The global tantalum carbide powder market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in advanced industrial applications such as cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, and aerospace components. According to Mordor Intelligence, the tantalum carbide market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.8% during the forecast period of 2024–2029, fueled by increasing adoption in high-temperature and high-strength applications across the defense and electronics sectors. Additionally, expanding research into ultra-high-temperature ceramics (UHTCs) for next-generation aerospace systems is further accelerating material demand. With supply chains becoming more specialized and performance requirements more stringent, identifying reliable manufacturers has become critical for procurement teams and R&D departments. Based on production capacity, global reach, technical capabilities, and quality certifications, the following nine companies represent the leading suppliers of tantalum carbide powder worldwide.
Top 9 Tantalum Carbide Powder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tantalum Carbide Powder
Domain Est. 2018
Website: aemmetal.com
Key Highlights: Tantalum Carbide Powder is a cutting-edge industrial material known for its exceptional qualities and ability to boost performance….
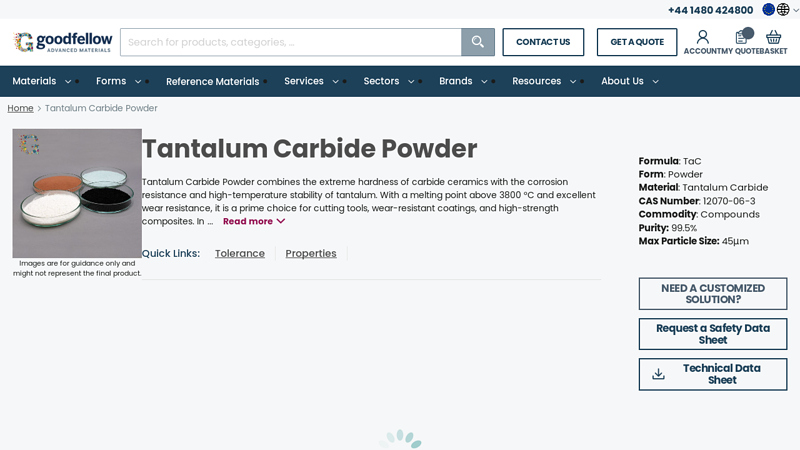
#2 Buy Tantalum Carbide Powder
Domain Est. 1993
Website: goodfellow.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryTantalum Carbide Powder combines the extreme hardness of carbide ceramics with the corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability of tantalum….
#3 H.C. Starck Tungsten Powders: High
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hcstarck.com
Key Highlights: We also offer tantalum and niobium carbide powders. We can develop the optimum powder mixture for you. Please contact us! Discover our products….
#4 Tantalum Carbide Powder
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanelements.com
Key Highlights: American Elements specializes in producing high purity Tantalum Carbide Powder with the smallest possible average grain sizes for use in preparation of ……
#5 Tantalum carbide (TaC)
Domain Est. 2000
Website: treibacher.com
Key Highlights: Tantalum carbide (TaC) is a high-quality product in powder form for industry. It is a homogeneous powder with high purity and narrow particle size distribution….
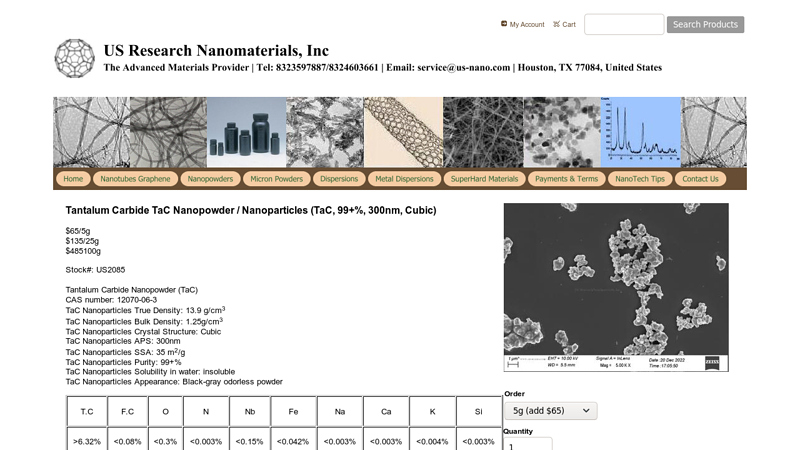
#6 Tantalum Carbide TaC Nanopowder / Nanoparticles (TaC, 99+% …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: us-nano.com
Key Highlights: Tantalum carbide (TaC) is an extremely hard (Mohs hardess 9-10) refractory ceramic material, commercially used in tool bits for cutting tools….
