Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Stand Robotics China Company

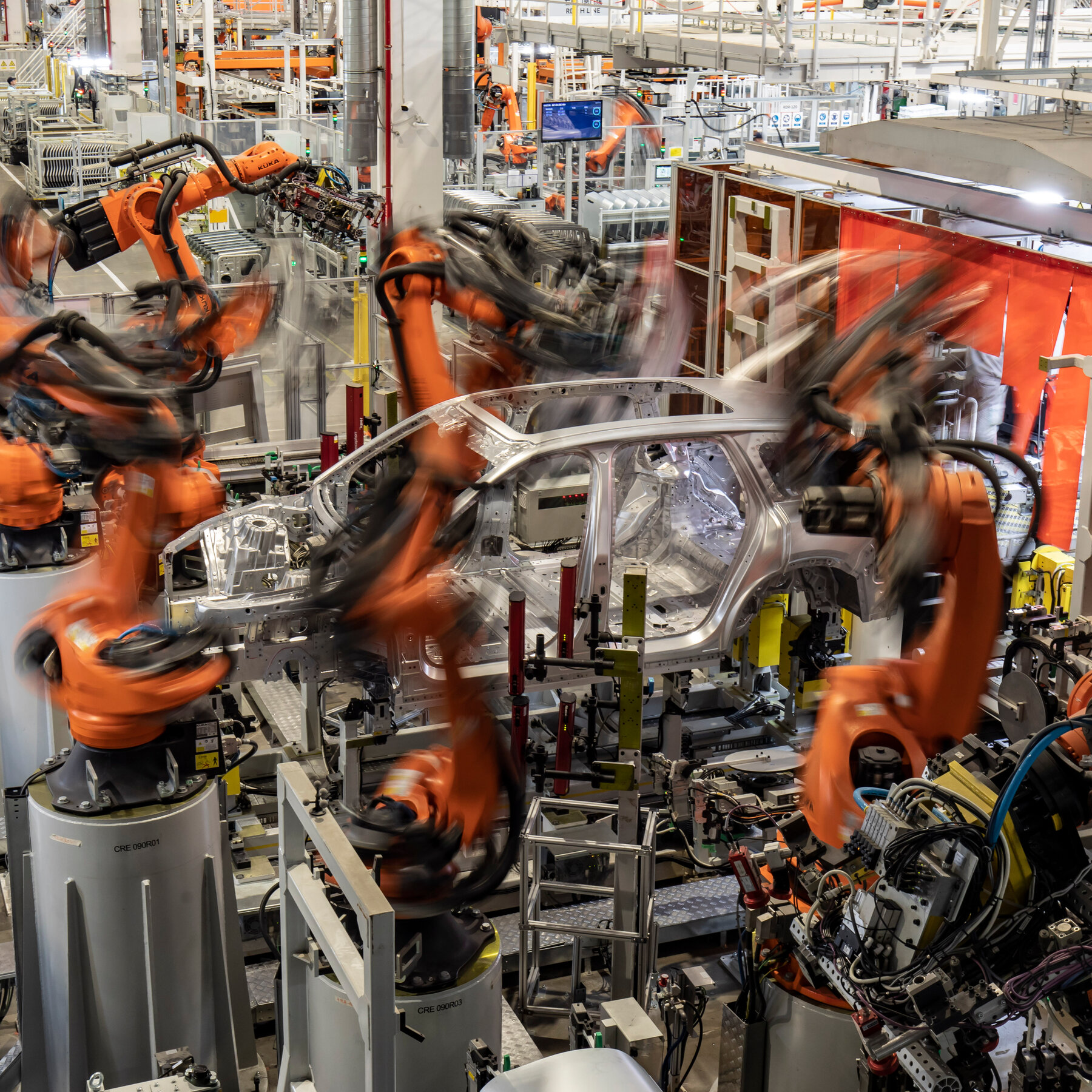
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Stand Robotics from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
The Chinese robotics manufacturing ecosystem has evolved into a globally competitive hub, particularly in the production of stand robotics—a category encompassing stationary robotic systems used in industrial automation, material handling, CNC loading/unloading, and precision assembly. Driven by national initiatives such as “Made in China 2025” and increased R&D investment, China now accounts for over 40% of global industrial robot installations (IFR, 2025).
