The global engineered wood market, including specialty products like swan wood—a decorative laminate prized for its elegant grain and moisture-resistant properties—is experiencing robust growth driven by rising demand in residential and commercial interior applications. According to Grand View Research, the global engineered wood market was valued at USD 218.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by urbanization, sustainable construction trends, and increased prefabrication in developing economies. As demand for aesthetically pleasing, durable surfacing solutions grows, manufacturers specializing in high-quality swan wood panels are gaining prominence. This list highlights the top eight swan wood manufacturers, evaluated based on production capacity, innovation in texture and design, geographic reach, and compliance with environmental standards—positioning them as key players in a competitive and expanding market.
Top 8 Swan Wood Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Idaho Power
Domain Est. 1994
Website: idahopower.com
Key Highlights: Small energy savings can go a long way — check out our energy-efficiency tips for winter, as well as our year-round programs to help you use energy wisely….
#2 Search for Ecolabelled products and services
Domain Est. 2003
Website: svanen.se
Key Highlights: The Nordic Swan Ecolabel. The Nordic Swan Ecolabel is the official ecolabel of the Nordic countries. … RAW Wood Primer. Nordic Swan Ecolabel / RAW / . PP ……
#3 Black Swan barrels
Domain Est. 2010
Website: blackswanbarrels.com
Key Highlights: Black Swan Wood Products is a family-owned cooperage, crafting exceptional barrels and aging solutions for distilleries, breweries, and wineries of all sizes….
#4 Swans Island Company
Domain Est. 2013 | Founded: 1992
Website: swansislandcompany.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $300 30-day returnsHandcrafted blankets & apparel from Maine since 1992. Renowned for our award-winning handwoven blankets, Swans Island Company is committed to …
#5 Eco
Domain Est. 2016
Website: woodswan.com
Key Highlights: WOODSWAN supports eco-friendly sustainable living by creating modern, minimalistic, organic furnishings and architectural elements derived from rescued fallen ……
#6 J.W. Swan & Sons
Domain Est. 2020
Website: jwswanandsons.com
Key Highlights: Located on the South shore of Lake Superior in Northern Wisconsin, specializing in building and restoring wooden boats and canoes, felling and milling ……
#7 Wood materials & sustainable forestry
Domain Est. 2022
Website: nordic-swan-ecolabel.org
Key Highlights: Discover how the Nordic Swan Ecolabel ensures wood is sustainably sourced — at least 70% certified wood, traceability via FSC/PEFC, bans on illegal timber ……
#8 Black Swan Wood Products
Domain Est. 2024
Website: blackswanbarrelsshop.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the Store. Quality You Can Taste, Sustainability You Can Trust. Shop Best Sellers. Shop By Category: HONEY COMB®. Squarrel….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Swan Wood
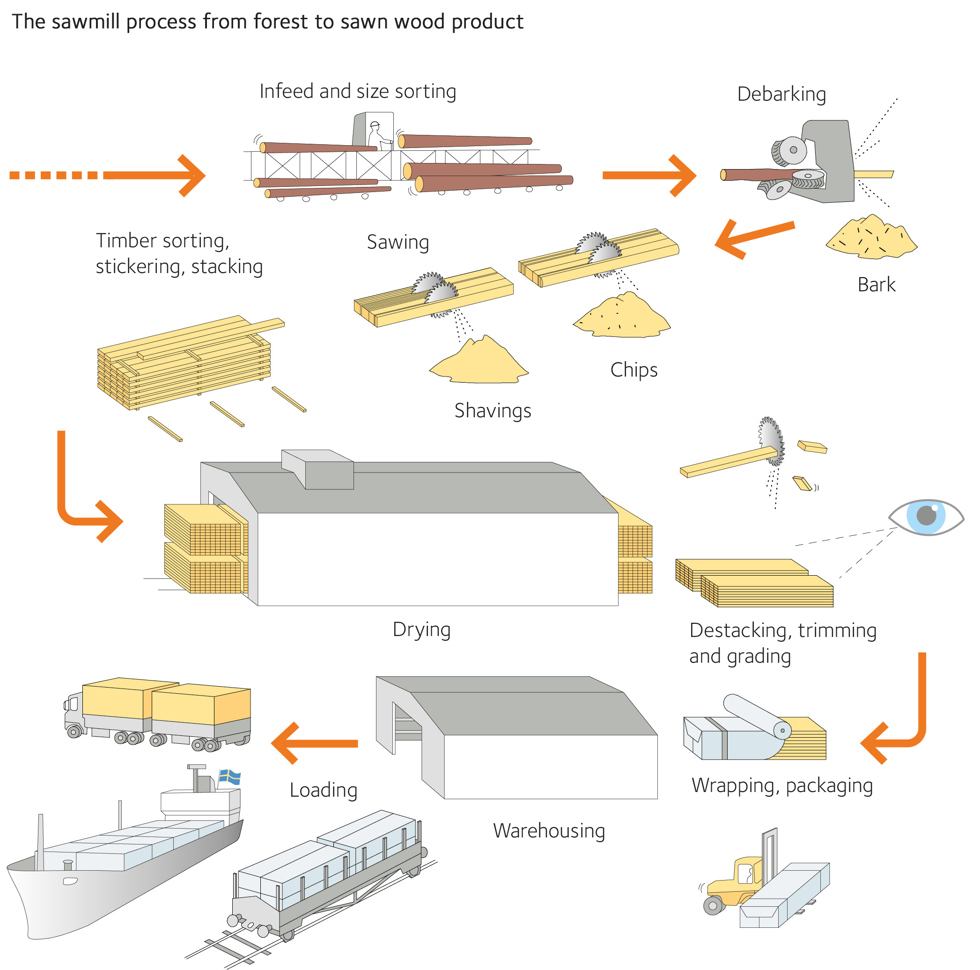
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Swan Wood
As of 2026, Swan Wood—a niche hardwood species known for its fine grain, durability, and aesthetic appeal in premium cabinetry and furniture—faces a dynamic market landscape shaped by sustainability demands, technological innovation, and evolving consumer preferences.
-
Sustainability and Certification Demand
