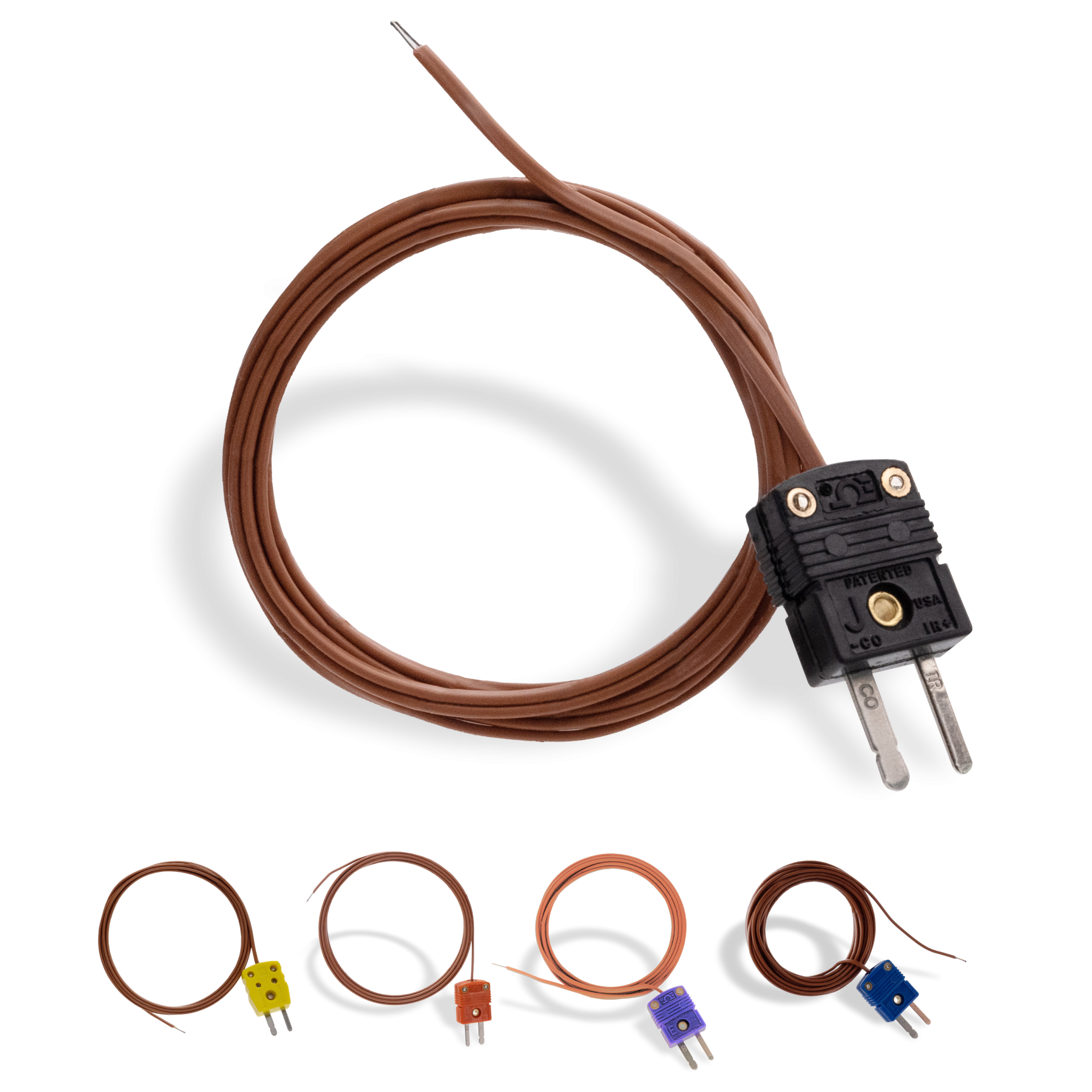
The global thermocouple probes market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision temperature measurement across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, energy, and healthcare. According to Mordor Intelligence, the thermocouple market was valued at approximately USD 2.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% over the forecast period (2024–2029). This expansion is fueled by increasing automation, stringent quality control standards, and the integration of advanced sensing technologies in industrial processes. As a result, the need for reliable and durable thermocouple probes has intensified, elevating the prominence of leading manufacturers who deliver high accuracy, long-term stability, and application-specific designs. In this landscape, six key players have distinguished themselves through innovation, global reach, and robust product portfolios—setting the benchmark in a competitive and evolving market.
Top 6 Thermocouple Probes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Temperature Probe
Website: thermocouplemanufactures.com
Key Highlights: Find temperature probe information and learn how manufacturers design, engineer, and manufacture different kinds of industrial temperature probes….
#2 Immersion Thermocouple Temperature Probe
Domain Est. 1996
Website: advancedenergy.com
Key Highlights: Thermocouple probes are ideal for many industrial applications. They offer fast response times, accuracy, and wide temperature ranges making thermocouple probes ……
#3 Thermocouple Probes
Domain Est. 2022
Website: dwyeromega.com
Key Highlights: Thermocouple probes with handles offer portable, precise temperature measurement for industrial monitoring, food processing, and lab testing….
