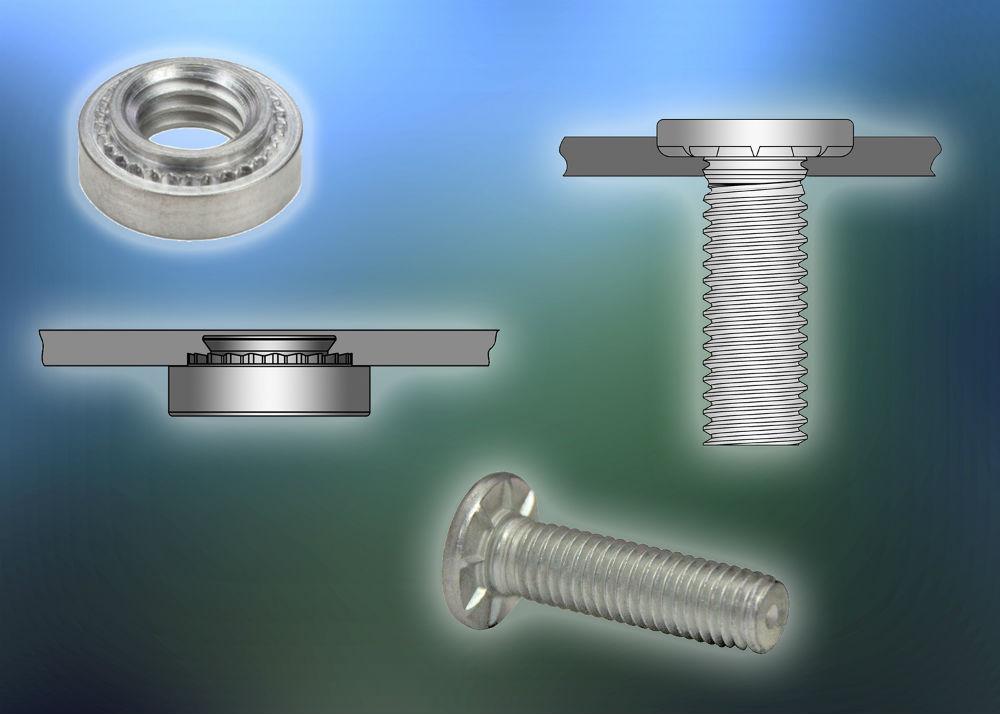
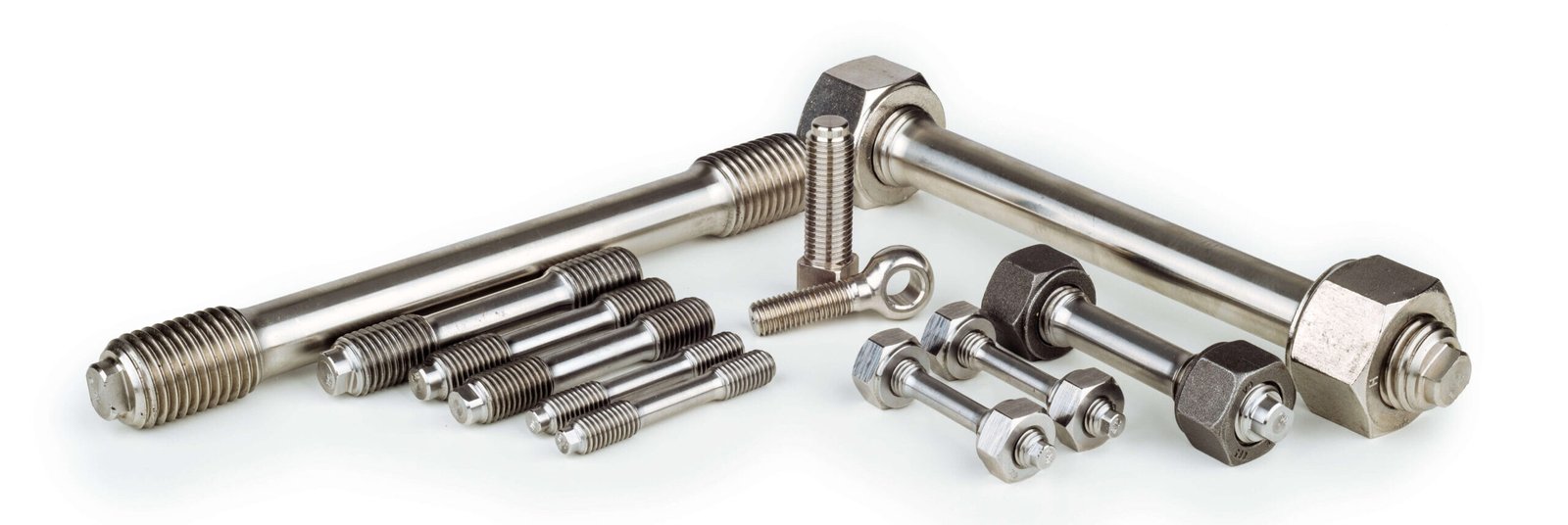
The global fastener market, which includes critical components such as threaded stud nuts and washers, continues to expand amid rising demand from automotive, construction, industrial machinery, and infrastructure sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global fastener market size was valued at USD 106.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is driven by increasing industrialization, urbanization, and the need for high-performance, corrosion-resistant fastening solutions in demanding applications. Mordor Intelligence further underscores this trend, noting steady demand from emerging economies and advancements in material technology—particularly in stainless steel, alloy steel, and specialty coatings—which are enhancing product durability and performance. As industries prioritize reliability and precision in assembly processes, the role of leading threaded stud nut and washer manufacturers becomes increasingly pivotal. In this report, we highlight the top 9 manufacturers shaping the market through innovation, scalability, and global supply chain reach.
Top 9 Threaded Stud Nut And Washer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Threaded Fasteners, Inc.
Domain Est. 2003
Website: threadedfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Threaded Fastener Manufacturer and Distributor of pole line hardware, anchor cages, anchor bolts, A325 Structural Bolts, nuts, bolts, washers….
#2 Fastener Supplier for OEM, Distributors, and Industrial Applications
Domain Est. 2021
Website: gobigbolt.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture almost all bolt and nut types in the United States and around the world. Non-standard parts, gap buys, per-print orders, prototypes, low-volume ……
#3 Haydon Bolts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: haydonbolts.com
Key Highlights: A family owned manufacturer specializing in domestic structural bolts and anchor rods, since 1864. We carry the largest inventory of Melted and Manufactured in ……
