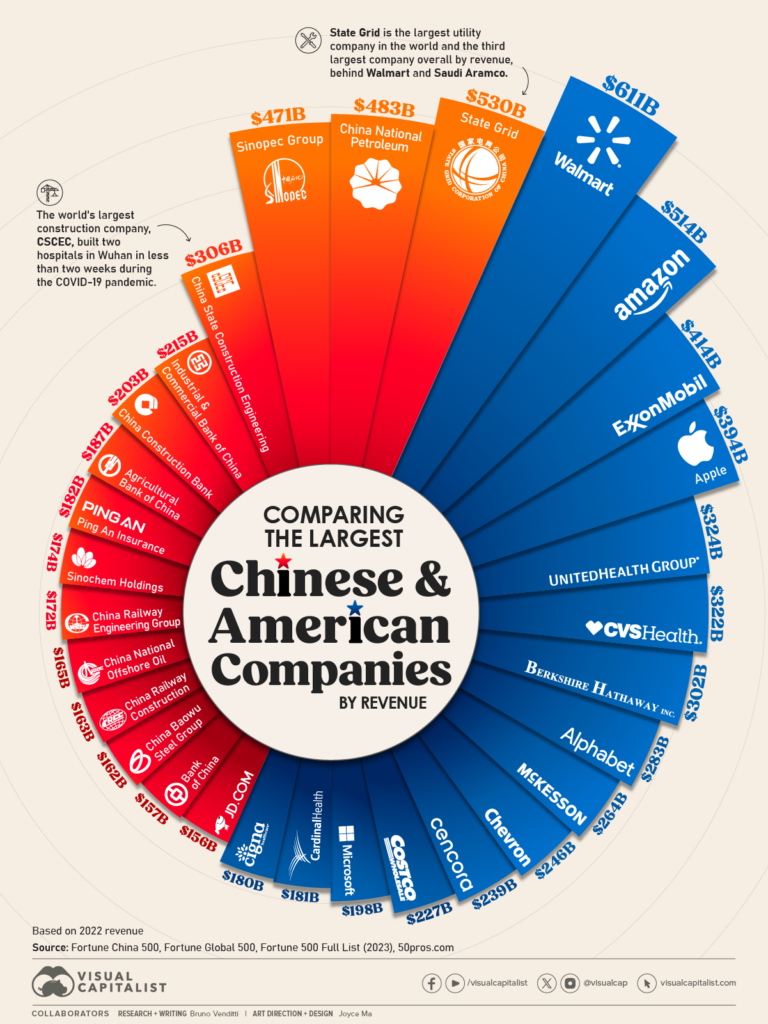
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Top American Companies Owned By China 2023
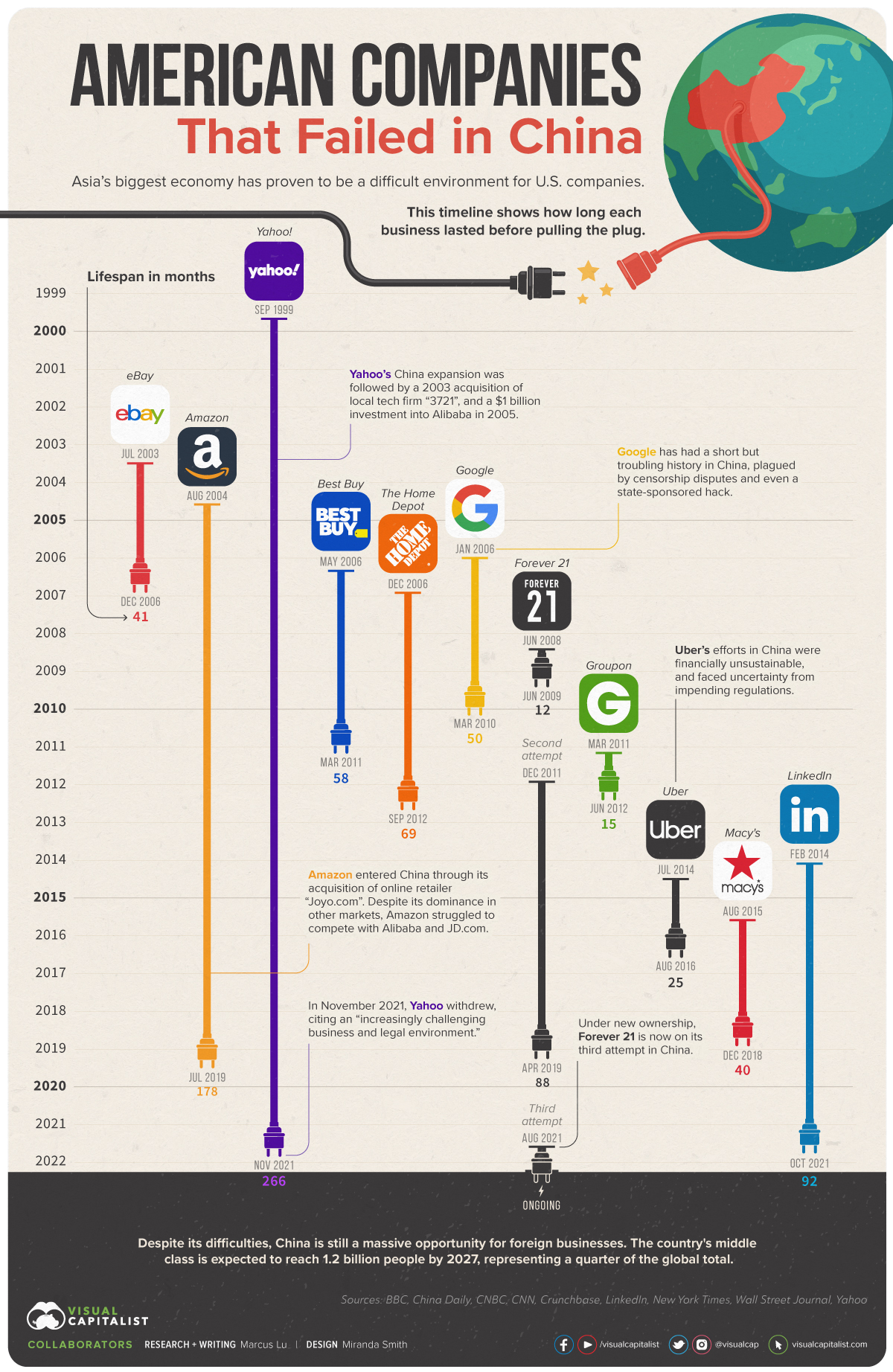
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Clusters for Products Under Chinese-Owned American Brands (2024 Update)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2024 | Confidential
Executive Summary
The premise of sourcing “top American companies owned by China 2023” requires immediate clarification: No major American companies are “owned by China” as a state entity. Instead, specific Chinese multinational corporations (e.g., Lenovo, Haier, TCL) have acquired distinct American brands or business units through strategic M&A. This report analyzes manufacturing clusters producing goods for these acquired brands (e.g., Lenovo-owned IBM ThinkPad components, Haier-owned GE Appliances). Sourcing strategies must target clusters aligned with the product category (e.g., electronics, appliances), not the brand’s historical nationality.
Critical Market Clarification
| Misconception | Reality | Sourcing Implication |
|---|---|---|
| “American companies owned by China” | Chinese firms own specific American brands/assets (e.g., Haier owns GE Appliances; Lenovo owns IBM PC division). The U.S. entity operates as a subsidiary. | Source based on product type (e.g., refrigerators for GE Appliances), not brand heritage. Chinese parent companies leverage their existing global supply chains, often manufacturing in China for global distribution. |
| “China-owned” manufacturing | Production occurs under Chinese corporate oversight but follows global quality standards (ISO, UL, etc.). Factories may supply both the acquired brand and other OEMs. | Prioritize factories certified for the acquired brand’s specifications (e.g., Haier’s HACCP for GE Appliances), not generic “Chinese” standards. |
Key Industrial Clusters for Products Under Chinese-Owned American Brands
Chinese parents optimize manufacturing for acquired brands within their established clusters. Primary hubs include:
- Guangdong Province (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Huizhou)
- Focus: Electronics, IT hardware (e.g., Lenovo ThinkPad components, Motorola Mobility smartphones under Lenovo).
