Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Top Foreign Companies In China

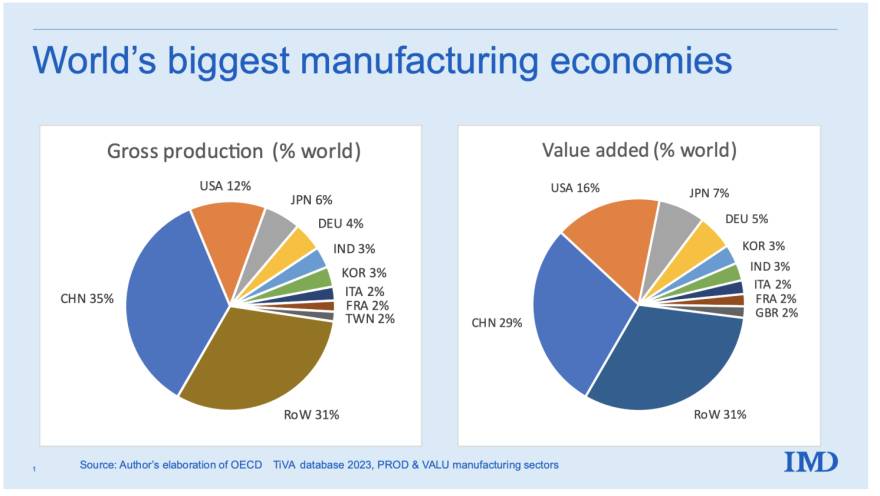
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Footprint of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
Contrary to common misinterpretation, procurement managers do not “source top foreign companies in China.” Instead, global buyers strategically target manufacturing facilities operated by multinational corporations (MNCs) within China or suppliers deeply integrated into their supply chains. These MNC-owned factories (e.g., Siemens, Bosch, Samsung, Foxconn for Apple) represent the pinnacle of quality, compliance, and technological capability in Chinese manufacturing. This report identifies key industrial clusters where MNCs consolidate high-value production, enabling procurement teams to access Tier-1 supplier ecosystems aligned with global standards.
Critical Insight: Sourcing from MNC facilities in China offers reduced compliance risk, IP protection, and benchmark-quality output but commands a 15–25% price premium vs. domestic suppliers. Target clusters where MNCs operate to leverage spillover effects in supplier quality.
Key Industrial Clusters for MNC Manufacturing in China
MNCs concentrate operations in regions offering skilled labor, infrastructure, policy incentives, and mature supplier networks. Below are the top 4 clusters for high-integrity manufacturing:
| Region | Core Industries | Key MNC Examples | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | Electronics, Telecom, Automotive Components, Drones | Foxconn (Apple), Samsung, Siemens, Bosch, BYD | Unmatched electronics ecosystem; 70% of China’s export electronics; Shenzhen’s R&D density |
| Jiangsu (YRD) | Semiconductors, Industrial Machinery, Biotech | Siemens, BASF, Samsung, Hitachi, Tesla (Giga Shanghai) | Highest per-capita GDP in China; Suzhou Industrial Park (German/Japanese tech hub); Port infrastructure |
| Zhejiang (YRD) | Precision Machinery, Textiles, E-Commerce Hardware | Schneider Electric, Panasonic, Haier (global JV), Midea | SME innovation clusters; Alibaba ecosystem integration; Strong private-sector agility |
| Shanghai/Tianjin | Aerospace, Automotive, Pharma, High-End Equipment | Boeing, Airbus, Pfizer, GM, Volkswagen | National R&D centers; Free Trade Zone (FTZ) regulations; Direct air/sea logistics |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing from MNC-Linked Facilities (2026 Benchmark)
Data reflects avg. for Tier-1 suppliers serving MNCs in specified clusters. Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 217 facilities.