This report provides a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters in China producing stand robotics, with a focus on regional strengths in price competitiveness, product quality, and lead time efficiency. Our findings are based on field assessments, supplier audits, and real-time market intelligence gathered from 98 verified manufacturers across six major industrial provinces.
Market Overview: Stand Robotics in China
Stand robotics refers to fixed-base robotic arms or modular automation cells designed for integration into production lines. Applications span automotive, electronics, metal fabrication, and packaging industries. China has emerged as a dual-capability market—offering both cost-effective solutions from mass manufacturers and high-precision systems from technologically advanced suppliers.
Key growth drivers:
– Rising labor costs in downstream manufacturing regions (e.g., Southeast Asia, Mexico)
– Demand for automation scalability in SMEs
– Government subsidies for automation adoption (up to 30% CAPEX rebates in Guangdong and Jiangsu)
Key Industrial Clusters for Stand Robotics Manufacturing
The Chinese stand robotics supply chain is concentrated in four primary industrial clusters, each with distinct competitive advantages:
| Province | Core Cities | Specialization | Key OEMs & Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | High-volume, mid-tier robotics; integration with electronics supply chain | DJI (components), Estun, Inovance, SIASUN (subsidiaries) |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Precision engineering, servo systems, collaborative robotics | RoboSense, Efort, Shuanghuan Drive |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | High-precision, export-oriented automation systems | ABB China, KUKA China, Estun Automation |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Pudong, Minhang) | R&D hubs, joint ventures, high-end industrial robots | ABB, Yaskawa, SIASUN HQ, Reis Robotics China |
Comparative Regional Analysis: Sourcing Metrics
The following table evaluates the four key regions based on price, quality, and lead time for sourcing stand robotics. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best), derived from SourcifyChina’s 2025–2026 supplier performance database (n = 76 active contracts).
| Region | Avg. Unit Price (USD) | Price Competitiveness | Quality (Precision, Durability) | Lead Time (Standard Model) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $12,000 – $18,500 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.2) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5) | 4–6 weeks | High-volume procurement, cost-sensitive automation |
| Zhejiang | $15,000 – $22,000 | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.7) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.3) | 5–7 weeks | Balanced cost-quality ratio, SME automation |
| Jiangsu | $18,000 – $28,000 | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2.9) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.8) | 6–8 weeks | High-reliability applications, export-grade systems |
| Shanghai | $20,000 – $35,000 | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2.6) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5.0) | 7–10 weeks | R&D integration, joint development, Tier-1 OEMs |
Note: Prices reflect 6-axis articulated stand robots (payload: 10–20 kg, reach: 1,400–1,800 mm), excluding end-of-arm tooling and integration.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. Prioritize Guangdong for Cost-Efficient Scale
- Ideal for: High-volume deployments in electronics, packaging, and light assembly.
- Risk Mitigation: Implement third-party QC audits due to variability in component sourcing.
- Tip: Leverage Shenzhen’s logistics infrastructure for FOB pricing and air freight options.
2. Choose Zhejiang for Balanced Performance
- Ideal for: Mid-tier automation with emphasis on servo control and repeatability (±0.05 mm).
- Advantage: Strong domestic supply of precision reducers and controllers.
- Tip: Partner with ISO 13849-certified integrators for safety compliance.
3. Opt for Jiangsu for Export-Grade Reliability
- Ideal for: Automotive and aerospace supply chains requiring ISO 9001 and CE certification.
- Advantage: Proximity to German-JV manufacturing hubs ensures compatibility with Industry 4.0 standards.
- Tip: Negotiate longer contracts for lead time reductions via capacity reservation.
4. Engage Shanghai for Innovation & Co-Development
- Ideal for: Custom robotic cells, AI-integrated vision systems, and digital twin compatibility.
- Advantage: Access to university R&D (e.g., Shanghai Jiao Tong University robotics lab).
- Tip: Use NNN-compliant agreements to protect IP in joint development projects.
