The global steel milling market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand from construction, automotive, and heavy machinery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steel market size was valued at USD 1.47 trillion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2024 to 2030. This growth trajectory underscores the critical role of precision steel milling in modern manufacturing, where tight tolerances and high durability are non-negotiable. As industries demand higher performance materials and efficient production processes, steel milling manufacturers are investing in advanced CNC technologies, automation, and sustainable practices to maintain competitiveness. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, distinguished by their innovation, scale, and global footprint. The following list highlights the top 10 steel milling manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through technological excellence and strategic market positioning.
Top 10 Steel Milling Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#2 Nucor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nucor.com
Key Highlights: North America’s largest steel manufacturer and recycler. We are a team forged around a vision for leading our industry by providing unparalleled customer care….
#3 UNITED MACHINING
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gfms.com
Key Highlights: UNITED MACHINING delivers comprehensive, integrated solutions for manufacturers of precision parts, tools, and mold-making — helping them move seamlessly ……
#4 EVRAZ North America
Domain Est. 2008
Website: evrazna.com
Key Highlights: EVRAZ North America is a frontrunner in engineering and producing steel products for rail, energy, and industrial end markets….
#5 Mill Products
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cmc.com
Key Highlights: Our mills produce steel long products including rebar, angles, channels, flats, rounds, squares, post, wire rod and other special sections….
#6 Kennametal
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kennametal.com
Key Highlights: Kennametal is a leading provider of productivity solutions for metalworking, earth cutting, and wear components, coatings, and powders….
#7 Mill Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millsteel.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in a comprehensive range of flat-rolled steel and aluminum. All of our products are evaluated and tested to ensure quality of metal and precision ……
#8 Delta Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: deltasteel.com
Key Highlights: Delta Steel is your one-stop-shop for all your structural steel needs. We can guarantee customer satisfaction built with steel!…
#9 Metal Fabrication Machinery
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mcmachinery.com
Key Highlights: MC Machinery Systems, a supplier of metal fabrication machines, provides EDM, milling, laser, press brake, finishing, and automation solutions….
#10 Ternium, a steel manufacturing company
Domain Est. 2005
Website: us.ternium.com
Key Highlights: Need steel for Metal Building. At Ternium we manufacture high-quality products to supply housing and infrastructure works. Used in the roofs of houses and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Steel Milling
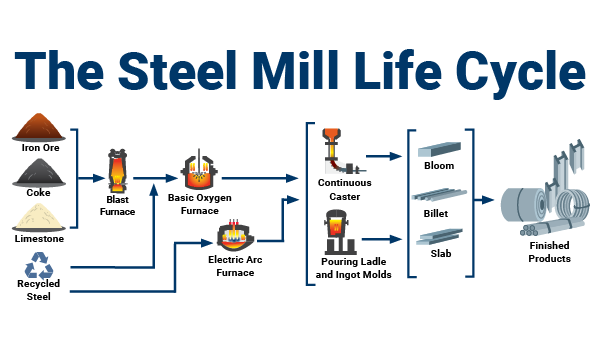
H2: Projected Market Trends in Steel Milling for 2026
As we approach 2026, the global steel milling industry is poised for significant transformation driven by technological innovation, regulatory shifts, evolving demand patterns, and increased emphasis on sustainability. Steel milling—the process of shaping steel into usable forms such as sheets, bars, and plates through rolling, cutting, and finishing—plays a critical role in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and energy sectors. The following analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape the steel milling landscape in 2026.
1. Accelerated Adoption of Digitalization and Industry 4.0 Technologies
By 2026, steel mills are expected to be deeply integrated with smart manufacturing technologies. The use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) will optimize milling processes by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced quality control. Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical milling operations—will allow operators to simulate production scenarios, reducing downtime and improving efficiency. This digital transformation is projected to increase overall productivity by 15–20% across leading steel-producing regions.
2. Growing Demand for High-Strength and Specialty Steels
The automotive and aerospace industries are driving demand for advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) and specialty alloys that offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and formability. In response, steel mills are investing in precision milling technologies capable of handling complex alloy compositions and thinner gauges with tighter tolerances. The shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) further amplifies this trend, as lightweight steel components are essential for improving battery efficiency and vehicle range.
3. Sustainability and Decarbonization Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing steel producers to reduce carbon emissions. By 2026, many steel mills are expected to transition toward low-carbon production methods, including the integration of electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) technologies. These changes will influence milling operations, requiring adaptations in temperature control, material handling, and energy sourcing. Mills that demonstrate lower carbon footprints will likely gain a competitive edge in markets with strict emissions standards, such as the European Union and North America.
