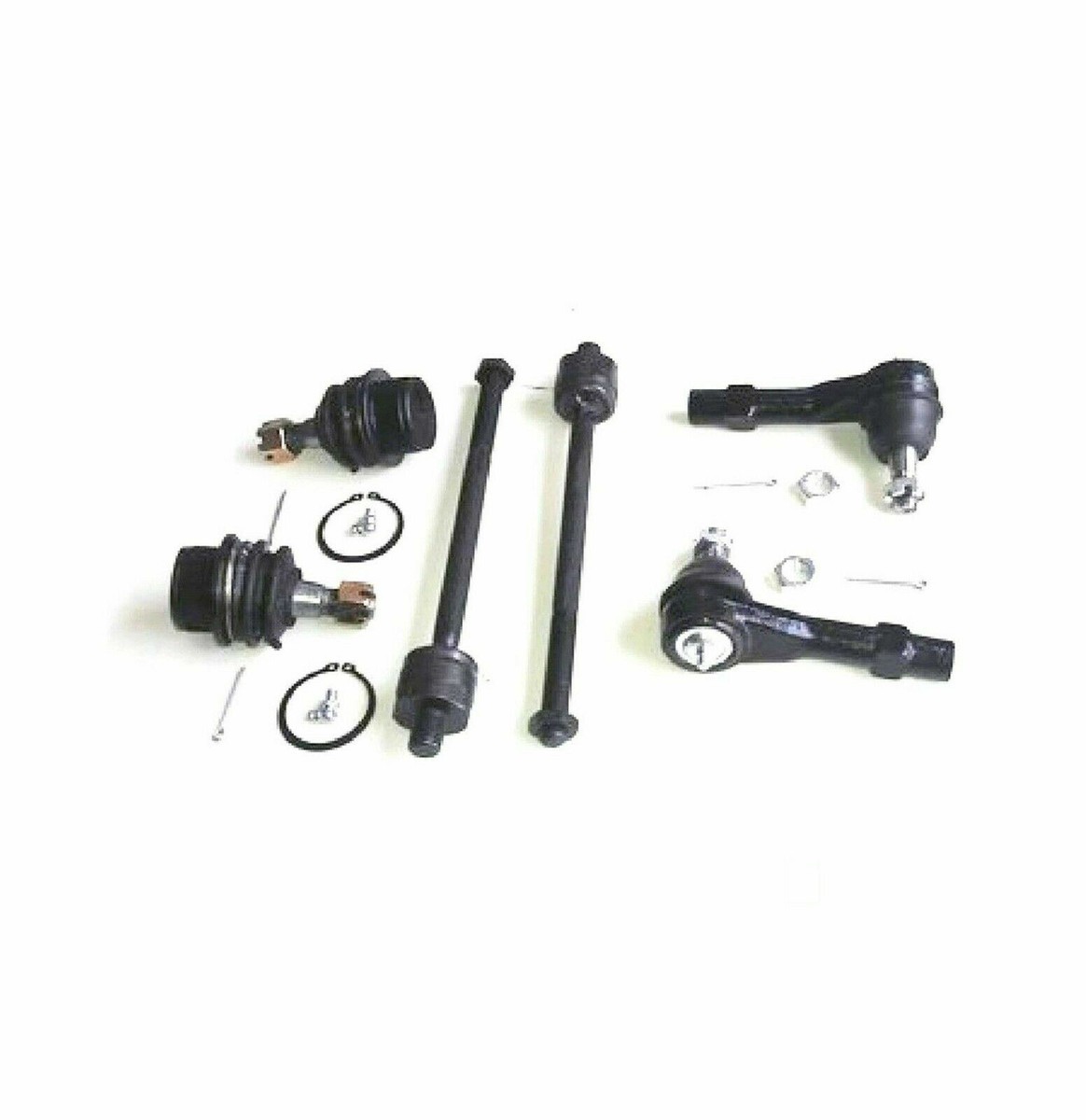
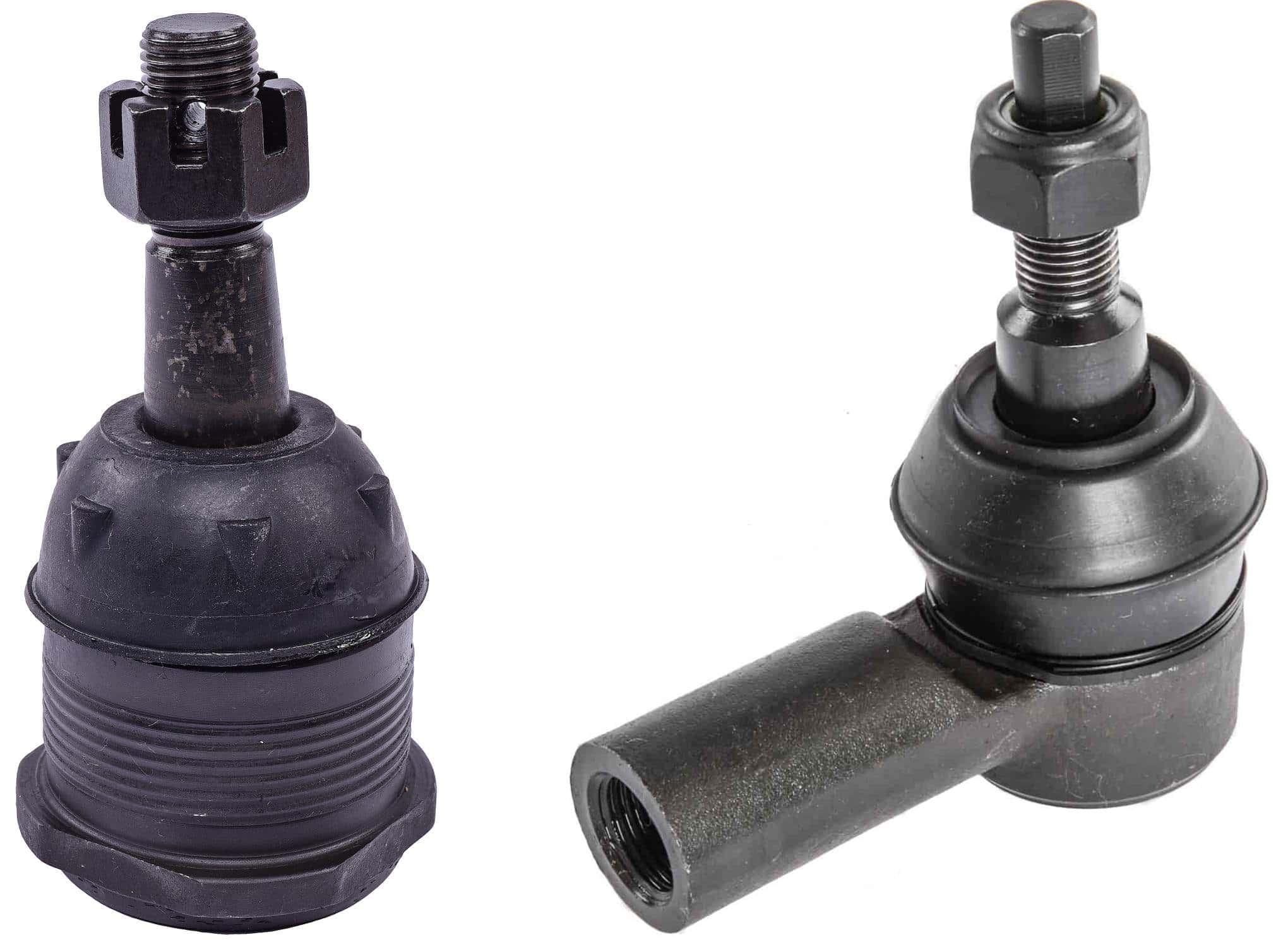
The global automotive suspension components market, which includes critical parts such as tie rod ends and ball joints, is experiencing steady expansion driven by rising vehicle production, increasing demand for aftermarket replacements, and the growing focus on vehicle safety and performance. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the automotive steering system market was valued at USD 44.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.3% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global suspension system market size reached USD 71.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 4.9% through 2030, fueled by advancements in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies that demand more precise and durable steering and suspension components. As demand intensifies, manufacturers of tie rod ends and ball joints are scaling innovation in materials, durability, and integration capabilities. In this competitive landscape, a select group of global suppliers are leading the way through high-quality engineering, extensive OEM partnerships, and strong aftermarket presence—making them key players in shaping the future of vehicle dynamics and safety.