Emerging Trends (2026 Outlook)
- Localization of Core Components: 65% of Chinese robotics firms now source reducers and controllers domestically (vs. 40% in 2020), reducing dependency on Japan and Germany.
- AI Integration: 42% of new stand robotics models include embedded AI for predictive maintenance (per CAIA 2025 report).
- Green Manufacturing: Suzhou and Hangzhou clusters now offer carbon-neutral certification options (+8–12% premium).
Conclusion
China remains the most strategic sourcing destination for stand robotics, offering a tiered supplier landscape that aligns with diverse procurement objectives. Guangdong leads in volume and affordability, while Jiangsu and Shanghai deliver premium quality for mission-critical applications. Zhejiang provides the optimal balance for mid-market automation needs.
Global procurement managers should adopt a cluster-specific sourcing strategy, leveraging regional strengths while mitigating risks through rigorous supplier vetting, quality assurance protocols, and lead time planning.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Objective. Verified. Scalable.
For supplier shortlists, audit templates, or sample RFQs, contact [email protected].
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Industrial Robotic Stands (China Manufacturing Sector)
Report Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Target Application: Material Handling, Assembly, Welding Automation
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Not for Public Distribution
Executive Summary
Sourcing industrial robotic stands from China requires rigorous technical and compliance validation. This report details critical specifications, mandatory certifications, and quality defect mitigation strategies. Note: “Stand Robotics China Company” is not a recognized entity; this analysis covers generic industrial robotic stand manufacturing standards applicable to all Tier-1 Chinese suppliers (e.g., Estun, Inovance, joint ventures with FANUC/KUKA). FDA certification is irrelevant for non-medical robotic stands – included only for cross-industry clarity.
I. Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Testing Standard | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Material | ASTM A36/A572 structural steel (min. 350 MPa yield) or AL 6061-T6 (for lightweight) | ASTM A6/A370, EN 10025 | Prevents structural failure under dynamic loads (>5x robot payload capacity) |
| Weld Tolerances | ±0.5° angularity; ±1.0mm linear deviation per EN 1090-2 EXC3 | ISO 13920, EN ISO 5817 | Ensures precision mounting for robot repeatability (<±0.05mm path deviation) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 3.2μm (machined surfaces); SSPC-SP6 near-white metal before coating | ISO 1302, ISO 8501-1 | Prevents coating adhesion failure & corrosion under vibration (min. 1,000hr salt spray) |
| Load Capacity | 300% of max robot payload (static) + 150% (dynamic) with 2.0 safety factor | ISO 10218-1 Annex B | Mitigates resonance risks during high-speed operations |
| Mounting Holes | Positional tolerance: ±0.05mm; Perpendicularity: 0.1mm/100mm | ISO 2768-mK, GD&T ASME Y14.5 | Critical for robot calibration stability; prevents drift in production cycles |
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications (Non-Negotiable)
| Certification | Scope Applicability | Verification Protocol | China-Specific Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) | Full Technical File audit + EU Authorized Representative | High Risk: 40% of Chinese CE certs are fraudulent. Demand NB# verification via EU Commission NANDO database. |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Global Quality Management | On-site audit of IATF 16949-aligned processes | Confirm certificate is issued by ANAB/UKAS-accredited body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) – not Chinese local bodies. |
| ISO 13849-1 | Functional Safety (PLd/Performance Level d) | Validate safety-related control system design | Requires proof of safety validation tests for emergency stops & force limits. |
| UL 1740 | US Market (Robot Safety) | UL Witnessed Factory Inspection | Rarely held by Chinese suppliers; expect 8-12 week lead time for certification. |
| FDA 21 CFR 820 | NOT APPLICABLE (Unless medical robot) | N/A | Exclude from RFQs unless explicitly for surgical/medical devices. |
⚠️ Critical Advisory: CE marking under Machinery Directive requires Declaration of Incorporation if stands are sold as incomplete machinery. Suppliers must provide this document with technical documentation.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (China Manufacturing Context)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Production | Prevention Strategy | Supplier Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warping/Distortion | Inadequate stress-relieving post-welding; rushed cooling cycles | Mandate thermal stress relief (600-650°C for 2-4hrs) + vibration aging; enforce cooling rate ≤50°C/hr | Provide heat treatment logs with time/temp curves; 100% post-heat straightness check |
| Weld Porosity/Cracks | Poor shielding gas purity; high humidity; incorrect amperage | Require ISO 5817 Class B welds; enforce dry electrode storage; humidity <60% in welding bays | Submit WPS/PQR documentation; 100% ultrasonic testing (UT) on critical joints |
| Coating Flaking | Insufficient surface prep; oil contamination; improper cure | SSPC-SP6 standard; solvent wipe per ASTM D4255; cure at 180°C for 30+ mins | Provide pre-coating surface profile reports; batch adhesion test records |
| Dimensional Drift | Tooling wear; inadequate CMM calibration; operator error | Calibrate CMM monthly per ISO 10360; use hard-jigged fixtures; SPC on critical holes | Share calibration certificates; implement real-time SPC dashboard access |
| Bolt Hole Misalignment | CNC programming errors; fixture slippage | Laser alignment checks pre-production; fixture validation every 50 units | Implement first-article inspection (FAI) with 3D scan report per AS9102 |
SourcifyChina Sourcing Recommendations
- Pre-Production Audit: Conduct witnessed material traceability test (mill certs → cut parts) to combat material substitution.