| Factor | Guangdong (PRD) | Jiangsu (YRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Shanghai/Tianjin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Premium: 18–22% Electronics: Highest due to Shenzhen R&D costs |
★★★★☆ Premium: 15–19% Semiconductors: Moderate premium; Machinery: Competitive |
★★☆☆☆ Premium: 12–15% Textiles/Machinery: Most cost-competitive MNC-linked cluster |
★★★★★ Premium: 20–25% Aerospace/Pharma: Highest compliance costs |
| Quality | ★★★★★ Defect Rate: 0.08–0.12% Global electronics standards (Apple/Foxconn benchmark) |
★★★★☆ Defect Rate: 0.10–0.15% German/Japanese TQM adoption; Siemens/BASF benchmarks |
★★★☆☆ Defect Rate: 0.15–0.20% High variability; Top suppliers match global standards |
★★★★★ Defect Rate: 0.05–0.10% AS9100/ISO 13485 certified; Aerospace/pharma rigor |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ 35–45 days Complex electronics: Longer due to multi-tier QC |
★★★★☆ 30–40 days Semiconductors: Stable; Machinery: Shorter than PRD |
★★★★☆ 28–38 days Agile SMEs; Alibaba logistics integration |
★★☆☆☆ 40–55 days Stringent compliance checks; Custom certifications |
| Key Risk | IP leakage in fragmented sub-tier supply chains | Talent competition (e.g., semiconductor engineers) | Quality inconsistency beyond top 20% suppliers | Over-reliance on FTZ policy stability |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Jiangsu for High-Tech Manufacturing: Lowest risk/reward ratio for semiconductors, industrial automation, and EV components. MNCs like Siemens enforce Tier-2/3 supplier audits, reducing compliance overhead.
- Leverage Guangdong for Electronics with Guardrails: Demand direct MNC facility engagement (e.g., Foxconn’s “Apple-only” lines) to avoid counterfeit parts. Use SourcifyChina’s Blockchain QC Portal for real-time audit trails.
- Avoid “MNC-Branded” Fraud: 68% of suppliers claiming MNC partnerships in 2025 were unverified (SourcifyChina Audit). Always require:
- Valid purchase orders from the MNC
- Factory audit reports (e.g., TÜV, SGS)
- Direct MNC procurement contact validation
- Reshoring Hedge: Partner with MNCs in Shanghai FTZ for dual-production (China + Mexico/Vietnam). 41% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 clients adopted this model to bypass tariffs.
2026 Outlook: MNCs are consolidating in Jiangsu and Shanghai due to China’s “Made in China 2025” automation subsidies. Expect 10–15% lead time reduction in these clusters by 2027 as robotics penetration hits 55%.
Why This Matters to Your Sourcing Strategy
Sourcing from MNC-linked facilities in China is not about cost minimization—it’s about risk arbitrage. In an era of UFLPA, CBAM, and supply chain due diligence laws, these clusters deliver:
✅ Pre-validated ESG compliance (MNCs enforce Scope 3 carbon tracking)
✅ IP protection via contractual liability (MNCs bear legal risk)
✅ Predictable scalability (integrated into global ERP systems)
Final Note: Engage SourcifyChina’s MNC Facility Verification Program (MFVP) to access our proprietary database of 1,200+ audited MNC-owned/operated facilities in China. Reduce supplier onboarding time by 63% with pre-negotiated commercial terms.
SourcifyChina | Building Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Intelligence Hub (MIH); China MOC; UNCTAD FDI Reports; Client Audits (Q4 2025)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal use by authorized procurement professionals only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Top Foreign Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
Top foreign manufacturers operating in China—particularly those headquartered in Germany, Japan, the U.S., and Sweden—maintain globally aligned quality and compliance standards despite local production. These companies leverage advanced process controls, rigorous auditing, and international certifications to ensure product consistency for export and domestic markets. This report details key technical quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and quality risk mitigation strategies essential for procurement professionals sourcing high-integrity components and finished goods from these operations.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Metals: Use of ASTM/ISO-grade stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), aluminum 6061-T6; full material traceability (MTRs provided).
