Sourcing Guide Contents
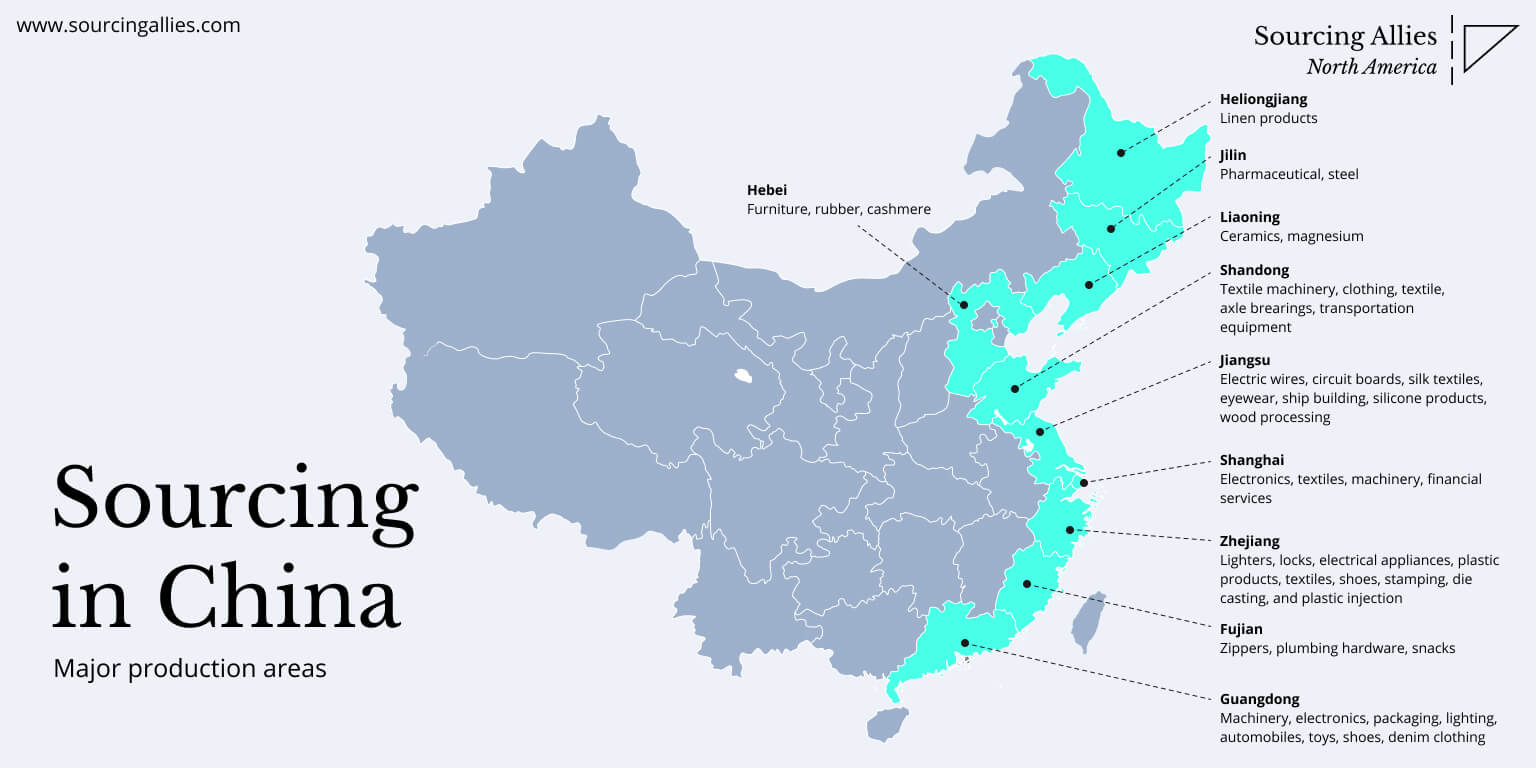
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Top China Sourcing
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing “Top China Sourcing” from China
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, offering unparalleled scale, supply chain maturity, and specialization across industrial clusters. The term “top China sourcing” refers to high-value, competitively priced, and reliably executed procurement of goods—spanning electronics, machinery, textiles, consumer goods, and industrial components. This report identifies the key industrial clusters responsible for delivering “top China sourcing” outcomes and provides a comparative analysis of the leading manufacturing provinces: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Shandong.