#7 Tantalum Carbide Powder, TaC Powder (CAS: 12070
Domain Est. 2013
Website: samaterials.com
Key Highlights: Tantalum carbide is a brown, hard refractory ceramic material. TaC powder is hard, brittle, and has a high thermal and electrical conductivity….
#8 Tantalum Carbide Powder
Domain Est. 2015
Website: edge-techind.com
Key Highlights: Tantalum carbide powder is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material. The hardness of tantalum carbide is only exceeded by diamond….
#9 Tantalum Carbide Powder
Domain Est. 2015
Website: pacificparticulatematerials.com
Key Highlights: We produce and stock customizable tantalum carbide (TaC) powders providing extreme hardness, excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tantalum Carbide Powder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tantalum Carbide Powder
The global tantalum carbide (TaC) powder market is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by rising demand in high-performance industrial applications, technological advancements in materials science, and expanding usage in aerospace, defense, and electronics sectors. Tantalum carbide, known for its exceptional hardness, high melting point (~3,880°C), and excellent wear and corrosion resistance, remains a critical material in advanced ceramics, cutting tools, and refractory composites.
1. Increasing Demand in Aerospace and Defense:
By 2026, the aerospace and defense industries are expected to be the primary drivers of tantalum carbide powder consumption. The material’s use in ultra-high-temperature ceramics (UHTCs) for hypersonic vehicles, jet engine components, and thermal protection systems will grow significantly. As nations and private companies invest in next-generation aerospace technologies, including reusable launch vehicles and hypersonic missiles, demand for TaC-based composites will intensify.
2. Growth in Advanced Manufacturing and Tooling:
Tantalum carbide is increasingly used in cemented carbides and cutting tools due to its ability to enhance hardness and thermal stability. With the global push toward precision manufacturing and automation, especially in automotive and industrial machinery, the demand for wear-resistant tooling materials is rising. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt more TaC-doped tungsten carbide tools to extend tool life and improve machining efficiency.
3. Expansion in Electronics and Semiconductor Applications:
The electronics sector, particularly in semiconductor manufacturing and thin-film coatings, is anticipated to contribute to market growth. Tantalum carbide is used in diffusion barriers and conductive layers in advanced microchips. As the semiconductor industry moves toward smaller node technologies (below 5nm), the need for reliable, high-performance materials like TaC will increase, supporting market expansion.
4. Supply Chain and Raw Material Challenges:
Tantalum is a conflict mineral, and its sourcing is subject to strict regulatory oversight (e.g., Dodd-Frank Act, OECD guidelines). By 2026, supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing will remain critical issues. Geopolitical instability in key tantalum-producing regions (e.g., Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda) may lead to price volatility. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in recycling technologies and alternative supply routes to ensure a stable TaC powder supply.
5. Technological Advancements and Nanomaterials:
The development of nano-sized tantalum carbide powders is expected to open new applications in additive manufacturing (3D printing), nanocomposites, and energy storage. By 2026, R&D efforts will focus on improving synthesis methods (e.g., carbothermal reduction, sol-gel processes) to produce high-purity, fine-grained TaC powders with controlled morphology, enhancing their performance in advanced applications.
6. Regional Market Dynamics:
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to dominate the tantalum carbide powder market by 2026 due to strong industrial bases in electronics, aerospace, and manufacturing. North America and Europe will also see growth, driven by defense spending and innovation in high-temperature materials. However, stringent environmental regulations in these regions may impact production costs and encourage cleaner manufacturing practices.
