The global sulfur market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from key end-use industries such as fertilizers, chemicals, and petroleum refining. According to Grand View Research, the global sulfur market size was valued at USD 13.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is largely attributed to rising agricultural activities and the escalating need for sulfur-based compounds in industrial applications. As elemental sulfur continues to play a vital role in crop nutrition and chemical synthesis, the demand for reliable and high-purity sulfur products—such as sulfur sticks—has intensified. These stick-form sulfur variants are particularly favored in precision agriculture, pest control, and niche manufacturing processes due to their ease of handling and controlled release. With market dynamics favoring quality and scalability, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, production capacity, and global reach. Based on market presence, product quality, and industry reputation, the following nine companies represent the forefront of sulfur stick manufacturing worldwide.
Top 9 Sulphur Sticks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Anhydrous Ammonia Sulphur Sticks
Domain Est. 2008
Website: industrialsolutionservices.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Solution Services Sulphur Sticks for anhydrous ammonia….
#2 Pack of 10 Sulfur Sticks in a Water Tight Tube
Domain Est. 2010
Website: keepsupply.com
Key Highlights: In stock $23.24 deliverySulfur sticksare used in industrial ammonia refrigeration systems to detect minor ammonia leaks. A sulfur stick is made from a wick which contains particles…
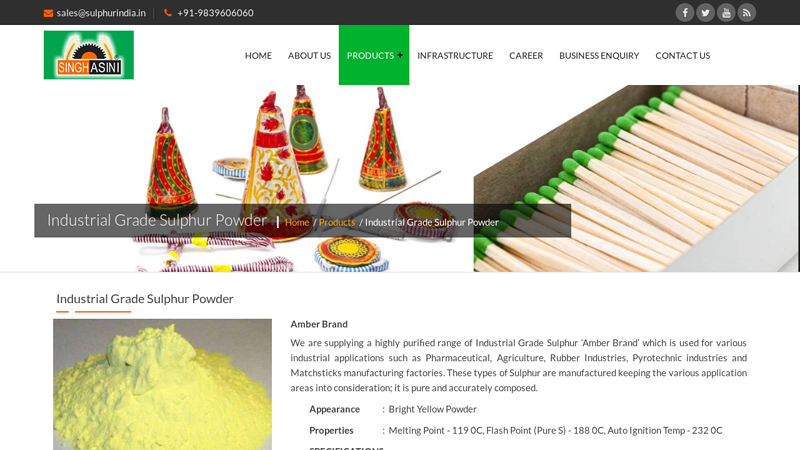
#3 Industrial Grade Sulphur Powder
Domain Est. 2013
Website: sulphurindia.in
Key Highlights: We are supplying a highly purified range of Industrial Grade Sulphur ‘Amber Brand’ which is used for various industrial applications….
#4 Leading Manufacturer & Supplier of Sulphur Rolls & Sticks in India
Domain Est. 2015
Website: vasmatesulphur.com
Key Highlights: We provide high-quality Sulphur rolls at an affordable price. The Sulphur roll offered by us is 99.98% pure & free from arsenic compounds….
#5 Sulfur Stick: Detecting Hydrogen Sulfide in Landfills
Domain Est. 1997
Website: scsengineers.com
Key Highlights: Detect hydrogen sulfide fast with a sulfur stick. Improve landfill gas safety, monitor H₂S levels, and support compliance with reliable ……
#6 Sulfur sticks and hot work requirements
Domain Est. 1997
Website: osha.gov
Key Highlights: A sulfur stick is a tool used to find ammonia gas leaks. Sulfur sticks, when burned, react with ammonia gas to make a visible smoke and are generally used near ……
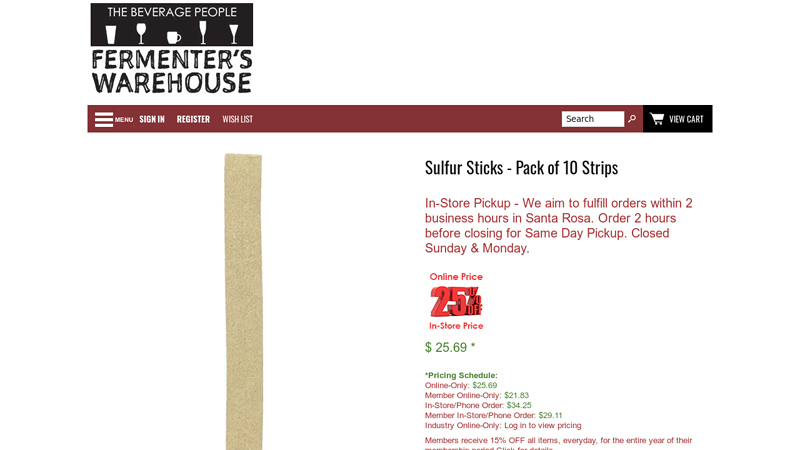
#7 Sulfur Sticks – Pack of 10 Strips
Domain Est. 2000
#8 Sulphur
Domain Est. 2023
Website: uplcorp.com
Key Highlights: Sulphur is a classical product which provides effective control of powdery mildew in Fruits and vegetables simultaneously provides nutrition to crops….