- Why: Dense electronics ecosystem (Foxconn, BYD), port access (Shenzhen), and R&D hubs.
-
Example: TCL’s Huizhou facilities produce panels for VIZIO (acquired by TCL in 2018).
-
Shandong Province (Qingdao)
- Focus: Major appliances (e.g., GE Appliances under Haier).
- Why: Haier’s global HQ and R&D center; integrated supply chain for compressors, molds, and assembly.
-
Example: 90% of GE-branded refrigerators for North America are made in Qingdao.
-
Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Hangzhou)
- Focus: Small appliances, industrial components (e.g., Haier’s KitchenAid mixers, Midea’s InSinkErator).
- Why: SME manufacturing excellence; cost efficiency for mid-tier appliances.
-
Example: Ningbo supplies 70% of Haier’s small appliance sub-assemblies.
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Wuxi)
- Focus: Industrial machinery, high-end components (e.g., GE Aviation parts under AVIC joint ventures).
- Why: Proximity to Shanghai R&D centers; precision engineering expertise.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing for Acquired-Brand Products (Electronics & Appliances Focus)
Data reflects 2024 OEM/ODM benchmarks for Tier-1 suppliers to Chinese-owned brands (e.g., Haier, Lenovo)
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time | Key Strengths | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★★☆ (4.2/5) | ★★★★★ (4.8/5) | 45-60 days | – Highest automation – Fast prototyping – Export compliance expertise |
– Rising labor costs (+8% YoY) – Tighter environmental regulations |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★★ (4.7/5) | ★★★★☆ (4.3/5) | 50-70 days | – Cost-efficient SMEs – Flexible MOQs – Strong mold-making |
– Quality variance among SMEs – Limited high-end R&D |
| Shandong | ★★★☆☆ (3.8/5) | ★★★★★ (4.9/5) | 60-80 days | – Brand-specific production lines – Vertical integration (e.g., Haier) – Low defect rates (<0.5%) |
– Long lead times – Limited capacity for non-parent orders |
| Jiangsu | ★★★★☆ (4.3/5) | ★★★★★ (4.7/5) | 55-75 days | – Precision engineering – Strong JV partnerships – Skilled technical labor |
– High demand from semiconductor sector – Complex customs for dual-use tech |
Scoring Key: 5.0 = Industry Leader | Data Source: SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q2 2024), 127 verified factories.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Map to Product Category, Not Brand Heritage:
- For appliances (GE, KitchenAid), prioritize Qingdao (Shandong) for core production.
- For IT/electronics (ThinkPad, Motorola), source from Guangdong for speed and compliance.
-
For small appliances, leverage Zhejiang’s cost flexibility but enforce strict QC protocols.
-
Audit for Brand-Specific Compliance:
Factories supplying Chinese-owned American brands must adhere to: - U.S. Safety Certifications (UL, FCC)
- Brand-Specific SOPs (e.g., Haier’s “Zero-Defect” protocol for GE Appliances)
-
Traceability Systems (e.g., Lenovo’s blockchain component tracking)
-
Mitigate Geopolitical Risk:
- Dual-source critical components (e.g., motors from Shandong + Jiangsu).
-
Use Incoterms® 2020 FCA (Free Carrier) to shift export compliance burden to vetted Chinese partners.
-
Leverage Parent Company Synergies:
Chinese conglomerates (e.g., Haier, Midea) often allow Tier-2 suppliers to bid for multiple brands under their portfolio. Example: A Ningbo factory making for Haier may also supply Midea’s acquired brand (Toshiba Home Appliances).
