The global temperature controller market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision control in industrial automation, HVAC systems, and manufacturing processes. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in digital control technologies, increasing adoption of smart manufacturing practices, and the need for energy-efficient process control solutions. As industries prioritize accuracy, reliability, and integration with IoT-enabled systems, the role of leading temperature controller manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. Based on market presence, innovation, product range, and global reach, the following ten companies have emerged as key players shaping the future of temperature control technology.
Top 10 Temperature Controller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Dixell
Domain Est. 1995
Website: copeland.com
Key Highlights: Dixell technology is leading the way in electronic regulation and control in the fields of refrigeration, air conditioning and heating, and retail….
#2 SELCO Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: selcoproducts.com
Key Highlights: Temperature controller manufacturer Selco Products offers a range of customizable temperature controller products. Learn more!…
#3 Athena Controls
Domain Est. 1996
Website: athenacontrols.com
Key Highlights: Athena Controls offers precision temperature controllers, power controls and sensors ideal for a variety of industrial equipment. Get a free quote!…
#4 Thermalogic Builds Temperature & Humidity Controls & Sensors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: thermalogic.com
Key Highlights: Thermalogic makes built-to-order temperature, humidity and process controls and sensors for OEMs and Volume Users….
#5 Temperature Controllers
Domain Est. 1993
Website: eurotherm.com
Key Highlights: Temperature Controllers. High accuracy Eurotherm temperature controllers improve process efficiency, product quality and minimise waste….
#6 Temperature Controllers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: automation.omron.com
Key Highlights: Keep your operations at the precise temperature necessary to ensure quality and maximize production with Omron’s PID process controllers….
#7 Temperature Controllers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: fujielectric.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide variety of temperature controllers to meet your needs. Explore our products and find the best for your application….
#8 NOVUS Automation
Domain Est. 2004
Website: novusautomation.com
Key Highlights: NOVUS Automation manufactures innovative instruments for control, signal conditioning, data acquisition devices and software and SCADA systems….
#9 Temperature Controllers –
Domain Est. 2008
Website: wittmann-group.com
Key Highlights: WITTMANN Tempro temperature controllers offer reliability and ease-of-use. Due to a smaller heat exchanger there is less circulating water….
#10 Temperature Controllers & Process Controllers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: west-cs.com
Key Highlights: Temperature Control experts combining the strengths of CAL, Partlow, PMA & West for high performance process and PID temperature controllers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Temperature Controller

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Temperature Controllers
The global temperature controller market in 2026 is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and shifting industrial demands. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of key trends shaping the market:
1. Dominance of Smart and Connected Controllers (Industry 4.0 Integration):
* Ubiquitous Connectivity: By 2026, IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) integration will be standard, not optional. Temperature controllers will increasingly feature built-in Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and cellular connectivity (e.g., 5G, LPWAN) for seamless integration into broader industrial automation and SCADA systems.
* Advanced Data Analytics & AI/ML: Controllers will leverage onboard processing and cloud-based platforms for predictive maintenance (forecasting sensor/element failure), adaptive control algorithms that self-optimize based on process conditions, and energy consumption optimization, moving beyond simple setpoint regulation.
* Remote Monitoring & Control: Cloud dashboards and mobile apps will enable real-time monitoring, configuration, and troubleshooting from anywhere, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
2. Rise of Software-Defined and Modular Platforms:
* Flexibility & Scalability: Demand will grow for controllers with software-defined functionality. Users will configure control logic, communication protocols, and display interfaces via software, enabling the same hardware platform to serve diverse applications (e.g., switching between PID, ON/OFF, ramp/soak profiles).
* Open Architecture & APIs: Controllers with open APIs will facilitate easier integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), ERP systems, and custom software, breaking down data silos and enabling holistic process optimization.
* Modular Design: Systems allowing easy expansion (adding I/O modules, communication cards) will gain favor for scalability and future-proofing.
3. Focus on Energy Efficiency & Sustainability:
* Green Manufacturing Drivers: Stricter global regulations (e.g., EU Green Deal, carbon pricing) and corporate ESG goals will push demand for controllers with advanced energy management features.
* Optimized Control Algorithms: Wider adoption of sophisticated algorithms (e.g., Fuzzy Logic, Model Predictive Control – MPC) will minimize energy waste by precisely matching heating/cooling output to actual process needs, especially in HVAC, plastics processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
* Integration with Renewable Energy: Controllers will increasingly manage processes powered by intermittent renewable sources, requiring sophisticated load balancing and storage integration capabilities.
