The global polyester market, which includes terylene—a trademarked form of polyester fiber—is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand in textiles, packaging, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global polyester fiber market size was valued at USD 57.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, fast fashion trends, and advancements in sustainable fiber technologies. As a key variant of polyester, terylene remains integral to performance-driven textiles due to its strength, wrinkle resistance, and cost efficiency. With Asia-Pacific dominating production and consumption, innovation and scale are concentrated among a select group of manufacturers leading the charge in quality, sustainability, and global supply chain integration. Below are the top five terylene material manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 5 Terylene Material Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Terylene Fibre Manufacturer and Supplier, Factory
Domain Est. 2023
Website: zhongyapolymer.com
Key Highlights: Looking for a reliable Terylene Fibre manufacturer? Our China-based factory is a trusted supplier, offering high-quality products. Contact us today!…
#2 terylene fabric Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2024
Website: jt-fabric.com
Key Highlights: terylene fabric 20 years expertise textiles industry, Wuhan Jinteng Industry and Trade Co., Ltd. specializes a producing globals workwear, camouflages, medical- ……
#3 Terylene Cotton Hoodie Fabric
Domain Est. 2021
Website: chinaknittingfabricfactory.com
Key Highlights: Terylene Cotton Hoodie Fabric. Soft touch close to the feeling of nature,60% cotton, 40% polyester,Gram weight 300g width 180cm,Moisture – absorbing and ……
#4 Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nurel.com
Key Highlights: NUREL is the reliable and high quality supplier of reference of nylon 6 and 66 for the textile market….
#5 Polyester (Terylene)
Domain Est. 1998
Website: par-group.co.uk
Key Highlights: Polyester (commonly referred to as Terylene) is resistant to stretching, shrinking, wrinkling and abrasion. It is also food approved….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Terylene Material
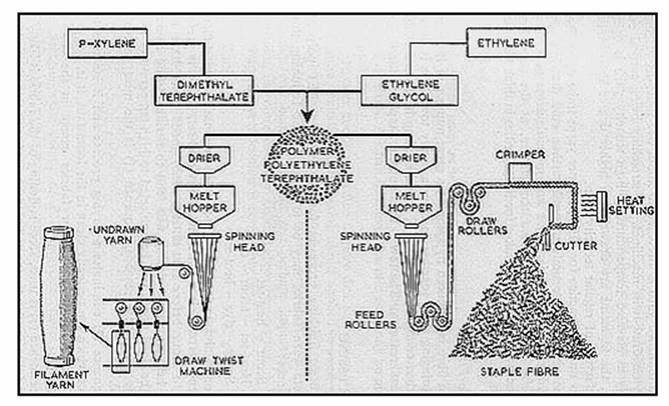
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Terylene Material
Terylene, a brand name for polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is a widely used synthetic fiber and plastic in the textile, packaging, and industrial sectors. As the global economy evolves and sustainability becomes a central focus, the market for Terylene material is expected to undergo significant changes by 2026. Key trends shaping the Terylene market include rising demand for sustainable packaging, technological advancements in recycling, shifts in textile manufacturing, and regional market dynamics.
1. Surge in Sustainable and Recyclable Packaging Demand
By 2026, environmental regulations and consumer preferences will continue to drive demand for recyclable materials. Terylene, particularly in the form of PET bottles and containers, remains a top choice due to its high recyclability. Governments across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia are enforcing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) policies and plastic tax schemes, prompting brands to increase their use of recycled Terylene (rPET). The push for a circular economy is expected to elevate the global rPET market, with Terylene playing a central role.
2. Advancements in Chemical Recycling Technologies
Mechanical recycling of Terylene has limitations in maintaining fiber quality after multiple cycles. However, by 2026, chemical recycling methods—such as glycolysis, methanolysis, and enzymatic depolymerization—are anticipated to scale up significantly. These technologies break down Terylene into its monomers, enabling the production of virgin-quality recycled material. Major chemical and packaging companies are investing heavily in these innovations, which will enhance the sustainability profile of Terylene and expand its applications in high-end packaging and textiles.
3. Growth in Textile and Apparel Applications
The global textile industry continues to adopt Terylene due to its durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness. In 2026, demand for Terylene in sportswear, outdoor gear, and fast fashion is expected to grow, especially in emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Africa. Furthermore, brands are increasingly blending recycled Terylene with natural fibers to meet eco-friendly commitments. Innovations in dyeing and finishing technologies are also improving the aesthetic and performance qualities of Terylene fabrics, broadening market appeal.
