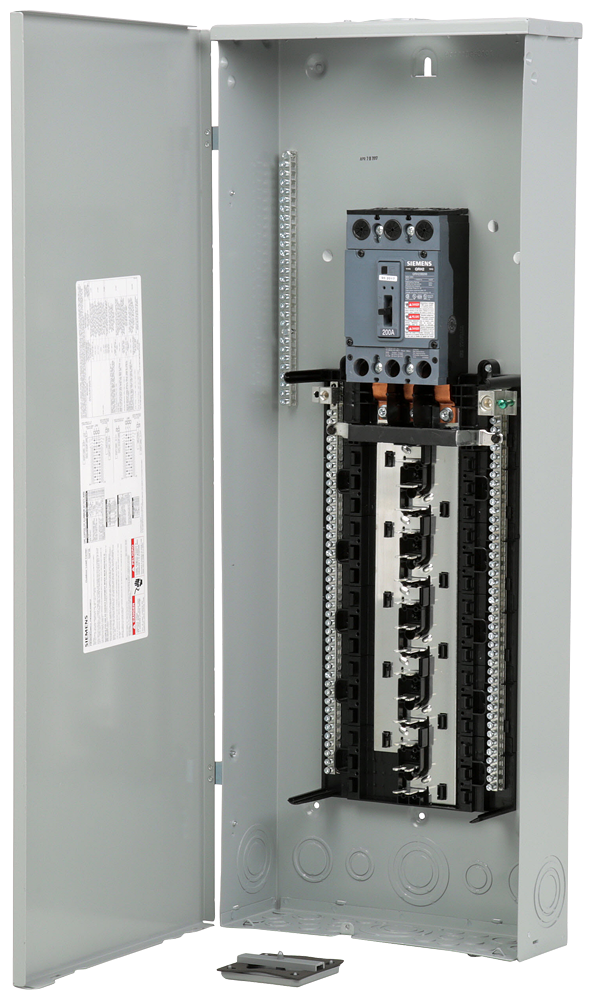
The global market for electrical distribution equipment, including three-phase sub panels, is experiencing steady growth driven by rising industrialization, infrastructure development, and the expansion of commercial and industrial facilities. According to Mordor Intelligence, the electrical distribution and control equipment market was valued at approximately USD 160 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth trajectory reflects increasing demand for reliable and efficient power distribution solutions, particularly in manufacturing plants, data centers, and renewable energy installations. Three-phase sub panels—critical for load management and circuit protection in industrial and large-scale commercial applications—are central to this trend. As reliability, safety, and energy efficiency become paramount, manufacturers are investing in innovation and compliance with international standards. Based on market presence, product quality, and technological advancement, here are the top six three-phase sub panel manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 6 Three Phase Sub Panel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
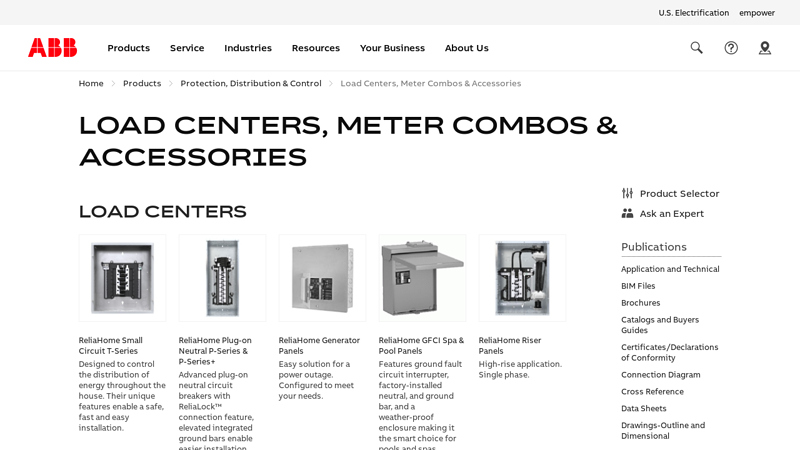
#1 Load Centers, Meter Combos & Accessories
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB ReliaHome load centers and accessories are designed for quick and reliable installation, ensuring you can complete jobs with confidence….