4. Regional Shifts in Production and Trade Dynamics
Asia, particularly China and India, will remain dominant in steel milling output, but trade patterns are expected to evolve. China’s focus on high-value steel products and domestic consumption may reduce exports of lower-grade milled steel, creating opportunities for producers in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. Meanwhile, the U.S. and EU are expected to strengthen domestic steel milling capacity through reshoring initiatives and trade protections aimed at ensuring supply chain resilience.
5. Increased Automation and Workforce Transformation
Labor shortages and rising operational costs are accelerating automation in steel mills. By 2026, robotic arms, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and computerized process control systems will be standard in modern milling facilities. While this reduces manual labor requirements, it increases demand for skilled technicians and data analysts capable of managing and maintaining advanced systems. Workforce upskilling programs will become a strategic priority for steel producers.
6. Rising Raw Material and Energy Cost Volatility
Fluctuations in iron ore, scrap metal, and energy prices will continue to challenge steel milling operations. In response, mills are expected to adopt more flexible production models and invest in energy-efficient technologies. On-site renewable energy installations, such as solar and wind, may become more common to mitigate electricity costs and improve ESG credentials.
7. Expansion of Circular Economy Practices
Recycling and reuse of scrap steel will gain prominence as part of the circular economy. EAF-based steelmaking, which relies primarily on recycled scrap, supports this shift and aligns with green manufacturing goals. Mills investing in closed-loop systems and scrap sorting technologies will benefit from reduced material costs and improved sustainability metrics.
Conclusion
By 2026, the steel milling industry will be characterized by smarter, cleaner, and more agile operations. Success will depend on the ability of producers to embrace digital transformation, adapt to sustainability mandates, and meet the growing demand for high-performance steel products. Companies that proactively invest in innovation, workforce development, and supply chain resilience will lead the market in the next phase of industrial evolution.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Steel Milling Services: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing steel milling services, particularly for precision components or proprietary designs, introduces significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to manage these areas can lead to costly delays, legal disputes, and compromised competitiveness.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inadequate Supplier Qualification: Selecting a milling provider based solely on price or proximity without thoroughly vetting their capabilities, equipment calibration, quality control processes (e.g., ISO 9001 certification), and track record with similar materials and tolerances often results in subpar output, high scrap rates, and rework.
- Unclear or Insufficient Specifications: Providing vague drawings, incomplete tolerances, or undefined surface finish requirements leaves room for interpretation, leading to parts that don’t meet functional needs, even if they technically pass a basic inspection.
- Lack of Robust Quality Assurance (QA) Protocols: Failing to establish clear in-process inspections, final inspection criteria (including acceptance sampling plans), and requirements for material traceability (e.g., mill test reports) increases the risk of receiving non-conforming batches.
- Material Verification Neglect: Not requiring or verifying the mill test reports (MTRs) for the specific steel grade used can lead to incorrect material properties, impacting part performance and potentially causing failures in the field.
- Process Capability Mismatch: Assuming a supplier can hold tight tolerances without verifying their actual process capability (Cp/Cpk) for the specific machining operations required can result in parts that are consistently out of spec.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
- Absence of a Comprehensive NDA: Engaging a supplier without a legally binding Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) that explicitly covers all provided information (drawings, specifications, processes, business plans) leaves your IP vulnerable to unauthorized use or disclosure.
- Insufficient IP Clauses in Contracts: Failing to include clear clauses in the master services agreement or purchase order regarding ownership of designs, tooling, and any IP developed during the project, as well as restrictions on reverse engineering, creates ambiguity and potential disputes.
- Over-Exposure of Sensitive Data: Sharing full, unredacted design files containing proprietary features or trade secrets without necessity, or without technical safeguards, increases the risk of IP theft or replication.
- Lack of Control Over Tooling and Fixtures: Not specifying ownership and secure storage requirements for custom tooling, jigs, or fixtures created for your parts can allow a supplier to use them for competitors or demand exorbitant fees for their return.
- Inadequate Supplier Vetting for IP Security: Not assessing the supplier’s internal security measures (physical security, IT security, employee NDAs, access controls) to protect sensitive information they will handle increases the risk of data breaches or industrial espionage.
- Jurisdictional Risks: Sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement regimes significantly increases the risk of design copying and competition from counterfeit parts, even with strong contracts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Steel Milling Operations
Steel milling involves complex logistics and stringent regulatory requirements to ensure safety, quality, and environmental responsibility. This guide outlines key considerations in managing the transportation, handling, and compliance aspects of steel milling operations.