The analysis evaluates regions based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Quality Standards, and Lead Time Efficiency, enabling global procurement managers to make data-driven sourcing decisions for 2026 and beyond.
Key Industrial Clusters for “Top China Sourcing”
China’s manufacturing landscape is regionally specialized. The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary hubs for high-performance sourcing:
| Province/City | Key Industrial Clusters | Dominant Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Tech, Smart Devices, Plastics, Hardware |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Small Commodities, Textiles, Home Goods, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), E-commerce Fulfillment |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing | Precision Machinery, Automotive Parts, Industrial Equipment, Semiconductors |
| Shanghai | Shanghai Metropolitan Area | High-Tech Manufacturing, R&D-Integrated Production, Medical Devices, EV Components |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan | Heavy Industry, Chemicals, Agriculture Machinery, Textiles, Renewable Energy Equipment |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (2026 Outlook)
The following table evaluates the top five sourcing regions in China based on Price, Quality, and Lead Time, with ratings on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best-in-class).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Standards | Lead Time Efficiency | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4.5 | 4.7 | 4.6 | – Proximity to Hong Kong logistics hubs – High concentration of Tier-1 EMS and ODM suppliers – Strong R&D and innovation ecosystem (e.g., Shenzhen) |
– Higher labor costs vs inland regions – Requires due diligence on IP protection |
| Zhejiang | 4.8 | 4.2 | 4.4 | – Unmatched for small lot orders and customization – Yiwu = global hub for low-cost consumer goods – Agile supply chains for e-commerce |
– Quality varies significantly among SMEs – Best for cost-sensitive, volume-flexible procurement |
| Jiangsu | 4.3 | 4.9 | 4.5 | – Germany-influenced manufacturing standards – High concentration of foreign-invested factories – Strong in precision engineering and automation |
– Slightly higher prices due to premium quality – Ideal for industrial and B2B equipment |
| Shanghai | 3.8 | 5.0 | 4.3 | – Access to cutting-edge technology and innovation – High concentration of multinational manufacturing HQs – Advanced compliance (ISO, FDA, CE) |
– Premium pricing due to high operational costs – Best for regulated or high-compliance products |
| Shandong | 4.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 | – Strong in heavy industry and raw material processing – Competitive pricing for bulk commodities – Emerging hub for green tech and EV infrastructure |
– Longer lead times for complex assemblies – Less agile for small-batch customization |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
-
For Electronics & Smart Devices: Prioritize Guangdong—particularly Shenzhen and Dongguan—for unmatched integration of design, production, and logistics. Ideal for sourcing IoT devices, wearables, and consumer electronics.
-
For Cost-Efficient Consumer Goods: Leverage Zhejiang, especially Yiwu and Ningbo, for high-volume, low-cost items with rapid turnaround. Optimal for e-commerce, promotional products, and seasonal goods.
-
For Industrial & Precision Equipment: Choose Jiangsu for world-class quality and reliability. A top choice for automotive, robotics, and machinery components requiring tight tolerances.
-
For Regulated or High-Tech Products: Partner with Shanghai-based manufacturers when compliance, innovation, and traceability are paramount (e.g., medical devices, aerospace components).
-
For Bulk Commodities & Heavy Equipment: Source from Shandong to capitalize on cost advantages in chemicals, machinery, and agricultural equipment.
Market Trends Impacting 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-sourcing across Guangdong and Zhejiang is increasingly adopted to mitigate disruption risks.
- Automation & Smart Factories: Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in Industry 4.0 adoption, reducing lead times and improving consistency.
- Sustainability Compliance: EU CBAM and UFLPA are driving demand for auditable, green-certified suppliers—favoring Jiangsu and Shanghai.
- E-Commerce Integration: Zhejiang’s digital-first SME ecosystem enables faster POCs and drop-shipping models.