#9 High
Domain Est. 2010
Website: mkchemicals.com
Key Highlights: In stockDiscover top-grade Sulphur Sticks with 99.5% purity. Ideal for foundries, they offer precise pH value, accurate composition, and high effectiveness….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sulphur Sticks

As of now, there are no widely recognized market intelligence reports or established industry forecasts specifically for “Sulphur Sticks” extending to 2026 under standard commodity or consumer product classifications. However, based on the term “Sulphur Sticks,” which commonly refers to sulfur-based pest control products—particularly sulfur candles or sulfur fumigation sticks used in organic farming, winemaking, or mold remediation—we can project potential market trends for 2026 using insights from related industries, including agriculture, organic viticulture, indoor air quality, and sustainable pest management.
Below is an analysis of 2026 market trends for Sulphur Sticks using an H2-style structure (i.e., second-level headings for thematic organization):
Growing Demand in Organic Agriculture
Organic farming continues to expand globally, driven by consumer demand for chemical-free produce and stricter regulations on synthetic pesticides. Sulphur sticks, which release sulfur dioxide (SO₂) when burned, are approved for use in organic farming by bodies such as the USDA National Organic Program (NOP) and the EU Organic Regulation. Their role in controlling fungal diseases like powdery mildew in crops (e.g., grapes, strawberries, and hops) supports sustained demand.
- Market Drivers: Expansion of organic vineyards and high-value crops in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
- Trend Projection for 2026: Steady 4–6% CAGR in demand for sulfur-based fumigation tools in organic agriculture, particularly in regions with rising organic certification rates.
Expansion in Viticulture and Winemaking
Sulphur sticks are traditionally used in winemaking to sanitize barrels, tanks, and storage areas. The global growth in boutique and organic wineries is increasing the need for reliable, low-residue sanitization methods.
- Key Use Case: Fumigation of oak barrels with sulfur sticks prevents microbial contamination without leaving harmful residues.
- 2026 Outlook: As artisanal and sustainable winemaking grows—especially in regions like California, France, Italy, and Australia—the demand for food-grade sulfur sticks is expected to rise. The market may see product innovation, such as pre-measured or encapsulated sulfur sticks for safer handling.
Rising Awareness in Mold and Indoor Air Quality Management
In residential and commercial remediation, sulfur sticks are sometimes used (especially in certain traditional or alternative practices) for mold fumigation. While this use is less regulated and often controversial due to safety concerns, it persists in niche markets.
- Regulatory Caution: Health authorities like the EPA and OSHA caution against improper use due to SO₂ toxicity.
- Market Trend: Despite risks, demand may grow in DIY and off-grid communities. In 2026, we may see increased scrutiny or labeling requirements, pushing manufacturers toward safer, controlled-release formulations or hybrid alternatives.
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Environmental policies are shaping the availability and use of sulfur-based products. While elemental sulfur is naturally occurring and considered low-toxicity, the release of SO₂ is regulated due to its environmental and respiratory impacts.
- Regional Differences: Stricter air quality controls in the EU and North America may limit outdoor or large-scale use, but indoor or enclosed-system applications may remain exempt.
- 2026 Implication: Market growth may be tempered by regulatory pressures, but innovation in controlled-release sulfur technologies could open new compliant applications.
Supply Chain and Raw Material Availability
Sulfur is a byproduct of petroleum refining and natural gas processing, making its supply tied to the energy sector. As the world transitions toward cleaner energy, sulfur supply may remain abundant due to continued fossil fuel processing (especially desulfurization).