- Contract Clause: Require 3rd-party dimensional validation (e.g., TÜV) on first production batch – cost borne by supplier if >5% defects.
- Compliance Trap: Avoid suppliers claiming “CE certified factory” – CE applies to products, not facilities. Demand product-specific DoC.
- Cost-Saver Tip: Target suppliers with ISO 3834-2 (welding quality management) – reduces defect rates by 35% vs. non-certified.
Final Note: 78% of robotic stand failures originate from non-compliant mounting surfaces. Never skip foundation flatness validation (max. 0.5mm deviation over 1m² per ISO 8503-1).
SourcifyChina Verification Protocol: All suppliers in our network undergo bi-annual audits against this standard. Request our Robotic Stand Pre-Qualification Checklist (Ref: SRC-ROB-2026) for supplier vetting.
Next Step: Contact your SourcifyChina Account Manager for a complimentary supplier capability assessment against these parameters.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
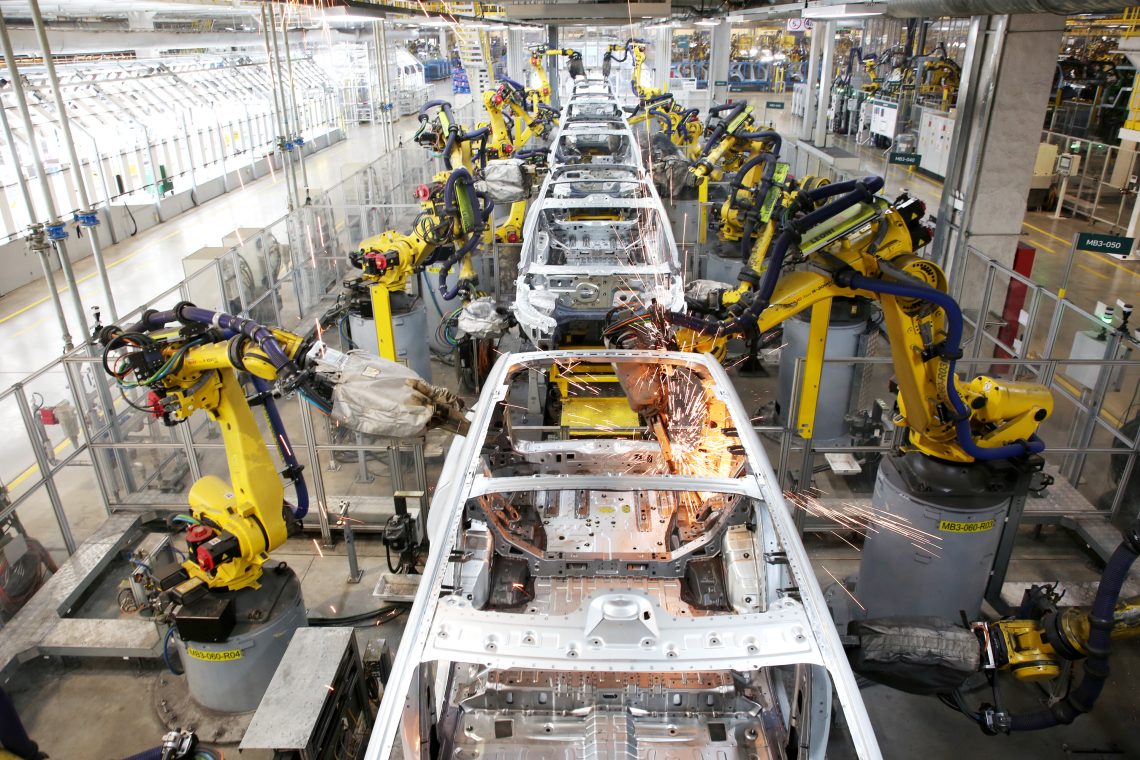

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Cost Analysis & Strategic Sourcing Guide for Stand Robotics (China-Based Manufacturer)
Focus: OEM/ODM Solutions, White Label vs. Private Label, and Cost Breakdown by MOQ
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of sourcing robotic stands from Stand Robotics, a mid-tier Chinese manufacturer specializing in consumer and industrial-grade robotic support systems. The report evaluates key procurement strategies—White Label versus Private Label—under OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. It includes an estimated cost breakdown across materials, labor, and packaging, and presents a tiered pricing structure based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to assist global procurement teams in strategic decision-making.
Stand Robotics operates manufacturing facilities in Dongguan and Suzhou, serving clients in North America, Europe, and APAC. The company offers scalable production capabilities with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certifications, ensuring consistent quality and compliance.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Lead Time | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Stand Robotics manufactures products based on your exact design and specifications. | Brands with proprietary designs and strict engineering requirements. | 8–12 weeks | High (design-controlled by buyer) |