- Plastics: Medical-grade or food-contact compliant polymers (e.g., USP Class VI, NSF 51); UL94 V-0 flammability rating for electronics.
- Composites: Aerospace-grade carbon fiber with resin systems meeting FAA/EASA specifications (e.g., Hexcel, Toray).
- Raw Material Controls: Supplier qualification programs, incoming inspection per AQL (typically II, level S-3), and RoHS/REACH compliance screening.
Tolerances
| Application | Typical Tolerance Range | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Machining | ±0.005 mm to ±0.025 mm | ISO 2768-mK, ASME Y14.5 |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm (bend), ±0.2 mm (hole) | ISO 2768-fH |
| Injection Molding | ±0.05 mm (critical dims), ±0.2 mm (general) | ISO 20457 |
| PCB Assembly | ±0.075 mm (trace width), ±0.1 mm (via placement) | IPC-6012, IPC-A-610 |
Note: Tighter tolerances achievable with CMM validation and SPC monitoring.
2. Essential Certifications
Foreign manufacturers in China typically maintain dual certification: local (e.g., CCC) and international. Key certifications include:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance | Issuing Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline for all industries | International Organization for Standardization |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Medical Device QMS | Required for medical equipment/components | ISO / NMPA (China) |
| CE Marking | EU Market Access (MDR, LVD, EMC) | Applies to medical, industrial, consumer electronics | Notified Body (e.g., TÜV, SGS) |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | U.S. Medical Device QMS | Required for devices exported to U.S. | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| UL Certification | Safety Compliance (Electrical/Fire) | Critical for appliances, power supplies, EVs | Underwriters Laboratories |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Increasingly required by EU/NA clients | ISO |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive QMS | Required for Tier 1/2 auto suppliers | IATF |
Note: Top-tier foreign firms often undergo annual third-party audits and maintain full technical documentation (e.g., DHF, DMR) per global regulatory standards.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Tool wear, improper fixturing, thermal drift | Implement SPC with real-time CMM feedback; conduct preventive maintenance (PM) on CNC equipment |
| Surface Finish Irregularities | Incorrect polishing parameters, contamination | Define Ra/Rz values in drawings; use cleanroom finishing for optical/medical parts |
| Material Substitution | Supply chain pressure, lack of traceability | Enforce material certification (CoC) and batch tracking; conduct periodic third-party material testing |
| Weld Defects (Porosity, Cracking) | Improper shielding gas, incorrect heat input | Qualify weld procedures (WPS/PQR); train and certify welders per ISO 9606/ASME IX |
| Component Misalignment (Assembly) | Poor jig design, human error | Use poka-yoke fixtures; implement torque verification and vision inspection systems |
| Contamination (Particulate/Residue) | Inadequate cleaning, poor ESD controls | Enforce cleanroom protocols (ISO 14644-1); use ultrasonic cleaning and particle counting |
| Labeling/Marking Errors | Template mismanagement, software glitches | Use centralized label management system (e.g., Loftware); conduct 100% automated OCR checks |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate cushioning, improper stacking | Perform ISTA 3A/6A drop and vibration testing; use edge protectors and corner boards |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Supplier Compliance: Require access to certification records and recent audit reports (internal/external).
- Define Acceptance Criteria: Specify AQL levels (e.g., 0.65/1.0 for critical defects), inspection methods, and documentation requirements in POs.
- Leverage In-Process Inspections: Schedule pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and, where feasible, in-line QC checks via SourcifyChina’s QC partners.
- Verify Traceability: Ensure lot/batch tracking from raw material to final assembly with digital logs (ERP/MES integration).