4. Growth in Advanced Applications & Miniaturization:
* High-Tech Manufacturing: Explosive growth in semiconductor fabrication (especially for advanced nodes), battery manufacturing (EVs, energy storage), and biopharma (cell culture, lyophilization) will drive demand for ultra-precise, high-stability controllers with advanced diagnostics and compliance features (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 11).
* Medical & Laboratory Devices: Miniaturized, ultra-reliable controllers will be critical for portable medical devices, lab-on-a-chip systems, and advanced diagnostic equipment.
* Electric Vehicles & Charging: Thermal management systems for EV batteries and power electronics, along with high-power DC fast chargers, will require robust, high-performance controllers.
5. Enhanced Cybersecurity & Functional Safety:
* Non-Negotiable Security: As controllers become networked endpoints, robust cybersecurity (secure boot, encryption, access control, regular patching) will be a primary selection criterion, especially in critical infrastructure (energy, water, pharma).
* Safety Integration: Increased demand for controllers certified to functional safety standards (e.g., IEC 61508, IEC 61511) for applications where temperature excursions pose safety risks (chemical processing, nuclear).
6. Shift Towards Digital Twin & Simulation:
* Virtual Commissioning & Optimization: Digital twins of temperature control loops will be used for virtual testing, optimization, and operator training before physical deployment, reducing commissioning time and risk.
* Predictive Performance: Simulations based on real-time data will predict process behavior under varying conditions, enabling proactive adjustments.
7. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization:
* Diversification: The lessons from recent disruptions will lead manufacturers to diversify component sourcing and consider regionalized manufacturing hubs to mitigate risks, potentially impacting global supply chains and pricing.
* Focus on Reliability & Longevity: End-users will prioritize suppliers with proven reliability and long-term support commitments.
Conclusion for 2026:
The 2026 temperature controller market will be characterized by intelligent, connected, and sustainable solutions. Success will depend on vendors offering more than just hardware; they must provide integrated software platforms, data analytics, cybersecurity assurance, and energy optimization services. The line between a “controller” and a “process intelligence node” will blur significantly. Companies that embrace software-defined flexibility, deep IIoT integration, and a strong focus on energy efficiency and security will lead the market, while those offering only basic, isolated devices will face intense commoditization pressure.

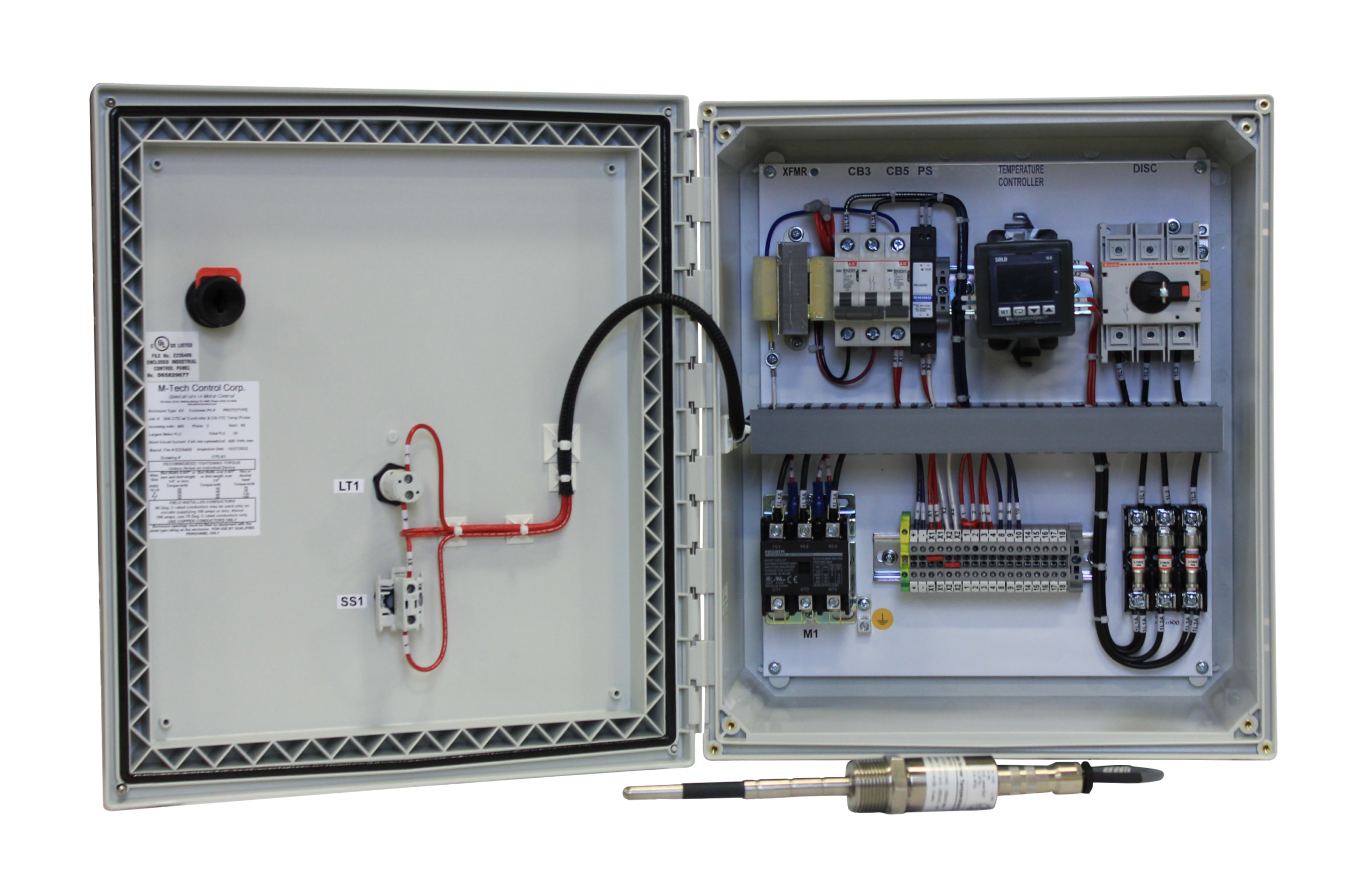
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Temperature Controllers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing temperature controllers involves navigating several potential challenges that can impact system performance, reliability, and compliance. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings is particularly common and can lead to costly failures. Below are some of the most frequent pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Low Cost Over Long-Term Quality
