The global market for threaded connectors has seen robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as oil and gas, industrial manufacturing, aerospace, and infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, the global pipe fittings and flanges market—of which threaded connectors are a key component—was valued at USD 31.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising infrastructure development, stringent safety regulations, and the expansion of pipeline networks in emerging economies. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects continued demand for high-performance, corrosion-resistant connectors in hazardous and high-pressure environments, particularly in offshore drilling and chemical processing. As industries prioritize reliability and leak-proof performance, leading manufacturers are focusing on material innovation, precision engineering, and compliance with international standards such as ASME, API, and ISO. In this evolving landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as key players, combining technological expertise, global reach, and a broad product portfolio to meet the growing demand for high-quality threaded connectors.
Top 9 Threaded Connectors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Connectivity
Domain Est. 1996
Website: harting.com
Key Highlights: As one of the largest manufacturers of industrial connection technology, HARTING has a comprehensive portfolio of circular connectors in all common sizes and ……
#2 Amphenol Industrial Operations
Domain Est. 2001
Website: amphenol-industrial.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol Industrial stands at the forefront of innovation as a premier manufacturer of circular connectors, boasting an expansive and dynamic product line….
#3 Full Product List – Connectors & Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ittcannon.com
Key Highlights: Browse ITT Cannon’s full range of connectors, built for aerospace, defense, industrial, and transportation applications….
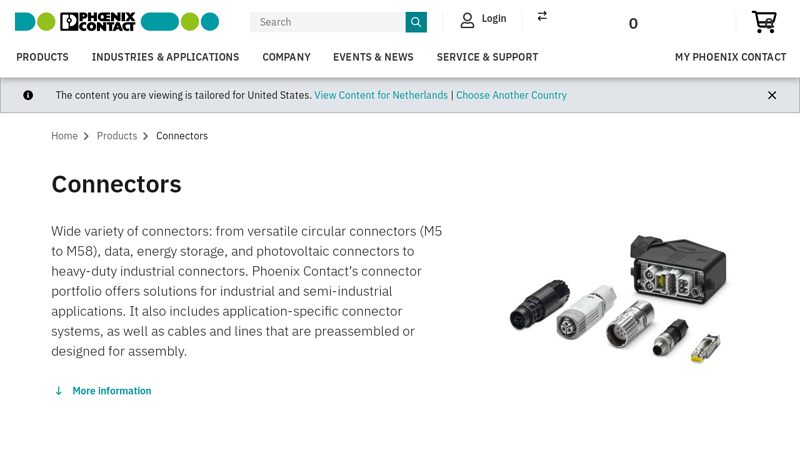
#4 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phoenixcontact.com
Key Highlights: Phoenix Contact offers circular connectors in numerous sizes for industrial automation. From small to large, straight or angled, molded or designed for assembly ……
#5 Connectors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: Molex offers a wide variety of Board-to-Board Connectors for microminiature, high-speed, high-density, and high-power applications….
#6 Simpson Strong
Domain Est. 1995
Website: strongtie.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the Simpson Strong-Tie homepage showcasing our resources, products and services designed to help people build safer, stronger structures….
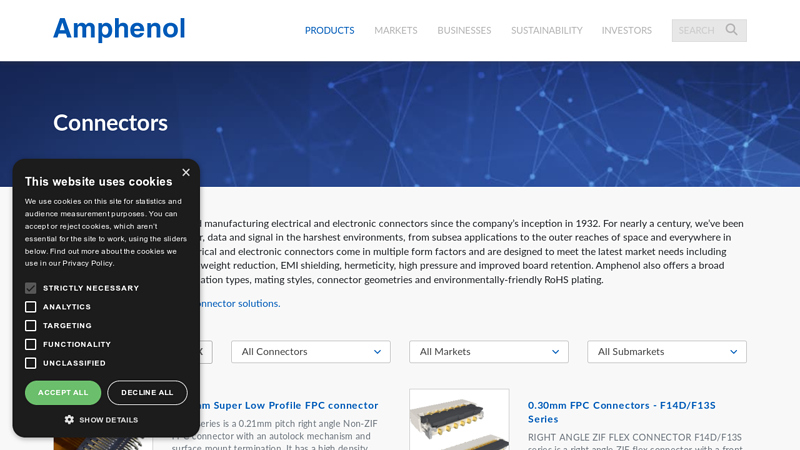
#7 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amphenol.com
Key Highlights: Our wide array of electrical and electronic connectors come in multiple form factors and are designed to meet the latest market needs….