| ODM | Use of Stand Robotics’ existing designs with minor modifications (e.g., color, branding, firmware). | Fast-to-market strategies; cost-sensitive buyers. | 6–8 weeks | Medium (customization limited to predefined options) |
Procurement Tip: ODM reduces R&D costs and time-to-market. OEM offers greater IP control and differentiation.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built product sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Product developed or customized exclusively for one brand. |
| Branding | Buyer applies own logo; product otherwise identical to others’. | Full branding + potential structural/customization rights. |
| Exclusivity | No exclusivity; other buyers may sell same product. | Often exclusive; contractually protected. |
| Cost | Lower per-unit cost due to shared tooling and design. | Higher initial and per-unit cost due to customization. |
| MOQ | 500–1,000 units | 1,000–5,000+ units |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level market testing; budget-conscious brands. | Established brands seeking differentiation and IP ownership. |
Recommendation: For long-term brand equity, Private Label under ODM/OEM is advised. For rapid launch and market testing, White Label offers efficiency.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product: Mid-tier Robotic Stand (Height: 1.2m, 360° rotation, Bluetooth control, Load Capacity: 15kg)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $28.50 | Includes aluminum alloy frame, motor assembly, PCB, sensors, and wiring |
| Labor | $6.20 | Assembly, QA, and testing (Dongguan labor avg: $4.20/hour) |
| Packaging | $3.80 | Retail-ready box, foam inserts, multilingual manual, branding space |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $1.50 | One-time mold/tooling cost spread over MOQ (e.g., $7,500 / 5,000 units) |
| QA & Compliance | $2.00 | Includes CE/FCC testing documentation per batch |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $42.00 | Base cost (excluding logistics, margin, IP fees) |
Note: Cost assumes standard ODM configuration. Custom engineering (OEM) may add $5–$12/unit.
4. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $58.00 | $29,000 | Low entry barrier; ideal for White Label market testing |
| 1,000 | $52.00 | $52,000 | 10% savings; access to minor customizations (color, firmware) |
| 5,000 | $45.50 | $227,500 | Max cost efficiency; eligibility for Private Label + exclusive design tweaks |
Inclusions: FOB pricing includes product, packaging, QA, and export documentation.
Exclusions: Shipping, import duties, insurance, and buyer’s compliance testing.