Top 10 Tie Rod Ends And Ball Joints Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FK Rod Ends
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fkrodends.com
Key Highlights: FK Bearings is the leading USA manufacturer of rod ends, spherical bearings, custom-engineered bearings, and related products. Established in ……
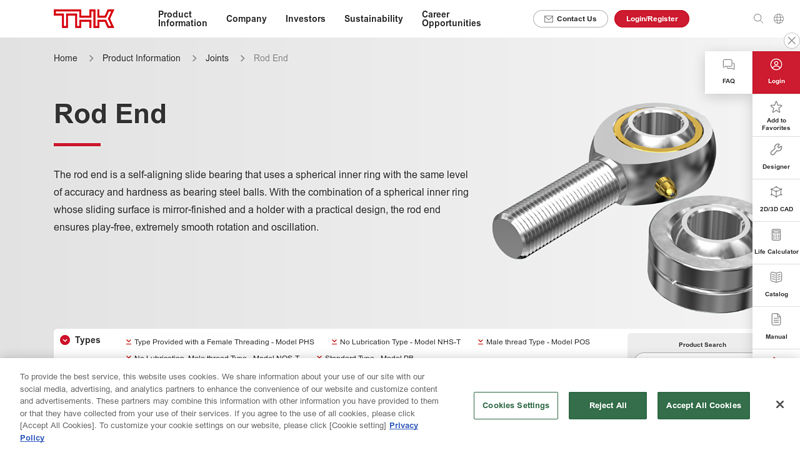
#2 Rod End|Joints|Product Information
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: The rod end is a self-aligning slide bearing that uses a spherical inner ring with the same level of accuracy and hardness as bearing steel balls….
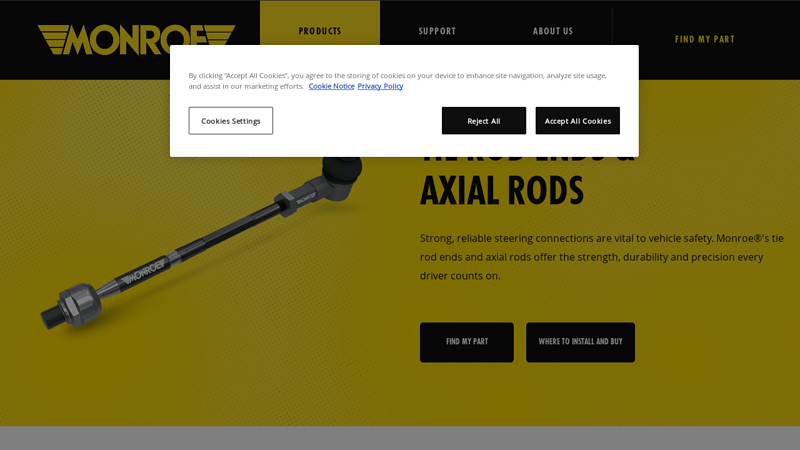
#3 Exact-Replacement Tie Rod Ends and Axial Rods
Domain Est. 1995
Website: monroe.com
Key Highlights: Monroe tie rod ends and axial rods are manufactured exclusively from highly durable, premium-grade steel, then protected with an advanced phosphate coating to ……
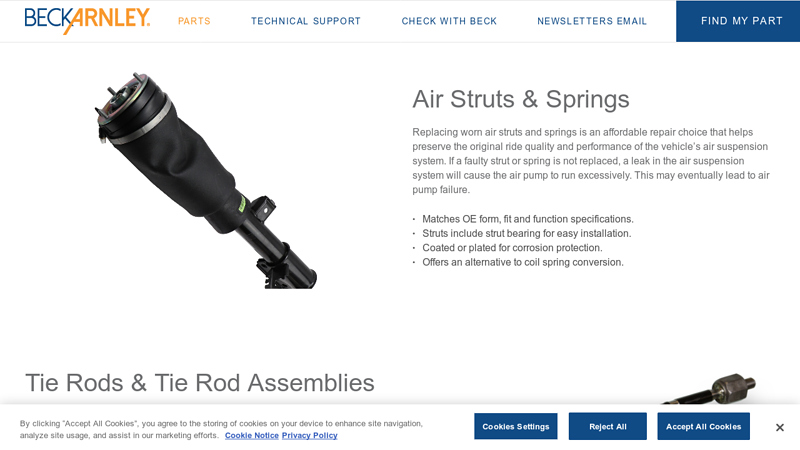
#4 Suspension Parts & Steering Components
Domain Est. 1996
Website: beckarnley.com
Key Highlights: Offers an alternative to coil spring conversion. Tie Rods & Tie Rod Assemblies. OE form, fit and function; Ball studs are pre-greased and sealed units; Coated ……
#5 Mevotech
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mevotech.com
Key Highlights: Engineered for Technicians, Designed for the Ride · Control Arms · Ball Joints · Stabilizer Links · Outer Tie Rod · Inner Tie Rod · Wheel Hub Assemblies ……
#6 Rod End Supply
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rodendsupply.com
Key Highlights: 1-day delivery 30-day returnsRod End Supply has the assortment of rod ends, radius rods and specialty products that will help you lead the field in performing at your maximum poten…
#7
Domain Est. 2007
Website: spcalignment.com
Key Highlights: Tie Rod & Toe · Wheel Service · xAxis™ Flex Joints · xAxis™ Rod End Joints · xAxis™ Receivers · Rod End Receivers · Spherical Bearing Receivers · Flared Hole ……
#8 Proforged Severe Duty Chassis Parts
Domain Est. 2010
Website: proforged.com
Key Highlights: Shop Proforged for high-performance, severe-duty chassis parts with a million-mile warranty. Discover durable ball joints, tie rod ends, control arms, and…
#9 Vehicle steering and suspension parts
Domain Est. 2015
Website: rts-sa.com
Key Highlights: Tie rod ends; Tie rod assemblies; Inner tie rods; Drag links. Suspension. Silentblocks; Stabilising links; Supports; Wishbone arms; Ball joints; Track control ……
#10 Product Information
Website: sankei-555.co.jp