By 2026, there is increased regulatory and consumer pressure for sustainable forestry practices. Swan Wood, which grows slowly and in limited regions, is now predominantly sourced from Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)-certified forests. Importers and manufacturers are prioritizing traceability, with blockchain-enabled supply chains gaining traction to verify ethical sourcing. This shift has led to a premium pricing structure for certified Swan Wood, reflecting both scarcity and environmental responsibility. -
Rising Demand in Luxury and Bespoke Markets
Swan Wood continues to be favored in high-end residential and commercial interior design. In 2026, the luxury furniture and architectural millwork sectors show strong growth, particularly in North America and Europe. Custom craftsmanship and artisanal appeal drive demand, with Swan Wood’s natural luster and workability making it a top choice for designers emphasizing timeless elegance. -
Competition from Alternative Materials
Despite its desirability, Swan Wood faces competition from engineered wood alternatives and sustainably fast-growing hardwoods like bamboo and eucalyptus. Innovations in wood modification technologies (e.g., acetylation and thermal treatment) have produced substitutes that mimic Swan Wood’s appearance and performance at lower cost and with greater environmental credentials. -
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Challenges
The primary growing regions of Swan Wood—located in parts of Southeast Asia and Oceania—have experienced tighter export regulations and climate-related yield fluctuations. In 2026, supply constraints have led to price volatility. Importers are diversifying sourcing strategies and investing in local reforestation initiatives to secure long-term access. -
Technology Integration in Processing
Adoption of CNC machining, AI-driven grain optimization, and digital finishing techniques has improved yield efficiency and reduced waste in Swan Wood manufacturing. These advancements allow producers to maximize value from limited raw material inputs, supporting profitability despite higher input costs. -
Consumer Shift Toward Heirloom and Low-Waste Design
A growing segment of eco-conscious consumers favors durable, repairable, and timeless furniture. Swan Wood aligns well with this “buy less, buy better” ethos. Brands emphasizing longevity, repair services, and circular design are successfully marketing Swan Wood products as sustainable investments.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Swan Wood market is characterized by premium positioning, sustainability-driven value chains, and resilience in luxury applications. While supply challenges and competition persist, strategic investments in certification, technology, and brand storytelling are enabling stakeholders to maintain relevance and profitability in an increasingly conscious marketplace.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Swan Wood (Quality, IP)
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Grading
One major pitfall when sourcing Swan Wood is encountering inconsistent quality due to lack of standardized grading. Suppliers may vary significantly in their assessment of color, grain pattern, and defect presence (such as knots or resin pockets). Without clear specifications or third-party verification, buyers risk receiving material that doesn’t meet project requirements, leading to delays or increased waste during fabrication.
Misrepresentation of Wood Origin and Species
Swan Wood—often referring to Acacia species or similar exotic hardwoods—can be misrepresented in terms of botanical origin. Some suppliers may label lower-grade or alternative species as Swan Wood to command higher prices. This mislabeling affects both quality and durability, and may result in legal or reputational risks if the material fails to perform as expected.