#4 Custom Fasteners Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nationalbolt.com
Key Highlights: National Bolt and Nut Corporation is a ISO Certified Nationwide custom fasteners manufacturer of nuts, washers, bolts and fasteners. Contact us today!…
#5 Wilson
Domain Est. 2005
Website: wilsongarner.com
Key Highlights: Wilson-Garner specializes in short-run quantities of custom bolts, screws, & studs made from alloy or carbon steel. Our parts are American-made….
#6 Nuts, Bolts, Washers, Threaded Rods
Domain Est. 1996
#7 NutsandBolts.com
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nutsandbolts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 30-day returnsYour one-stop shop for fasteners. Seamless shopping with expert support for your projects. Shop Now Essential Fastener Kits Stay prepared with …
#8 PEM – PennEngineering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: PEM offers innovative fastening solutions for a variety of applications across industries like Automotive Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Datacom and more….
#9 DIN Fasteners
Domain Est. 2017
Website: din-fasteners.com
Key Highlights: Ferrobend offers complete range of DIN standard bolts, screws, studs, threaded rods, nuts, washers, pins, rivets, plugs, and other fixings and fasteners….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Threaded Stud Nut And Washer

H2: Market Trends for Threaded Stud, Nut, and Washer Industry in 2026
As global industrial activity rebounds and infrastructure investments accelerate, the threaded stud, nut, and washer market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. These essential fastening components are critical across construction, automotive, energy, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors. Several macroeconomic, technological, and regulatory trends are shaping the industry landscape, driving innovation, supply chain adjustments, and shifting demand patterns.