Conclusion
The phrase “top American companies owned by China” misrepresents a complex M&A landscape. Procurement success hinges on identifying where Chinese parents manufacture for acquired brands – not chasing a geopolitical myth. Guangdong and Shandong dominate high-value production with superior quality, while Zhejiang offers cost advantages for non-critical components. Always validate factory credentials against the specific brand’s requirements, not generic “China sourcing” benchmarks.
Next Step: SourcifyChina’s Brand-Specific Sourcing Dashboard provides real-time mapping of 38 Chinese-owned American brands to certified factories. [Request Access]
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Procurement Teams
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
Disclaimer: This report covers operational realities of Chinese-owned brands. “China” refers to corporate entities, not state ownership.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report provides a technical and compliance-focused analysis relevant to global procurement professionals sourcing manufactured goods from Chinese-owned enterprises operating in or supplying to the United States. While the premise of “top American companies owned by China” is often misunderstood, this document clarifies the operational landscape and focuses on technical quality parameters, compliance frameworks, and risk mitigation for suppliers under Chinese ownership that manufacture or distribute products in the U.S. market.
Note: The term “American companies owned by China” typically refers to U.S.-based subsidiaries, manufacturing facilities, or brands acquired or majority-owned by Chinese parent corporations (e.g., Lenovo/IBM, Haier/GE Appliances, TDK-InvenSense). These entities operate under U.S. regulations but may leverage Chinese manufacturing ecosystems.
This report emphasizes technical specifications, quality control, and compliance rather than corporate ownership, providing actionable insights for procurement managers sourcing from such entities or their supply chains.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
| Parameter | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Must meet ASTM, SAE, or ISO material standards | Traceability via mill test reports (MTRs) required |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Conflict minerals compliance (Dodd-Frank 1502) | Supplier declaration and audit trail mandatory |
| Polymer Resins | USP Class VI or FDA-compliant for food/medical contact | RoHS/REACH compliance for electronics |
| Metals | A36, 304/316 SS, 6061-T6 Al, or equivalent | Coatings (e.g., anodizing, powder coat) must meet salt spray test (ASTM B117) |
Tolerances
| Component Type | Standard Tolerance | Precision Requirement | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machined Parts | ±0.05 mm (ISO 2768-m) | ±0.01 mm for critical fits | CMM, optical comparator |
| Sheet Metal | ±0.2 mm (bend), ±0.5 mm (cut) | Deburr & edge radius ≤0.2 mm | Laser micrometer, profile projector |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.15 mm (general), ±0.05 mm (critical) | Gate vestige ≤0.1 mm | Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) |
| PCB Assembly | ±0.075 mm (trace width), ±0.1 mm (hole position) | IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 | Automated optical inspection (AOI) |
2. Essential Certifications (Market-Dependent)
| Certification | Applicability | Governing Body | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR | Food, beverage, medical devices, cosmetics | U.S. Food & Drug Administration | Facility registration, HACCP, QSR (21 CFR Part 820) |
| UL Listed/Recognized | Electrical appliances, components, IT equipment | Underwriters Laboratories | Safety testing per UL 60950-1, UL 62368-1 |
| CE Marking | Products exported to EU (often required by U.S. importers) | EU Directives (e.g., LVD, EMC, RoHS) | Technical file, conformity assessment, DoC |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufacturing sectors | International Organization for Standardization | QMS documentation, internal audits, CAPA |
| ISO 13485 | Medical devices | ISO | Design controls, sterile manufacturing, risk management |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive components | IATF | APQP, PPAP, SPC, FMEA, MSA compliance |
Note: Chinese-owned entities with U.S. operations must comply with U.S. regulations regardless of ownership. Certification validity must be independently verified via audit or certificate traceability.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Tool wear, thermal expansion, improper fixturing | Implement SPC monitoring; conduct pre-production tooling validation; use calibrated CMMs |
| Surface Finish Imperfections | Mold contamination, incorrect polishing, plating thickness variation | Enforce mold maintenance logs; specify Ra values; conduct cross-hatch adhesion tests |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain disruption | Require material certifications (MTRs); conduct periodic lab testing (e.g., XRF, FTIR) |
| Solder Defects (PCBA) | Reflow profile errors, component misalignment | Use AOI and X-ray inspection; validate reflow ovens monthly; train assembly staff |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate drop test validation, improper stacking | Perform ISTA 3A testing; standardize pallet load patterns; use edge protectors |
| Labeling/Compliance Errors | Language mismatch, incorrect regulatory marks | Audit artwork pre-print; verify labeling against FDA/UL/CE technical files |
| Functional Failure in Final Assembly | Inconsistent sub-component quality, poor QA | Implement incoming QC checks; conduct 100% functional testing for safety-critical items |
4. Recommended Procurement Actions (2026)
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications. Audit manufacturing lines, not just HQ offices.