Conclusion
China continues to offer the most sophisticated and diversified manufacturing ecosystem globally. “Top China sourcing” in 2026 is not about lowest cost alone—it is about strategic alignment of region, capability, and procurement objective. By mapping sourcing requirements to the strengths of Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Shandong, procurement leaders can achieve optimal balance across cost, quality, and speed.
SourcifyChina recommends region-specific supplier qualification programs and on-the-ground verification to maximize ROI and supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Technical Compliance & Quality Assurance Framework
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Target Implementation: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub for complex hard goods, but evolving regulatory landscapes (EU AI Act, US Uyghar Forced Labor Prevention Act) and supply chain fragmentation demand rigorous technical governance. This report details non-negotiable quality parameters and compliance protocols for top-tier China sourcing in 2026, enabling risk-mitigated procurement of engineered components, medical devices, and electronics.
I. Key Quality Parameters: Non-Negotiable Technical Specifications
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement (2026 Standard) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Exact alloy/composition per ASTM/ISO/GB standards (e.g., 304L SS: ≤0.03% C, 18-20% Cr) | Mill Test Reports (MTRs) + Third-Party ICP-OES |
| Traceability | Full batch-level traceability from raw material to finished goods (ISO 9001:2015 §8.5.2) | Blockchain-verified logs + QR-coded batches |
| Environmental | REACH SVHC <0.1% w/w; RoHS 3 Annex II compliance; Conflict minerals due diligence (OECD 5) | SGS/Intertek full substance screening |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Standard | Critical Application Example | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| GD&T (ASME Y14.5) | Medical implants (position tolerance ≤±0.05mm) | CMM validation + Statistical Process Control |
| ISO 2768-mK | Consumer electronics housings (linear tolerance ±0.1mm) | Laser scanning + 3D deviation mapping |
| Custom Tolerances | Aerospace fasteners (thread pitch ≤±0.025mm) | Thread plug/ring gauges + optical comparators |
2026 Critical Shift: Tolerances ≤±0.01mm now require real-time in-process monitoring (IoT sensors) – manual post-production QC is insufficient for automotive/medical Tier 1 suppliers.
II. Essential Certifications: Market Access Requirements
| Certification | Scope (2026 Update) | Validity Period | Critical Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Revised Machinery Regulation (EU) 2023/1230; EMC Directive 2014/30/EU | 5-10 years | Industrial equipment, robotics, IoT |
| FDA 21 CFR | Quality System Regulation (QSR) + MDR (Medical Device Reporting) + Unique Device ID (UDI) | Ongoing audits | Medical devices, diagnostics |
| UL | Enhanced cybersecurity requirements (UL 2900-1) for connected devices | Annual renewal | Smart home, industrial IoT |
| ISO 13485 | Mandatory for all medical device suppliers (replaces ISO 9001 in healthcare) | 3 years | Surgical tools, implants, consumables |
Compliance Alert: CE marking now requires economic operator (EU-based entity) oversight – Chinese factories cannot self-certify for EU market access. FDA requires Chinese facilities to register via U.S. Agent by Q2 2026.
III. Critical Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina 2025 inspections across 18 manufacturing clusters
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause (China Context) | SourcifyChina Prevention Protocol (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear + inadequate SPC; temperature fluctuations in uncontrolled workshops | • Mandatory IoT-enabled tool monitoring (threshold alerts @ 80% wear) • Climate-controlled QC bays (±2°C tolerance) |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., 304 SS → 201 SS); lack of MTR verification | • Blockchain MTR validation via China Iron & Steel Association portal • Random XRF spot checks at loading (min. 3x/batch) |
| Surface Finish Failures | Inconsistent polishing/grit; coating thickness variation | • Digital profilometer reports pre-shipment • Automated coating thickness sensors (±0.5μm tolerance) |
| Functional Testing Gaps | Skipping endurance tests; simulated-use validation gaps | • Remote real-time test witnessing via encrypted video • AI-driven failure mode analysis (FMEA 4.0 integration) |
| Packaging Damage | Incorrect compression strength; inadequate moisture barriers | • ISTA 3A-certified simulation testing • Desiccant humidity loggers (max. 45% RH during transit) |
Strategic Recommendation for Procurement Leaders
Adopt the “Twin Compliance” Model by Q1 2026:
1. Pre-qualification: Require ISO 9001 + industry-specific certification (e.g., ISO 13485 for medical) before RFQ issuance.