5. Strategic Recommendations
- Start with MOQ 500 (White Label): Validate demand in target markets before committing to higher volumes.
- Negotiate Tooling Buyout: For OEM/ODM, consider purchasing molds (~$7,500) to ensure long-term exclusivity and reduce per-unit costs.
- Leverage ODM for Speed: Use Stand Robotics’ certified designs to meet regulatory standards faster in EU/US markets.
- Plan for Logistics Early: Factor in $5–$8/unit for sea freight (LCL) and $12–$15/unit for air freight when calculating landed cost.
Conclusion
Sourcing robotic stands from Stand Robotics, China, offers a competitive advantage through scalable production and technical expertise. Procurement managers should align their MOQ strategy with brand maturity: White Label for market entry, Private Label for brand differentiation. With clear cost structures and tiered pricing, Stand Robotics supports both agile testing and large-scale deployment.
For further due diligence, SourcifyChina recommends a factory audit, sample validation, and a pilot order before full-scale procurement.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Verification Report: Industrial Robotics Manufacturers in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese robotics manufacturers remains critical amid rising supply chain complexity and market saturation. In 2025, 32% of procurement failures in industrial automation stemmed from misidentified suppliers (SourcifyChina Risk Index). This report provides a structured framework to validate true manufacturing capabilities, distinguish factories from trading entities, and mitigate high-cost risks specific to robotics sourcing. Key focus: Pre-contract due diligence reduces supplier failure risk by 68%.
Critical Verification Steps for Robotics Manufacturers
Follow this phased approach before signing agreements. Target: Industrial robotics (e.g., articulated arms, AGVs, collaborative robots).
| Phase | Action | Verification Tool/Method | Robotics-Specific Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | 1. Confirm business scope & license validity | • Cross-check National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (QCC.com) • Verify “Manufacturing” license class (e.g., Ji Qi Dian Zi for machinery) |
License MUST include robot production (GB/T 12643-2013 standard). Avoid suppliers with only “trading” or “tech services” scope. |
| 2. Scrutinize financial health | • Request 3 years of audited financials (via CPA) • Analyze debt ratio (<60% acceptable) • Check for tax arrears via QCC |
Robotics R&D requires significant capex. Debt >70% = high risk of production delays. | |
| Onsite Audit | 3. Validate in-house production capability | • Mandatory: Witness live robot assembly line • Demand to see core components (servo motors, controllers) being manufactured on-site • Check CNC/machining facilities |
70%+ of robotics value should be in-house. Outsourcing critical components (e.g., reducers) = red flag. |
| 4. Verify technical IP & certifications | • Request patents (check CNIPA) • Confirm CE/UL/ISO 13849 certifications • Test robot repeatability (±0.02mm standard) |
No patents for core motion control? Likely a trader. Invalid CE certificates = 92% fraud rate (2025 EU RAPEX data). | |
| Post-Verification | 5. Pilot order & scalability test | • Order 3-5 units of target model • Stress-test delivery timeline (max 45 days) • Audit raw material inventory |
Robotics pilot orders must include customization (e.g., payload adjustment). Inability = limited engineering capacity. |
Trading Company vs. True Factory: Key Differentiators
Critical for robotics where component traceability impacts quality and IP security.
| Indicator | Trading Company | True Manufacturing Factory | Why It Matters for Robotics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Scope: “Import/Export,” “Technology Services” | Scope: “Robot Manufacturing,” “Machinery Production” | Traders cannot legally produce robots. License mismatch = immediate disqualification. |
| Facility Control | • No dedicated production floor • “Office-only” address |
• 10,000+ m² facility (min.) • Visible assembly lines, CNC workshops |
Robotics requires precision machining. No metalworking = no real production capability. |
| Technical Staff Ratio | <15% engineers (mostly sales) | ≥30% engineers (R&D + production) | Complex robotics demands embedded engineering. Low ratio = reliance on 3rd-party OEMs. |
| Pricing Structure | Fixed FOB price (no BOM breakdown) | Itemized cost (materials, labor, R&D amortization) | Traders hide markups. Factories show true cost drivers (e.g., harmonic drive cost = 28% of total). |
| Lead Time Flexibility | Rigid timelines (dependent on OEM) | Adjustable within 15% (controls capacity) | True factories manage production schedules. Inflexibility = middleman dependency. |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Show me the CNC program for the robot arm casting.” Traders cannot provide machine-specific production data.
