The global tire recycling market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing environmental regulations, rising awareness of sustainable waste management, and the growing demand for recycled rubber materials. According to Grand View Research, the global tire recycling market size was valued at USD 6.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is amplified by stricter landfill bans on whole tires and the increasing adoption of recycled rubber in construction, sports surfaces, and consumer products. Central to this recycling ecosystem is the tire shredder machine—a critical piece of equipment that enables efficient size reduction of scrap tires for downstream processing. With demand on the rise, a competitive landscape of manufacturers has emerged, offering advanced shredding solutions tailored to varying capacities, input materials, and operational needs. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and global reach, the following are the top 10 tire shredder machine manufacturers shaping the future of tire recycling.
Top 10 Tire Shredder Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SSI Shredding Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ssiworld.com
Key Highlights: SSI designs & manufactures 1, 2, 3 and 4-shaft industrial shredders & systems, primary reducers and transfer station compactors….
#2 Industrial Tire Shredders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: franklinmiller.com
Key Highlights: Our tire shredders can shred car, off-road and light truck tires without debeading. Our tire shredders provide cost-effective tire shredding….
#3 CM Shredders
Domain Est. 1999
Website: cmshredders.com
Key Highlights: CMS Shredders: Global leader in industrial shredders, tire recycling systems, and turnkey solutions for sustainable waste management….
#4 Tire Shredding Machines
Domain Est. 1999
Website: tireshredders.com
Key Highlights: Barclay Roto-Shred manufactures tire recycling machines and industrial shredder equipment for scrapping tires into quality crumb rubber….
#5 Industrial Shredders for Sale
Domain Est. 2004
Website: bca-industries.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture stationary and portable shredders for tires, plastic, electronic waste, and more. … Shredder and recycling equipment that can travel with you….
#6 Tire Shredder for Tire Recycling
Domain Est. 1996
Website: shred-tech.com
Key Highlights: Shred-Tech’s tire shredders make tire recycling both simple and efficient, which is essential for the rapidly growing scrap tire processing industry….
#7 Tire Shredders For Recycling Tires
Domain Est. 2000
Website: vecoplanllc.com
Key Highlights: Vecoplan RTR tire re-shredding machines are built to handle the difficult process of re-shredding tires to create tire-derived fuel or recycled rubber products….
#8 Tire Shredders Tire Recycling Equipment Systems from …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: shredderhotline.com
Key Highlights: We are a full service, worldwide manufacturing company offering tire shredders, tire recycling equipment, bottle & glass shredders, metal shredders, low hp ……
#9 Liberty Tire Recycling
Domain Est. 2004
Website: libertytire.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Liberty Tire Recycling. Discover how we turn end-of-life tires into safe, eco-friendly products through our tire recycling processing and ……
#10 Tire Shredding Equipment & Rubber Recycling Machinery by Eco …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ecogreenequipment.com
Key Highlights: Eco Green Equipment is the global leader in cost-effective turnkey tire recycling systems. Our systems deliver optimum production performance and profitability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tire Shredder Machine
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tire Shredder Machines
The tire shredder machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, environmental regulations, and rising demand for recycled rubber materials. As global awareness of tire waste management increases, the industry is witnessing a surge in innovation and investment, shaping key trends that will define the market landscape.
-
Increasing Demand for Recycling and Waste Management
With over 1.5 billion waste tires generated annually worldwide, governments and private sectors are intensifying efforts to manage tire disposal sustainably. By 2026, stringent environmental regulations in regions like North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are expected to mandate higher recycling rates, directly boosting demand for efficient tire shredder machines. These regulations will encourage the adoption of advanced shredding technologies to convert end-of-life tires into reusable materials such as crumb rubber, tire-derived fuel (TDF), and rubberized asphalt. -
Technological Advancements in Shredding Efficiency
The integration of smart technologies and automation into tire shredder machines is a growing trend. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer shredders equipped with IoT-enabled monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and energy-efficient motors. These enhancements will improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and lower energy consumption—key factors for large-scale recycling facilities aiming to maximize throughput and minimize costs. -
Growth in End-Use Applications for Recycled Rubber
The expanding application of recycled rubber in construction, automotive, and consumer goods industries is fueling the need for high-capacity shredding systems. By 2026, growing use of crumb rubber in synthetic turf, playground surfaces, and noise-reducing road materials will drive investment in primary and secondary tire shredders capable of producing consistent, high-quality output. This diversification of end markets will support sustained growth in the tire shredder machine sector. -
Regional Market Expansion
Emerging economies in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are expected to witness substantial growth in tire shredder adoption by 2026. Rapid urbanization, increasing vehicle ownership, and rising environmental concerns will lead to the development of new recycling infrastructure. Countries like India, Brazil, and South Africa are likely to become hotspots for tire recycling, prompting both local and international manufacturers to expand their footprint in these regions. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Global push toward circular economy models will continue to influence the tire shredder market. By 2026, more companies will adopt closed-loop recycling systems, where tire waste is converted into valuable secondary raw materials. This shift will encourage the deployment of modular and scalable shredder systems that can be integrated into comprehensive waste-to-resource solutions, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and ESG criteria.