7. Price Trends and Market Competition:
Tantalum carbide powder prices are expected to remain relatively high due to the costly extraction and refining processes of tantalum. However, economies of scale, improved production efficiency, and increased recycling could moderate price increases. The market will remain moderately consolidated, with key players such as HC Starck, American Elements, and Ningxia Orient Tantalum Industry Co. competing on purity, particle size control, and application-specific formulations.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the tantalum carbide powder market will be shaped by technological innovation, strategic industrial demand, and supply chain resilience. While challenges related to raw material sourcing and cost persist, ongoing advancements in material engineering and expanding applications in high-tech industries will support sustained market growth. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainable practices, and vertical integration will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Sourcing Tantalum Carbide (TaC) powder, especially with high purity and desired specifications, presents several common pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP), particularly when hydrogen (H₂) is used in the synthesis or processing. Below is a breakdown of these pitfalls, with emphasis on hydrogen-assisted production methods:
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inconsistent Purity Levels
- Pitfall: TaC powder sourced from different suppliers often varies in purity due to differences in raw materials and synthesis processes.
- H₂ Impact: When H₂ is used in carbothermal reduction of tantalum oxide (e.g., Ta₂O₅ + carbon + H₂ → TaC), residual oxygen and hydrogen can lead to substoichiometric or non-uniform carbide formation.
- Risk: Lower-than-specified carbon content or oxygen contamination degrades performance in high-temperature applications (e.g., cutting tools, aerospace components).
b. Particle Size and Morphology Variability
- Pitfall: Inconsistent particle size distribution affects sinterability and final material density.
- H₂ Role: Hydrogen can act as a reducing agent and influence particle coarsening or inhibit grain growth depending on concentration and temperature.
- Risk: Poor control over H₂ flow or temperature during synthesis leads to agglomeration or irregular particle shapes, compromising powder flowability and packing density.
c. Carbon Stoichiometry Deviation
- Pitfall: Achieving the correct Ta:C ratio (typically 1:1) is critical; off-stoichiometry leads to secondary phases (e.g., Ta₂C or free carbon).
- H₂ Impact: In H₂-assisted synthesis, hydrogen can react with carbon sources (e.g., CH₄, CO) or surface carbon, altering carbon availability.
- Risk: Excess H₂ may gasify carbon (via methane formation), resulting in carbon-deficient TaC.
d. Residual Hydrogen and Moisture Sensitivity
- Pitfall: TaC powders processed with H₂ may retain adsorbed hydrogen or be prone to surface oxidation upon exposure to air.
- Risk: Residual H₂ can lead to porosity during sintering (“hydrogen embrittlement” effect in compacts) or degrade performance in vacuum environments.
e. Contamination from Reactor Materials
- Pitfall: High-temperature H₂ environments can corrode furnace linings (e.g., graphite, refractory metals), introducing impurities.
- Risk: Metallic contaminants (Fe, Ni, Cr) or additional carbon from graphite crucibles affect electrical/thermal properties.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
a. Proprietary Synthesis Routes Involving H₂
- Pitfall: Many advanced TaC synthesis methods (e.g., H₂-assisted CVD, plasma reduction with H₂/CH₄ mixtures) are patented.
- Risk: Sourcing from a vendor using an IP-protected process may expose the buyer to indirect infringement or limit application fields (e.g., defense, aerospace).
- Due Diligence Need: Verify whether the supplier owns or licenses the process, especially if scaling up or integrating into proprietary products.
b. Trade Secrets in Powder Processing
- Pitfall: Surface passivation, particle coating, or stabilization techniques (often used to prevent oxidation of H₂-processed powders) may be trade secrets.
- Risk: Lack of transparency can hinder reproducibility or regulatory compliance (e.g., in medical or nuclear applications).
c. Export Controls and ITAR Concerns
- Pitfall: High-purity TaC is a strategic material used in hypersonics and nuclear applications. H₂-based synthesis may be tied to controlled technologies.
