The global thread insert market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for durable fastening solutions across automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global inserts market size was valued at USD 3.2 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by rising industrial automation, the need for lightweight materials with high tensile strength, and growing investments in repair and maintenance technologies. As thread inserts become increasingly critical in enhancing thread reliability and product longevity, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, precision engineering, and global supply chain efficiency. Based on market presence, production capabilities, and technological advancements, the following ten manufacturers represent the top players shaping the future of threaded insertion solutions.
Top 10 Thread Insert Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Acme Industrial Co.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: acmeindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Acme Industrial Company is a leading manufacturer of precision machined components for industrial, commercial, aerospace and military markets….
#2 ABA Tech Inc
Domain Est. 2016 | Founded: 2004
Website: thread-insert.com
Key Highlights: ABA Tech Inc was founded in 2004. We have factory in Shen zhen China over 20 years . We supply threaded inserts for metals, plastics, hardwood and plywood….
#3 Yardley Inserts
Domain Est. 2019 | Founded: 1946
Website: yardleyinserts.com
Key Highlights: A US-based manufacturer, has produced threaded metal insert fasteners since 1946. We offer over 24 million inserts in stock ready for immediate shipment….
#4 Threading Tools, Thread Turning & Tapping
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kennametal.com
Key Highlights: Kennametal’s threading tools & inserts are made with tungsten carbide materials and offer precision for thread turning and tapping….
#5 ++ TIME
Domain Est. 1996
Website: timesert.com
Key Highlights: perfection thread repair system, professional thread repair. Time-Sert ® thread repair kits and screw thread inserts for stripped threads damaged threads….
#6 ITA
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: ITA-M3 · Pilot diameter and undercuts allow plastic to flow into grooves providing high pullout resistance. · Aluminum inserts ideal for light weight designs….
#7 Threaded Inserts
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ezlok.com
Key Highlights: We offer an extensive inventory of threaded inserts for wood, plastic and metal, along with thread repair kits, installation tools and more….
#8 Thread Turning Inserts
Domain Est. 2004
Website: carmexusa.com
Key Highlights: Carmex Precision Tools specialize in threading tools for turning and milling – Thread Turning Inserts and Tool Holders, Thread Mills and Swiss Lathe Tooling ……
#9 Heli-Coil Wire Insert Systems
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stanleyengineeredfastening.com
Key Highlights: Heli-Coil covers a vast array of high quality automotive threaded inserts, wire threaded inserts and installation tools designed to meet the needs of ……
#10 Threaded Inserts by MW Components
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: MW Components offers a wide range of threaded inserts designed specifically for plastics. Styles include chevron, tapered, expansion, press-in, mold-in, and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Thread Insert

2026 Market Trends for Thread Insert
The global thread insert market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials science, rising demand from key industries, and the increasing emphasis on lightweight and durable engineering solutions. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the thread insert landscape in 2026 under the H2 framework—highlighting growth drivers, technological innovations, regional dynamics, and competitive strategies.
H2: Growth Drivers in the Thread Insert Market
Several macroeconomic and industrial factors are fueling demand for thread inserts through 2026. The automotive and aerospace sectors remain primary consumers, with manufacturers prioritizing weight reduction and fuel efficiency. The adoption of aluminum and composite materials, which have lower inherent thread strength, necessitates reliable threaded reinforcement—making thread inserts essential.
Additionally, the expansion of the electronics and medical device industries is introducing new applications. Miniature thread inserts are increasingly used in compact electronics and surgical instruments, where precision and reliability are critical. The renewable energy sector, particularly wind turbine manufacturing, also contributes to market growth due to high-stress environments requiring durable fastening systems.
Urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging economies are further boosting construction-related applications, including concrete and masonry thread inserts used in structural anchoring.
H2: Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
In 2026, the thread insert market will see accelerated innovation in materials and design. Stainless steel remains dominant for its corrosion resistance and strength, but emerging alternatives such as high-performance polymers, titanium alloys, and carbon-fiber-reinforced composites are gaining traction—especially in aerospace and medical fields.
Self-tapping and spiral-wound thread inserts are evolving with improved geometries and surface treatments to enhance torque resistance and thread engagement. Coatings like PTFE, zinc-nickel, and DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) are being adopted to improve wear resistance and reduce galling.
Smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 integration are also influencing production. Automated insertion systems and AI-driven quality control are improving precision and reducing waste, making thread insert installation faster and more reliable in high-volume manufacturing environments.
H2: Regional Market Dynamics
Regional trends indicate a shift in production and consumption patterns by 2026. Asia-Pacific is expected to lead global market growth, driven by robust manufacturing in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Localized production of automobiles, consumer electronics, and industrial machinery supports strong demand for thread inserts.
North America remains a mature but innovative market, with significant R&D investment in aerospace and defense applications. The U.S. government’s focus on reshoring critical manufacturing is likely to boost domestic demand for high-performance fastening solutions.
Europe maintains a strong presence, particularly in Germany and France, where precision engineering and green technologies support steady growth. Stringent regulatory standards for sustainability are pushing manufacturers toward recyclable and long-life thread insert solutions.
Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East are emerging as niche markets, with growth tied to infrastructure projects and energy sector investments.
H2: Competitive Landscape and Strategic Outlook
The competitive environment in the thread insert market is intensifying as key players focus on differentiation through product specialization and service integration. Major companies such as Stanley Engineered Fastening, Emhart Teknologies, and Bossard are expanding their portfolios to include application-specific inserts and digital inventory management systems.
Strategic partnerships with OEMs and adoption of e-commerce platforms are enabling faster delivery and customization. Sustainability is becoming a competitive differentiator, with leading firms investing in eco-friendly manufacturing and circular economy models—such as recyclable insert systems and reduced packaging.
By 2026, companies that combine innovation, regional agility, and digital transformation are expected to capture greater market share, while smaller players may focus on niche applications and custom engineering to remain competitive.
In conclusion, the 2026 thread insert market will be defined by technological sophistication, regional diversification, and sustainability-driven innovation. Stakeholders who align with these H2 trends—growth drivers and strategic adaptation—will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly dynamic global landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Thread Inserts (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing thread inserts—especially for high-performance or safety-critical applications—can present significant challenges related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to product failures, compliance issues, or legal liabilities. Below are key areas to watch for:
Inconsistent or Substandard Material Quality
One of the most common quality issues arises when suppliers use inferior materials or fail to adhere to specified alloy standards (e.g., stainless steel grades like 304 or 316). Some manufacturers may claim compliance but substitute cheaper, non-certified materials, leading to reduced corrosion resistance, strength, or durability.
Lack of Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance Control
Thread inserts must meet precise dimensional specifications to ensure proper fit and function. Poorly manufactured inserts often exhibit variations in thread pitch, outer diameter, or length. These inconsistencies can cause cross-threading, reduced load capacity, or assembly difficulties—especially in automated production environments.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Coating Defects
Improper surface treatments or coatings (e.g., PTFE, zinc plating, or passivation) can compromise performance. Defects such as uneven coating thickness, peeling, or inadequate corrosion protection reduce the insert’s lifespan and reliability. Additionally, some suppliers may omit required surface treatments to cut costs.
Absence of Traceability and Certification
Reputable thread inserts should come with material test reports (MTRs), ISO certifications, or other documentation proving compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 2338, ASME B1.13M). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide traceability increases the risk of receiving non-conforming parts, particularly in regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Counterfeit or Non-OEM Compliant Products
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” thread inserts that mimic well-known branded products (e.g., Helicoil, Emhart). While not always illegal, these copies may infringe on trademarks or patented designs. Using such products can expose your company to intellectual property litigation, especially if the design is protected by utility or design patents.
Patent and Design Infringement Risks
Thread insert designs—particularly those with unique geometries, locking mechanisms, or installation tools—may be protected by patents. Sourcing generic versions without conducting proper IP due diligence can result in unintentional infringement. This is especially critical when importing from regions with weaker IP enforcement.
Misrepresentation of Performance Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate performance characteristics such as load capacity, temperature resistance, or vibration resistance without independent testing. Relying on unverified claims can lead to field failures and damage to your brand reputation.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaqueness in the supply chain—such as subcontracting to unapproved factories or tier-2 suppliers—increases the risk of inconsistent quality and IP breaches. Without full visibility into manufacturing locations and processes, ensuring compliance becomes challenging.
Failure to Audit Suppliers and Conduct Pre-Shipment Inspections
Relying solely on supplier self-certifications without third-party audits or incoming inspections can result in undetected defects. Regular quality audits and sample testing are essential to verify ongoing compliance with technical and IP requirements.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, clear contractual specifications, IP clearance checks, and quality assurance protocols—companies can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legally compliant thread insert sourcing.