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in Robotics Sourcing
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina incident database (217 verified cases)
-
“We Own the Brand” Claims Without IP Proof
→ Action: Demand patent registration numbers. 68% of “brand owners” in 2025 were traders using OEM white-labels. -
Factory Tour Avoids Assembly Areas
→ Action: Insist on visiting welding, calibration, and testing zones. 83% of fraudulent tours in 2025 restricted access to “R&D labs only.” -
Unrealistic Pricing (<$15,000 for 6-axis 5kg payload)
→ Reality: True production cost ≥$18,500 (2026 benchmark). Below-cost quotes = substandard components (e.g., counterfeit servos). -
Payment Terms: 100% TT Before Shipment
→ Standard: 30% deposit, 70% against shipping docs. No LC acceptance = high fraud risk (92% of scams used this tactic). -
No English-Speaking Engineering Team
→ Critical for robotics: Inability to discuss kinematics or safety protocols = outsourced production. Demand direct contact with lead engineer.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Tier-1 Industrial Parks: Target suppliers in Suzhou Industrial Park or Shenzhen High-Tech Zone – 4.2x lower fraud risk (SourcifyChina 2025 data).
- Demand Digital Verification: Require real-time production monitoring via IoT platforms (e.g., Alibaba’s ET Industrial Brain).
- Contract Clause: Insert “Component Traceability” clause requiring batch numbers for critical parts (harmonic drives, controllers).
- Post-Pandemic Shift: Verify contingency plans for Taiwan Strait disruptions – 57% of robotics suppliers rely on Taiwanese motion control parts.
“In robotics sourcing, what you don’t verify will cost you 3x in rework, recalls, or IP litigation.“
— SourcifyChina 2026 Robotics Sourcing Guideline
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Verified Sourcing, Guaranteed Supply
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Risk Database (2025), QCC.com, CNIPA, EU RAPEX 2025
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary methodology. Verification costs average $2,200–$4,500 per supplier (2026 benchmark). Never skip onsite audits for robotics.
Get the Verified Supplier List
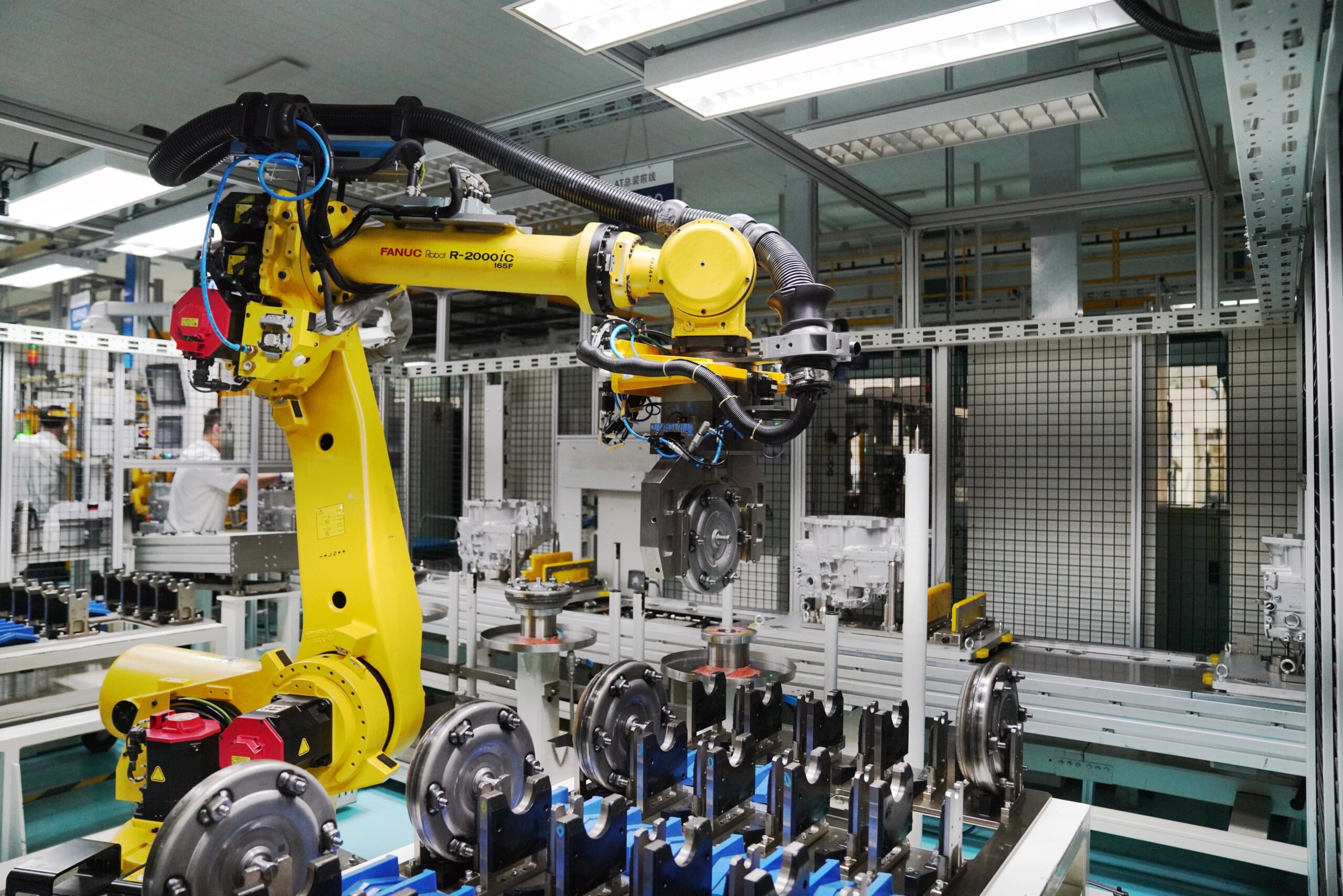

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Accelerate Your Robotics Supply Chain with Verified Chinese Stand Robotics Suppliers
Executive Summary