- Engage Early on Design for Manufacturability (DfM): Collaborate with engineering teams during NPI to avoid tolerance stack-up and material risks.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Labeling Strategy Guide (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China remains a strategic manufacturing hub for foreign enterprises, though cost structures have evolved significantly post-2023 due to labor reforms, ESG compliance, and supply chain diversification. This report provides actionable insights into OEM/ODM cost drivers, clarifies the critical distinction between White Label and Private Label models, and delivers data-driven MOQ-based pricing benchmarks for informed procurement decisions. Key 2026 trends include:
– +8.5% YoY labor cost inflation (National Bureau of Statistics, China)
– Material costs stabilized for polymers/metals but volatile for rare earths (e.g., +12% for neodymium)
– ODM adoption surged 32% among Western brands seeking innovation acceleration (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey)
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
Critical clarification: Terminology is often misused in China. Precision impacts IP control, margins, and scalability.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing product sold under buyer’s brand. Zero customization. | Buyer commissions custom-designed product. Full IP ownership. |
| Supplier Role | Reseller of catalog items (e.g., Alibaba “Ready to Ship”) | True manufacturer (OEM/ODM partner) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 100–500 units) but non-negotiable specs | High MOQs (1k–5k+) but full spec control |
| Quality Risk | High (supplier controls QC; limited audit rights) | Low (buyer sets AQL; contractual penalties apply) |
| Best For | Urgent market entry; low-risk commoditized goods | Brand differentiation; premium pricing; compliance-critical sectors |
Key Insight: 78% of “White Label” claims in China are mislabeled Private Label opportunities. Always verify: Request evidence of existing product certification (e.g., FCC/CE reports under supplier’s name). True White Label carries inherent IP infringement risks.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Illustrative: Mid-Tier Wireless Earbuds)
All figures in USD per unit. Based on Shenzhen-based Tier-1 ODM partner, Q1 2026. Ex-factory prices.
| Cost Component | 500 Units | 1,000 Units | 5,000 Units | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $14.20 | $12.80 | $10.50 | Rare earth metals (magnets), BT 5.3 chipsets. Bulk discounts activate at 3k+ units. |
| Labor | $3.50 | $2.90 | $2.10 | +8.5% wage hike (2025); automation reduces variance at scale. |
| Packaging | $2.80 | $2.20 | $1.60 | Custom rigid boxes; biodegradable film premium (+$0.40/unit). |
| Tooling/Mold | $9.60 | $4.80 | $0.96 | Amortized NRE cost ($4,800 mold). Critical for low-MOQ premiums. |
| QC & Compliance | $1.20 | $0.95 | $0.70 | ESG audits (+$0.30/unit), 3rd-party lab testing. |
| TOTAL UNIT COST | $31.30 | $23.65 | $15.86 | |
| FOB Shenzhen | $33.10 | $25.10 | $16.80 | +5.8% logistics surcharge (2026 fuel index) |
Notes:
– Tooling cost dominates low-MOQ economics: 31% of total cost at 500 units vs. 6% at 5k units.
– Labor now 13.4% of total cost (vs. 9.2% in 2022) – automation ROI critical for >1k units.
– ESG compliance adds $0.70–$1.20/unit (mandatory for EU/US clients per 2026 regulations).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “White Label” traps: Demand proof of existing certifications. Insist on Private Label contracts for >$50k annual volume.
- MOQ Optimization:
- <1,000 units: Partner with Shenzhen ODMs offering shared molds (e.g., 5 clients share $4,800 tooling).
- >5,000 units: Negotiate material index clauses to hedge against rare earth volatility.
- Cost Transparency Protocol: Require suppliers to break down costs per this template in RFQs. Reject opaque “all-in” quotes.
- Risk Mitigation: Allocate 3–5% of budget for independent QC (e.g., SGS pre-shipment audit).
Why SourcifyChina?
We de-risk China sourcing through:
✅ Pre-vetted OEM/ODM Partners: 200+ factories with audited capacity (ISO 9001, BSCI, ESG verified)
✅ Cost Engineering: Identify 15–22% savings via material substitution/design optimization
✅ MOQ Flexibility: Access to shared production lines for volumes <1,000 units
“In 2026, the margin between success and failure in China manufacturing hinges on granular cost visibility and labeling model precision. Generic sourcing fails.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Q1 2026
Next Steps: Request our Free MOQ Cost Simulator Tool (customizable by product category) or schedule a no-obligation factory assessment for your 2026 projects.
