The global biofertilizer market, driven by increasing demand for sustainable agricultural inputs, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. As part of this expansion, tea seed meal—a nutrient-rich byproduct of tea oil extraction—has emerged as a valuable organic fertilizer and natural pesticide. With its high saponin content and slow-release nitrogen profile, tea seed meal supports soil health and crop yield without synthetic additives. This rising demand for eco-friendly soil amendments has spurred the growth of specialized manufacturers across Asia, Europe, and North America. Based on production capacity, export volume, and certifications, the following nine companies are leading the global tea seed meal market.
Top 9 Tea Seed Meal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tea Seed Meal from China Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pxhay.goldsupplier.com
Key Highlights: Explore Tea Seed Meal products at Pingxiang Red An Yuan Humic Acid Co., Ltd., reliable China manufacturer. Contact us for more details!…
#2 Tea seed cake, powder, or meal Manufacturers, with SDS
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1976
Website: mubychem.com
Key Highlights: Supplier, Manufacturer, Exporter of Tea seed cake or powder or meal, Muby Chemicals of Mubychem Group, established in 1976, is the original manufacturers of ……
#3 Mei Shan Tea Seed oil Manufactory cooperation Leader Superior
Domain Est. 2010
Website: teaseed-oil.com.tw
Key Highlights: Mei Shan Tea Seed oil Manufactory cooperation has 70 years press experience producing oil. we have export to 12 countries . we made only nature and superior ……
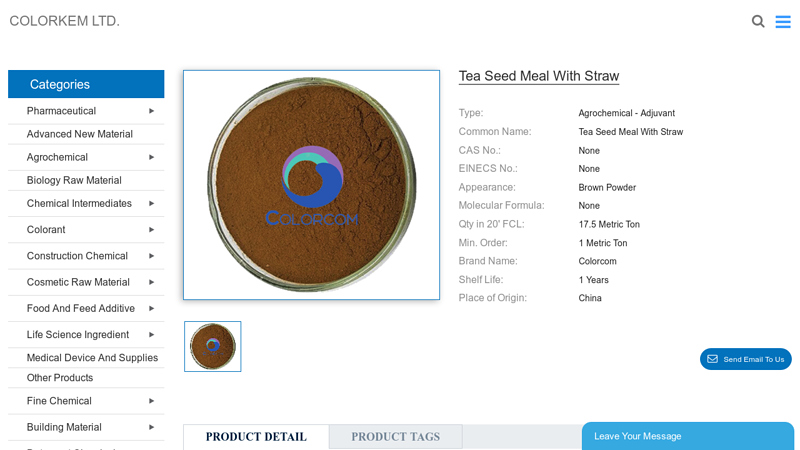
#4 China Tea Seed Meal With Straw Manufacturer and Supplier
Domain Est. 2019
Website: colorkem.com
Key Highlights: Tea Seed Meal With Straw ; Brand Name: Colorcom ; Shelf Life: 1 Years ; Place of Origin: China ; Active Content. ≥15% ; Package. 10KG, 20KG, 25KG, 50KG….
#5 Tea Seed Meal
Domain Est. 1998
Website: taiwantrade.com
Key Highlights: Camellia seed meal is a natural, eco-conscious by-product of camellia oil pressing. Rich in saponins, it has become a trusted solution in ……
#6 Tea Seed Meal、Tea Saponin
Domain Est. 2004
Website: en.chemisky.com
Key Highlights: We have been producing and exporting the below 6 kinds of products: Tea Seed Meal With Straw、Tea Seed Meal Without Straw、 Tea Seed Powder、Tea Seed Pellet、 ……
#7 China Tea seed meal
Domain Est. 2011
Website: sunsirs.com
Key Highlights: We, China Tea seed meal supplier, provide the Tea seed meal with high quality and competitive price to global buyers….