#8 ODU Connector Systems
Domain Est. 2014
Website: odu-connectors.com
Key Highlights: Development & production of connector systems for reliable transmission of ✓power, ✓signals & ✓data → ODU, based in Mühldorf am Inn….
#9 Pipe Fittings
Domain Est. 2020
Website: asc-es.com
Key Highlights: Anvil standard and extra heavy cast iron threaded fittings are manufactured in accordance with ASME-B16.4 (except plugs and bushings, ASME B16 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Threaded Connectors

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Threaded Connectors
The global threaded connectors market is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and macroeconomic shifts. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Rising Demand in Infrastructure and Construction:
The global push for infrastructure modernization—particularly in North America, Europe, and emerging Asian economies—will significantly boost demand for threaded connectors. Projects involving water and wastewater systems, gas pipelines, and industrial construction rely heavily on robust, leak-proof connections. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and similar initiatives worldwide will continue to fuel procurement through 2026.
2. Growth in Oil & Gas and Energy Sectors:
Despite the energy transition, oil and gas exploration, production, and transmission infrastructure will remain key consumers of high-performance threaded connectors, especially in offshore and high-pressure applications. Additionally, the expanding natural gas network and development of hydrogen-ready pipelines will require corrosion-resistant and high-integrity connectors, driving innovation in materials like stainless steel and specialty alloys.
3. Emphasis on Sustainability and Material Efficiency:
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push manufacturers toward recyclable materials and energy-efficient production processes. Lightweight yet durable connectors made from engineered alloys or composites may gain traction, reducing transportation emissions and improving installation efficiency. End-of-life recyclability will become a differentiating factor in procurement decisions.
4. Technological Advancements and Smart Integration:
While traditionally mechanical, the integration of smart monitoring technologies into critical pipeline systems could lead to the emergence of “smart” threaded connectors with embedded sensors for pressure, temperature, or leak detection. Although not widespread by 2026, pilot implementations in high-value industrial or municipal applications are expected, paving the way for future digitalization.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization:
Geopolitical uncertainties and post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to regionalize sourcing. By 2026, there will be increased investment in local manufacturing hubs for threaded connectors, particularly in North America and Europe, to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers and ensure faster delivery times.
6. Stringent Regulatory and Safety Standards:
Growing emphasis on safety and reliability—especially in hazardous environments—will drive adoption of connectors compliant with international standards (e.g., ASME, API, ISO). Certification and quality assurance will become even more critical, favoring established manufacturers with rigorous testing protocols.
7. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation:
The market will likely see continued consolidation as larger players acquire niche manufacturers to expand product portfolios and geographic reach. Innovation in product design—such as tamper-resistant or quick-connect threaded solutions—will differentiate competitors in saturated segments.
In summary, the 2026 threaded connectors market will be characterized by steady demand growth, enhanced material and technical performance, and a strategic shift toward resilience and sustainability. Companies that invest in innovation, quality compliance, and localized production are best positioned to capture market share.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Threaded Connectors (Quality, IP)
When sourcing threaded connectors—commonly used in fluid power, instrumentation, and industrial systems—overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material and Manufacturing Quality
Sourcing connectors made from substandard materials (e.g., low-grade brass, zinc alloys without proper plating) or manufactured with inconsistent threading can result in leaks, galling, or premature failure under pressure or vibration. Always verify compliance with recognized standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, NPT) and request material certifications.
Inadequate Thread Compatibility
Mismatched thread types (e.g., NPT vs. BSPP) or poor thread tolerances can cause improper sealing, cross-threading, or assembly issues. Ensure connectors match both thread form and pitch, and consider using thread sealants or tapes where appropriate—but never rely solely on them to compensate for poor fit.
Misunderstanding IP Ratings
Assuming all threaded connectors provide environmental protection is a critical error. IP ratings indicate resistance to dust and moisture, but many standard threaded fittings lack defined IP protection unless specifically designed with seals (e.g., O-rings under the thread). Always confirm the IP rating applies to the mated connection, not just the connector alone.
Lack of Sealing Mechanism
Threaded connectors without integrated elastomeric seals (e.g., O-ring face seal, bonded seals) may not maintain an effective environmental or pressure seal, especially in dynamic or vibration-prone environments. Specify connectors with appropriate sealing technology for the application (e.g., ISO 1179 for metric thread with elastomeric seal).
Overlooking Corrosion Resistance
In harsh environments (e.g., outdoor, marine, chemical), connectors without adequate corrosion protection (e.g., nickel plating, stainless steel construction) can degrade quickly. Verify corrosion resistance through salt spray testing data or material specs.
