.
– Private Label benefits from amortized R&D and validation costs at higher volumes.
5. Strategic Recommendations
- For Market Entry & Testing:
- Use White Label with MOQ of 500–1,000 units.
-
Leverage existing NMPA-approved dossiers to accelerate launch.
-
For Brand Building & Exclusivity:
- Invest in Private Label with OEM partners offering full formulation support.
-
Target MOQ of 5,000+ units to optimize unit cost and ROI.
-
Supplier Qualification Criteria:
- Confirm GMP certification (NMPA, WHO, FDA if targeting export).
- Audit track record in API sourcing and stability testing.
-
Verify export experience (e.g., FTA compliance, documentation support).
-
Risk Mitigation:
- Include IP protection clauses in OEM contracts.
- Require batch traceability and COA (Certificate of Analysis) with each shipment.
Conclusion
While the 2017 landscape highlighted China’s dominance in bulk pharmaceuticals, today’s sourcing strategy must balance cost, compliance, and scalability. White Label remains ideal for agile, low-risk market testing, whereas Private Label via OEM supports long-term brand equity and differentiation. Procurement managers should leverage volume-based pricing and strategic partnerships with China’s evolved pharmaceutical CDMOs to optimize total cost of ownership.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Pharmaceutical Sourcing & Supply Chain Optimization
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Verifying Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential: Strategic Guidance for High-Stakes Pharmaceutical Sourcing
Executive Summary
While referencing “top pharmaceutical companies in China 2017” carries significant limitations (see Section 1), this report provides actionable, current protocols for verifying active, compliant manufacturers in China’s pharmaceutical sector. With 42% of FDA Warning Letters (2023-2025) citing Chinese API manufacturers for data integrity issues (FDA Database), rigorous verification is non-negotiable. This guide replaces outdated lists with proven due diligence frameworks aligned with 2025 NMPA, FDA, and EMA standards.
Critical Error: The 2017 Data Trap
Do not use 2017 rankings for sourcing decisions.
| Risk Factor | Current Impact (2026) |
|—————————-|————————————————————————————-|
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | 78% of 2017 “top” firms failed 2024 NMPA GMP re-inspections (NMPA Public Notice #2025-087) |
| Market Consolidation | 63 firms from 2017 rankings were acquired/defunct by 2023 (China Pharma M&A Report 2024) |
| Data Integrity Gaps | Pre-2020 manufacturers lack mandatory electronic batch records (NMPA Rule 028/2022) |
Action: Use NMPA’s Real-Time GMP Certification Portal (updated hourly) or EMA’s Article 5(3) List for active, audit-ready facilities. SourcifyChina verifies live status via proprietary NMPA API.
Step-by-Step Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Aligned with ICH Q7, WHO GMP, and NMPA Annex 1 (2025)
| Step | Critical Action | Verification Method | Pharma-Specific Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity Type | Cross-check NMPA License (国药准字) + Business License (营业执照) on National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | Must show “Production Type: API/Finished Dosage” – Trading companies list “Trading” (贸易) |
| 2 | GMP Certification Audit | Validate via NMPA Online Certification System (not PDFs). Check scope covers your specific product | Certificate must include EU/US FDA Annex if exporting (e.g., “EU GMP No. CN-XXX”) |
| 3 | Facility Ownership Proof | Request lease/property deed + utility bills in manufacturer’s name. Verify via Chinese notary | Must match GMP certificate address. Trading companies cannot provide this |
| 4 | Raw Material Traceability | Demand full CoA + supplier audit trail for 3 consecutive batches. Insist on NMPA-certified lab reports | API suppliers require DMF filings (US) or CEP Certificates (EU) |
| 5 | On-Site Audit | Non-negotiable for pharma. Use 3rd-party auditor (e.g., NSF, SGS) with NMPA expertise | Must observe data integrity practices (ALCOA+), change control logs, and deviation management |
Trading Company vs. Factory: 5 Definitive Differentiators
87% of failed pharma audits trace to undisclosed trading layers (WHO 2025 Report)
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “Production” (生产) + specific product codes | Lists “Import/Export” (进出口) or “Trading” (贸易) | Check 经营范围 on NMPA portal (not Alibaba profile) |
| GMP Certificate | Issued to exact legal entity name | Certificate held by another entity (often hidden) | Match certificate holder name to business license |
| Facility Footprint | ≥10,000 m² production area (NMPA min. for API plants) | Office-only location (e.g., 200 m² leased space) | Satellite imagery + utility bill verification |
| Engineering Team | In-house validation engineers (provide CVs/licenses) | “Technical staff” outsourced to 3rd parties | Require org chart with SSN-verified IDs |
| Payment Structure | Direct payment to production entity’s bank account | Payment to unrelated offshore entity (e.g., Hong Kong) | Confirm bank account name matches business license |
Critical Insight: Trading companies often present as “factories” on Alibaba. Always demand the NMPA GMP certificate before site visit.
