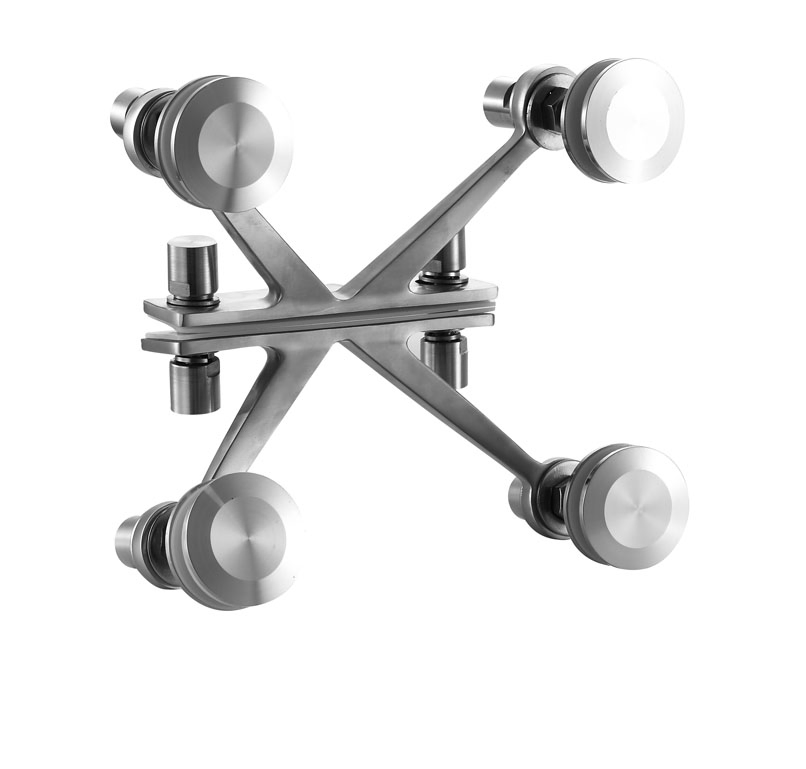
The global market for precision mechanical components, including spider fittings—critical elements in universal joints and drivetrain systems—has seen steady expansion driven by rising demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global universal joint market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing vehicle production, particularly in emerging economies, and the need for high-performance power transmission systems in industrial automation. As demand for reliability and efficiency rises, manufacturers of spider fittings are under pressure to innovate in materials, durability, and precision engineering. In this competitive landscape, a select group of suppliers has emerged as leaders, combining advanced manufacturing capabilities with rigorous quality standards to meet evolving industry needs. Based on production scale, global reach, technological innovation, and customer base, the following nine companies represent the top manufacturers in the spider fitting sector.
Top 9 Spider Fitting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ozone India
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ozone.in
Key Highlights: Ozone is the leading manufacturer & supplier of Architectural Hardware Fittings & Security Solutions that include glass fittings, Smart Locks & Safes, ……
#2 China Spider Fittings Manufacturers and Supplier
Domain Est. 2016
Website: ourschina.com
Key Highlights: Aozheng Metal offers high – strength, safe and steady spider fittings. Our company is a successful manufacturer and supplier which has been devoted to ……
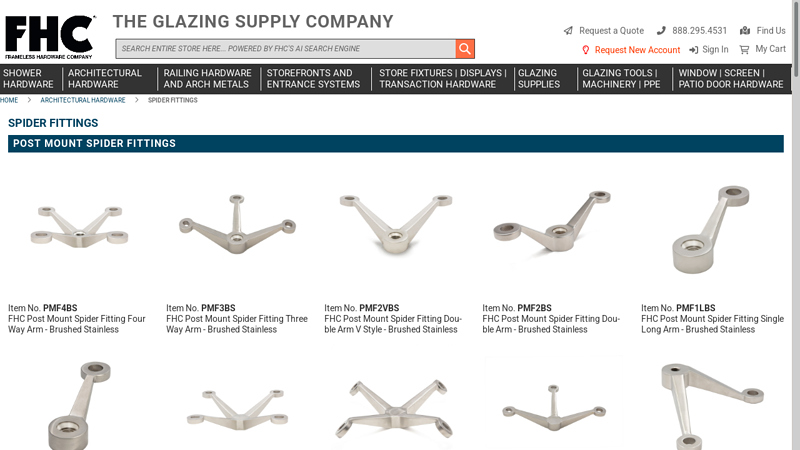
#3 FHC
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fhc-usa.com
Key Highlights: Frameless Hardware Company LLC is a manufacturer and supplier to the glass, glazing, and fenestration industries. We provide a complete range of tools and ……
#4 Spider Fittings for Glass
Domain Est. 1995
Website: crlaurence.com
Key Highlights: A spider fitting is architectural hardware designed to secure large glass panels without heavy framing, allowing for clean lines and expansive, unobstructed ……
#5 Grimco
Domain Est. 1996
Website: grimco.com
Key Highlights: Grimco’s goal is to help you find the best fit for your sign and graphics production needs. We have a team of industry professionals ready to assist you!…
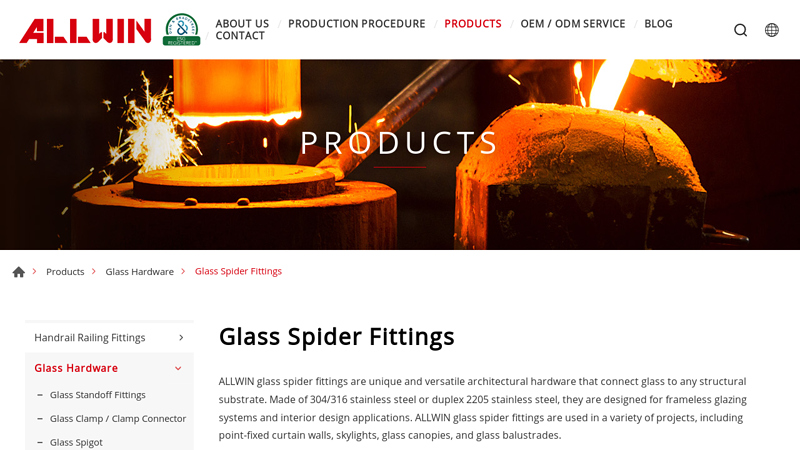
#6 Glass Spider Fittings
Domain Est. 2006
Website: allwinhardware.com
Key Highlights: ALLWIN glass spider fittings are unique and versatile architectural hardware that connect glass to any structural substrate. Made of 304/316 stainless steel ……
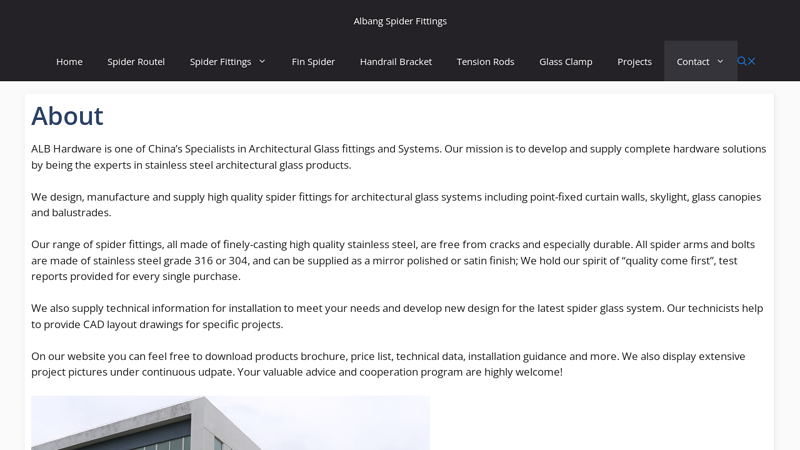
#7 About
Domain Est. 2011
Website: spiderfittings.org