Insufficient Quality Assurance
Procuring from suppliers without proper QA processes (e.g., no batch testing, lack of traceability) increases the risk of inconsistent quality. Require documentation such as Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and conduct periodic audits or sample testing.
Ignoring Application-Specific Requirements
Using general-purpose connectors in high-pressure, high-temperature, or sanitary applications can lead to failure. Always match the connector’s pressure rating, temperature range, and cleanliness standards (e.g., FDA, 3A) to the operational demands.
By addressing these pitfalls during the sourcing process, you can ensure reliable, safe, and long-lasting performance of threaded connector assemblies.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Threaded Connectors
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence of threaded connectors across global supply chains.
Regulatory Compliance
Threaded connectors must comply with a range of international, regional, and industry-specific standards depending on their application and destination. Key compliance areas include:
- Material Standards: Ensure connectors meet material specifications such as ASTM, ISO, DIN, or JIS. For example, ASTM A193 covers alloy-steel and stainless steel bolting materials for high-temperature service.
- Thread Standards: Adhere to recognized thread standards including Unified National (UN/UNF), ISO Metric (M-series), or NPT (National Pipe Taper) as applicable.
- Industry-Specific Regulations:
- Oil & Gas: API 6A, API 17D for subsea and wellhead equipment.
- Aerospace: NAS (National Aerospace Standards) and AS (Aerospace Standards).
- Construction: AISC and local building codes requiring certified fasteners.
- RoHS and REACH Compliance: For connectors used in electronics or EU markets, compliance with Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is mandatory.
- Certifications: Maintain mill test certificates (MTCs), Certificate of Conformance (CoC), and third-party inspection reports (e.g., from SGS, BV) as required.
Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for product integrity and customs clearance:
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use moisture-resistant, anti-corrosive packaging (e.g., VCI paper) for metal connectors.
- Securely bundle connectors by size/type to prevent damage and enable easy inventory management.
- Use export-grade wooden or plastic crates for bulk shipments, compliant with ISPM-15 standards for wood packaging.
- Labeling:
- Include product specifications (size, grade, material, standard).
- Mark with batch/lot numbers and traceability codes.
- Affix hazard labels if applicable (e.g., sharp edges).
- Include shipping marks, barcodes, and HS codes for customs.
Transportation and Handling
Ensure safe and efficient movement of threaded connectors through the supply chain:
- Mode of Transport:
- Ocean freight: Ideal for bulk shipments; use containerized or break-bulk depending on volume.
- Air freight: For urgent, high-value, or low-volume orders.
- Ground transport: For regional distribution with climate-controlled options if needed.
- Handling Precautions:
- Use proper lifting equipment to avoid deformation or damage.
- Prevent cross-threading or impact damage during loading/unloading.
- Store in dry, temperature-stable environments to avoid corrosion.
- Weight and Dimension Considerations: Optimize palletization and container loading to maximize space and minimize freight costs.
Customs and Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation ensures compliance and avoids delays at borders:
- Required Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
- Certificate of Origin
- Product-specific certifications (e.g., CoC, MTC)
- HS Code Classification: Use appropriate Harmonized System codes (e.g., 7318.15 for threaded steel bolts) for accurate duty assessment.
- Export Controls: Verify if connectors are subject to export regulations (e.g., ECCN under EAR for dual-use items).
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain quality and regulatory traceability throughout the supply chain:
- Implement a documented Quality Management System (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections and in-process audits.
- Maintain traceability from raw material to final product using lot tracking systems.
- Address non-conformances through corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
- Follow guidelines for responsible sourcing of raw materials (e.g., conflict minerals reporting if applicable).
- Comply with waste disposal regulations for packaging and production byproducts.
- Optimize logistics to reduce carbon footprint (e.g., route planning, modal shifts).
By adhering to this guide, suppliers, distributors, and end-users can ensure that threaded connectors are transported efficiently and meet all legal, safety, and quality standards across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Threaded Connectors:
In conclusion, sourcing threaded connectors requires a strategic approach that balances quality, compatibility, cost, and supplier reliability. It is essential to clearly define application requirements—such as material specifications, thread type, size, pressure ratings, and environmental resistance—to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Evaluating suppliers based on certifications, manufacturing standards, lead times, and technical support helps mitigate risks related to product failure or supply chain disruptions. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond unit price—can lead to more cost-effective and reliable sourcing decisions. By adopting a comprehensive and well-documented procurement strategy, organizations can secure high-quality threaded connectors that meet technical demands while supporting operational efficiency and project success.