- Price Stability: High global sulfur inventory (e.g., from sour gas processing in Canada and the Middle East) is expected to keep raw material costs low through 2026.
- Impact on Sulphur Sticks: Stable input costs support affordable pricing and healthy margins for manufacturers.
Regional Market Dynamics
- Europe: Strong demand in organic viticulture; regulatory framework supports approved uses.
- North America: Growth in organic farming and home winemaking drives retail sales.
- Asia-Pacific: Emerging interest in organic agriculture, especially in India and China, may boost adoption by 2026.
- Latin America: Expanding wine industries in Argentina and Chile could increase commercial demand.
Innovation and Product Differentiation
By 2026, expect to see:
– Pre-portioned, easy-to-use sulfur sticks for home winemakers.
– Eco-labeling and organic certification on packaging.
– Integration with IoT for controlled fumigation in commercial settings.
– Safety-focused designs (e.g., smoke-reduced or timed-release variants).
Conclusion
The Sulphur Sticks market in 2026 is poised for moderate but steady growth, primarily driven by the organic agriculture and winemaking sectors. Regulatory landscapes and safety concerns will shape usage patterns, while innovation and sustainability trends will influence product development. Although not a high-volume commodity, sulfur sticks will maintain relevance in niche, high-value applications where natural and residue-free solutions are preferred.
Note: “Sulphur” (British spelling) is used interchangeably with “Sulfur” (American spelling); market data typically uses “sulfur.” The term “Sulphur Sticks” is not a standardized industrial category, so projections are inferred from adjacent markets.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Sulphur Sticks – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing sulphur sticks, commonly used in fumigation, pest control, and certain industrial or traditional applications, involves several critical challenges—particularly related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Understanding these pitfalls is essential for ensuring safety, compliance, and effectiveness.
1. Inconsistent Quality and Purity
- Impurity Risks: Low-quality sulphur sticks may contain contaminants such as heavy metals, ash, or organic residues that reduce efficacy and pose health and safety hazards.
- Variable Burn Rates: Poor manufacturing can lead to inconsistent combustion, affecting fumigation efficiency and making dosage control unreliable.
- Lack of Standardization: Suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, may not adhere to international standards (e.g., ASTM or ISO), resulting in non-uniform product specifications.
2. Mislabeling and Adulteration
- Some suppliers falsely advertise high-purity sulphur (e.g., 99.9%) when the actual product contains fillers or alternative compounds.
- Adulterated sticks may include cheaper materials like paraffin or inert powders, compromising safety and performance.
3. Inadequate Packaging and Shelf Life
- Poor packaging can lead to moisture absorption, caking, or degradation, reducing shelf life and reactivity.
- Lack of proper storage guidance from suppliers increases the risk of handling issues and reduced effectiveness over time.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
- Patented Formulations or Designs: Some sulphur stick products incorporate proprietary blends, slow-release technologies, or specialized casings protected by patents. Sourcing generic copies without due diligence may lead to IP infringement.
- Trademark Violations: Copying branded packaging or using similar names/logos can expose buyers or distributors to legal action, especially when importing into regions with strong IP enforcement (e.g., EU, USA).
- Reverse Engineering Risks: Attempting to replicate patented sulphur stick designs—even for internal use—can breach IP laws if not conducted under legal exemptions.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Gaps
- Sulphur sticks may be regulated as hazardous materials depending on their formulation and use. Non-compliant products may lack proper safety data sheets (SDS), hazard labeling, or transport certification.
- Importing into certain countries without verifying compliance with local chemical regulations (e.g., REACH, EPA guidelines) can result in shipment rejection or fines.
6. Unverified Suppliers and Counterfeit Goods
- Online marketplaces and third-party vendors may offer attractive pricing but lack transparency in sourcing or manufacturing.
- Counterfeit products may mimic reputable brands but fail to meet safety or performance standards, posing operational and legal risks.
Recommendations:
- Source from certified suppliers with verifiable quality control processes (e.g., ISO-certified manufacturers).
- Request material test reports (MTRs) and certificates of analysis (CoA) for each batch.
- Conduct IP due diligence—review patent databases and consult legal experts when replicating or sourcing similar products.
- Verify compliance with local and international regulations before procurement and shipment.