In conclusion, the 2026 tire shredder machine market will be shaped by regulatory pressures, technological innovation, and the expanding utility of recycled rubber. Stakeholders across the value chain—manufacturers, recyclers, and policymakers—will need to collaborate to meet the growing demand for efficient, sustainable tire waste processing solutions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Tire Shredder Machine: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a tire shredder machine involves significant investment and technical considerations. Buyers, especially those procuring from international suppliers, often encounter challenges related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls can help mitigate risks and ensure long-term operational success.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Machine Build and Material Standards
Many low-cost suppliers use substandard materials (e.g., low-grade steel or inferior bearings) to cut production costs. This leads to premature wear, high maintenance costs, and reduced machine lifespan. Without proper verification of material certifications (e.g., ISO or ASTM standards), buyers may receive equipment that cannot handle continuous industrial use.
2. Lack of Third-Party Quality Inspections
Skipping independent quality inspections during or after manufacturing can result in undetected defects. Buyers often rely solely on supplier-provided photos or videos, which may be misleading. On-site or third-party inspections are essential to verify workmanship, component quality, and assembly accuracy.
3. Misleading Performance Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate machine capabilities, such as throughput (tons per hour), particle size output, or power efficiency. These claims may not reflect real-world performance under continuous operation. Requesting test reports, client references, or live demonstrations helps validate performance data.
4. Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers with limited global support networks can lead to extended downtimes due to delayed technical assistance or unavailability of spare parts. Ensure the supplier offers a comprehensive service package and maintains spare parts inventory.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Counterfeit or Copycat Designs
A major risk when sourcing from certain regions is receiving machines that infringe on patented designs or technologies. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer branded shredders without licensing, offering “look-alike” machines at lower prices. Using such equipment may expose buyers to legal liabilities, especially in IP-sensitive markets.
2. Lack of IP Documentation and Compliance
Reputable suppliers should be able to provide proof of IP ownership or licensing for critical components (e.g., rotor design, control systems). Absence of such documentation increases the risk of purchasing infringing equipment. Always request IP compliance statements and conduct due diligence.
3. Exposure to Legal Action in Target Markets
If a tire shredder uses patented technology without authorization, the end user—especially in the U.S., EU, or other IP-enforcing jurisdictions—could face cease-and-desist letters, fines, or equipment seizure. This risk is often overlooked during procurement but can have severe financial and operational consequences.
4. Inadequate Software and Control System Licensing
Modern shredders often include proprietary software for automation, monitoring, and diagnostics. Unauthorized or pirated software not only poses cybersecurity risks but may also violate licensing agreements, leading to system failures or legal exposure.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier vetting, including site visits and reference checks.
- Require material test reports, performance validation, and third-party inspections.
- Insist on IP compliance documentation and warranty-backed authenticity guarantees.
- Partner with legal experts to assess IP risks, especially when importing into regulated markets.
By addressing these quality and IP pitfalls proactively, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable, compliant, and durable tire shredding solutions.
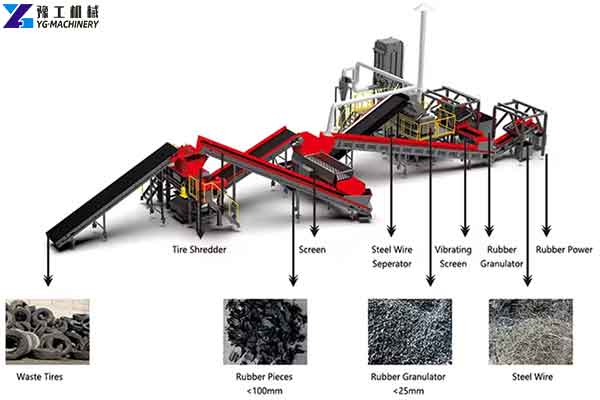
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tire Shredder Machine
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the procurement, transportation, installation, and operation of a tire shredder machine. Adhering to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and safety across the supply chain and facility.