#4 Thermocouple Products
Domain Est. 1995
Website: copeland.com
Key Highlights: We have one of the most extensive lines of thermocouple probes found in the foodservice industry and offer custom manufacturing for unique applications….
#5 Thermocouple Probes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: madgetech.com
Key Highlights: MadgeTech offers a variety of thermocouples including Type J, K, T, & E. Glass braided, PFA insulated, and stainless steel sheath options available….
#6 Thermocouple Probes
Domain Est. 2001
Website: smithsinterconnect.com
Key Highlights: Thermocouple probe is an ungrounded, thermally conductive probe used for the measurement of variations in temperature….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Thermocouple Probes

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Thermocouple Probes
The global thermocouple probe market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across industrial automation, energy, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors. Key trends shaping the market include technological advancements, rising emphasis on process efficiency, and the integration of smart sensing technologies.
-
Growth in Industrial Automation and IoT Integration
The proliferation of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is accelerating the adoption of intelligent thermocouple probes. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize probes with digital interfaces, wireless connectivity, and real-time data transmission capabilities. These smart probes enable predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and enhanced process control, particularly in sectors like oil & gas, chemical processing, and power generation. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The global shift toward clean energy and electrification is creating new applications for thermocouple probes. In solar thermal plants, battery management systems (BMS) for EVs, and hydrogen fuel cells, precise temperature monitoring is critical for safety and efficiency. Demand for high-accuracy, rugged probes capable of withstanding extreme environments is expected to surge, especially in battery testing and charging infrastructure. -
Miniaturization and Material Innovation
Advancements in materials science are enabling the development of smaller, more durable thermocouple probes with improved response times and longevity. Probes made from high-performance alloys and ceramic coatings are gaining traction in aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, and medical devices. Miniaturized probes are particularly valuable in applications requiring non-invasive or localized temperature measurements. -
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Safety Compliance
Increasing regulatory scrutiny around safety and emissions in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing is driving demand for calibrated and traceable temperature sensors. By 2026, compliance with standards like ISO/IEC 17025 and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 will become a competitive differentiator, prompting manufacturers to offer pre-certified and documentation-ready probe solutions. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the thermocouple probe market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand due to modernization of aging infrastructure and investments in smart manufacturing. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East will see gradual uptake, supported by energy and construction projects. -
Sustainability and Lifecycle Management
Environmental concerns are influencing product design, with a growing focus on recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Extended producer responsibility (EPR) initiatives may lead to increased adoption of modular, repairable probe designs to reduce electronic waste.
In summary, the 2026 thermocouple probe market will be characterized by digital transformation, application diversification, and regional expansion. Companies investing in innovation, compliance, and sustainability are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Thermocouple Probes: Quality and IP Rating Considerations
Sourcing thermocouple probes involves more than just matching temperature ranges and connector types. Overlooking critical aspects like quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings can lead to unreliable measurements, premature failures, safety hazards, and increased operational costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid in these two key areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Prioritizing Low Cost Over Long-Term Reliability
Choosing the cheapest available probe often results in substandard materials, poor construction, and inconsistent calibration. These probes may fail prematurely in demanding environments—especially under thermal cycling, vibration, or chemical exposure—leading to unplanned downtime and higher total cost of ownership. -
Uncertified or Inconsistent Calibration
Some suppliers provide probes without proper traceable calibration certificates (e.g., NIST-traceable). Using uncalibrated or poorly calibrated probes introduces measurement inaccuracies, which can compromise process control, product quality, and regulatory compliance in industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing. -
Inferior Materials and Construction
Low-quality probes may use undersized thermocouple wire, thin sheathing (e.g., 304 SS instead of more robust 316L), or inadequate insulation. This reduces mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermoelectric stability, especially at high temperatures or in aggressive environments. -
Lack of Reputable Manufacturing Standards
Probes not manufactured to recognized standards (e.g., ASTM E230, IEC 60584) may exhibit inconsistent performance. Ensure suppliers follow rigorous quality control processes and can provide documentation on materials, testing, and manufacturing practices. -
Poor Weld or Junction Integrity
The thermocouple junction—where the two dissimilar wires meet—must be properly welded and insulated. Poor junctions can cause signal drift, open circuits, or shorting, especially under thermal stress. Grounded, ungrounded, or exposed junction types must be selected appropriately for the application.