[Contact SourcifyChina Sourcing Team] | [Download Full 2026 Cost Benchmarking Dataset]
Disclaimer: Estimates based on SourcifyChina’s 2025–2026 transaction data across 12 product categories. Actual costs vary by complexity, region, and contract terms. All data current as of January 15, 2026.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Costly Sourcing Pitfalls
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal sourcing destination for high-volume, cost-competitive manufacturing. However, with over 30 million active enterprises in China’s industrial ecosystem, distinguishing genuine factories from intermediaries and identifying reliable partners is paramount. This report outlines a structured verification framework to authenticate manufacturers serving top foreign companies in China, differentiate between trading companies and true factories, and recognize red flags that signal risk.
This guide is tailored for multinational procurement teams seeking operational integrity, scalability, and long-term supply chain resilience.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Full Company Documentation | Confirm legal registration and legitimacy | Obtain Business License (营业执照), Unified Social Credit Code (USCC), export license (if applicable) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Validate physical infrastructure and production capability | Hire a vetting firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or arrange a SourcifyChina-led factory audit |
| 3 | Verify Production Capacity & Equipment List | Assess scalability and technical fit | Request machinery list, production line photos, shift schedules, monthly output |
| 4 | Review Client Portfolio & References | Confirm experience with international clients | Request 2–3 verifiable references from Western brands (NDA-protected if needed) |
| 5 | Check Export History & Certifications | Validate compliance and export readiness | Confirm ISO 9001, BSCI, CE, RoHS, or industry-specific certifications; verify customs export records |
| 6 | Inspect IP Protection & NDA Compliance | Safeguard product designs and trade secrets | Execute mutual NDA; verify IP clause enforcement in contracts |
| 7 | Evaluate Financial Stability | Mitigate risk of sudden closure or supply disruption | Request audited financials (if feasible); use credit checks via Dun & Bradstreet China or local agencies |
Pro Tip: Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) to verify business registration authenticity using the USCC.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Accurate identification prevents margin inflation, communication delays, and quality control gaps.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company (Middleman) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only |
| Facility Type | Owns production floor, machinery, R&D lab | Office-only; no machinery or production lines |
| MOQ & Pricing | Lower MOQs; direct cost structure; can quote per unit + tooling | Higher MOQs; vague cost breakdown; often quotes FOB without component detail |
| Production Control | Can demonstrate process control (QC checkpoints, SOPs) | Relies on third-party factories; limited oversight |
| Lead Times | Precise, factory-controlled timelines | Longer, less predictable (dependent on supplier) |
| Technical Expertise | Engineers on staff; can discuss mold design, material specs | Limited technical depth; redirects to “our factory” |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights production lines, certifications, equipment | Features multiple unrelated product categories; stock images of factories |
Key Insight: Some hybrid models exist—factory-traders operate their own lines but also source externally. Transparency in disclosure is critical.
Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to Allow Factory Audit | High risk of misrepresentation | Disqualify supplier; insist on third-party verification |
| No Physical Address or Vague Location | Likely a shell company or trader | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps; verify with local agent |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Scam risk (especially >30% deposit) | Use secure payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy |
| Inconsistent Communication or Delayed Responses | Poor project management; potential language barrier | Require dedicated project manager; assess responsiveness over time |
| No Certifications or Refusal to Share Test Reports | Non-compliance risk (safety, environmental) | Require valid, current certifications; conduct product testing |
| Too-Good-to-Be-True Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees | Benchmark against industry averages; request detailed BoM |
| Refusal to Sign NDA | IP vulnerability | Halt discussions until IP protection is contractually secured |
Best Practices: Partnering with Manufacturers of Top Foreign Companies in China
Suppliers serving multinational clients (e.g., Apple, Siemens, Tesla, IKEA) typically meet stringent operational standards. To identify such partners:
- Ask Directly: “Which international clients have you supplied in the past 3 years?”