Choosing the cheapest available temperature controller often leads to poor build quality, inconsistent temperature regulation, and shorter product lifespans. Low-quality components may fail prematurely under continuous operation or in demanding environments, increasing downtime and maintenance costs.
2. Misunderstanding Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
Many buyers assume a generic “industrial” rating is sufficient without verifying the exact IP code. For example, selecting a controller with IP65 when the environment requires IP67 (submersion resistance) can result in water ingress, corrosion, and electronic failure—especially in washdown or outdoor settings.
3. Overlooking Environmental Compatibility
Temperature controllers may be rated for indoor use only but get installed in harsh environments with high humidity, dust, or chemical exposure. Failing to match the controller’s IP rating and material construction (e.g., polycarbonate vs. metal housing) to the actual operating conditions leads to early degradation.
4. Assuming All Controllers Meet Safety and Regulatory Standards
Not all suppliers adhere to international standards like UL, CE, or IEC. Sourcing from non-certified manufacturers risks non-compliance, safety hazards, and potential legal liabilities. Always verify certifications relevant to your region and application.
5. Ignoring Long-Term Supplier Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality controllers may become obsolete quickly if the supplier lacks ongoing support. Without access to firmware updates, technical documentation, or replacement units, system maintenance becomes difficult and costly.
6. Failing to Validate Sensor Compatibility and Accuracy
Some controllers are sold without compatible sensors or with poorly calibrated inputs. Mismatched or low-accuracy sensors undermine the controller’s effectiveness, leading to poor temperature control regardless of the controller’s internal quality.
7. Inadequate Heat Dissipation Design in Enclosed Spaces
Controllers generating significant heat may require ventilation or derating when installed in sealed enclosures. Overlooking thermal management—even with a high IP-rated unit—can cause overheating and failure, especially in high-ambient temperature environments.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in product specifications, supplier vetting, and environmental assessment. Investing time upfront ensures reliable, safe, and cost-effective temperature control over the system’s lifecycle.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Temperature Controllers
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, storage, and regulatory handling of Temperature Controllers. These devices are commonly used in HVAC systems, industrial processes, medical equipment, and cold chain applications. Due to their electronic nature and sensitivity, proper handling is critical to ensure performance, safety, and adherence to international standards.
Regulatory Compliance
Temperature controllers are subject to various regional and international regulations. Compliance ensures legal distribution and safe operation.
Electrical Safety Standards
- IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment used in measurement, control, and laboratory use.
- UL 61010-1 (North America): Equivalent to IEC standard, required for U.S. and Canadian markets.