IP Rating-Related Pitfalls
-
Ignoring Environmental Exposure Requirements
Selecting a probe without considering the actual operating environment is a critical error. For example, using a probe with no IP rating (or low IP20) in a washdown or outdoor setting exposes internal components to moisture and contaminants, leading to corrosion and electrical failure. -
Misunderstanding IP Code Meaning
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating consists of two digits: the first indicates protection against solids (like dust), and the second against liquids (like water). A common mistake is assuming IP65 (dust-tight and protected against water jets) is sufficient for submersion, when IP67 or IP68 (temporary or continuous submersion) may be required. -
Overlooking Connector and Cable Entry Protection
Even if the probe tip has a high IP rating, the connection point (e.g., connector or cable entry) might be a weak link. Ensure the entire assembly—including connectors, junction boxes, and cable glands—meets the required IP rating to maintain system integrity. -
Selecting Inadequate Ratings for Harsh Environments
In food & beverage, pharmaceutical, or outdoor industrial applications, probes frequently face high-pressure washdowns, dust, or continuous moisture. Using a probe with IP54 instead of IP66/IP67 can lead to internal contamination, sensor failure, and non-compliance with hygiene standards (e.g., FDA, EHEDG). -
Failing to Verify IP Certification
Not all suppliers rigorously test their probes for IP compliance. Request third-party test reports or certification documentation to confirm that the stated IP rating has been validated under real-world conditions.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always evaluate thermocouple probes based on certified quality, material suitability, calibration traceability, and verified IP ratings aligned with your application’s environmental demands. Partner with reputable suppliers who provide full technical documentation and support to ensure long-term measurement accuracy and reliability.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Thermocouple Probes
Product Classification and Documentation
Thermocouple probes are classified as precision temperature measurement instruments and may be subject to various regulatory standards depending on their intended use (e.g., food safety, pharmaceutical, industrial processes). Ensure accurate classification under the Harmonized System (HS) Code, commonly falling under 9025.19 (electrical thermometers) or 9030.82 (measuring or checking instruments). Maintain comprehensive technical documentation, including calibration certificates, material declarations, and conformity assessments, to support customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Compliance with international and regional standards is essential. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking – Required for sale in the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards under EU directives such as the Measuring Instruments Directive (MID) or the EMC Directive.
– UKCA Marking – Mandatory for the UK market post-Brexit, aligning with UK regulations.
– RoHS and REACH Compliance – Restricts hazardous substances and ensures safe chemical usage in electrical equipment sold in the EU.
– FDA and USDA Compliance – Required for probes used in food processing or medical applications in the United States.
– NIST Traceable Calibration – Critical for applications requiring measurement accuracy; ensure each probe is supplied with a NIST-traceable certificate.
Packaging and Shipping Considerations
Package thermocouple probes to prevent physical damage during transit. Use anti-static materials where applicable and include protective caps for probe tips. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include product identifiers such as model number, serial number, and compliance markings. For international shipments, provide a detailed commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading or air waybill. Verify voltage and plug compatibility if probes are shipped with associated instrumentation.
Import/Export Controls and Restrictions
Check for export control classifications under ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) in the U.S. Commerce Control List. While most thermocouple probes are EAR99 (low risk), specialized high-accuracy or high-temperature variants may require export licenses. Screen end-users and destinations against denied party lists (e.g., BIS, OFAC) to prevent violations. Some countries may impose import restrictions or require local approval (e.g., China’s CCC mark, India’s BIS certification); verify requirements prior to shipment.
Temperature and Environmental Sensitivity
While thermocouple probes are designed to measure extreme temperatures, they may be sensitive to thermal shock or moisture during storage and transport. Avoid exposing probes to rapid temperature changes or high humidity unless rated for such conditions. Store and ship within the manufacturer’s specified environmental range (typically -20°C to 60°C, <85% RH non-condensing) to maintain calibration integrity and prevent material degradation.
Calibration and Quality Assurance
Implement a quality management system compliant with ISO 9001. Perform pre-shipment calibration checks and maintain records for traceability. For regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals), ensure compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 if electronic records are used. Offer recalibration services and provide users with instructions for periodic verification to ensure long-term accuracy and regulatory adherence.
End-of-Life and Environmental Responsibility
Dispose of thermocouple probes in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU and similar recycling programs globally. Avoid landfill disposal due to metallic and electronic components. Provide customers with take-back options or recycling guidance to support environmental compliance and corporate sustainability goals.
Conclusion for Sourcing Thermocouple Probes
Sourcing thermocouple probes requires a strategic approach that balances accuracy, durability, environmental compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. After evaluating various suppliers, probe types (such as Type K, J, T, and N), and technical specifications—including temperature range, response time, sheath material, and connection styles—it is clear that selecting the right thermocouple probe depends heavily on the specific application requirements.
Key considerations include the operating environment (e.g., corrosive, high-pressure, or high-vibration settings), necessary response speed, and long-term reliability. Reputable suppliers offering ISO-certified manufacturing, traceable calibration, and responsive technical support provide added assurance of quality and consistency. Additionally, bulk purchasing agreements and partnerships with suppliers offering customization options can lead to significant operational efficiencies and cost savings.
In conclusion, a successful sourcing strategy involves thorough needs assessment, vendor evaluation, and ongoing performance monitoring. By prioritizing quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability, organizations can ensure accurate temperature measurement, reduce downtime, and maintain compliance with industry standards across critical processes.