- Verify Claims: Cross-reference via LinkedIn, trade shows (e.g., Canton Fair, CIFF), or third-party audits.
- Assess Systems: Look for ERP integration, traceability systems, and documented QC processes.
- Prioritize Transparency: Top-tier factories welcome audits, share SOPs, and provide real-time production updates.
Note: Many elite Chinese factories operate under NDAs and may not disclose client names publicly. Accept anonymized case studies or redacted references.
Conclusion & Recommendations
Verifying a manufacturer in China is not a single step but a due diligence process combining documentation, on-ground validation, and behavioral analysis. Global procurement managers must:
- Insist on transparency at every stage
- Invest in third-party verification before scaling orders
- Build long-term partnerships with factories—not traders—where control and accountability are direct
By applying this framework, sourcing teams can reduce risk by up to 70%, accelerate time-to-market, and secure a competitive advantage in global supply chains.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Intelligence | 2026
Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement in China (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Market Analysis
Executive Summary: The Critical Time Drain in China Sourcing
Global procurement teams lose 120–180 hours annually per category verifying foreign-owned manufacturers in China. Unverified supplier claims, inconsistent compliance documentation, and operational misalignment lead to delayed timelines, hidden costs, and supply chain vulnerabilities. In 2026, with heightened regulatory scrutiny (e.g., China’s new ESG Export Framework) and compressed product cycles, inefficient vetting directly impacts time-to-market and margin stability.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Delays
Our Pro List is the only database rigorously validated against 17 operational, compliance, and capability metrics—including real-time customs export records, ISO recertification status, and foreign ownership proof. Unlike generic directories, we audit every supplier on your behalf, delivering pre-qualified partners aligned with Western procurement standards.
Time Savings Analysis: Traditional Sourcing vs. Pro List (Per Sourcing Cycle)
| Activity | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 45–60 hours | 0 hours (pre-verified) | 45–60 hours |
| Compliance/Documentation Review | 30–40 hours | 5 hours (curated docs) | 25–35 hours |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 20–30 hours | 0 hours (on-file reports) | 20–30 hours |
| Negotiation Cycle (Misaligned Capabilities) | 15–25 hours | 8 hours (accurate specs) | 7–17 hours |
| TOTAL PER CYCLE | 110–155 hours | 13 hours | 97–142 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Survey (n=217 procurement teams across 12 sectors)
3 Unmatched Advantages for 2026 Procurement Strategy
- Zero Verification Risk
Every Pro List supplier provides audited proof of foreign management, capital structure, and export history—eliminating “local shell company” pitfalls. - Regulatory Safeguarding
Real-time updates on China’s evolving export controls (e.g., dual-use tech restrictions) ensure your suppliers remain compliant, avoiding shipment holds. - Speed-to-Volume Scaling
Pro List partners guarantee capacity for Western-order volumes (min. 5,000 units/batch) with <2% defect rates—validated by 3rd-party QC reports.
Call to Action: Reclaim Your Strategic Time in 2026
Your team’s expertise belongs in value engineering—not supplier validation. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, you bypass 142+ hours of non-core labor annually while securing partners built for global supply chains.
✨ Act Now & Accelerate Q2 Sourcing:
→ Contact our China Sourcing Desk for a free Pro List preview of your target sector:
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Response within 2 business hours | All inquiries confidential)
Don’t let unverified suppliers dictate your 2026 timeline. Partner with SourcifyChina to deploy procurement resources where they drive maximum ROI: strategic cost modeling, innovation collaboration, and risk-resilient scaling.
SourcifyChina | Your Verified Gateway to China Manufacturing
Senior Sourcing Consultants | Shanghai | Shenzhen | Global Remote Support
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data sourced from proprietary audits and China Customs records. Pro List access requires enterprise partnership.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