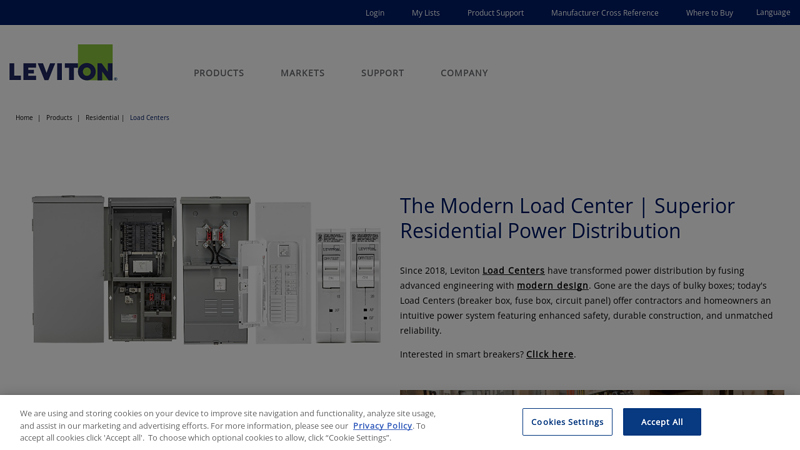
#2 Leviton Load Center
Domain Est. 1995
Website: leviton.com
Key Highlights: Leviton offers a comprehensive catalog of load center products including main breaker, main lug, indoor, outdoor, branch circuit breakers, and accessories….
#3 Panelboard fundamentals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: The power panel is more of an intermediary component of the power distribution system and contains mostly three-phase loads, whether connected directly to a ……
#4 Panelboards / Switchboards and Switchgear
Domain Est. 1997
Website: se.com
Key Highlights: Square D™ NF and NQ Panelboards provide best-in-class overcurrent and advanced function protection for AC final distribution circuits and sub-panels….
#5 Load center, QO, 3 phase, 12 spaces, 12 circuits, 125A fixed main …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: granitecityelectric.com
Key Highlights: There is 3 types of mains available. There is main circuit breaker, main lugs, and generator panel. Single and three phase options are available. The bus bars ……
#6 Three-Phase Load Centers
Domain Est. 2013
Website: contractor.compas.siemens-info.com
Key Highlights: Siemens three-phase load centers is the smart choice for contractors when value and quick installation is the highest priority….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Three Phase Sub Panel

2026 Market Trends for Three-Phase Sub Panels
The market for three-phase sub panels is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by global shifts in energy infrastructure, industrial modernization, and technological innovation. As industries and commercial facilities increasingly demand reliable, efficient, and scalable power distribution, three-phase sub panels are becoming central to electrical system design. Below is an analysis of the key market trends expected to shape the landscape through 2026.
Rising Demand in Industrial Automation and Manufacturing
Industrial automation is accelerating worldwide, particularly in emerging economies and advanced manufacturing hubs. Three-phase sub panels are essential for powering high-capacity machinery such as CNC machines, robotic assembly lines, and large-scale HVAC systems. As factories adopt smart manufacturing principles (Industry 4.0), the need for modular and scalable power distribution units like sub panels grows. By 2026, investments in automated production facilities will continue to drive demand for robust, easily integrable three-phase sub panels capable of supporting dynamic load requirements.
Growth in Commercial and Data Center Infrastructure
The expansion of data centers, commercial office buildings, and retail complexes is a major driver for three-phase power systems. Data centers, in particular, require high-density power distribution to support server racks and cooling systems. Three-phase sub panels enable balanced load management and efficient power delivery across large-scale installations. With digital transformation accelerating and cloud computing demand surging, data center construction is expected to remain strong through 2026, directly boosting the market for industrial-grade sub panels.
Electrification of Buildings and Adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Building electrification—especially in commercial and multifamily residential developments—is pushing demand for higher-capacity electrical systems. As buildings integrate heat pumps, electric boilers, and EV charging stations, the need for three-phase power distribution increases. Sub panels are used to segregate and manage these high-load circuits safely. By 2026, widespread EV adoption will necessitate three-phase EV charging infrastructure in commercial parking facilities, further increasing reliance on three-phase sub panels for load balancing and circuit protection.
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Smart Grid Integration
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability goals are pushing the adoption of intelligent power management systems. Three-phase sub panels equipped with monitoring capabilities, remote disconnects, and IoT integration are gaining traction. These “smart” sub panels allow facility managers to track energy usage, detect imbalances, and prevent overloads. As smart grid technologies expand, sub panels with communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, BACnet) will become standard, enabling real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance—key trends expected to grow through 2026.
Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America
While North America and Europe maintain mature markets for electrical infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region—especially countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia—is witnessing rapid industrialization and urban development. This growth is creating robust demand for reliable power distribution solutions, including three-phase sub panels. Similarly, Latin American countries are investing in industrial parks and commercial real estate, driving market expansion. By 2026, these regions are expected to represent the fastest-growing segments for sub panel adoption.
Supply Chain Optimization and Localized Manufacturing
Ongoing supply chain disruptions and geopolitical factors are prompting manufacturers to localize production. Companies are increasingly establishing regional manufacturing hubs to reduce lead times and comply with local content requirements. This shift is expected to improve the availability of three-phase sub panels in developing markets and support just-in-time delivery models. Additionally, modular designs and standardized components will enhance customization and installation speed, a trend likely to accelerate by 2026.
Emphasis on Safety, Compliance, and Sustainability
Regulatory standards such as NEC (National Electrical Code), IEC, and regional safety certifications are becoming more stringent. Manufacturers are focusing on sub panels with enhanced arc-fault protection, better thermal management, and environmentally friendly materials. Sustainable manufacturing practices and recyclable components are also becoming competitive differentiators. By 2026, compliance with both safety and environmental standards will be a critical factor in product selection across all market segments.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for three-phase sub panels will be defined by technological advancement, growing electrification, and global infrastructure development. Stakeholders—from manufacturers to contractors—must adapt to trends in automation, smart integration, and regional demand shifts to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Three-Phase Sub Panel (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a three-phase sub panel requires careful consideration of both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance. However, several common pitfalls can compromise system performance and longevity if not addressed.
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Standards
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting sub panels based on price alone without verifying the quality of internal components such as busbars, circuit breakers, and insulation materials. Low-quality panels may use undersized copper busbars or inferior-grade plastics that degrade under heat and load. Always verify that the panel meets recognized standards such as IEC 61439 or UL 891, and prefer panels from reputable manufacturers with certified production processes.
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Rating Requirements
The IP rating defines the level of protection against solid objects and liquids. A common error is selecting a sub panel with an inadequate IP rating for the installation environment. For example, using an IP30-rated panel in a dusty or outdoor setting can lead to contamination, short circuits, or corrosion. Indoors, IP30 may suffice, but outdoor or industrial environments typically require IP54 or higher. Always match the IP rating to the environmental conditions.
Inadequate Short-Circuit Withstand Rating (Icw)
Some sourced sub panels may not be rated for the available fault current at the installation point. Using a panel with insufficient short-circuit withstand capacity creates a serious safety hazard. Always confirm that the sub panel’s Icw rating meets or exceeds the prospective fault current of the supply, as determined by a fault analysis.
Poor Thermal Management Design
Three-phase systems generate significant heat, especially under continuous load. Low-quality sub panels may lack proper ventilation or spacing, leading to overheating and premature component failure. Ensure the panel design includes adequate thermal management, such as ventilation slots (if applicable) and proper spacing between components, especially when housed in high-temperature environments.
Non-Compliance with Local Electrical Codes
Different regions have specific regulations regarding grounding, labeling, and installation methods. Sourcing panels not compliant with local codes—such as NEC in the U.S. or IEC standards in Europe—can result in failed inspections or unsafe installations. Always confirm regional compliance before purchase.
Compromising on Enclosure Material and Corrosion Resistance
In humid, coastal, or chemically aggressive environments, using a steel enclosure without proper coating can lead to rust and structural failure. Stainless steel or polycarbonate enclosures with high corrosion resistance are better choices in such conditions. Confirm the enclosure material suits the environmental exposure.
Incomplete Documentation and Lack of Traceability
Low-cost or uncertified panels may lack proper technical documentation, test reports, or traceable certification marks. This can hinder maintenance, inspections, and compliance audits. Always source panels with full documentation, including test certificates and single-line diagrams.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can ensure a reliable, safe, and code-compliant three-phase sub panel installation. Prioritize certified quality, appropriate IP ratings, and environmental suitability during the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Three Phase Sub Panel
Installing a three-phase sub panel involves careful planning, adherence to regulations, and proper logistical coordination. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, code-compliant, and efficient deployment.