#8 Planet Turf:
Domain Est. 2017
Website: planetturfusa.com
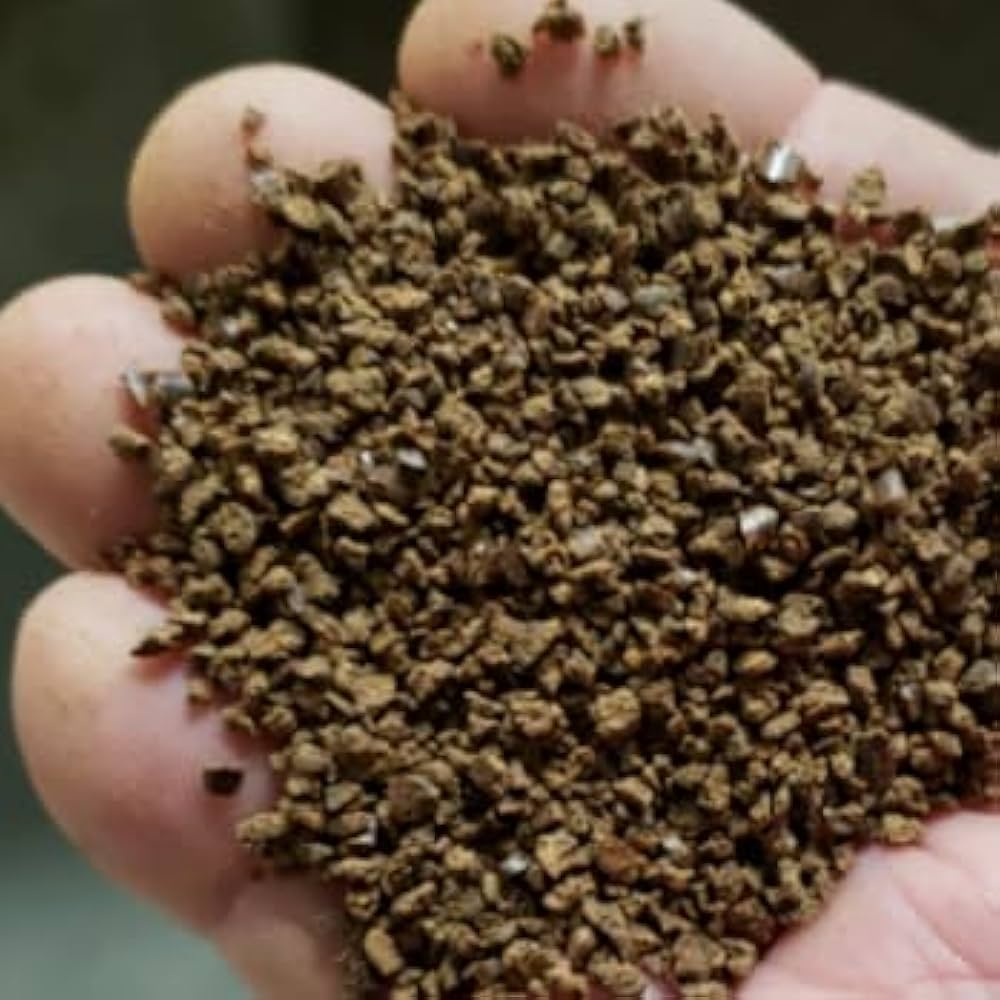
Key Highlights: Planet Turf Tea Seed Meal. PLANET TURF PROVIDES HIGH QUALITY, EASY TO APPLY, TEA SEED MEAL. Here’s an alt tag for the image: Handful of instant coffee ……
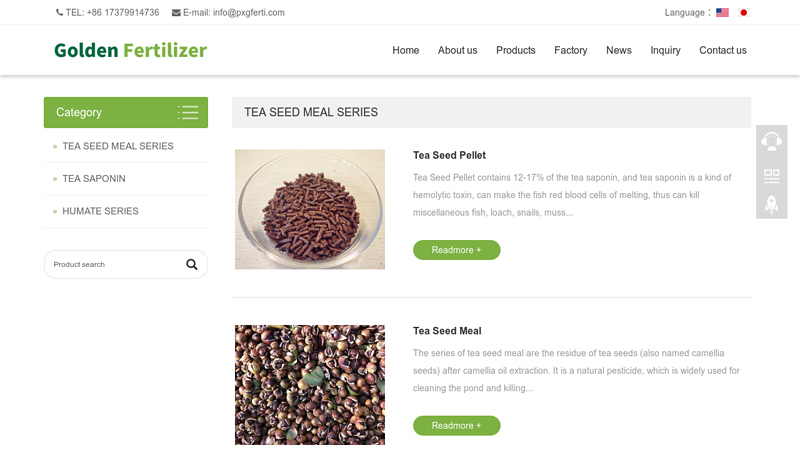
#9 TEA SEED MEAL SERIES
Domain Est. 2020
Website: pxgferti.com
Key Highlights: The series of tea seed meal are the residue of tea seeds (also named camellia seeds) after camellia oil extraction. It is a natural pesticide….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tea Seed Meal

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tea Seed Meal
The global market for tea seed meal, a byproduct of tea seed oil extraction derived primarily from Camellia oleifera, is projected to experience notable growth and transformation by 2026. Driven by increasing demand for sustainable, eco-friendly agricultural inputs and the rising popularity of organic farming, tea seed meal is gaining recognition for its multifunctional properties. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the tea seed meal industry by 2026:
-
Expansion in Agricultural Applications
Tea seed meal is rich in saponins, proteins, and natural nutrients, making it a valuable organic fertilizer and soil conditioner. Its ability to improve soil structure, enhance microbial activity, and promote root development is fueling adoption among organic farmers. By 2026, increased investment in sustainable agriculture—particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America—is anticipated to drive demand. Additionally, its natural nematicidal and antimicrobial properties are boosting its use as a bio-pesticide alternative, aligning with global efforts to reduce synthetic chemical inputs. -
Growth in Aquaculture and Animal Feed Sectors
Tea seed meal’s saponin content exhibits antimicrobial and growth-promoting effects, making it an attractive additive in aquaculture and livestock feed. In countries like China, Vietnam, and India, tea seed meal is increasingly used to improve water quality in fish ponds and enhance feed efficiency. By 2026, regulatory support for natural feed additives and rising consumer demand for antibiotic-free seafood and meat products are expected to expand its use in animal husbandry. -
Rising Environmental and Regulatory Support
With growing awareness of environmental pollution caused by chemical fertilizers and pesticides, governments and environmental agencies are promoting organic and bio-based alternatives. Policies supporting circular economy models and waste valorization are encouraging the use of tea seed meal as a high-value byproduct. By 2026, stricter environmental regulations in Europe and North America may open new export opportunities for certified organic tea seed meal products. -