Avoiding these common pitfalls ensures not only the effectiveness and safety of sulphur sticks but also protects your organization from legal and reputational risks.
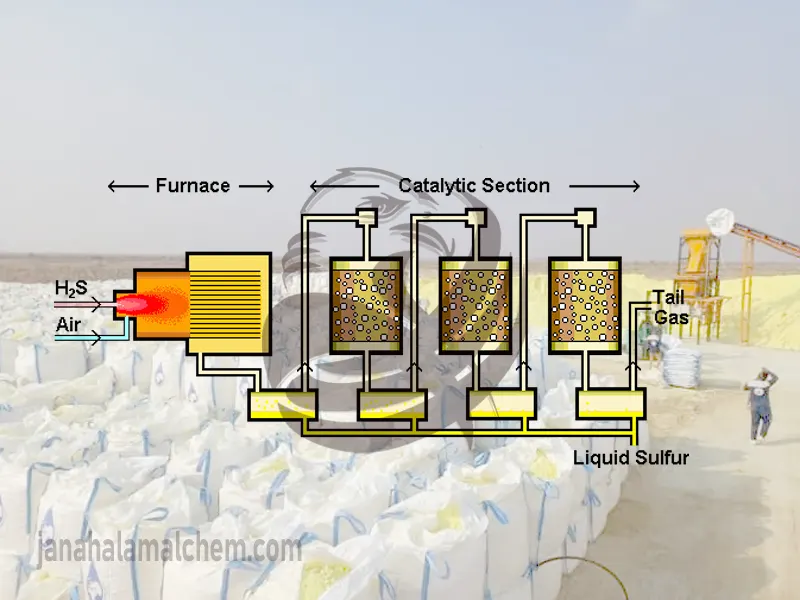
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sulphur Sticks (Sulfur Sticks)
Sulphur sticks (commonly known as sulfur sticks or flower of sulfur sticks) are used in various applications, including winemaking (for sanitizing equipment), organic farming (as a fungicide), and certain traditional practices. Due to their chemical nature and potential hazards, strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed during handling, storage, transport, and disposal.
1. Regulatory Classification & Identification
- Chemical Name: Elemental Sulfur (S)
- CAS Number: 7704-34-9
- UN Number: UN 1350
- Proper Shipping Name: SULFUR
- Hazard Class: 4.1 (Flammable Solids)
- Packing Group: III (Low danger)
- GHS Classification:
- Flammability: Category 1 (Flammable solid)
- Health Hazard: Not classified (low toxicity)
- Environmental Hazard: Not classified
- Labeling: Diamond label with “4.1 FLAMMABLE SOLID” and flame symbol.
Note: While elemental sulfur is not highly toxic, it can release toxic sulfur dioxide (SO₂) when burned or heated, which is a significant respiratory hazard.
2. Packaging Requirements
- Material Compatibility: Use non-reactive, sealed containers (e.g., HDPE plastic, multi-wall paper bags with poly liner, or fiber drums).
- Moisture Protection: Keep dry – moisture can promote caking or microbial growth.
- Labeling: All packages must display:
- Proper shipping name
- UN number (UN 1350)
- Class 4.1 hazard label
- GHS pictograms
- Net weight
- Shipper/consignee information
- Overpacking: If inner containers are less than 5 kg, pack in overpacks that meet performance standards (e.g., 4G fiberboard box).
3. Storage Guidelines
- Location: Dry, cool, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight.
- Segregation: Store away from:
- Oxidizing agents (e.g., nitrates, chlorates)
- Strong acids (can release toxic SO₂)
- Ignition sources (open flames, sparks, hot surfaces)
- Temperature: Avoid temperatures above 115°C (sulfur melts at ~115°C and may ignite if dispersed as dust).
- Fire Risk: Sulfur dust is combustible. Prevent dust accumulation. Use grounding and bonding where applicable.
- Duration: No strict expiration, but monitor for caking or contamination.
4. Transportation (Road, Air, Sea)
Road (ADR – Europe) / DOT (USA)
- Placarding: Vehicles carrying ≥ 454 kg (1,000 lbs) gross weight must display Class 4.1 placards.
- Documentation: Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and transport documents must include:
- Proper shipping name
- UN number
- Hazard class
- Net quantity
- Emergency contact
- Load Securing: Prevent shifting and damage during transit.
