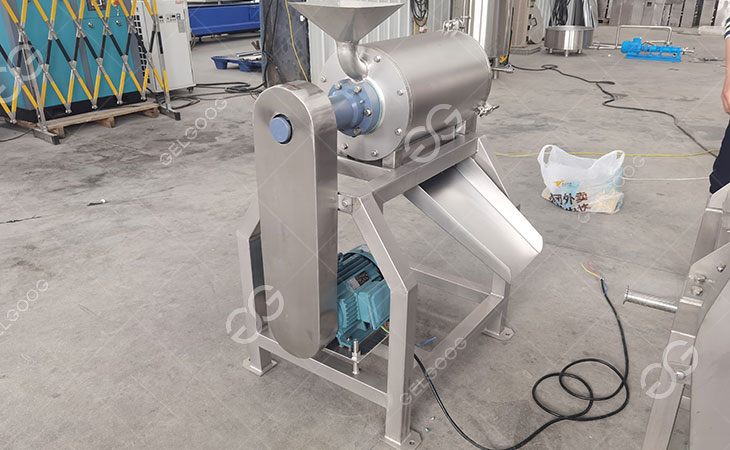
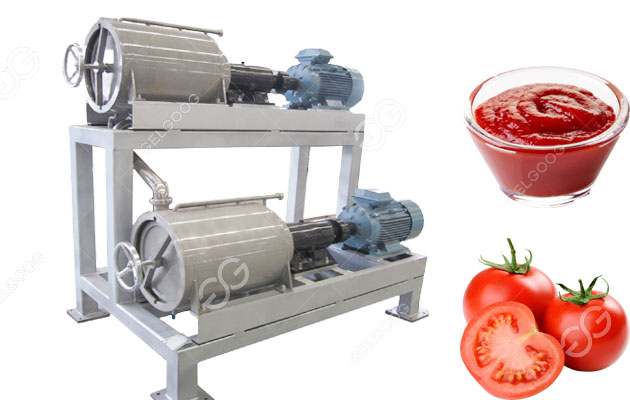
The global tomato processing equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for processed tomato products such as paste, sauce, and ketchup. According to Mordor Intelligence, the tomato paste market alone is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueling increased investments in efficient and scalable processing machinery. As production volumes rise, pulping machines—critical for separating tomato pulp from seeds and skins—have become essential in industrial lines. This surge in demand has led to a competitive landscape of manufacturers offering advanced, high-capacity solutions. Based on production capacity, technological innovation, global reach, and customer reviews, here are the top 9 tomato pulping machine manufacturers shaping the future of tomato processing.
Top 9 Tomato Pulping Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
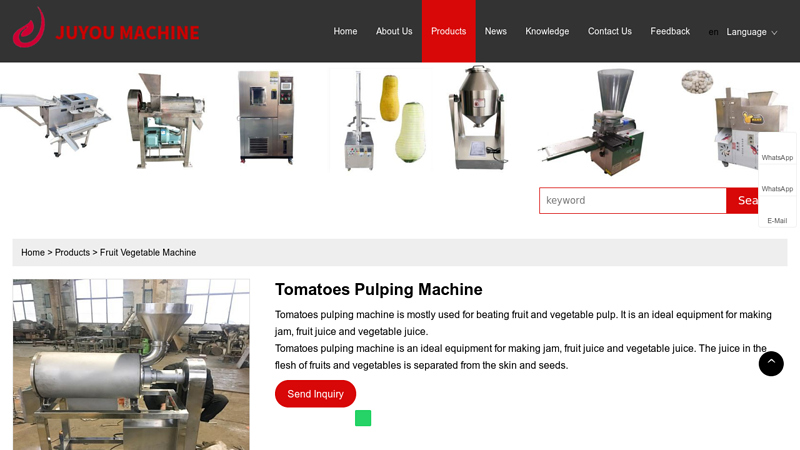
#1 China Tomatoes Pulping Machine Manufacturers, Suppliers, Factory
Domain Est. 2018
Website: juyoufoodmachine.com
Key Highlights: Tomatoes pulping machine is mostly used for beating fruit and vegetable pulp. It is an ideal equipment for making jam, fruit juice and vegetable juice….