- EN 61010-1 (Europe): Harmonized standard under the EU Low Voltage Directive (LVD).
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- IEC/EN 61326-1: EMC requirements for measurement, control, and laboratory equipment.
- FCC Part 15 (U.S.): Regulates electromagnetic interference for digital devices.
- CISPR 11 / EN 55011: Applicable for industrial environments.
Environmental & Material Regulations
- RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU): Restricts hazardous substances (e.g., lead, mercury) in electrical equipment.
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): Requires disclosure of substances of very high concern (SVHC).
- WEEE (2012/19/EU): Mandates proper recycling and disposal of electronic waste.
- Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act): Requires reporting of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold sourcing.
Regional Certifications
- CE Marking (Europe): Required for market access; indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
- UKCA Marking (UK): Required for products placed on the UK market post-Brexit.
- FCC ID (USA): For devices with wireless communication capabilities.
- PSE Mark (Japan): Mandatory for electrical appliances under the DENAN Law.
- RCM Mark (Australia/New Zealand): Indicates compliance with electromagnetic and safety standards.
Packaging & Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling ensure product integrity and regulatory compliance during transit.
Packaging Requirements
- Use anti-static packaging for sensitive electronic components.
- Include cushioning materials (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent physical shock.
- Seal in moisture-resistant bags if shipping to high-humidity regions.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
Labeling Compliance
- Include product name, model number, serial number, and batch/lot number.
- Affix required certification marks (e.g., CE, FCC, UL).
- Provide voltage, current, and power ratings as per IEC 60417.
- Include manufacturer/importer contact information and country of origin.
- Attach RoHS compliance symbol if applicable.
Transportation & Logistics
Temperature controllers require careful handling due to their sensitivity to environmental and mechanical stress.
Temperature & Humidity Control
- Store and transport within the operating range specified by the manufacturer (typically -10°C to +60°C).
- Avoid condensation by minimizing rapid temperature changes.
- Use climate-controlled containers for extreme environments.
Shock & Vibration Protection
- Use shock-absorbing packaging to meet ISTA 3A or similar standards.
- Avoid stacking heavy items on top of controller packages.
- Monitor vibration levels during road or air transport.
Shipping Documentation
- Include commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading.
- Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if batteries are included.
- Declare dual-use items if applicable (e.g., for industrial control systems).
- Comply with Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, DDP) agreed upon with the buyer.
Import/Export Compliance
- Verify export control classifications (e.g., ECCN under U.S. EAR or UK Export Control Order).
- Obtain necessary export licenses for restricted destinations.
- Ensure compliance with customs regulations (e.g., HTS codes, tariff classifications).
- Maintain records for audit purposes (minimum 5 years in most jurisdictions).
Storage Guidelines
Improper storage can compromise device functionality and safety.
Environmental Conditions
- Store in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Maintain temperatures between 15°C and 30°C and relative humidity below 75%.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, corrosive gases, or dust.
Shelf Life & Rotation
- Follow first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices.
- Monitor shelf life, especially for units with batteries or sealed components.
- Periodically inspect stored units for packaging integrity and signs of moisture.
End-of-Life & Recycling
Proper disposal supports environmental compliance and corporate sustainability goals.
Take-Back Programs
- Implement or participate in WEEE-compliant take-back and recycling programs.
- Provide customers with return instructions and prepaid labels where required.
Disposal Guidelines
- Do not dispose of in regular municipal waste.
- Partner with certified electronic waste recyclers.
- Ensure data security if controllers contain programmable memory or network access.
Conclusion
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures that temperature controllers are safely transported, legally distributed, and responsibly managed throughout their lifecycle. Regular audits, staff training, and updates to regulatory changes are recommended to maintain ongoing compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Temperature Controller
In conclusion, sourcing a temperature controller requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, and supplier reliability. It is essential to select a controller that matches the desired accuracy, control method (on/off, PID, etc.), input/output configurations, and environmental conditions of the intended application. Factors such as sensor compatibility, communication protocols, durability, and ease of integration must be considered to ensure optimal performance and long-term reliability.
Additionally, cost-effectiveness should be balanced with quality and support—opting for reputable suppliers with proven track records, strong technical support, and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., CE, UL, ISO) helps mitigate risks and ensures seamless operation. Whether for industrial processes, laboratory environments, or HVAC systems, a well-sourced temperature controller enhances process control, energy efficiency, and system safety.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach—combining technical assessment, vendor evaluation, and lifecycle cost analysis—will lead to a reliable, scalable, and efficient solution tailored to specific operational needs.