-
Rising Infrastructure Development Driving Demand
Governments worldwide, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, are prioritizing infrastructure modernization and expansion. Initiatives such as the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and China’s “New Infrastructure” program are expected to boost construction and industrial projects. This surge in public and private investment directly increases the need for high-strength fasteners like threaded studs, nuts, and washers, especially in bridges, power plants, and high-rise buildings. -
Growth in Renewable Energy Projects
The global push toward clean energy is a major catalyst. Wind turbines, solar panel mounting systems, and hydroelectric plants require durable and corrosion-resistant fasteners. By 2026, the renewable energy sector is projected to become one of the fastest-growing end-user markets for threaded studs and associated hardware. Demand will be particularly strong for stainless steel, galvanized, and high-tensile alloy components engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions. -
Advancements in Material Science and Coatings
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced materials and protective coatings to enhance product performance and longevity. Innovations such as duplex coatings (zinc-aluminum), ceramic coatings, and the use of weathering steel alloys are expected to gain traction. These improvements help fasteners resist corrosion, UV degradation, and extreme temperatures—critical attributes for applications in offshore, chemical processing, and transportation sectors. -
Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping fastener production. By 2026, smart factories leveraging IoT-enabled monitoring, robotic assembly, and predictive maintenance will enhance precision, reduce waste, and improve supply chain responsiveness. This shift enables manufacturers to offer customized stud-nut-washer assemblies with tighter tolerances and faster turnaround times, catering to complex engineering requirements. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to localize production and diversify sourcing. Nearshoring and friend-shoring strategies are expected to grow, especially in North America and Europe. This regional shift supports faster delivery times and reduces dependency on single-source suppliers, particularly from Asia. As a result, local manufacturers will expand capacity, fostering innovation and competitiveness in the threaded fastener market. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations are tightening, especially in the EU and North America. By 2026, standards such as REACH, RoHS, and ISO 14001 will push manufacturers to adopt greener production methods, reduce carbon footprints, and ensure traceability in raw materials. Recyclability of fasteners and the use of low-impact manufacturing processes will become key differentiators in winning contracts, particularly in public infrastructure and green building projects. -
Increasing Demand for Customized and High-Performance Solutions
End-users in aerospace, defense, and oil & gas industries are demanding specialized threaded fasteners tailored to unique operational conditions. Custom lengths, thread types (e.g., UNF, metric fine), and load-bearing capabilities are driving demand for engineered solutions. By 2026, companies offering end-to-end design support, prototyping, and certification services will gain competitive advantage. -
Digital Procurement and E-Commerce Expansion
B2B e-commerce platforms are transforming how fasteners are bought and sold. Digital marketplaces offering real-time inventory, CAD integration, and automated reordering will become mainstream. By 2026, a growing number of industrial buyers will rely on digital channels for procurement, increasing transparency and efficiency in the supply chain.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for threaded studs, nuts, and washers will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and resilience. Driven by infrastructure growth, renewable energy expansion, and digital transformation, the industry is evolving beyond commodity status toward value-added, high-performance solutions. Companies that invest in technology, regional supply chains, and eco-friendly practices will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
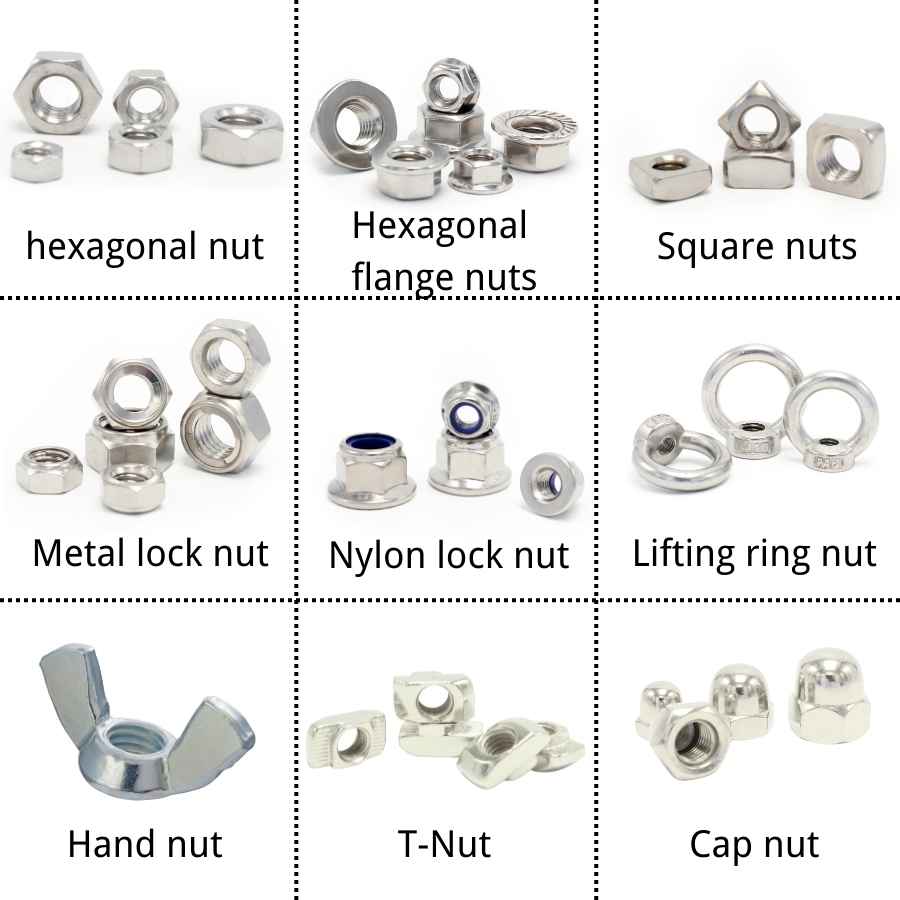