Technological Advancements in Processing and Product Formulation
Innovations in extraction and processing technologies are enhancing the consistency, safety, and efficacy of tea seed meal. Companies are developing defatted, low-saponin, or fermented variants tailored for specific applications. By 2026, advanced product formulations—such as granulated, soluble, or encapsulated tea seed meal—are expected to improve user convenience and broaden market reach across diverse industries. -
Geographic Market Expansion
While China remains the largest producer and consumer of tea seed meal due to its extensive Camellia oleifera cultivation, other regions are emerging as key growth markets. Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America are witnessing increased interest in tea seed cultivation and meal utilization. By 2026, international partnerships and technology transfer are likely to stimulate production and application in these regions. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Development
As part of broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) initiatives, companies are investing in vertically integrated supply chains—from tea seed farming to meal processing. Certification of sustainable sourcing and fair trade practices is expected to become a competitive advantage. By 2026, transparency and traceability in the tea seed meal supply chain will be critical for market access, especially in premium organic and eco-conscious markets.
In conclusion, the tea seed meal market in 2026 is poised for robust growth, supported by its dual role as a sustainable agricultural input and a natural bioactive ingredient. With increasing emphasis on environmental stewardship, food safety, and circular bioeconomy principles, tea seed meal is set to become a cornerstone product in the global transition toward greener and more resilient agricultural systems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tea Seed Meal: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing Tea Seed Meal (TSM), a byproduct of tea seed oil extraction used primarily as an organic fertilizer and natural pesticide, presents several challenges—particularly in ensuring consistent quality and navigating intellectual property (IP) issues. Buyers, especially in agriculture, aquaculture, and organic product manufacturing, must be aware of the following common pitfalls.