Supply Chain & Raw Material Logistics
Efficient logistics begin with reliable sourcing and transportation of raw materials such as iron ore, coal, scrap metal, and alloying elements. Coordination with suppliers, rail carriers, shipping lines, and trucking companies is critical to maintain continuous production. Bulk materials are often delivered via rail or maritime transport, requiring transloading infrastructure at port or rail terminals. Just-in-time inventory strategies must be balanced with buffer stock to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
In-Plant Material Handling
Internal logistics within the steel mill include ladle transfer systems, overhead cranes, conveyors, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). Proper routing and scheduling of molten metal and semi-finished products (slabs, blooms, billets) are essential for operational efficiency and worker safety. Thermal management and structural integrity of handling equipment must be regularly monitored to prevent accidents.
Finished Product Distribution
Finished steel products—such as coils, plates, bars, and structural sections—are distributed via rail, truck, or vessel depending on destination and volume. Load optimization, proper packaging (e.g., strapping, coating, wrapping), and protection against corrosion are vital to maintain product quality. Distribution centers and third-party logistics (3PL) providers may be used to serve regional or international markets.
Regulatory Compliance Overview
Steel milling is subject to multiple regulatory frameworks at the local, national, and international levels. Compliance ensures operational legality, worker safety, and environmental protection.
Environmental Regulations
Steel mills must comply with air and water emission standards, waste management protocols, and noise control regulations. Key requirements include:
- Emissions Control: Compliance with limits on particulate matter, sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as per EPA (U.S.), EU Industrial Emissions Directive, or equivalent local standards.
- Wastewater Treatment: Proper treatment of process water and runoff to remove heavy metals and oils before discharge.
- Waste Disposal: Safe handling and disposal of slag, dust, and sludge in accordance with hazardous waste regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.).
- Carbon Reporting: Mandatory greenhouse gas (GHG) reporting under programs such as the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) or the U.S. GHG Reporting Program.
Occupational Health & Safety (OHS)
Worker safety is paramount in high-risk steel milling environments. Compliance with OHS regulations includes:
- Adherence to OSHA (U.S.), HSE (UK), or equivalent national safety standards.
- Implementation of lockout/tagout (LOTO), confined space entry, and hot work permit systems.
- Provision of personal protective equipment (PPE) including heat-resistant clothing, helmets, gloves, and respiratory protection.
- Regular training, emergency drills, and incident reporting procedures.
Transportation & Hazardous Materials Compliance
When shipping certain steel products or by-products (e.g., molten metal, scale, or coated materials), regulations for hazardous or dangerous goods may apply:
- DOT (U.S.) / ADR (Europe): Classification, labeling, placarding, and documentation for materials transported by road.
- IMDG Code: Compliance for maritime transport of steel products that may be classified as hazardous (e.g., oily scrap or chemically treated coils).
- Rail Transport Regulations: FRA (U.S.) or ERA (EU) standards for secure loading and rail car integrity.
Quality & Industry Standards
Steel products must meet recognized quality specifications to ensure market acceptance and regulatory compliance:
- ASTM, ISO, EN Standards: Adherence to mechanical, chemical, and dimensional specifications.
- Mill Test Certificates (MTCs): Documentation of material composition and mechanical properties for traceability.
- Certifications: ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and OHSAS 18001 / ISO 45001 (Safety).
Import/Export & Trade Compliance
International shipments require adherence to customs regulations, trade agreements, and anti-dumping laws:
- Accurate HS code classification for tariffs and duties.
- Compliance with export controls (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) for dual-use technologies.
- Adherence to sanctions lists and denied party screening.
- Proper documentation including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Recordkeeping & Audits
Maintaining comprehensive records is essential for compliance verification:
- Environmental monitoring data (emissions, effluents).
- Safety training logs and incident reports.
- Maintenance records for pollution control and material handling equipment.
- Chain-of-custody documentation for raw materials and finished goods.
Regular internal and third-party audits help ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance in steel milling require integrated planning, robust systems, and continuous monitoring. By aligning operational practices with regulatory requirements and industry best practices, steel mills can enhance safety, reduce environmental impact, and maintain competitiveness in global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Steel Milling
In conclusion, sourcing steel milling services requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead times, and supplier reliability. The selection of the appropriate steel grade, milling technique, and a capable manufacturing partner is critical to ensuring the performance and durability of end components, especially in demanding industries such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
Key considerations include evaluating supplier credentials, technical capabilities, quality control processes, and adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Additionally, factors such as geographic location, logistics, scalability, and communication efficiency play a significant role in maintaining a smooth supply chain.
By conducting thorough due diligence, leveraging supplier audits, and fostering long-term partnerships, companies can secure consistent, high-precision milling services that meet technical specifications and support overall operational efficiency. Ultimately, effective sourcing of steel milling contributes to improved product quality, reduced production downtime, and enhanced competitiveness in the market.