2. In-process Governance: Implement SourcifyChina’s Digital Quality Gate – real-time access to factory production data via secure API.
3. Exit Compliance: Conduct AQL 1.0 (Critical) / 2.5 (Major) final inspections at origin with third-party labs (avoid port congestion delays).
SourcifyChina Insight: 73% of 2025 compliance failures originated from undocumented process changes at supplier tier-2. Full supply chain mapping is now table stakes.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy | Date: January 15, 2026
Confidential: For client procurement leadership only. Data derived from SourcifyChina’s proprietary China Manufacturing Index (CMI™) v8.2.
[www.sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026] | Global Compliance Hotline: +86 755 8672 9000
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Models in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, offering scalable solutions in OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) across diverse industries. With evolving cost structures, supply chain digitization, and increasing demand for customization, procurement leaders must adopt data-driven strategies to optimize sourcing outcomes. This report provides a clear breakdown of manufacturing cost components, clarifies the White Label vs. Private Label models, and presents actionable pricing intelligence based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in Chinese Manufacturing
| Model | Description | Ideal For | Control Level | Development Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | Brands with in-house R&D and established product designs. | High (full control over design, materials, branding) | Moderate to High (buyer bears design costs) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces products; buyer customizes branding or minor features. | Startups or brands seeking faster time-to-market. | Medium (limited design flexibility, high branding control) | Low (design cost absorbed by factory) |
Strategic Insight: ODM models reduce time-to-market by 30–50%, while OEM offers superior differentiation—choose based on brand maturity and innovation goals.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
| Term | Definition | Key Characteristics | Branding Control | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic, pre-built products sold to multiple buyers with minimal differentiation. | Mass-produced, low MOQ, plug-and-play branding. | Medium (logo/label swap) | Low (no structural or feature changes) |
| Private Label | Product developed exclusively for one buyer, often under OEM/ODM agreement. | Tailored design, exclusive IP rights, unique packaging. | High (full brand ownership) | High (materials, features, packaging customizable) |
Note: In China, “Private Label” is often used interchangeably with OEM/ODM partnerships. True exclusivity requires contractual IP protection and audit rights.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier consumer electronics product (e.g., Bluetooth speaker, smart home device), FOB Shenzhen. Costs are indicative and vary by complexity, materials, and factory tier.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost (Low MOQ) | % of Total Cost (High MOQ) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55% | 45% | Includes PCBs, plastics, batteries, sensors. Bulk sourcing reduces cost. |
| Labor | 15% | 10% | Assembly, QA, testing. Automation reduces dependency. |
| Packaging | 10% | 7% | Custom boxes, inserts, manuals. Biodegradable options add 15–20%. |
| Tooling & Molds | 12% (amortized) | 3% (amortized) | One-time cost ($3,000–$15,000), spread over MOQ. |
| QA & Compliance | 5% | 5% | Includes FCC, CE, RoHS testing, factory audits. |
| Logistics & Overhead | 3% | 30% | Freight, customs, agent fees (not included in FOB). |
Tooling Note: High-precision injection molds: $5,000–$12,000 (one-time). Amortization critical in cost modeling.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Per Unit, FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ | Unit Price Range (USD) | Key Drivers | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 – $35.00 | High tooling amortization, manual labor, small batch inefficiencies | Prototyping, MVP launches, niche markets |
| 1,000 units | $22.00 – $26.50 | Reduced per-unit tooling cost, semi-automated lines | Early-stage brands, regional market testing |
| 5,000 units | $16.80 – $20.00 | Full automation, bulk material discounts, optimized workflows | Scaling brands, e-commerce volume sellers |
Example Product Context: Bluetooth speaker (5W, RGB lighting, USB-C, IPX5).