4. Regional Market Shifts and Manufacturing Hubs
Asia-Pacific remains the dominant region in both production and consumption of Terylene. China and India are expanding their PET manufacturing capacities, driven by domestic demand and export opportunities. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on localized recycling infrastructure and sustainable sourcing, reducing dependency on virgin polymer production. The Middle East is emerging as a key raw material supplier, leveraging low-cost paraxylene and ethylene glycol feedstocks to support global Terylene supply chains.
5. Price Volatility and Feedstock Dependency
Terylene prices are closely tied to crude oil and purified terephthalic acid (PTA) markets. Geopolitical tensions, fluctuating oil prices, and supply chain disruptions could lead to volatility in 2026. However, growth in bio-based PET—derived from renewable sources like bio-ethanol and bio-PTA—offers a potential hedge against fossil fuel dependency. Companies such as Toray Industries and Indorama Ventures are piloting bio-Terylene solutions, which could gain commercial traction by 2026.
6. Regulatory and ESG Pressures
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are influencing investment and procurement decisions. By 2026, corporations using Terylene will face heightened scrutiny over carbon footprints, waste management, and supply chain transparency. This is likely to accelerate the adoption of digital tracking systems (e.g., blockchain for material traceability) and third-party certifications (e.g., Global Recycled Standard) across the Terylene value chain.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Terylene material market will be shaped by a confluence of sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and shifting global supply dynamics. While challenges related to feedstock volatility and environmental impact persist, the industry’s shift toward circularity and high-performance applications positions Terylene as a resilient and evolving material in the global polymer landscape. Companies that invest in recycling infrastructure, sustainable sourcing, and product innovation are likely to lead the market in the coming years.
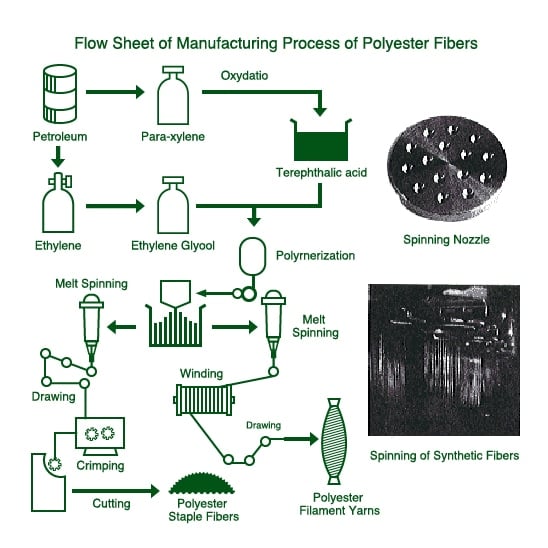
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Terylene Material (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Terylene—a registered trademark for a type of polyester fiber originally developed by ICI—can present several challenges, particularly concerning material quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers to avoid legal risks, production delays, and substandard end products.
Quality Inconsistencies and Misrepresentation
One of the primary risks in sourcing Terylene or Terylene-like polyester materials is encountering inconsistent or misrepresented quality. Since “Terylene” is a branded name, many suppliers may offer generic polyester fibers while implying equivalence or superior performance without proper validation.
- Lack of Standardization: Generic polyester fibers marketed as “Terylene-type” may vary significantly in tensile strength, dye affinity, thermal stability, and UV resistance. Without rigorous quality control and testing protocols, these variations can lead to product defects or performance failures.
- Inadequate Documentation: Suppliers may fail to provide detailed technical data sheets (TDS), certificates of conformance (CoC), or batch-specific test results. This opacity makes it difficult to verify that the material meets required specifications.
- Counterfeit or Substandard Materials: In some markets, especially in regions with weak regulatory oversight, counterfeit or adulterated fibers are common. These materials may degrade faster, shrink unevenly, or exhibit poor color fastness, impacting final product quality.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Trademark Infringement
The term “Terylene” is a protected trademark, historically owned by ICI and currently managed by companies within the SABIC or related corporate lineage. Misuse of the name can lead to serious legal consequences.
- Unauthorized Use of Trademark: Referring to generic polyester as “Terylene” in product descriptions, marketing materials, or supply contracts constitutes trademark infringement. This exposes the buyer and seller to potential legal action, fines, or forced rebranding.
- Supplier Mislabeling: Some suppliers may incorrectly label their products as “Terylene” to imply premium quality or authenticity. Sourcing such materials—even unknowingly—can entangle your business in IP disputes, particularly in export markets with strict IP enforcement (e.g., EU, USA).
- Licensing and Authorization Gaps: Legitimate use of the Terylene name typically requires proper licensing. Sourcing from unauthorized producers or distributors increases the risk of IP violations, especially if the material is rebranded or resold under the Terylene name.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Specify materials using generic terms like “polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fiber” or “polyester filament yarn” unless sourcing directly from a licensed Terylene supplier.