Inconsistent Product Quality
One of the most significant challenges in sourcing Tea Seed Meal is variability in quality. Since TSM is often derived from Camellia species (such as Camellia oleifera), differences in seed origin, processing methods, and storage conditions can drastically affect its saponin content—the active compound responsible for its pesticidal and antimicrobial properties.
- Variable Saponin Levels: Saponin concentration can range widely (typically 10–20%), impacting efficacy. Without third-party testing or certification, buyers risk receiving underperforming batches.
- Contaminants and Additives: Poor processing may lead to residual oils, molds, heavy metals, or chemical contaminants, especially if sourced from unregulated producers.
- Moisture and Shelf Life: High moisture content can promote spoilage and reduce shelf life. Improper drying or storage leads to clumping and microbial growth.
To mitigate this, buyers should require Certificates of Analysis (CoA), conduct independent lab testing, and establish clear quality specifications in supply contracts.
Lack of Standardization and Certification
There is no universal standard for Tea Seed Meal, leading to inconsistent labeling and claims. Some suppliers may misrepresent their product as “high-saponin” or “organic” without certification.
- Absence of Global Standards: Unlike regulated agricultural inputs, TSM lacks harmonized quality benchmarks across regions.
- Misleading Organic Claims: Not all TSM is certified organic. Buyers must verify certifications (e.g., USDA Organic, EU Organic) if required for their use case.
Due diligence, including site audits and supply chain transparency, is essential to ensure authenticity and compliance.
Intellectual Property and Biopiracy Risks
Tea Seed Meal production often relies on traditional knowledge related to Camellia oleifera cultivation and processing, particularly from regions in China and Southeast Asia. This raises potential IP and ethical sourcing concerns.
- Traditional Knowledge Exploitation: Foreign companies may commercialize TSM-based products without fair compensation to local communities who developed or preserved the knowledge.
- Patent Landscapes: Some processing methods or formulations using TSM may be patented. Unknowingly infringing on existing patents—especially in bio-pesticide applications—can lead to legal disputes.
- Geographical Indications (GIs): Certain high-quality TSM may originate from specific regions with unique growing conditions. Misrepresenting origin could violate GI protections or mislead consumers.
To avoid IP pitfalls, companies should:
– Conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before product development.
– Engage in benefit-sharing agreements when leveraging traditional knowledge.
– Respect local regulations and community rights in source regions.
Conclusion
Sourcing Tea Seed Meal effectively requires attention to both quality control and ethical/legal considerations. Buyers must implement rigorous vetting of suppliers, demand transparency in sourcing and processing, and remain vigilant about intellectual property rights to avoid reputational, legal, and operational risks.
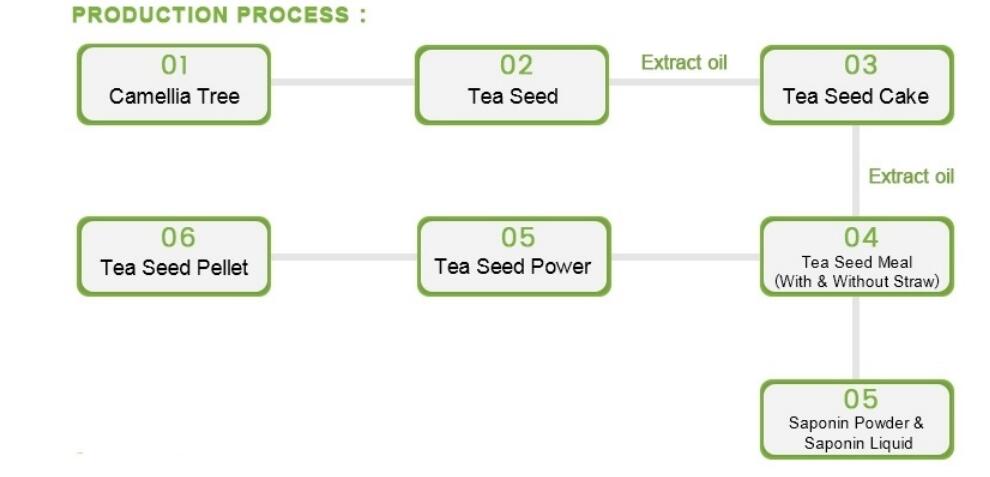
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tea Seed Meal
Overview of Tea Seed Meal
Tea Seed Meal, a byproduct of tea (Camellia sinensis) seed oil extraction, is widely used as an organic fertilizer, soil conditioner, and natural piscicide (fish poison) in aquaculture pond preparation. Due to its bioactive saponin content, proper logistics and compliance procedures are essential to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and product efficacy.