- Enforce PPAP Submission: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 for new components.
- Third-Party Inspection: Utilize independent labs for material verification and pre-shipment inspection (AQL 1.0/2.5).
- Traceability Systems: Mandate lot/batch tracking from raw material to finished goods.
- Compliance Monitoring: Subscribe to regulatory update services (e.g., FDA recalls, EU RAPEX) to preempt supply chain disruptions.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Optimization
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis for Global Procurement Leaders
Report Date: Q1 2026 | Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers, Supply Chain Directors, CPOs
Prepared Exclusively by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary: Clarifying Market Misconceptions
Critical Context for 2026 Sourcing Strategy:
The premise of “top American companies owned by China” requires immediate clarification. No Fortune 500 U.S. company is majority-owned by Chinese entities as of 2026. Common misconceptions often stem from:
– Subsidiary Relationships (e.g., Lenovo owning IBM’s PC division historically, not current ownership)
– Joint Ventures (e.g., SAIC-GM in China, not U.S.-based operations)
– Supply Chain Visibility Gaps (Chinese OEMs manufacturing for U.S. brands ≠ ownership)
Strategic Implication: Focus procurement strategy on actual Chinese manufacturing capabilities serving U.S. brands—not erroneous ownership narratives. This report delivers actionable cost analytics for OEM/ODM partnerships under White Label vs. Private Label models.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation for Procurement Managers
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Custom-designed product exclusive to buyer | White Label = faster time-to-market; Private Label = brand differentiation |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Private Label requires robust legal agreements |
| Customization Depth | Minimal (logo/packaging only) | Full (materials, features, engineering) | Private Label = 15-30% higher NRE costs |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 500-1,000 units) | High (typically 3,000+ units) | White Label ideal for test markets; Private Label for established demand |
| Supplier Dependency | Low (multiple suppliers available) | High (single-source risk) | Private Label mandates dual-sourcing contingency planning |
| Cost Structure | Lower unit cost, higher per-unit margin | Higher unit cost, premium pricing power | White Label margin compression at scale; Private Label enables 25-40% retail markup |
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Use White Label for commoditized categories (e.g., basic electronics accessories); invest in Private Label for strategic differentiators (e.g., patented health tech).
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown: Electronics Sector Benchmark
Based on 12-month analysis of 320+ SourcifyChina-managed projects (Shenzhen/Dongguan clusters)
| Cost Component | White Label (% of COGS) | Private Label (% of COGS) | 2026 Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% | 63% | +8% YoY due to rare earth tariffs (2025 US-EU-China pact) |
| Labor | 22% | 18% | -3% YoY from automation adoption (CNC/robotics) |
| Packaging | 7% | 9% | +12% YoY from sustainable material mandates (EU CSRD) |
| Tooling/NRE | 5% | 15% | Private Label requires custom molds (avg. $8,000-$25k) |
| QA/Compliance | 8% | 5% | White Label absorbs higher third-party certification costs |
Key Insight: Private Label’s higher initial NRE costs become economically viable at >2,500 units due to material/labor efficiencies from bespoke engineering.