Pre-Shipment Planning
- Machine Specifications: Confirm dimensions, weight, voltage, and power requirements to plan transportation and site readiness.
- Export Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin. Include HS code (e.g., 8477.80 for rubber recycling machinery).
- Export Licenses: Check if export controls apply based on destination country and machine technology.
- Incoterms Selection: Define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) to clarify shipping costs, risk transfer, and insurance.
International Shipping
- Freight Mode: Choose sea freight (most common for heavy machinery), air freight (urgent, lightweight components), or multimodal transport.
- Crating and Packaging: Use seaworthy wooden crates with shock-absorbing materials; secure all components to prevent movement.
- Hazardous Components: Declare batteries, hydraulic fluids, or lubricants per IMDG/IATA regulations if applicable.
- Customs Clearance: Provide accurate documentation to avoid delays; consider using a customs broker in the destination country.
Import Compliance
- Import Duties and Taxes: Determine applicable tariffs, VAT, and import fees based on the destination country’s tariff schedule.
- Regulatory Approvals: Verify if the machine requires pre-approval from local environmental, safety, or industrial authorities.
- CE, UL, or Other Certifications: Ensure the machine meets regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards (e.g., CE for EU, UL for USA).
- Local Standards: Confirm compliance with electrical, noise, and mechanical safety codes in the operating country.
On-Site Delivery and Handling
- Site Preparation: Ensure clear access route, load-bearing capacity of floors, and adequate space for installation.
- Lifting Equipment: Use appropriate cranes, forklifts, or rigging gear with trained personnel; follow load charts and safety protocols.
- Unloading Supervision: Inspect machine for transit damage before signing delivery documents; document any issues immediately.
Installation and Commissioning
- Qualified Technicians: Use manufacturer-trained or certified personnel for assembly and electrical connections.
- Utility Compliance: Verify alignment with local electrical codes, grounding, and ventilation requirements.
- Safety Systems: Install emergency stops, guards, and warning labels per OSHA (USA), ISO 13849, or local regulations.
Environmental and Operational Compliance
- Waste Management: Comply with local regulations for handling tire-derived materials (TDF, crumb rubber); obtain necessary permits for storage and processing.
- Emissions and Noise: Monitor dust, particulate matter, and noise levels; install filtration and sound-dampening systems if required.
- Permitting: Secure permits for hazardous waste operations, air quality, and industrial zoning as applicable.
- Record Keeping: Maintain logs for maintenance, waste disposal, emissions, and employee training for regulatory audits.
Worker Safety and Training
- OSHA/Local Safety Standards: Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO), personal protective equipment (PPE), and machine guarding.
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training on safe operation, emergency procedures, and maintenance.
- Hazard Communication: Label chemicals and maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all fluids used.
Ongoing Regulatory Compliance
- Inspections and Audits: Schedule regular equipment and facility inspections per local environmental and safety agencies.
- Compliance Updates: Monitor changes in regulations related to tire recycling, machinery safety, and environmental protection.
- Documentation Retention: Keep shipping records, permits, training logs, and maintenance reports for the required retention period.
End-of-Life and Decommissioning
- Proper Disposal: Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) or local regulations for recycling machine components.
- Environmental Remediation: Address any soil or water contamination from hydraulic leaks or fuel spills during decommissioning.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of a tire shredder machine requires proactive planning for logistics and strict adherence to compliance standards at every stage. Partnering with experienced suppliers, freight forwarders, and regulatory consultants ensures efficient operations and minimizes legal and operational risks.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Tire Shredder Machine:
Sourcing a tire shredder machine is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation of various technical, financial, and operational factors. After assessing different suppliers, machine specifications, capacity requirements, energy efficiency, maintenance needs, and long-term return on investment, it is evident that selecting the right shredder is crucial for the success and sustainability of tire recycling operations.
The ideal machine should align with the volume of waste tires processed, offer reliable performance with minimal downtime, and comply with environmental and safety regulations. Additionally, considering after-sales support, spare parts availability, and the supplier’s reputation enhances operational efficiency and reduces potential disruptions.
In conclusion, a well-researched and thoughtful sourcing process ensures the acquisition of a durable, efficient, and cost-effective tire shredder that supports both environmental goals and business profitability. Investing in the right technology today lays the foundation for scalable and sustainable waste tire management tomorrow.