The global market for precision mechanical components, including threaded shafts, has seen steady expansion driven by rising demand across industrial automation, automotive, and aerospace sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global lead screw market—closely tied to threaded shaft applications—was valued at USD 582 million and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by increasing adoption of linear motion systems in manufacturing and robotics, where threaded shafts play a critical role in converting rotational to linear motion with high accuracy. As industries prioritize efficiency and precision, the need for high-quality, durable threaded shafts has intensified, positioning key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and reliability. In this landscape, the following eight manufacturers stand out for their technical expertise, global reach, and commitment to meeting evolving industry standards.
Top 8 Threaded Shaft Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Threaded Rod
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vulc.com
Key Highlights: Vulcan Steel Products is the nation’s largest domestic manufacturer and supplier of threaded products. Vulcan’s success is not just coincidence….
#2 Threaded Rod Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2000
Website: baystandard.com
Key Highlights: We are the largest manufacturer of threaded rod in the Western United States producing more than 2 million pounds of finished product a month….
#3 L&H Threaded Rods Corp.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: lhrods.com
Key Highlights: L&H Threaded Rods Corp. is a Threaded Rod and U-Bolt Manufacturer. We support the heavy-duty aftermarket industry by providing innovative products and services….
#4 Threaded Shaft Collars
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ruland.com
Key Highlights: Ruland manufactures them with drilled holes for mounting flexibility or threaded holes for the most secure connection between the collar and mated component….
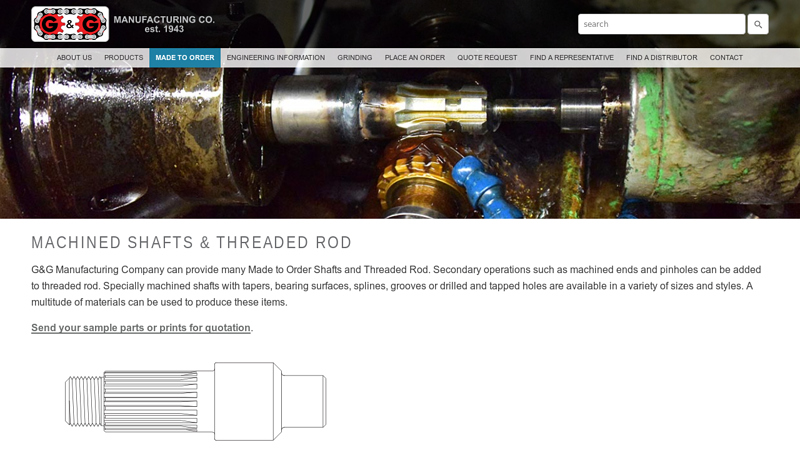
#5 Machined Shafts & Threaded Rod
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ggmfg.com
Key Highlights: G&G Manufacturing can provide many Made to Order Shafts and Threaded Rod. Secondary operations such as machined ends and pinholes can be added to threaded ……
#6 Threaded Rod
Domain Est. 2002
#7 Threaded rod
Domain Est. 2006
Website: tsamfg.com
Key Highlights: TSA manufactures all thread in a variety of diameters, lengths, materials and finishes. We stock common sizes in plain, zinc, and galvanized finish….