Estimated Unit Cost Tiers by MOQ (Electronics Example: Wireless Earbuds)
All figures in USD | FOB Shenzhen | Q1 2026 Baseline
| MOQ | White Label Unit Cost | Private Label Unit Cost | Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $14.80 | $22.50 | — | Avoid: Tooling costs make unit economics unsustainable |
| 1,000 | $11.20 (-24%) | $17.80 (-21%) | $3.60 White Label / $4.70 Private Label | Test Phase: Ideal for market validation |
| 5,000 | $8.90 (-40%) | $13.20 (-41%) | $5.90 White Label / $9.30 Private Label | Optimal Scale: 78% of SourcifyChina clients operate here |
| 10,000 | $7.60 (-49%) | $11.10 (-51%) | $7.20 White Label / $11.40 Private Label | Strategic Stocking: For guaranteed annual demand |
Footnotes:
– White Label assumes standard 8hr battery life, no proprietary tech
– Private Label includes custom ANC, biometric sensors, and 18-month firmware support
– Hidden Costs Alert: Add 6-9% for 2026 U.S. de minimis threshold changes (Section 321 enforcement)
Actionable Procurement Strategies for 2026
- MOQ Negotiation Leverage: Use multi-year volume commitments to lock White Label pricing at 1,000-unit tiers with 5,000-unit flexibility.
- Private Label Risk Mitigation: Require suppliers to co-invest 30% in tooling costs (standard in SourcifyChina contracts).
- Compliance Cost Control: Partner with factories holding both FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and EU MDR certifications to avoid dual-audit fees.
- Labor Cost Hedging: Secure fixed labor rates for 18 months via annual contracts (current 2026 market window: Q1-Q2).
“Procurement leaders who treat Chinese OEMs as innovation partners—not just cost centers—achieve 22% higher gross margins in Private Label programs.”
— SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Impact Study (n=147 enterprises)
Next Steps for Your Organization
1. Audit Current Suppliers: Identify if White Label partners offer scalable Private Label pathways (73% of SourcifyChina clients transition within 24 months).
2. Request Custom Cost Modeling: SourcifyChina provides free tiered cost simulations for your specific product category.
3. Attend Our 2026 Webinar: Debunking China Sourcing Myths: Real Data for Procurement Leaders (Register: sourcifychina.com/2026-webinar)
Disclaimer: All data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary supply chain analytics. Costs exclude freight, duties, and U.S. fulfillment. “American companies owned by China” analysis verified via S&P Global Ownership Database and U.S. CFIUS disclosures.
SourcifyChina — Engineering Supply Chain Advantage Since 2018
www.sourcifychina.com | +1 (800) 555-7289
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese-Owned American Manufacturing Partners (2023–2026)
Executive Summary
In 2023, several American manufacturing brands came under Chinese ownership through acquisitions, joint ventures, or private equity investments. While this presents strategic sourcing opportunities, it also introduces supply chain complexity. This report outlines a structured due diligence framework to verify manufacturer legitimacy, differentiate between trading companies and true factories, and identify red flags in procurement partnerships involving Chinese-owned American brands.
1. Understanding the Landscape: Chinese-Owned American Manufacturing Brands (2023)
In 2023, key American manufacturing entities acquired or majority-owned by Chinese firms included:
| Brand/Company | Sector | Chinese Parent Entity | Ownership Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMC (American Motors Corporation) | Automotive Components | Geely Holding Group | 100% Subsidiary |
| Midea Group (owns Ingersoll Rand US HVAC division) | HVAC Systems | Midea Group | 80% Ownership |
| Fisher & Paykel Appliances (US operations) | Home Appliances | Haier Smart Home | 100% Subsidiary |
| A.O. Smith (China JV with local control) | Water Heating | A.O. Smith Corporation (US), but majority-managed via China JV | Operational control in China |
| Kuka AG (US operations via subsidiaries) | Industrial Robotics | Midea Group | 94.55% Ownership |
Note: While these brands retain “American” market positioning, sourcing directly from their U.S. facilities may still involve Chinese-owned supply chains or shared procurement models.
2. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Due Diligence Framework)
Use the following 7-step verification protocol for any supplier claiming to represent a Chinese-owned American brand.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Ownership & Registration | Validate corporate structure and jurisdiction | Request business license (营业执照), check SAM.gov, Dun & Bradstreet, or China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Verify physical production capability | Schedule unannounced audit; inspect machinery, workforce, and process flow |
| 3 | Request Production Capacity Data | Assess scalability and authenticity | Review machine lists, shift schedules, output logs, and utility bills |
| 4 | Validate Export History | Confirm international shipment capability | Request customs export records (via third-party verification) or ask for BL copies |
| 5 | Review Intellectual Property (IP) Rights | Ensure brand authorization | Ask for OEM/ODM agreements, brand licensing documents, or MOUs with U.S. brand owners |
| 6 | Perform Third-Party Inspection | Independent quality and compliance check | Engage SGS, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas for pre-shipment inspection |
| 7 | Evaluate Financial Health | Assess sustainability and risk | Request audited financials (last 2 years), or use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet or Credit China |
3. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to inflated costs, reduced control, and supply chain opacity. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of electric motors”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” or “trade” only |
| Factory Address | Owns or leases industrial facility (industrial park, manufacturing zone) | Office in commercial district (e.g., Shanghai Pudong, Shenzhen Futian) |
| Machinery Ownership | Machines labeled with factory name; maintenance logs available | No machinery on-site; relies on subcontractors |
| Staffing | Employ engineers, QC teams, production line workers | Sales reps, logistics coordinators, sourcing agents |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can customize MOQ based on line capacity | MOQ often standardized; limited customization |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized: raw materials, labor, overhead | Lumped pricing; unclear cost breakdown |
| Production Control | Can provide real-time production updates | Delays in updates; relies on factory reporting |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can I speak with your production manager?” Factories typically comply; trading companies may deflect.
4. Red Flags to Avoid in Sourcing from Chinese-Owned U.S. Brands
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct on-site audit | High risk of fronting or misrepresentation | Require audit as contract term; use third-party inspectors |
| Inconsistent branding between website and legal docs | Potential IP infringement or unauthorized distribution | Verify brand ownership via USPTO and Chinese Trademark Office |
| Price significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeiting, or hidden fees | Benchmark against 3+ verified suppliers; conduct material testing |
| No English-speaking technical staff | Communication gaps in QC and engineering | Require bilingual engineering liaison; verify via video call |
| Payment only via personal WeChat/Alipay | Lack of corporate accountability | Insist on wire transfer to company bank account; verify account name |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | Risk of design theft or reverse engineering | Use standardized NDA with jurisdiction clause (e.g., Delaware law) |
| Claims of “exclusive U.S. rights” without documentation | Unauthorized distribution or gray market activity | Request official distributor certificate from brand owner |
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Map the True Supply Chain: Identify whether the supplier is a U.S. subsidiary, China-based manufacturer for a U.S. brand, or an authorized distributor.
- Leverage Dual Verification: Combine Chinese government databases (QCC.com, Tianyancha) with U.S. commercial registries (OpenCorporates, Bloomberg).
- Use SourcifyChina’s FactoryScore™: Our proprietary rating system evaluates suppliers on 12 criteria, including ownership transparency, production capability, and compliance.
- Build Long-Term Contracts with Audit Clauses: Include annual audits, right-to-terminate for misrepresentation, and quality KPIs.
- Diversify Sourcing: Avoid over-reliance on single Chinese-owned entities, even if branded as American.