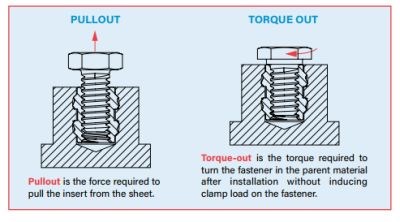
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Thread Inserts
Thread inserts are essential fastening components used across industries to provide durable internal threads in soft materials or to repair damaged threads. Ensuring proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance is crucial for operational efficiency and legal adherence. Below is a comprehensive guide structured to support smooth distribution and use of thread inserts.
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
Efficient logistics begins with a robust supply chain strategy. Thread inserts—whether coil, solid, or key-lock types—should be sourced from certified suppliers who adhere to quality standards such as ISO 9001. Maintain accurate inventory records using barcode or RFID systems to track stock levels, batch numbers, and shelf life (if applicable). Implement just-in-time (JIT) or vendor-managed inventory (VMI) models where feasible to reduce carrying costs and minimize stockouts.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Thread inserts must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use anti-static, moisture-resistant packaging where applicable—especially for stainless steel or corrosion-prone materials. Individual compartments or blister packs can prevent tangling of coiled inserts (e.g., Helical-coil inserts). Label all packages with:
- Product name and part number
- Material specification (e.g., 304 SS, brass, carbon steel)
- Thread size and pitch (e.g., M6 x 1.0)
- Quantity per pack
- Manufacturer and batch/lot number
- Country of origin
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
Ensure labels comply with regional requirements (e.g., GHS for hazardous materials if coatings are used).
Transportation & Handling
Use secure, climate-controlled transport when shipping thread inserts, especially in extreme environments. Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. During handling:
- Use non-magnetic tools when working with stainless steel inserts to prevent contamination.
- Store inserts off the floor on pallets or shelves.
- Segregate different thread types and materials to avoid cross-contamination or mix-ups.
Follow standard freight classification guidelines (e.g., NMFC codes in North America) to ensure correct shipping cost calculations.
Import/Export Compliance
When shipping thread inserts internationally:
- Verify Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 7318.19 for threaded fittings of iron or steel).
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Comply with export control regulations such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) if inserts are used in defense or aerospace applications.
- Check for sanctions or embargoes on destination countries via official government databases (e.g., U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security).
Regulatory & Safety Standards
Ensure thread inserts comply with relevant industry standards:
- ISO 4014, ISO 4017 (metric threaded fasteners)
- ASME B1.1 (Unified Inch Screw Threads)
- IFI standards for coil thread inserts
- ASTM A193/A194 (for high-pressure/temperature applications)
If inserts are used in regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace, automotive), additional certifications such as AS9100, IATF 16949, or FDA 21 CFR may apply.
Environmental & RoHS Compliance
Verify that thread inserts and their coatings meet environmental regulations:
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) for electrical/electronic applications.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU.
- Conflict minerals reporting (e.g., Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502) if applicable.
Use material declarations (e.g., IMDS for automotive) to document compliance throughout the supply chain.
End-of-Life & Recycling
Promote sustainability by:
- Recycling metal packaging and scrap inserts.
- Partnering with suppliers who offer take-back programs for used or excess inserts.
- Documenting waste streams in compliance with local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., WEEE in the EU).
Training & Documentation
Train logistics and warehouse staff on proper handling, storage, and compliance procedures. Maintain up-to-date documentation including:
- Certificates of Conformity (CoC)
- Material Test Reports (MTR)
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if inserts are coated or treated
- Audit trails for traceability
Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing compliance and process improvement.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the reliable, safe, and legal distribution and use of thread inserts across global operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Thread Inserts:
Sourcing the appropriate thread insert requires a careful evaluation of application requirements, material compatibility, environmental conditions, and installation methods. Selecting the right type—such as helical wire inserts, solid bushings, or key-locking inserts—ensures enhanced thread strength, durability, and resistance to wear, vibration, and corrosion. A successful sourcing strategy involves partnering with reliable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical support, and compliance with industry standards. By prioritizing precision, performance, and long-term reliability, organizations can reduce maintenance costs, minimize downtime, and improve the overall integrity of threaded connections across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.