Key Highlights: Our range of spider fittings, all made of finely-casting high quality stainless steel, are free from cracks and especially durable. All spider arms and bolts ……
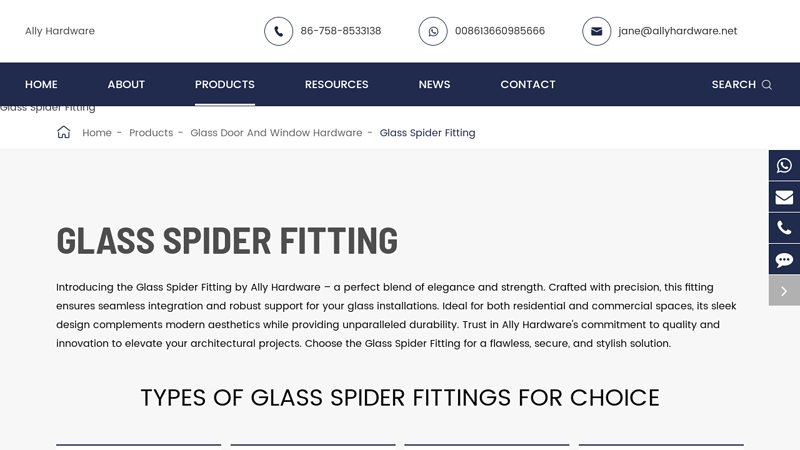
#8 Glass Spider Fitting
Domain Est. 2019
Website: allyhardware.com
Key Highlights: Spider fittings are versatile hardware used in frameless glass installations, providing a sleek and modern aesthetic. They can be used with various types of ……
#9 Regular Spider Fittings
Domain Est. 2022
Website: glassrailinghardware.com
Key Highlights: A Regular Spider Fitting is a hardware component used to attach glass panels to structural members in a railing system….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Spider Fitting

2026 Market Trends for Spider Fitting
As we approach 2026, the market for Spider Fitting—a specialized component commonly used in structural glazing, façade engineering, and architectural design—is undergoing significant transformation driven by advancements in materials science, sustainability demands, and evolving architectural trends. Spider fittings, known for their ability to support glass panels with minimal visual interruption, are becoming increasingly integral to modern building designs. Below are the key market trends shaping the Spider Fitting industry in 2026.
Rising Demand for Minimalist and Transparent Architecture
Architects and developers continue to favor sleek, frameless glass façades that emphasize openness and natural light. This design preference is fueling demand for high-performance spider fittings that enable large spans of structural glass with reduced support structures. In 2026, urban high-rises, commercial complexes, and luxury residential projects are increasingly incorporating spider-fitted curtain walls to achieve transparency and aesthetic elegance.
Growth in Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Building Standards
With global emphasis on green building certifications such as LEED, BREEAM, and WELL, there is a growing integration of spider fittings in energy-efficient façade systems. The fittings are being optimized to work seamlessly with insulated glass units (IGUs) and smart glazing technologies, contributing to improved thermal performance and reduced energy consumption. Manufacturers are responding by developing corrosion-resistant, low-maintenance fittings using recycled or low-carbon materials.
Advancements in Material Technology and Engineering