Classification & Regulatory Status
Tea Seed Meal is typically classified as an agricultural input or organic soil amendment. In many jurisdictions, it may be regulated under organic farming standards (e.g., USDA NOP, EU Organic Regulation) if marketed as organic. It is not intended for human or animal consumption and may be restricted or prohibited in certain countries due to its piscicidal properties.
International Shipping & Export Compliance
When exporting Tea Seed Meal, exporters must comply with the following:
– Customs Classification: Use HS Code 2308.00 (residues of vegetable origin, primarily from oil seeds or oleaginous fruits), though country-specific variations may apply.
– Phytosanitary Certificates: Often required to confirm the product is free from pests and pathogens.
– Import Restrictions: Some countries (e.g., Australia, New Zealand, parts of the EU) regulate or ban tea seed products due to environmental concerns. Verify with the destination country’s agricultural authority prior to shipment.
– Labeling: Labels must include product name, saponin content (if applicable), origin, net weight, batch number, and safety warnings (e.g., “Not for human or animal consumption,” “Harmful to aquatic life”).
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Packaging: Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging such as multi-wall poly bags or woven PP bags with inner liners. Typical sizes: 20–25 kg per bag.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight. Avoid contact with food, feed, or water sources.
- Handling Precautions: Use PPE (gloves, mask) during handling to avoid inhalation of dust or skin irritation due to saponins.
Transportation Guidelines
- Domestic Transport: Complies with general freight regulations for non-hazardous agricultural goods in most countries.
- International Transport: Generally not classified as hazardous under IMDG (sea), IATA (air), or ADR (road), but must be declared accurately with proper documentation.
- Temperature Control: Not required, but prolonged exposure to high humidity or heat may reduce saponin efficacy.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
- Piscicidal Use: In aquaculture, use only in accordance with local environmental regulations. Discharge into natural water bodies is often prohibited.
- Saponin Content Disclosure: Provide safety data sheets (SDS) indicating saponin concentration and environmental hazards.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of unused product and packaging in accordance with local solid waste regulations; do not dump in drains or waterways.
Documentation & Certification
Essential documents include:
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA) – detailing saponin content, moisture, and purity
– Organic Certification (if applicable)
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– Commercial Invoice and Packing List
– Phytosanitary Certificate (export)
– SDS (Safety Data Sheet) compliant with GHS standards
Country-Specific Considerations
- United States: Regulated by EPA if used as a pesticide; registration may be required for piscicidal claims.
- European Union: Subject to REACH and biocidal products regulation (BPR) if marketed for pest control.
- Southeast Asia: Widely used in aquaculture; generally permitted with standard agricultural import protocols.
- Australia/NZ: Strict biosecurity controls; import permit often required from DAFF or MPI.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Verify import requirements with the destination country before shipping.
- Maintain batch traceability and retain documentation for at least 2 years.
- Train staff on safe handling and emergency procedures.
- Partner with certified suppliers who provide full compliance documentation.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management are critical for the international trade of Tea Seed Meal. Adhering to regulatory standards, ensuring accurate labeling, and maintaining transparent documentation will facilitate smooth customs clearance and responsible use of this valuable agricultural byproduct.
In conclusion, sourcing tea seed meal presents a sustainable and valuable opportunity for various applications, particularly in organic agriculture and animal feed. As a byproduct of tea seed oil extraction, tea seed meal is rich in nutrients and bioactive compounds, making it an excellent natural fertilizer and a potential feed additive with growth-promoting and antimicrobial properties. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, saponin content (which can be toxic if not properly processed), and compliance with local regulations. Establishing transparent supply chains, supporting environmentally responsible production practices, and conducting thorough quality testing are essential steps to ensure the safe and effective use of tea seed meal. With growing demand for eco-friendly agricultural inputs, tea seed meal stands out as a promising resource that supports circular economy principles and sustainable development.