#2 EN Pulper
Domain Est. 2009
Website: iftitalia.com
Key Highlights: This machine transforms unpeeled tomato in crushed tomatoes, using the extrusion method. Tomato pulper is made of the following parts:….
#3 Industrial Tomato Pulping Refining Machine Tomato Processing
Domain Est. 2021
Website: processtomato.com
Key Highlights: The tomato pulping refining machine is mainly used for tomato pulping, peeling and seeding in the large-scale tomato sauce production line….
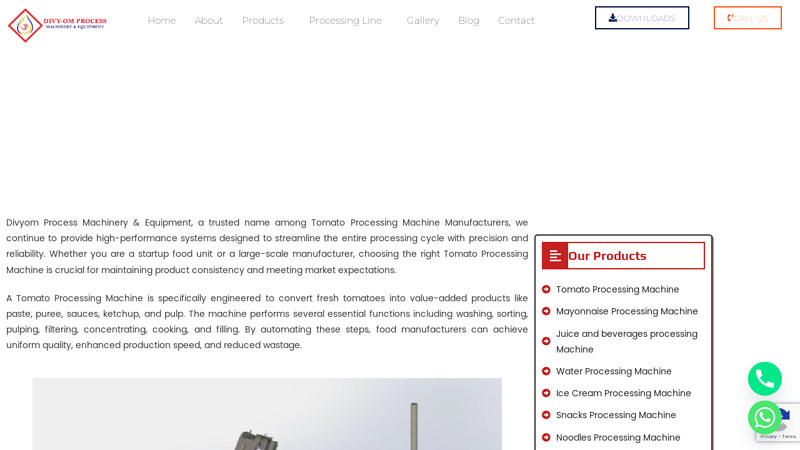
#4 Tomato Processing Machine Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2023
Website: divyomprocessmachinery.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (46) A Tomato Processing Machine is specifically engineered to convert fresh tomatoes into value-added products like paste, puree, sauces, ketchup, and pulp. The ……
#5 Tomato Pulp Machine
Domain Est. 2013
Website: jwalaengineering.net
Key Highlights: Automatic: Yes. Capacity: 500 – 5,000 Kg/hr. Material: Stainless Steel. Warranty: 1 Year. Delivery Time: 3 Months. FOB Port: Mumbai….
#6 Tomato pulp machine
Domain Est. 2016
Website: processing-machines.com
Key Highlights: We have brought forth a wide and comprehensive consignment Tomato Pulper Machine of Using finest grade basic material along with modern tools and tackles….
#7 Single Channel Tomato Paste Pulper Machine
Domain Est. 2018
Website: tomatoprocess.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (795) Single Channel Tomato Paste Pulper Machine is used to make tomatoes into tomato paste. It is designed to separate the seeds and skin from the pulp of to…
#8 100kg/h Tomato Pulp Extraction Machine For Tomato Sauce Making
Domain Est. 2020
Website: juiceprocessline.com
Key Highlights: The tomato pulp extraction machine is mainly used for beating and peeling the berries such as tomato 100kg /h after crushing and pre-cooking….