Key Highlights: TIE ROD END … Built to provide the best steering experience. Sankei offers a wide selection for vehicles ranging from light cars to trucks….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tie Rod Ends And Ball Joints

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tie Rod Ends and Ball Joints
The global market for tie rod ends and ball joints is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive technology, shifts in manufacturing practices, and evolving consumer demands. As critical components of a vehicle’s suspension and steering systems, tie rod ends and ball joints are essential for ensuring vehicle safety, stability, and handling. Below is an in-depth analysis of key market trends expected to shape the industry in 2026.
1. Growth Driven by Rising Vehicle Production and Aftermarket Demand
The global automotive industry continues to expand, particularly in emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa. Increased vehicle production directly fuels demand for original equipment manufacturer (OEM) components like tie rod ends and ball joints. Simultaneously, the aftermarket segment is growing due to the rising average vehicle age and increased maintenance requirements. By 2026, the aftermarket is projected to account for over 60% of total sales in mature markets like North America and Western Europe.
2. Shift Toward Lightweight and Durable Materials
Automakers are under pressure to reduce vehicle weight to meet fuel efficiency and emissions regulations. This trend is pushing manufacturers of suspension components to adopt advanced materials such as high-strength alloys, composite polymers, and corrosion-resistant coatings. By 2026, tie rod ends and ball joints made from lightweight yet durable materials are expected to dominate new vehicle platforms, especially in electric and hybrid vehicles where weight savings directly impact range.
3. Electrification and EV-Specific Component Design
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping design requirements for suspension components. EVs typically have higher curb weights due to battery packs, placing increased stress on steering and suspension systems. As a result, tie rod ends and ball joints designed specifically for EV applications—featuring enhanced load-bearing capabilities and improved sealing against moisture and debris—are gaining traction. Component suppliers are collaborating closely with EV OEMs to develop tailored solutions, a trend expected to accelerate through 2026.