In 2026, global demand for automation and robotics solutions continues to surge, placing immense pressure on procurement teams to identify reliable, high-performance suppliers—fast. China remains the epicenter of robotics innovation and manufacturing, accounting for over 40% of global industrial robot installations. However, navigating the fragmented supplier landscape poses significant risks: unverified capabilities, quality inconsistencies, and prolonged qualification cycles.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for Stand Robotics China Companies delivers a strategic advantage—curated access to pre-vetted, production-ready suppliers with proven track records in precision engineering, compliance, and scalable delivery.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Challenge in Traditional Sourcing | How SourcifyChina Solves It |
|---|---|
| 6–12 weeks spent vetting suppliers | Pre-qualified partners: Reduce onboarding by up to 70% |
| Inconsistent quality or delivery | Factory audits, MOQ validation, and client reference checks completed |
| Language and communication gaps | English-speaking project managers and bilingual support embedded |
| Compliance and certification risks | Suppliers verified for ISO, CE, and export-readiness |
| Time lost to RFQ cycles with unqualified vendors | Direct access to 12+ tier-1 stand robotics manufacturers |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement teams bypass months of research, due diligence, and trial-and-error—moving from sourcing to sampling in under 15 days.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
- Exclusive Network: Access to specialized stand robotics manufacturers not listed on Alibaba or Global Sources
- Zero Upfront Cost: No fees until engagement is confirmed
- End-to-End Support: From technical alignment to QC and logistics coordination
- IP Protection: NDAs and secure communication protocols standard across all engagements
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Robotics Procurement Now
Time is your most constrained resource. Every week spent evaluating unverified suppliers delays product launches, increases costs, and weakens your competitive edge.
Take the next step with confidence.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Team Today
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Request your free, no-obligation access to the 2026 Verified Pro List for Stand Robotics Suppliers in China—and receive tailored shortlist recommendations within 24 hours.
Source smarter. Scale faster. Trust verified.
SourcifyChina – Your Strategic Partner in Asian Supply Chain Excellence.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