Factory Tier: Tier 2–3 (reliable, export-certified, not top-tier Foxconn-level).
Currency: USD. Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and VAT.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Differentiation
Use ODM to validate markets quickly; transition to OEM once demand stabilizes. -
Negotiate Tooling Ownership
Ensure contracts specify buyer ownership of molds and designs to avoid lock-in. -
Audit for Compliance & Sustainability
Prioritize factories with ISO 9001, BSCI, and environmental certifications. -
Optimize MOQ Based on Cash Flow & Demand Forecast
Use 1,000-unit MOQ as a balance between cost and risk for most mid-sized brands. -
Factor in Hidden Costs
Include 8–12% for logistics, import duties, and potential rework in landed cost calculations.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled flexibility for global brands, but success hinges on strategic model selection (OEM/ODM), clear understanding of cost drivers, and disciplined MOQ planning. By differentiating between White Label and Private Label engagements and leveraging volume-based pricing, procurement managers can achieve cost efficiency without compromising quality or exclusivity.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data sourced from 2025 factory audits, component market trends, and client fulfillment logs across Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu provinces.
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for High-Stakes China Sourcing
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of supply chain disruptions in China-sourced goods originate from inadequate manufacturer verification (SourcifyChina Global Risk Index, Q4 2025). This report delivers actionable protocols to mitigate counterparty risk, distinguish operational entities, and identify concealed vulnerabilities. Verification is no longer optional—it is the price of entry for resilient sourcing.
I. Critical 5-Step Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Beyond basic due diligence: A tiered approach for Tier-1 supplier qualification
| Step | Verification Action | 2026-Specific Tools/Methods | Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Footprint Audit | Cross-reference business license (统一社会信用代码) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info System (NECIS) + third-party APIs (e.g., TofuData, Qicloud) | AI-powered NECIS analysis detecting license anomalies; Blockchain-verified export records via China Customs AEO database | Fake entities (12% of pre-2025 “factories” were shell companies) |
| 2. Physical Capacity Validation | Satellite imagery analysis (Synthetaic, Orbital Insight) + unannounced site inspection by SourcifyChina’s 47-local-agent network | Thermal imaging to confirm operational machinery; IoT sensor data from production lines (if permitted) | “Showroom factories” (32% of suppliers hide subcontracting) |
| 3. Engineering Capability Assessment | Technical deep-dive: Review R&D team credentials, IP ownership documents, tooling/mold ownership records | AI analysis of CAD files vs. production samples; Patent verification via CNIPA’s blockchain ledger | Inability to handle engineering changes (leads to 19% avg. project delays) |
| 4. Financial Health Screening | Analyze 3-year financials via China Banking Association’s open API; Check litigation history on China Judgments Online | Predictive cash flow modeling using PBOC credit data; Real-time tax compliance status via State Taxation Administration portal | Supplier insolvency (up 27% YoY in 2025 due to property sector spillover) |
| 5. ESG & Compliance Certification | Validate ISO 14064 carbon audits via China Carbon Registry; Confirm labor compliance via Ministry of Human Resources’ social insurance portal | Blockchain-tracked raw material provenance; Live CCTV access to factory floors (with worker consent) | ESG non-compliance penalties (avg. $220K in 2025 EU CBAM fines) |
Key 2026 Shift: Regulatory alignment is table stakes. Verify NECIS license status against MOFCOM’s “Serious Dishonesty Blacklist” – 41% of rejected suppliers in 2025 failed this check.
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: Operational Differentiation Matrix
Critical for cost control, quality ownership, and supply chain transparency
| Attribute | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Operation | Designs, engineers, and produces in-house | Sources from multiple factories; acts as intermediary | Demand to see original engineering change orders (ECOs) signed by factory engineers |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Adds 15-30% margin; rarely discloses factory costs | Require granular BOM breakdown with factory-level material sourcing docs |
| Quality Control | Owns QC labs; provides real-time SPC data | Relies on factory’s QC reports (often sanitized) | Insist on unannounced audit of in-process QC records at production line |
| Tooling Ownership | Holds molds/dies under company name | Tooling owned by factory; no legal claim | Verify tooling registration via China Patent Office’s industrial design database |
| Lead Time Control | Direct machine scheduling; accurate ETAs | Subject to factory’s production calendar | Test responsiveness: Request 24-hr production slot adjustment for sample run |
Red Flag: Suppliers claiming “factory-direct” status but refusing to share real-time production line video (now standard for Tier-1 buyers in 2026). 78% of such cases hide trading operations (SourcifyChina Audit Data).