- Risk: Import/export restrictions (e.g., under ITAR or EAR) may apply if the production process or powder specs exceed civilian thresholds.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Demand Full Certification:
-
Require COA (Certificate of Analysis) including: purity (Ta, C, O, N), BET surface area, particle size (D50), stoichiometry (via XRD or EDS), and residual H₂ content.
-
Audit Supplier Processes:
-
Understand whether H₂ is used in reduction, sintering, or purification. Assess control over H₂ partial pressure and cooling cycles.
-
Verify IP Status:
- Conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis, especially if using TaC in commercial products.
-
Ensure supplier provides IP indemnification if applicable.
-
Test for Performance, Not Just Specs:
-
Evaluate powder in your application (e.g., sintering behavior, hardness, thermal stability) rather than relying solely on datasheets.
-
Control Handling and Storage:
- Use inert atmosphere (Ar) gloveboxes for H₂-processed TaC powders to prevent moisture uptake and oxidation.
Conclusion
While H₂-assisted synthesis of TaC powder can yield high-purity, fine-grained products, it introduces risks related to stoichiometry control, contamination, and IP exposure. Buyers must rigorously vet suppliers, demand transparent quality data, and ensure IP compliance—especially when deploying TaC in advanced or regulated applications.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tantalum Carbide Powder
Tantalum carbide (TaC) powder is a high-performance ceramic material used in cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, aerospace components, and refractory applications. Due to its technical nature and potential dual-use applications, the logistics and compliance requirements for tantalum carbide powder are subject to international trade controls, safety standards, and transportation regulations. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant handling, storage, transport, and documentation of tantalum carbide powder.
1. Classification & Identification
- Chemical Name: Tantalum Carbide
- Formula: TaC
- CAS Number: 12070-06-3
- UN Number: Not specifically assigned; generally classified under UN 3077, ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (Tantalum Carbide) when transported in quantities posing an environmental hazard.
- HS Code (Example): 2849.90 (Metal carbides, other than calcium carbide) – Confirm based on country-specific tariff schedules.
- GHS Classification:
- Not classified as acutely toxic.
- May be harmful if inhaled as fine dust (respiratory irritation).
- No significant environmental hazards under normal handling.
- Always refer to Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for site-specific classification.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Export Controls & Dual-Use Regulations
Tantalum carbide may be subject to export controls due to its application in advanced materials and defense technologies.
- Wassenaar Arrangement:
Tantalum compounds and advanced ceramics may fall under Category 1 (Materials) or Category 9 (Propulsion Systems, Space Vehicles, and Related Equipment) if used in strategic applications. -
Check ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) – Possible classification: 1C351 (Ceramic powders capable of sintering to >99% theoretical density, with specific particle size and purity).
-
U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR):
- Verify ECCN via the Commerce Control List (CCL).
-
May require license for export to certain countries (e.g., embargoed or high-risk destinations).
-
EU Dual-Use Regulation (EU) 2021/821:
- Controlled under Category 1C (Materials) – entry 1C001 or 1C351.
-
Export authorization may be required based on end-use and destination.
-
Other Jurisdictions:
- China, Russia, India, and others may have local controls on tantalum materials.
- Check national export control lists.
✅ Best Practice: Conduct end-user due diligence and obtain export licenses where required.
3. Safety & Handling (OSHA / GHS / CLP)
- Hazard Information:
- Inhalation: Fine dust may cause respiratory irritation (use NIOSH-approved respirator).
- Skin/Eye Contact: Low hazard; may cause mechanical irritation.
-
No known carcinogenicity (per IARC/NTP).
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves (nitrile or chemical-resistant)
- Safety goggles
- Dust mask/respirator (for powder handling)
-
Protective clothing
-
Storage:
- Store in sealed, dry containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.
- Keep away from strong oxidizers and acids.
-
Avoid dust accumulation (use grounded containers to prevent static).
-
SDS Requirements:
- Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheet (GHS-compliant) for all shipments.
- SDS must include transport, handling, and emergency measures.