– Conduct supplier audits, request third-party test reports, and verify material certifications.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts to protect against infringement claims.
– Consult legal counsel to ensure branding and sourcing practices comply with trademark laws in target markets.
By focusing on technical specifications rather than brand names and conducting due diligence on supplier legitimacy, companies can mitigate both quality and IP risks when sourcing polyester materials.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Terylene Material
Terylene, a brand name for polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is widely used in textiles, packaging, and industrial applications. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure safe handling, regulatory adherence, and supply chain efficiency. This guide outlines key considerations for transporting and managing Terylene materials.
Material Classification and Identification
Terylene, as a form of PET, is generally classified as a non-hazardous solid in its polymerized form. However, accurate classification is crucial for compliance. Identify the material according to its form—e.g., resin pellets, fibers, or finished fabric—and confirm its UN number and transport classification. While bulk PET pellets typically fall under non-hazardous goods (UN3082 may apply if contaminated), always verify with the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer.
Packaging and Storage Requirements
Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging such as multi-wall poly-lined bags or bulk containers for Terylene pellets or fibers. Ensure containers are sealed to prevent contamination and moisture absorption, which can affect material quality. Store in dry, well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent degradation. Stack packages securely to avoid collapse, especially in containerized shipping.
Transportation Guidelines
Terylene materials can be transported via road, rail, sea, or air using standard freight practices. For international shipments, comply with IMDG Code (sea), ADR (road in Europe), IATA (air), or applicable regional regulations. Although non-hazardous in solid form, declare the cargo accurately on shipping documents. Use container desiccants if shipping across humid climates to prevent condensation. Label packages with product name, batch number, net weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Protect from Moisture”).
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to local and international regulations such as REACH (EU), TSCA (USA), and RoHS where applicable. Ensure Terylene materials meet required standards for restricted substances. If used in food-contact applications (e.g., PET bottles), compliance with FDA 21 CFR or EU 10/2011 for food-grade plastics is mandatory. Maintain documentation including Certificates of Conformance (CoC), SDS, and compliance statements for audits and customs clearance.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Terylene is recyclable, and logistics plans should support circular economy goals. Encourage returnable or recyclable packaging. Dispose of contaminated or off-spec material in accordance with local waste regulations. Report any spills immediately; although PET is not acutely toxic, proper cleanup prevents environmental litter and ensures workplace safety.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain detailed records for full traceability, including batch numbers, origin, and destination. Include proper product descriptions on commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading. For cross-border shipments, ensure correct HS codes are used—typically 3907.60 for PET in primary forms. Digital tracking systems are recommended to monitor shipments and respond to disruptions.
Safety and Handling Procedures
Train personnel in safe handling practices. Use PPE such as gloves and safety glasses when handling bulk materials to avoid skin irritation or eye contact with dust. Ensure adequate ventilation in storage and handling areas to minimize dust accumulation. Implement housekeeping routines to clean spills promptly and reduce slip hazards.
Emergency Response
Although Terylene is stable under normal conditions, establish protocols for fire, spill, or contamination incidents. In case of fire, use water spray, foam, or dry chemical extinguishers; combustion may release hazardous fumes (e.g., carbon monoxide, acetaldehyde). Have SDS readily accessible and ensure emergency contacts are posted in handling areas.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for Terylene material rely on accurate classification, proper packaging, regulatory adherence, and robust documentation. By following these guidelines, companies can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant transportation and storage of Terylene across global supply chains.
Conclusion on Sourcing Terylene Material:
Sourcing Terylene (a brand name for polyester fiber, primarily polyethylene terephthalate or PET) requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. As a durable, weather-resistant, and versatile synthetic fiber, Terylene is widely used in textiles, packaging, and industrial applications. When sourcing this material, it is essential to identify reputable suppliers with consistent manufacturing standards, especially those compliant with international quality and environmental certifications.
Considerations such as raw material origin, production processes (e.g., virgin vs. recycled PET), and the environmental impact of manufacturing should be evaluated to meet sustainability goals. With increasing demand for eco-friendly materials, sourcing recycled Terylene can enhance corporate social responsibility and reduce environmental footprint.
Additionally, geopolitical factors, logistics, and fluctuating petrochemical prices can influence availability and cost, highlighting the need for diversified suppliers and long-term contracts where feasible. In conclusion, successful sourcing of Terylene material involves a comprehensive assessment of technical specifications, ethical sourcing practices, and market dynamics to ensure a reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable supply chain.