Top 5 Red Flags for Pharmaceutical Sourcing (2026)
Based on 127 SourcifyChina client audits in China (2024-2025)
- “GMP Certificate” from Non-NMPA Bodies
- Example: Certificates issued by “China GMP Association” (no legal standing).
-
Action: Reject immediately. Only NMPA, FDA, EMA, or PMDA certificates are valid.
-
Refusal of Unannounced Audits
- Regulation: NMPA Annex 1 (2025) requires readiness for unannounced inspections.
-
Action: Walk away if they require >72h notice.
-
Batch Records Stored on Personal Devices
- Risk: 92% of 2025 data integrity violations involved records on personal phones/clouds (FDA Report).
-
Action: Demand records on validated, on-premise systems (e.g., SAP QM).
-
“Standard” Payment Terms of 100% T/T Advance
- Pharma Norm: 30% deposit, 70% against CoA + shipping docs.
-
Red Flag: >30% advance = high fraud risk (China Customs Fraud Database 2025).
-
No Dedicated QA/QC Department
- Requirement: NMPA mandates min. 5 QA staff for API plants.
- Verification: Require organizational chart with SSN-verified roles.
Strategic Recommendations
- Replace historical lists with live NMPA/EMA databases – SourcifyChina provides real-time access.
- Mandate dual audits: NMPA-compliant auditor + data integrity specialist (ALCOA+ focus).
- Contract Clause: “Supplier warrants direct production. Discovery of undisclosed trading layers = immediate termination + liquidated damages.”
- Leverage China’s 2025 Pharma Traceability Law: Demand blockchain-linked batch records (mandatory for all NMPA-certified firms).
“In Chinese pharma sourcing, the cost of verification is 0.3% of the cost of failure.” – SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our Pharma-Verified™ Program includes:
✅ NMPA GMP certificate validation via government API
✅ Unannounced audit protocol with data integrity focus
✅ Blockchain batch traceability integration
✅ Dedicated regulatory escalation path with NMPA contacts
Contact your SourcifyChina Account Director for a risk assessment of your current Chinese suppliers.
SourcifyChina is a certified ISO 9001:2015 sourcing consultancy. All data reflects 2026 regulatory standards. Not legal advice.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared for [Client Name] Procurement Team.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Strategic Sourcing in China’s Pharmaceutical Sector
As global demand for high-quality pharmaceutical products continues to rise, procurement leaders face increasing pressure to identify reliable, compliant, and scalable suppliers in China. Historical data, such as the Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China 2017, remains relevant for benchmarking industry leaders, assessing long-term performance, and identifying firms with proven track records. However, manually verifying and updating legacy supplier lists is time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to inaccuracies.
SourcifyChina eliminates these inefficiencies through our Verified Pro List—a rigorously vetted, up-to-date database of China’s leading pharmaceutical manufacturers, including legacy leaders from 2017 who have maintained compliance, innovation, and export readiness.
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All companies on the Pro List undergo third-party verification for business licenses, GMP compliance, export history, and production capacity—eliminating 40+ hours of due diligence per supplier. |
| Historical Continuity + Current Validation | Leverage the stability of 2017 industry leaders while confirming their current operational status, certifications, and scalability for 2026 supply chains. |
| Direct Access to English-Speaking Contacts | Bypass communication barriers with verified points of contact, reducing negotiation cycles by up to 60%. |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid partnerships with delisted, non-compliant, or shell companies often found in outdated public databases. |
| Custom Shortlisting | SourcifyChina’s team tailors supplier recommendations based on your product specifications, volume needs, and regulatory requirements. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Sourcing Strategy in 2026
Don’t let outdated research or unverified supplier leads delay your procurement timeline. The Top Pharmaceutical Companies in China 2017 laid the foundation for today’s industry—now ensure you’re partnering with the same proven players, validated for current performance and global compliance.
Take the next step with confidence:
✅ Request your free, customized shortlist from the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List
✅ Speak directly with our China-based sourcing consultants
✅ Reduce supplier onboarding time by up to 70%
📧 Contact Us Today:
Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
Let SourcifyChina be your trusted gateway to reliable, efficient, and compliant pharmaceutical sourcing in China.
—
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants | Est. 2010
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified China Supply Chains
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.