#8 All Thread Rod
Domain Est. 2013
Website: allthreadrod.com
Key Highlights: All thread rod (ATR) is a common, readily available fastener that is used in multiple construction applications. Rods are continuously threaded from one end ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Threaded Shaft

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Threaded Shafts
The global threaded shaft market is projected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand across industrial and automation sectors, and evolving material innovations. Below are key market trends anticipated to shape the industry landscape:
-
Growing Demand in Automation and Robotics
The increasing adoption of automation in manufacturing, logistics, and precision engineering is fueling demand for high-precision threaded shafts. Industries such as automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals are integrating linear motion systems—where threaded shafts are critical components—leading to enhanced efficiency and repeatability. The rise of collaborative robots (cobots) and smart factories is expected to amplify this trend through 2026. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy Applications
Threaded shafts are finding expanded use in solar tracking systems, wind turbine pitch control mechanisms, and hydroelectric installations. As global investments in renewable energy continue to grow, especially under national decarbonization goals, the need for durable, corrosion-resistant threaded components will rise. This positions manufacturers to innovate with materials like stainless steel and coated alloys suited for outdoor and harsh environments. -
Material and Coating Innovations
By 2026, market leaders are likely to shift toward advanced materials such as high-strength alloys, titanium composites, and engineered polymers to improve performance under high load, temperature, and corrosive conditions. Anti-friction coatings (e.g., PTFE, DLC) and surface treatments (e.g., nitriding, black oxide) will become more prevalent to extend product life and reduce maintenance. -
Customization and Miniaturization
With increasing demand in medical devices, aerospace, and micro-mobility applications, there is a trend toward smaller, customized threaded shafts with tighter tolerances. This requires investments in precision machining, CNC grinding, and quality control systems. OEMs will increasingly seek suppliers capable of just-in-time delivery and design collaboration. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, is expected to dominate growth due to rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and government support for manufacturing. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on high-value, technologically advanced shafts for aerospace, defense, and automation, supported by Industry 4.0 initiatives. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria will push manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices, including recycling of metal scraps, energy-efficient production, and longer product lifecycles. Recyclable and lightweight designs could become competitive advantages. -
Digital Integration and Smart Components
Integration of IoT-enabled sensors into mechanical systems may lead to the development of “smart” threaded shafts capable of monitoring wear, load, and alignment in real time. While still emerging, this trend could gain momentum by 2026, especially in predictive maintenance frameworks.
In summary, the 2026 threaded shaft market will be characterized by technological refinement, sector-specific customization, and sustainability-focused innovation, with strong growth driven by automation, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Threaded Shaft (Quality, IP)
Sourcing threaded shafts involves more than just matching dimensions—overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to performance failures, legal risks, and supply chain disruptions. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material and Dimensional Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving threaded shafts that fail to meet specified material properties or dimensional tolerances. Low-quality suppliers may use substandard steel, incorrect heat treatments, or imprecise threading processes. This can result in reduced strength, premature wear, or improper fit in assemblies. Always verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and require first-article inspections or third-party testing when sourcing from new or unproven suppliers.
Inadequate Thread Accuracy and Surface Finish
Threaded shafts must meet specific standards (e.g., ISO, ASME, or DIN) for pitch, major/minor diameter, and thread form. Poor thread accuracy leads to assembly issues, galling, or reduced load capacity. Similarly, rough surface finishes increase friction and wear. Ensure suppliers adhere to required thread class tolerances and provide surface roughness specifications (e.g., Ra values) in procurement documentation.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Without proper traceability—such as lot numbers, heat numbers, and inspection reports—it’s difficult to verify quality or manage recalls. In regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace), missing certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, or PPAP) can result in compliance failures. Require full documentation packages and audit suppliers’ quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or reverse-engineered components, especially if the shaft design is proprietary or patented. Unauthorized production may violate design patents or technical copyrights. Conduct due diligence on suppliers, include IP protection clauses in contracts, and consider using custom tooling or unique features that are harder to replicate.
Inconsistent Surface Treatments and Corrosion Protection
Many threaded shafts require plating (e.g., zinc, chrome) or coatings (e.g., black oxide, PTFE) for corrosion resistance or lubricity. Inconsistent or subpar treatments lead to rust, hydrogen embrittlement, or reduced service life. Specify coating types, thicknesses, and testing methods (e.g., salt spray tests) and verify compliance through batch testing.
Overlooking Geometric Tolerances and Straightness
Even with correct thread dimensions, a shaft that is bent or out-of-round can cause misalignment and binding. Geometric tolerances like straightness, concentricity, and runout are critical in precision applications. Ensure drawings include GD&T callouts and that suppliers have the capability to measure and control these parameters.