4. Integration of Smart and Condition-Monitoring Technologies
While still in early stages, the integration of sensors into suspension components is emerging as a future trend. By 2026, some premium and commercial vehicles may feature smart ball joints or tie rod ends equipped with wear sensors that feed data to onboard diagnostics systems. This enables predictive maintenance, reducing the risk of sudden failure and improving vehicle uptime—particularly valuable in fleet and commercial operations.
5. Consolidation and Regional Manufacturing Shifts
The global supply chain for automotive parts has been reevaluated post-pandemic and amid geopolitical tensions. By 2026, there is a growing trend toward regionalization of manufacturing, with companies establishing local production facilities in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers. Additionally, industry consolidation is expected to continue, with larger Tier 1 suppliers acquiring niche component manufacturers to strengthen their portfolios.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness are pushing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices. By 2026, leading producers of tie rod ends and ball joints are expected to increase the use of recycled materials, reduce energy consumption in production, and offer remanufactured components as cost-effective and eco-friendly alternatives. The remanufactured parts market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% through 2026, particularly in Europe and North America.
7. Price Pressure and Competition from Emerging Markets
Intense competition, especially from manufacturers in China and India, continues to exert downward pressure on prices. While this benefits OEMs and aftermarket consumers, it challenges profit margins for traditional suppliers. To remain competitive, established companies are investing in automation, lean manufacturing, and R&D to differentiate through quality, durability, and innovation rather than price alone.
Conclusion
By 2026, the tie rod ends and ball joints market will be shaped by the convergence of electrification, material innovation, digitalization, and sustainability. Suppliers who adapt to these trends—by developing EV-compatible components, embracing smart technologies, and optimizing regional supply chains—will be best positioned to capture growth in both OEM and aftermarket segments. The industry’s evolution reflects broader shifts in the automotive landscape, where safety, efficiency, and environmental responsibility are paramount.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Tie Rod Ends and Ball Joints (Quality, IP)
Sourcing tie rod ends and ball joints—critical components in a vehicle’s suspension and steering systems—requires careful consideration to avoid performance, safety, and legal issues. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers and suppliers should be aware of.
Poor Material Quality and Manufacturing Defects
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing these components is receiving parts made from substandard materials or with inconsistent manufacturing processes. Low-grade steel, improper heat treatment, or poor sealing can lead to premature wear, joint failure, or complete breakdown under stress. These defects compromise vehicle handling and safety, increasing the risk of accidents and costly recalls.
Lack of Compliance with OEM Specifications
Many aftermarket or imported tie rod ends and ball joints fail to meet Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) performance and dimensional standards. Even if parts appear similar, differences in tolerances, load ratings, or lubrication methods can drastically reduce service life and reliability. Sourcing components without proper validation against OEM specs may result in fitment issues or system incompatibility.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Parts
The automotive aftermarket is rife with counterfeit components that mimic branding, packaging, and part numbers of reputable manufacturers. These parts often violate intellectual property rights and may falsely claim certifications or OEM equivalency. Purchasing such items exposes businesses to legal liability, warranty disputes, and reputational damage. Always verify authenticity through authorized distributors and check for trademarks, holograms, or traceability codes.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reliable tie rod ends and ball joints should undergo rigorous testing for durability, corrosion resistance, and load capacity. However, many low-cost suppliers skip or falsify test reports. Absence of certifications such as ISO/TS 16949, SAE J490, or DIN standards is a red flag. Without proper documentation, there’s no assurance the parts meet industry safety and performance benchmarks.
Insufficient Traceability and Documentation
Traceability is crucial for quality control and recall management. Poorly sourced components often lack batch numbers, manufacturing dates, or supplier documentation. This makes it difficult to investigate failures or comply with regulatory requirements. Always insist on full traceability and maintain records of supplier credentials and material certifications.
Overreliance on Price Over Performance
While cost is a major factor, prioritizing the lowest price often leads to compromised quality. Extremely low-cost tie rod ends and ball joints may use inferior materials, outdated designs, or unregulated production methods. This false economy can result in higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements, labor expenses, and potential liability from part failure.
Ignoring Regional Regulatory Requirements
Different markets have specific regulations for automotive parts, including emissions, safety, and labeling (e.g., DOT in the U.S., E-mark in Europe). Sourcing components that don’t meet these regional standards can lead to import denials, fines, or legal action. Always confirm that parts comply with the target market’s regulatory framework.