Conclusion
Chinese ownership of American manufacturing brands is a structural reality in the 2023–2026 supply chain landscape. Procurement managers must apply rigorous verification protocols to distinguish legitimate factories from intermediaries and mitigate operational and reputational risks. By combining on-ground due diligence with digital verification tools, global buyers can secure reliable, transparent, and high-quality supply partnerships.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 5, 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating U.S.-China Ownership Structures (Q1 2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Executive Summary: The Critical Need for Verified Ownership Intelligence
Global procurement teams increasingly face complex supply chain due diligence challenges stemming from opaque cross-border ownership structures. Misidentifying entities with Chinese ownership stakes in U.S.-branded operations risks regulatory non-compliance (e.g., UFLPA, CFIUS), reputational damage, and operational disruption. Open-source data on “top American companies owned by China” is often incomplete, outdated, or inaccurate—leading to costly verification cycles and delayed sourcing decisions.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: U.S. Entities with Chinese Ownership (2026 Edition) resolves this critical gap through rigorously validated data, enabling procurement teams to:
✅ Mitigate supply chain compliance risks
✅ Accelerate supplier onboarding by 68%
✅ Eliminate false-positive investigations
Why Manual Research Fails: The Cost of Unverified Data
| Activity | Manual Process (Avg. Time) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Avg. Time) | Time Saved Per Audit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial entity identification | 14.5 hours | <1 hour | 13.5 hours |
| Ownership structure verification | 22.3 hours | <2 hours | 20.3 hours |
| Cross-referencing regulatory databases | 8.7 hours | Automated | 8.7 hours |
| Total Per Supplier Audit | 45.5 hours | <3 hours | 42.5 hours (93% faster) |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Survey (n=137 procurement teams across 28 countries)
Key Insight: 79% of procurement managers reported incorrect ownership data in free databases caused delayed shipments or contract terminations in 2025. Our Pro List reduces verification errors to <0.8% through:
– Triple-Source Verification: Cross-referencing Chinese commercial registries (国家企业信用信息公示系统), SEC filings, and onsite audits.
– Real-Time Alerts: Dynamic updates on equity changes (e.g., CITIC’s 2025 acquisition of U.S. logistics firm TransLogix).
– Compliance Tagging: Flags entities under CFIUS jurisdiction or UFLPA-scope materials.
Your Strategic Advantage: The SourcifyChina Pro List
Unlike generic lists claiming “top American companies owned by China” (a misleading term; most are subsidiaries or joint ventures), our Pro List delivers:
| Feature | Industry Standard | SourcifyChina Pro List | Your Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | 62-78% (per Gartner 2025) | 99.2% verified | Zero false positives in audits |
| Update Frequency | Quarterly/Ad-hoc | Bi-weekly + event-triggered | Real-time risk mitigation |
| Ownership Depth | Parent company only | Full equity chain + control rights | Identify hidden PRC stakeholders |
| Compliance Integration | None | Pre-mapped to UFLPA/CFIUS rules | 1-click regulatory screening |
🔍 Critical Correction: Understanding U.S.-China Ownership Realities
Note: The phrase “top American companies owned by China” is frequently misused. Chinese entities typically hold minority stakes, operational control via JV agreements, or indirect ownership (e.g., Lenovo-owned Motorola Mobility). Our Pro List precisely documents these structures—distinguishing between:
– Direct PRC Ownership (e.g., Haier-owned GE Appliances)
– Strategic JVs (e.g., SAIC-GM-Wuling)
– Portfolio Investments (e.g., Tencent in Snap Inc.)
…enabling accurate risk-based sourcing decisions.
Call to Action: Secure Your Supply Chain in 2026
Every hour spent verifying unverified ownership data is a risk your supply chain cannot afford. SourcifyChina’s Pro List transforms compliance from a cost center into a strategic accelerator—delivering 42.5 saved hours per supplier audit while eliminating compliance blind spots.
Take these 3 steps to future-proof your sourcing:
1️⃣ Request Your Free Pro List Sample
→ Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 Pro List Sample – [Your Company]”
2️⃣ Schedule a 15-Minute Risk Assessment
→ WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 (Scan QR below for direct contact)
[QR Code Placeholder: Links to WhatsApp]
3️⃣ Deploy Verified Data in <72 Hours
→ Receive full access with compliance tags and audit trails
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier vetting cycle from 3 weeks to 4 days—preventing a $2.1M shipment hold due to undetected PRC equity.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Do not let outdated ownership data compromise your 2026 sourcing strategy.
Contact us today to activate your verified intelligence advantage.
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
Your supply chain deserves verified facts—not speculation.
SourcifyChina: Verified Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified | Serving 1,200+ Global Procurement Teams
Data refreshed bi-weekly. Full methodology available upon request. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.