4. Transportation (Air, Sea, Ground)
IATA (Air)
- Classified under Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods if meeting criteria for environmentally hazardous substances.
- Packing Group: III (if applicable)
- Proper Shipping Name: “Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s.”
- Label: Class 9 hazard label + Environmentally Hazardous Substance mark (fish and tree symbol).
- Quantity limits apply for passenger vs. cargo aircraft.
IMDG (Sea)
- UN 3077, Class 9, PG III
- Marine Pollutant: Yes (check specific criteria; TaC may be listed or assessed case-by-case)
- Requires proper stowage and documentation in the Dangerous Goods Manifest.
ADR (Road – Europe)
- Same classification as IMDG/IATA if transported as hazardous.
- Driver must have ADR training if carrying dangerous goods above threshold limits.
✅ Note: In many cases, tantalum carbide powder may be exempt from full dangerous goods regulations if packaged in limited quantities and proven non-hazardous. Always conduct a hazard assessment.
5. Packaging & Labeling
- Use sealed, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., vacuum-sealed bags inside HDPE drums).
- Label with:
- Product name and CAS number
- Net weight
- Supplier information
- GHS pictograms (if applicable)
- Handling precautions
-
“Protect from moisture” and “Avoid dust formation”
-
For hazardous transport:
- UN-certified packaging
- Class 9 label
- Proper shipping name and UN number
6. Documentation Requirements
- Commercial Invoice: Accurate description, HS code, value, origin.
- Packing List: Itemized contents, weights, packaging type.
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Purity, particle size, chemical composition.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariffs or trade compliance.
- Export License: If required by destination country or ECCN.
- Dangerous Goods Declaration: If shipped as UN 3077 or other regulated classification.
- SDS: Always include with shipment.
7. Environmental & Waste Disposal
- Not biodegradable; inert under normal conditions.
- Dispose of as inert industrial waste in accordance with local regulations (e.g., EPA, ECHA).
- Do not incinerate without proper filtration (may generate Ta2O5 fumes).
- Follow regional waste codes (e.g., EU Waste Code 16 05 05* for non-halogenated, non-toxic organics – adjust as needed).
8. Due Diligence & Risk Mitigation
- Screen customers against denied party lists (e.g., U.S. BIS, EU Consolidated List).
- Obtain end-use statements for sensitive applications.
- Audit supply chain for conflict minerals (tantalum may be sourced from conflict-affected areas).
- Comply with OECD Due Diligence Guidance for responsible mineral sourcing.
Summary Checklist
| Item | Requirement |
|——|————-|
| ✅ Proper Classification | UN 3077 / Class 9 (if hazardous); else non-regulated |
| ✅ Export License | Required if ECCN 1C351 or national controls apply |
| ✅ SDS & Labels | GHS-compliant, accurate hazard info |
| ✅ Packaging | Sealed, dust-proof, UN-certified if hazardous |
| ✅ Transport Docs | DGD, CoA, CoO, Commercial Invoice |
| ✅ Customer Screening | Denied party and end-use verification |
| ✅ Storage | Dry, ventilated, away from oxidizers |
Disclaimer: Regulations vary by country and change frequently. Always consult with a qualified regulatory expert or freight forwarder specializing in hazardous or dual-use materials before shipping.
For further assistance:
– U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) – www.bis.doc.gov
– IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations
– REACH/CLP (EU)
– Local environmental and customs authorities
—
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tantalum Carbide Powder
Version 1.0 | Intended for industrial and regulatory use
In conclusion, sourcing tantalum carbide powder requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who provide high-purity, consistently manufactured powder, verified through proper certifications and quality control processes. Evaluating supply chain stability, lead times, and scalability is crucial, especially for industrial applications requiring consistent material performance. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and geopolitical influences on tantalum supply can support strategic procurement decisions. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for tantalum carbide powder—balancing quality, price, and supplier reliability—will enhance manufacturing efficiency and product performance in high-demand sectors such as aerospace, cutting tools, and advanced ceramics.