By recognizing and addressing these pitfalls, businesses can ensure they source high-quality, legally compliant tie rod ends and ball joints that meet both performance expectations and IP integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tie Rod Ends and Ball Joints
Product Description and Classification
Tie rod ends and ball joints are critical components of a vehicle’s suspension and steering systems. Tie rod ends connect the steering rack to the steering knuckle, enabling directional control, while ball joints serve as pivot points between the control arms and steering knuckles, allowing smooth wheel movement. These parts are typically made of steel, with grease-sealed or maintenance-free designs, and are subject to rigorous performance standards due to their safety-critical nature.
Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Accurate HS code classification is essential for international shipping and customs clearance. Common HS codes for tie rod ends and ball joints include:
– 8708.93.60: For ball joints and tie rod ends when classified under “Steering gear and other steering components.”
– 8708.29.50: May apply to suspension system parts, including control arms with ball joints.
Always verify codes with the destination country’s customs authority, as classifications can vary by region and specific product design.
Import/Export Regulations
- Documentation: Required documents include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin.
- Product Certification: Many markets (e.g., EU, USA, Canada) require compliance with automotive safety standards such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or DOT certification.
- Country-Specific Rules: The European Union may require ECE R78 certification for suspension components, while the U.S. enforces FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards) compliance.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Packaging: Must be durable to prevent damage during transit. Individual parts should be sealed against moisture and corrosion, often using vacuum sealing or VCI (Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor) paper.
- Labeling: Each package must include part number, quantity, manufacturer name, country of origin, HS code, and any required compliance marks (e.g., CE, DOT). Barcodes and batch/lot numbers are recommended for traceability.
Transportation and Handling
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, or ground freight. Sea freight is most cost-effective for bulk shipments; air freight is preferred for urgent or small-volume orders.
- Handling: Parts must be stored and transported in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent rust and degradation. Stack weight limits should be observed to avoid crushing.
- Hazardous Materials: Standard tie rod ends and ball joints are not classified as hazardous, but greased components may require documentation if lubricants are flammable.
Quality and Compliance Standards
- IATF 16949: International standard for quality management in automotive production; highly recommended for suppliers.
- ISO 9001: General quality management certification.
- Testing Requirements: Components may need to undergo load testing, durability cycles, and salt spray corrosion tests to meet OEM or aftermarket standards.
Aftermarket vs. OEM Compliance
- OEM Parts: Must meet exact vehicle manufacturer specifications and often require direct certification.
- Aftermarket Parts: Must comply with regional safety and performance regulations. In the U.S., aftermarket parts are regulated under NHTSA guidelines and must not compromise vehicle safety.
Returns and Warranty Logistics
- Warranty Claims: Establish clear return material authorization (RMA) procedures. Defective parts should be inspected and documented per warranty terms.
- Reverse Logistics: Use trackable return shipments. Returned items must be quarantined and assessed for safety before recycling or disposal.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- End-of-Life Handling: Metal components are recyclable. Used parts contaminated with grease or oil must be processed according to local environmental regulations.
- REACH and RoHS Compliance: Ensure materials used (e.g., coatings, lubricants) comply with EU REACH and RoHS directives restricting hazardous substances.
Recommended Best Practices
- Partner with certified freight forwarders experienced in automotive parts.
- Maintain up-to-date compliance documentation for audits.
- Conduct regular reviews of import/export regulations in target markets.
- Implement traceability systems (e.g., ERP or inventory software) to track batches and manage recalls.
By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure smooth logistics operations and full regulatory compliance when shipping tie rod ends and ball joints globally.
In conclusion, sourcing tie rod ends and ball joints requires careful consideration of vehicle specifications, quality standards, and supplier reliability. It is essential to prioritize OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts that meet or exceed original equipment standards to ensure safety, performance, and longevity of the vehicle’s suspension and steering systems. Evaluating suppliers based on reputation, warranty offerings, and availability of technical support can help secure reliable components. Additionally, proper installation and regular inspection are critical to maintaining optimal vehicle handling and safety. By making informed sourcing decisions, fleet managers, repair shops, and vehicle owners can achieve cost-effective maintenance without compromising on safety or performance.