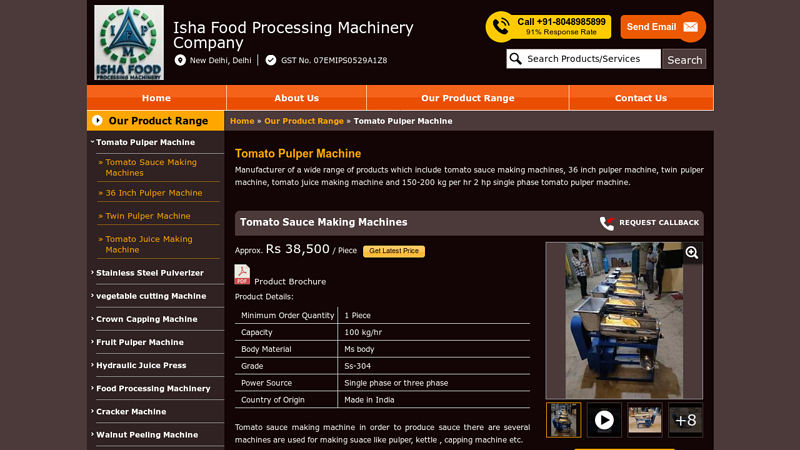
#9 Tomato Pulper Machine
Website: ishafoodmachinery.com
Key Highlights: 150-200 Kg Per Hr 2 HP Single Phase Tomato Pulper Machine · It is a machine used for preparation of fruit / vegetable for preservation by canning, Bottling or by ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tomato Pulping Machine
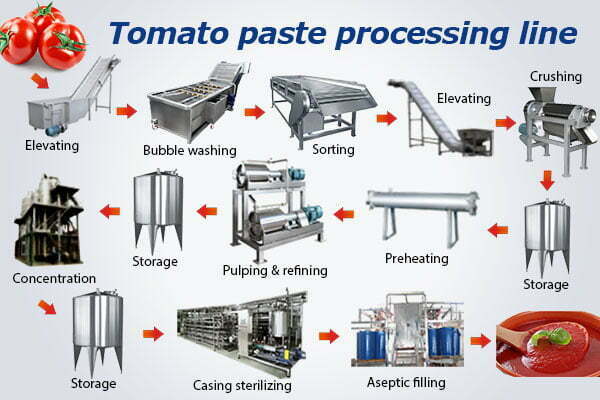
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tomato Pulping Machines
The global market for tomato pulping machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by rising demand for processed tomato products, technological innovation, and evolving food processing standards. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the industry and their implications for manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users.
-
Increased Demand for Processed Tomato Products
The steady growth in global consumption of tomato paste, ketchup, sauces, and canned tomatoes is fueling demand for efficient pulping equipment. With urbanization and changing dietary habits—especially in emerging economies—food manufacturers are scaling up production, necessitating high-capacity and automated tomato pulping machines. -
Adoption of Automation and Smart Technology
By 2026, automation is expected to become a standard feature in tomato pulping machines. Integration of IoT sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and AI-driven controls will enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product consistency. These smart machines will allow remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance, appealing to large-scale processors focused on minimizing costs and maximizing uptime. -
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Environmental regulations and rising energy costs are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient pulping systems. Machines with lower water and power consumption, along with recyclable material components, will gain market preference. Additionally, zero-waste processing technologies—such as seed and skin recovery systems—are likely to become more common, aligning with circular economy principles. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
Regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America are expected to lead market expansion by 2026. Increasing investments in agro-processing infrastructure, government support for local food production, and rising domestic consumption are creating strong demand for affordable and durable pulping machines tailored to regional crop varieties and processing needs. -
Customization and Modular Designs
Manufacturers are shifting toward modular and customizable pulping machines to meet diverse customer requirements. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in particular, are seeking scalable solutions that can adapt to fluctuating production volumes. Modular designs enable easier upgrades and integration with existing processing lines. -
Stringent Food Safety Regulations
With global food safety standards becoming more rigorous, tomato pulping machine producers are focusing on hygienic designs made from food-grade stainless steel and featuring easy-to-clean surfaces. Compliance with certifications such as CE, ISO 22000, and FDA standards will be a key selling point. -
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is witnessing increased competition, with established players and new entrants investing in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Innovations such as high-yield extraction systems, minimal pulp degradation technology, and multi-stage pulping units are expected to dominate product development by 2026.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the tomato pulping machine market will be characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability, and geographic diversification. Companies that embrace automation, energy efficiency, and customer-centric design will be best positioned to capitalize on growth opportunities in both developed and emerging markets.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tomato Pulping Machines (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a tomato pulping machine involves more than just finding the lowest price. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal risks, and long-term cost overruns. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Low-cost machines often use substandard materials such as non-food-grade stainless steel or inferior components that corrode or wear quickly. This compromises hygiene, increases maintenance costs, and shortens equipment lifespan. Always verify compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU 1935/2004) and ensure contact parts are made from 304 or 316 stainless steel.
Inadequate Processing Capacity and Efficiency
Machines may be mislabeled with inflated capacity ratings. Real-world performance can fall short due to inefficient design or motor power. Confirm actual throughput under continuous operation and assess yield (pulp recovery rate) to avoid bottlenecks in your production line.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Reputable suppliers provide documentation for CE, ISO, or other relevant certifications. Absence of these indicates potential non-compliance with safety or quality standards. Always request and verify certification documents before purchase.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Purchasing machines that infringe on patented designs or proprietary technology can expose your business to legal action. Avoid suppliers offering “replica” or “compatible” models at suspiciously low prices—these may copy protected innovations. Conduct due diligence on the original manufacturer and verify IP ownership.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many low-cost suppliers, particularly from certain regions, offer limited technical support or fail to supply spare parts. This leads to prolonged downtime when components fail. Confirm the availability of local service, technical documentation, and a responsive support network.