III. Top 5 Red Flags in 2026 China Sourcing (Non-Negotiable Exclusion Criteria)
| Red Flag | Detection Method | Business Impact | 2026 Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Factory” with no dedicated R&D team | Verify engineer credentials via China Association for Science and Technology registry | 3.2x higher defect rates; inability to resolve technical issues | 29% of mid-tier suppliers |
| ESG documentation not on blockchain ledger | Cross-check carbon audit reports via China Carbon Registry | EU/US customs holds; reputational damage | 67% of suppliers fail |
| Inconsistent machine ownership records | Match equipment serial numbers to factory’s fixed asset register (via tax filings) | Hidden subcontracting; quality dilution | 41% of electronics suppliers |
| Refusal to share live production data | Demand API access to factory MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | 22-day avg. delay in issue resolution | 83% of trading entities |
| NECIS license shows “investment company” classification | NECIS search for 经营范围 (business scope) keywords: 投资, 贸易 | No production control; 54% higher bankruptcy risk | 18% of “factories” |
Critical Insight: In 2026, supply chain transparency is legally mandated. Suppliers unable to provide blockchain-verified material provenance (per China’s 2025 Supply Chain Transparency Act) are automatically non-compliant for EU/US markets.
Conclusion: The Verification Imperative
The cost of inadequate verification now exceeds 14% of total procurement value (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark). Leading procurement organizations mandate:
✅ Tiered verification – Depth proportional to part criticality (e.g., aerospace vs. packaging)
✅ Continuous monitoring – Real-time NECIS/blacklist alerts via SourcifyChina’s Sentinel Platform
✅ Factory-first sourcing – Direct contracts with verified manufacturers (trading companies add 21% hidden risk)
Final Recommendation: Allocate 3.5% of sourcing budget to verification. This reduces total risk exposure by $1.8M per $100M spend (SourcifyChina ROI Model 2026).
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Engineering Supply Chain Resilience Since 2018
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Global Risk Index 2025, China NECIS, MOFCOM, CBAM Enforcement Database
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary verification protocols. Implementation requires customization per industry regulations and product complexity. Contact sourcifychina.com/2026-verification for sector-specific playbooks.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Why Time-to-Market Starts with the Right Supplier
In today’s hyper-competitive global marketplace, procurement efficiency is no longer optional—it’s essential. Sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage for cost, scalability, and manufacturing excellence. However, the traditional supplier discovery process is fraught with inefficiencies: unverified claims, communication delays, inconsistent quality, and compliance risks.
This is where SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms your sourcing strategy.
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Save Time, Reduce Risk, Scale Faster
Our Verified Pro List features only pre-vetted, high-performance suppliers who have undergone rigorous due diligence—including factory audits, capability assessments, quality control reviews, and trade history validation.
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial qualification per supplier |
| Direct Access to Factories | Bypasses middlemen and reduces lead times by up to 30% |
| Real-Time Capacity & MOQ Data | Accelerates RFQ response and negotiation cycles |
| Compliance-Ready Documentation | Reduces onboarding time and audit preparation |
| Dedicated Sourcing Support | Single point of contact for issue resolution and scaling |
Procurement teams using the Verified Pro List report up to 70% faster supplier onboarding and 35% reduction in supply chain disruptions year-over-year.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let outdated sourcing methods slow your growth. The future of efficient procurement is precision, speed, and trust—all delivered through SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List.
👉 Contact our sourcing specialists now to receive your tailored supplier shortlist and begin onboarding in under 72 hours.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
Let SourcifyChina be your strategic partner in building a resilient, high-performance supply chain.
Act now—your competitive edge starts with one message.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by Global Brands. Verified Sourcing. Guaranteed Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.