Supply Chain Reliance on Non-Disclosed Subcontractors
Some suppliers outsource production without disclosure, leading to inconsistent quality and obscured accountability. This also complicates IP protection and traceability. Require transparency in the manufacturing chain and conduct on-site audits when feasible.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through detailed specifications, supplier vetting, and robust quality controls—buyers can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of threaded shafts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Threaded Shaft
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transportation, handling, and regulatory adherence of threaded shafts in industrial and commercial applications.
Product Classification & Identification
Threaded shafts are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to metal fasteners, mechanical components, or general metal products. Common classifications include:
– 7318.15 – Threaded rods or bars, of iron or steel
– 7318.29 – Other bolts and screws, of iron or steel
– 8487.90 – Parts suitable for use with machinery (if part of an assembly)
Accurate product identification, including material type (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel), thread specification (e.g., metric M10x1.5, UNC 1/4-20), length, and surface finish, is essential for customs clearance and compliance.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transit and aligns with logistics standards:
– Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper, plastic wrap) for metal shafts to prevent rust
– Secure shafts in rigid containers or wooden crates to prevent bending or damage
– Label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” “This Side Up”)
– Bundle or palletize shafts to prevent shifting; use edge protectors for long pieces
– Comply with carrier-specific dimensional and weight limits
Transportation & Shipping
Consider the following during transportation:
– Mode of Transport: Threaded shafts may be shipped via air, sea, or ground. Long or heavy shafts may require specialized freight (e.g., LTL, FTL)
– Hazardous Materials: Non-hazardous under standard conditions unless coated with restricted substances
– Export Controls: Generally not subject to ITAR or EAR controls unless for defense or aerospace applications
– Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin must be accurate and complete
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to relevant regulations in origin, transit, and destination countries:
– REACH (EU): Confirm no restricted substances (e.g., SVHCs) in coatings or plating
– RoHS (EU): Applicable if shafts are part of electrical or electronic assemblies
– Proposition 65 (California): Disclose presence of listed chemicals (e.g., lead in plating) if applicable
– TSCA (USA): Comply with chemical substance regulations, especially for imported metal products
– Customs Valuation: Use transaction value method; include all costs (e.g., tooling, royalties) if applicable
Import & Tariff Considerations
- Verify duty rates based on HS code and country of origin
- Leverage Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, CETA) if components originate from qualifying countries
- Be aware of anti-dumping or countervailing duties on steel products in certain markets
- Maintain records for at least 5–7 years depending on jurisdiction
Quality & Certification
- Provide material certification (e.g., mill test report, EN 10204 3.1) upon request
- Comply with industry standards such as ISO, DIN, ANSI, or ASME for thread dimensions and tolerances
- Implement traceability systems for batch or lot tracking
Environmental & Sustainability Practices
- Recycle packaging materials and metal scraps
- Minimize use of hazardous substances in surface treatments
- Optimize shipping configurations to reduce carbon footprint
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for threaded shafts requires attention to classification, packaging, regulatory standards, and documentation. Proactive planning ensures timely delivery, reduces customs delays, and maintains regulatory conformity across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Threaded Shafts:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, material options, manufacturing capabilities, and cost considerations, the sourcing strategy for threaded shafts should focus on balancing quality, reliability, and cost-efficiency. It is recommended to partner with suppliers that demonstrate consistent quality control, adherence to industry standards (such as ISO or ANSI), and the ability to meet specified tolerances and material requirements.
Sourcing from suppliers with proven experience in producing precision components, along with strong scalability and on-time delivery performance, will ensure minimal production disruptions. Additionally, considering both domestic and international options allows for competitive pricing while maintaining oversight on lead times and logistics.
In conclusion, selecting a supplier that offers a combination of technical expertise, quality certifications, and responsive service—supported by long-term supply agreements if justified—will effectively meet the application requirements for threaded shafts and contribute to overall operational efficiency and product reliability.