Hidden Costs from Poor Energy Efficiency
Lower-priced machines may use outdated motors or inefficient designs, leading to higher energy consumption. Evaluate energy ratings and operational costs over time to understand the total cost of ownership.
Inadequate Testing and Factory Acceptance
Skipping a factory acceptance test (FAT) or on-site demonstration increases the risk of receiving a non-functional or underperforming machine. Always insist on live testing with actual tomato feedstock before finalizing the purchase.
By carefully evaluating both quality and IP aspects, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and ensure reliable, compliant, and efficient tomato processing operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tomato Pulping Machine
Product Overview and Specifications
A tomato pulping machine is industrial processing equipment used primarily in food production to separate tomato pulp from seeds and skins. Typical models are constructed from stainless steel (e.g., AISI 304 or 316), operate on electrical power (single or three-phase), and vary in capacity from small-scale units (1–2 tons/hour) to large industrial systems (10+ tons/hour). Key specifications include dimensions, weight, power requirements, and compliance certifications (e.g., CE, ISO, NSF).
International Shipping Considerations
When exporting or importing a tomato pulping machine, logistics must account for size, weight, and fragility. Machines are typically shipped via container freight (FCL/LCL) or flat-rack containers for oversized units. Proper crating, waterproof packaging, and shock-absorbing materials are essential to prevent damage. Ensure accurate HS Code classification—commonly 8437.80 (machines for cleaning, sorting, or grading seed, grain, or dried leguminous vegetables)—to determine tariffs and import duties.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Compliance with destination country standards is mandatory. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking (EU): Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
– NSF/ANSI 2 (USA): Verifies that equipment meets sanitation standards for food processing.
– CU-TR (Eurasian Economic Union): Required for Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and others.
– ISO 22000 or HACCP: Demonstrates adherence to food safety management systems.
Ensure electrical components comply with local voltage and frequency standards (e.g., 110V/60Hz in North America, 230V/50Hz in Europe).
Import Documentation and Customs Clearance
Prepare the following documents for smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice (indicating value, quantity, and terms of sale)
– Packing List (detailing weight, dimensions, and packaging type)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Test Reports and Compliance Certificates (CE, NSF, etc.)
– Import License (if required by the destination country)
Incorrect or incomplete documentation may result in delays, fines, or seizure.
Installation, Safety, and Operational Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure installation follows manufacturer guidelines and local safety regulations. Operators must be trained in machine handling, cleaning, and maintenance. The machine should be integrated into a food safety plan compliant with local health codes (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 117 in the U.S. or EU Regulation 852/2004). Regular sanitation and record-keeping are essential for audit readiness.
After-Sales Support and Warranty Compliance
Verify warranty terms, including coverage duration, service availability, and spare parts supply. Logistics for spare parts must be planned in advance, especially for remote locations. Provide multilingual operation manuals and technical support to ensure ongoing compliance with safety and performance standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Tomato Pulping Machine:
After a thorough evaluation of available options, it is evident that sourcing a tomato pulping machine is a strategic investment for improving efficiency, consistency, and productivity in tomato processing operations. The market offers a range of machines—from small-scale manual models to fully automated industrial systems—allowing flexibility based on production needs, budget, and scalability goals.
Key factors such as machine capacity, material quality (preferably food-grade stainless steel), ease of cleaning and maintenance, energy efficiency, and compliance with food safety standards (e.g., CE, ISO, or FDA) must be prioritized during selection. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers with proven after-sales support and service networks ensures long-term reliability and minimal downtime.
Cost considerations should go beyond the initial purchase price to include total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, and labor savings. While imported machines may offer advanced features, locally available models can provide quicker service response and lower logistical costs.
In conclusion, selecting the right tomato pulping machine requires a balanced assessment of technical specifications, operational needs, and supplier credibility. With the correct machine in place, businesses can enhance product quality, increase output, and gain a competitive edge in the food processing industry.