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Threaded Stud, Nut, and Washer Assemblies (Quality, IP)
Sourcing threaded stud, nut, and washer assemblies—especially where quality and intellectual property (IP) are critical—can be fraught with challenges. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to compromised product performance, safety risks, legal issues, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Control and Material Verification
One of the foremost risks is assuming supplier claims without independent verification. Many suppliers may advertise high-grade materials (e.g., ASTM A193 B7 studs, A194 2H nuts), but substandard or counterfeit materials are common, especially from low-cost regions. Without proper material test reports (MTRs), third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, EN), or in-house testing, buyers risk receiving components with incorrect tensile strength, chemical composition, or heat treatment—leading to premature failure under stress or in critical environments.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
High-integrity applications (e.g., oil & gas, power generation, aerospace) require full traceability of components. A frequent pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide lot traceability, proper marking (per ASME or EN standards), or comprehensive documentation (e.g., inspection reports, certificates of conformance). This becomes a major issue during audits or failure investigations and may violate regulatory or project-specific requirements.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Reverse Engineering Risks
When sourcing proprietary or patented fastener designs, there’s a real danger of IP theft. Some suppliers—particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement—may reverse-engineer samples provided during prototyping and sell identical copies to competitors. This not only undermines competitive advantage but can lead to legal battles. Always use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), work with trusted partners, and avoid sharing detailed drawings or specifications without legal safeguards.
Inconsistent Thread and Dimensional Tolerances
Even minor deviations in thread pitch, diameter, or length can cause assembly issues, galling, or reduced clamping force. Suppliers may meet visual inspection criteria but fail to adhere to tight tolerances specified in standards like ISO 965 or ASME B1.1. Without rigorous incoming inspection or supplier process audits, these inconsistencies can go undetected until field failures occur.
Improper Coatings and Corrosion Protection
Corrosion resistance is often critical, yet coatings (e.g., zinc plating, Dacromet, PTFE) are frequently applied inconsistently or substituted without approval. Some coatings may introduce hydrogen embrittlement risks in high-strength studs. Buyers often assume coating specifications are met without verifying coating thickness, adhesion, or salt spray test results—leading to premature rust and structural degradation.
Misalignment of International Standards and Specifications
Suppliers may claim compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ASTM), but actual production may not meet the required class or grade. For example, a nut may be labeled “Grade 8” but fail to meet the mechanical properties of ASTM A563 Grade C. This mismatch is common when suppliers interpret specifications loosely or lack calibration and testing equipment.
Overlooking Total Cost of Ownership
Focusing solely on unit price can be misleading. Low-cost assemblies may require higher inspection rates, rework, or field replacements—increasing the total cost of ownership. Hidden costs include downtime due to fastener failure, warranty claims, and reputational damage. A higher-priced, certified supplier often provides better long-term value through reliability and support.
Poor Communication and Specification Clarity
Vague or incomplete purchase specifications (e.g., missing thread class, finish requirements, or torque values) lead to misunderstandings. Suppliers may interpret ambiguous requests differently, resulting in non-conforming parts. Always provide detailed technical drawings, reference applicable standards, and confirm understanding before production.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls, buyers can ensure they source threaded stud, nut, and washer assemblies that meet both quality expectations and IP protection requirements.