Regulatory and Code Compliance
Ensure all work complies with national and local electrical codes. The primary reference in the United States is the National Electrical Code (NEC), particularly Articles 225 (Outside Branch Circuits and Feeders), 230 (Services), 240 (Overcurrent Protection), and 408 (Switchboards and Panelboards).
- NEC Article 408.36: Requires overcurrent protection for each ungrounded conductor at the point of supply for a three-phase sub panel.
- NEC Article 250: Governs grounding and bonding requirements. The sub panel must have separate neutral and ground busbars, with the ground bar bonded to the enclosure and connected to the main service ground or grounding electrode system.
- Local Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ): Always consult local building and electrical inspectors for permit requirements and inspections. Local amendments to the NEC may apply.
Equipment Specifications and Selection
Choose a sub panel rated for three-phase service, appropriate voltage (e.g., 120/208V or 277/480V), and adequate amperage capacity based on load calculations.
- Confirm NEMA rating (e.g., NEMA 3R for outdoor use, NEMA 1 for indoor).
- Verify short-circuit current rating (SCCR) is suitable for the available fault current at the installation point.
- Use only UL-listed or ETL-verified equipment.
Load Calculation and Sizing
Perform a detailed load calculation in accordance with NEC Article 220.
- Sum all connected loads (continuous and non-continuous).
- Apply demand factors where applicable.
- Size the feeder conductors, overcurrent protection, and sub panel busbars accordingly (NEC Table 310.16 for conductor ampacity).
Feeder Circuit Requirements
The feeder from the main panel to the sub panel must be properly sized and protected.
- Use appropriately sized conductors (phase, neutral, and ground) based on load and distance (consider voltage drop).
- Install a disconnecting means at or near the sub panel if located outside the main structure.
- Use conduit or raceway systems rated for the environment (e.g., EMT, RMC, or PVC).
Grounding and Bonding
Critical for safety and code compliance.
- Isolate the neutral bar from the enclosure in the sub panel.
- Bond the ground bar directly to the enclosure.
- Run a separate equipment grounding conductor (EGC) from the main panel to the sub panel ground bar.
- Do not bond neutral to ground in the sub panel—this must only occur at the main service disconnect.
Permitting and Inspection
- Obtain required electrical permits before beginning work.
- Schedule inspections at rough-in and final stages.
- Provide documentation including panel schedule, one-line diagram, and load calculation.
Logistics and Installation Planning
Coordinate delivery and site access for equipment.
- Confirm sub panel dimensions and weight; ensure pathway clearance for installation.
- Use proper lifting equipment if needed.
- Schedule work to minimize facility downtime, especially in commercial or industrial settings.
- Verify availability of qualified electricians licensed to perform three-phase installations.
Safety Protocols
- De-energize all circuits before working.
- Follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) rated for the system voltage.
- Test for dead before touching conductors.
Documentation and Maintenance
Maintain detailed records:
- As-built panel schedule and circuit labeling.
- One-line diagram of the electrical system.
- Inspection approval documents.
- Maintenance log for periodic thermal imaging and torque checks on connections.
Adhering to this guide ensures a compliant, safe, and reliable three-phase sub panel installation that meets both logistical and regulatory demands.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Three-Phase Sub Panel:
Sourcing a three-phase sub panel requires careful consideration of electrical specifications, load requirements, and compliance with local codes and regulations. It is essential to select a panel that matches the voltage (e.g., 120/208V or 277/480V), phase configuration (3-phase, 4-wire), and amperage rating needed for the intended application. Compatibility with the main service panel and proper coordination of overcurrent protection devices are critical for safety and performance.
When sourcing, prioritize reputable manufacturers (such as Square D, Siemens, Eaton, or GE) to ensure reliability and availability of components. Additionally, verify that the sub panel is listed by a recognized testing laboratory (e.g., UL) and meets NEC (National Electrical Code) standards. Proper installation by a licensed electrician is strongly recommended to ensure safety, code compliance, and long-term functionality.
In summary, a well-sourced three-phase sub panel enhances system efficiency, supports three-phase equipment needs, and contributes to a safe and code-compliant electrical infrastructure. Planning, technical accuracy, and professional guidance are key to a successful installation.