Lack of Chain-of-Custody and Sustainability Certification
Sourcing Swan Wood without proper chain-of-custody documentation increases the risk of supporting illegal logging or environmentally harmful practices. Buyers may unintentionally violate environmental regulations or corporate sustainability policies if the wood lacks certifications like FSC or PEFC, which verify responsible forestry practices.
Intellectual Property and Design Infringement Risks
When Swan Wood is used in premium furniture or design applications, there’s a risk of inadvertently infringing on protected designs or trade secrets. Some suppliers or manufacturers may offer products that mimic patented craftsmanship or proprietary finishes. Sourcing from unverified partners without IP indemnification can expose buyers to legal challenges, especially in high-end markets.
Inadequate Moisture Content and Pre-Conditioning
Swan Wood that hasn’t been properly dried or acclimatized can lead to warping, cracking, or joint failure after installation. Suppliers may overlook moisture content specifications, especially when shipping internationally. Failing to verify kiln-drying records or equilibrium moisture levels upon delivery can compromise the longevity and structural integrity of the finished product.
Limited Traceability and Supplier Transparency
Many Swan Wood suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, offer limited transparency about harvesting methods, processing, or treatment history. This lack of traceability makes it difficult to verify claims about quality, sustainability, or compliance with import regulations—leading to potential customs delays, fines, or consumer backlash.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Swan Wood
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance procedures for operations at Swan Wood. Adherence to these standards ensures safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance across all activities.
Site Access and Vehicle Management
All vehicles entering the Swan Wood site must be registered in the site access system prior to arrival. Drivers are required to present valid identification and complete a site induction if visiting for the first time. Speed limits are strictly enforced at 15 mph throughout the site. Designated parking and loading zones must be used at all times—unauthorized parking may result in towing.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Compliance
Swan Wood operates under strict health and safety protocols in accordance with the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 and related regulations. All personnel must wear appropriate PPE (hard hat, high-visibility clothing, safety footwear) at all times on site. Risk assessments must be conducted for all tasks, and safety data sheets (SDS) must be available for all hazardous materials handled. Environmental compliance includes adherence to waste disposal regulations, control of emissions, and prevention of soil and water contamination in line with the Environmental Protection Act 1990.
Goods In and Out Procedures
All incoming and outgoing shipments must be logged in the warehouse management system. Goods received must be inspected for damage and matched against purchase orders and delivery notes. Documentation, including consignment notes and proof of delivery (POD), must be retained for a minimum of five years. Export shipments require accurate classification under the UK Trade Tariff and completion of necessary export declarations via the CHIEF or CDS system where applicable.
Regulatory Compliance and Audits
Swan Wood complies with all relevant UK and EU regulations, including REACH, CLP, and the Customs and International Trade Act 1988. Regular internal audits will be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance. External audits by regulatory bodies or certification agencies (e.g., FORS, ISO) may occur with minimal notice; all staff are expected to cooperate fully and maintain accurate records.
Incident Reporting and Emergency Procedures
Any accidents, near misses, or compliance breaches must be reported immediately to the site safety officer using the designated incident reporting form. Emergency procedures—including fire evacuation, chemical spill response, and first aid—are posted at key locations throughout the site. All personnel must participate in quarterly emergency drills and be familiar with the location of fire exits, assembly points, and emergency equipment.
Training and Certification Requirements
All logistics personnel must hold valid certifications for relevant duties, including forklift operation, ADR (if handling dangerous goods), and manual handling. Refresher training is required annually. Compliance training, including data protection (UK GDPR) and anti-bribery policies, must be completed upon onboarding and every 12 months thereafter.
Data Protection and Record Keeping
Personal and operational data collected during logistics operations must be handled in accordance with the UK General Data Protection Regulation (UK GDPR). Access to sensitive data is restricted to authorized personnel only. Digital and physical records must be securely stored and retained per the company’s data retention policy—typically seven years for financial and compliance-related documentation.
In conclusion, sourcing Swan Wood—assuming this refers to a specific or specialty timber (potentially a misnomer or regional name; note that “Swan Wood” is not a widely recognized commercial timber species)—requires careful due diligence to ensure sustainability, legality, and quality. It is essential to verify the correct botanical name and origin of the wood to avoid misidentification and potential environmental harm. Responsible sourcing involves procuring from suppliers who adhere to certified forestry practices (such as FSC or PEFC), maintain transparent supply chains, and comply with international regulations like CITES when applicable.
If “Swan Wood” refers to a proprietary or branded product, direct engagement with trusted manufacturers or distributors becomes crucial. Additionally, considering the ecological impact, availability, and potential alternatives is advisable to support long-term sustainability. Ultimately, successful sourcing hinges on a balance between material authenticity, ethical procurement, and environmental stewardship.