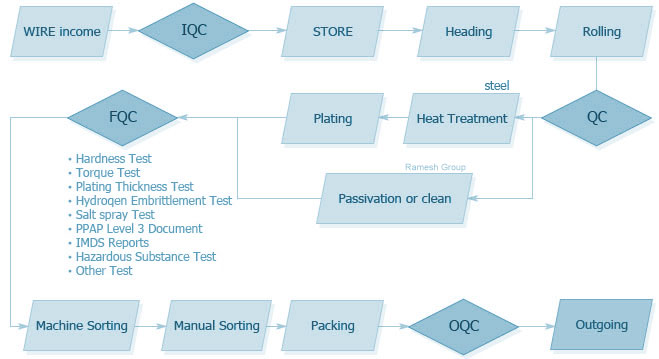
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Threaded Stud, Nut, and Washer Assemblies
Product Overview
Threaded stud, nut, and washer assemblies are fastening components widely used in construction, automotive, machinery, and industrial applications. These pre-assembled or individual components ensure secure joining of materials and must meet strict logistical handling and regulatory compliance standards.
Classification and HS Code
Accurate product classification is essential for international shipping and customs clearance.
– Typical HS Code: 7318.15 (Threaded studs), 7318.16 (Nuts), 7318.21 (Washers) – under Chapter 73: Articles of Iron or Steel.
– Note: Classification may vary by country and material composition (e.g., stainless steel, alloy steel). Verify with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and compliance with transportation regulations.
– Packaging: Use moisture-resistant, durable materials (e.g., sealed plastic bags, cardboard boxes with dividers, or wooden crates for bulk shipments).
– Labeling: Include:
– Product description (e.g., “Stainless Steel Stud M10x75, Hex Nut, Flat Washer”)
– Quantity per package
– Material grade (e.g., A2-70, Grade 8.8)
– Manufacturer or supplier name
– Lot or batch number
– Country of origin
– Compliance markings (e.g., ISO, ASTM, DIN)
– Hazard Labels: Not typically required unless packaged with lubricants or coatings classified as hazardous.
Shipping and Transportation
Ensure safe and compliant shipment via air, sea, or land.
– Weight and Dimensions: Optimize packaging to minimize dimensional weight for cost-effective air freight.
– International Shipments:
– Provide a commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
– Declare accurate value and origin to prevent customs delays.
– Environmental Protection: Prevent corrosion during transit using VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper or desiccants, especially for sea freight.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to international and regional standards based on destination market.
– Material Standards:
– ISO 898-1 (Mechanical properties of fasteners)
– ASTM A193/A193M (Alloy steel and stainless steel bolting)
– DIN 975 (Threaded studs), DIN 934 (Nuts), DIN 125 (Washers)
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) exceed allowable limits.
– Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act): Disclose use of tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold if applicable (rare in standard fasteners, but verify supply chain).
– Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT): Recommended for U.S.-bound shipments to expedite clearance.
Import and Export Documentation
Complete and accurate documentation is crucial for smooth customs processing.
– Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (preferential or non-preferential)
– Test Certificates (e.g., ISO 10474, Material Test Reports)
– Export Declaration (as required by exporting country)
– Free Trade Agreements (FTAs): Leverage agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-South Korea FTA) to reduce or eliminate tariffs with a valid Certificate of Origin.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain quality and compliance throughout the supply chain.
– Implement batch traceability using lot numbers.
– Conduct periodic audits of manufacturing and packaging processes.
– Provide test reports verifying tensile strength, hardness, and dimensional accuracy.
– Store products in dry, controlled environments to prevent rust or damage.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Waste Disposal: Packaging materials should comply with local recycling regulations.
- Worker Safety: Follow OSHA (or equivalent) guidelines during handling to prevent injury from sharp edges.
- Sustainability: Use recyclable packaging and source materials from certified sustainable suppliers where possible.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for threaded stud, nut, and washer assemblies ensures on-time delivery, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. Partner with certified suppliers, maintain accurate documentation, and stay updated on international trade regulations to minimize risks and optimize supply chain performance.
Conclusion:
Sourcing threaded stud nuts and washers requires careful consideration of specifications, material compatibility, quality standards, and supplier reliability. It is essential to define the required dimensions, thread type, tensile strength, and environmental resistance (e.g., corrosion protection) based on the application’s mechanical and operational demands. Partnering with certified suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ISO, ASTM, or DIN ensures consistent quality and performance. Additionally, evaluating cost-effectiveness, lead times, and scalability supports long-term supply chain efficiency. By establishing clear sourcing criteria and maintaining strong supplier relationships, organizations can ensure the reliable procurement of high-quality threaded stud nuts and washers critical to structural integrity and equipment safety.