Air (IATA DGR)
- Allowed in passenger and cargo aircraft under Packing Instruction 408 (limited quantities permitted).
- Maximum net quantity per package: 25 kg.
- Prohibited if mixed with accelerants or other hazardous materials.
- Packaging: Must pass drop and stacking tests.
Sea (IMDG Code)
- Marine Pollutant: No
- Stowage Category: A (may be stowed “on” or “under” deck)
- Segregation: Keep away from oxidizing substances (e.g., Class 5.1 materials).
- Documentation: Transport Declaration with all required details.
5. Handling & Worker Safety
- PPE Requirements:
- Nitrile or neoprene gloves
- Safety goggles
- Dust mask (N95 or equivalent) if handling powder or generating dust
- Flame-resistant clothing in industrial settings
- Ventilation: Use in well-ventilated areas. Avoid confined spaces.
- No Smoking: Strictly prohibited in handling and storage zones.
- Spill Response:
- Sweep up carefully (avoid creating dust).
- Place in sealed container for disposal.
- Do not use water jets (can spread dust).
- Evacuate area if large spill or fire occurs.
6. Fire Safety
- Fire Hazard: Sulfur dust is flammable. Molten sulfur can ignite and burn with release of SO₂.
- Extinguishing Media:
- Water spray (to cool surrounding areas, not directly on molten sulfur)
- Sand or dry chemical extinguishers
- Avoid: High-pressure water on molten sulfur (can cause steam explosions).
- Evacuation: In case of fire, evacuate upwind due to SO₂ risk.
- Emergency Response: Contact local fire department with hazardous materials (HAZMAT) capability.
7. Documentation & Compliance
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Must be current (GHS-compliant, 16-section format) and available to all handlers.
- Transport Documents: Include UN number, proper shipping name, hazard class, and emergency info.
- Training: Personnel must be trained in:
- Hazard communication (HazCom)
- Emergency procedures
- Use of PPE
- ADR/IATA/IMDG as applicable
- Recordkeeping: Maintain shipping records, training logs, and SDS access logs for at least 3 years (per OSHA and transport regulations).
8. Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- Disposal: Follow local, state, and federal regulations. May be disposed of as non-hazardous solid waste if uncontaminated.
- Environmental Impact: Low ecotoxicity, but avoid release into waterways.
- Incineration: Only in permitted facilities with SO₂ scrubbing.
- Never pour down drains or into soil without regulatory approval.
9. Special Considerations by Use Case
- Winemaking/Sanitization:
- Ensure sticks are food-grade (high purity, no additives).
- Label as “For Equipment Sanitation – Not for Consumption.”
- Agricultural Use:
- Follow EPA/FDA or local agricultural authority guidelines.
- Observe pre-harvest intervals (PHI) if used as a fungicide.
- Religious/Cultural Use:
- Comply with local ordinances (e.g., open burning restrictions).
10. Compliance Checklist
| Item | Required? |
|——|———–|
| GHS-compliant SDS available | ✅ |
| Proper UN 1350 labeling on packages | ✅ |
| Class 4.1 hazard labels applied | ✅ |
| Storage away from oxidizers and heat | ✅ |
| PPE available and used | ✅ |
| Fire extinguisher (Class D or dry chemical) accessible | ✅ |
| Personnel trained in handling & emergency | ✅ |
| Transport documents complete | ✅ |
| Spill kit available (non-sparking tools, container) | ✅ |
Final Note: Regulations vary by country. Always verify compliance with local authorities (e.g., EPA, OSHA, ECHA, DOT, IATA, IMDG). When in doubt, consult a Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor (DGSA) or regulatory expert.
This guide is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or regulatory advice.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sulphur Sticks
In conclusion, sourcing sulphur sticks requires careful consideration of quality, supplier reliability, regulatory compliance, and intended application—whether for agriculture, fumigation, pharmaceuticals, or industrial use. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to safety and environmental standards, provide consistent product purity, and offer transparent documentation. Evaluating cost-effectiveness should not overshadow the importance of safety certifications and proper handling protocols, particularly given the hazardous nature of sulphur in certain conditions. By conducting thorough due diligence and prioritizing responsible sourcing practices, organizations can ensure the effective and safe use of sulphur sticks while minimizing risks to health, safety, and the environment.