In 2026, spider fittings are increasingly manufactured using high-grade stainless steel (e.g., 316L), duplex alloys, and even titanium for high-stress or corrosive environments. Innovations in precision casting, CNC machining, and 3D modeling allow for custom-designed fittings tailored to complex geometries. Finite element analysis (FEA) and digital twin simulations are now standard in the design phase, ensuring structural integrity and safety under dynamic loads.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and parts of Africa are witnessing rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, driving demand for modern architectural solutions. Countries like China, India, UAE, and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in iconic glass-clad buildings, creating new opportunities for spider fitting suppliers. Local manufacturing hubs are emerging to reduce lead times and comply with regional building codes.
Integration with Smart Building Systems
Spider fittings are no longer passive structural elements. In 2026, they are being integrated with sensor networks for structural health monitoring (SHM), detecting stress, deflection, or corrosion in real time. This trend supports predictive maintenance and enhances building safety, particularly in seismic or high-wind zones. IoT-enabled fittings are becoming more common in smart city projects.
Customization and Digital Fabrication
Architectural projects increasingly demand bespoke solutions. With the help of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and parametric design tools, spider fittings are being customized to fit unique façade patterns, curvatures, and load requirements. Digital fabrication techniques such as robotic welding and automated assembly lines are improving precision and scalability.
Regulatory and Safety Standards Evolution
Global building codes are becoming stricter regarding façade safety, especially after high-profile glass failure incidents. In 2026, compliance with updated standards (e.g., ISO 12543 for laminated glass, EN 1364 for fire resistance) is critical. Spider fitting manufacturers are investing in rigorous testing protocols and third-party certifications to ensure reliability and gain market trust.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The spider fitting market is seeing consolidation as larger engineering firms acquire niche manufacturers to offer end-to-end façade solutions. At the same time, specialized players are differentiating through innovation, sustainability, and rapid prototyping services. Price competition remains moderate due to the high technical barriers and customization requirements.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for spider fittings is characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability integration, and global expansion. As architectural visions push the boundaries of glass and steel, spider fittings will remain a critical enabler of innovation in the built environment.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Spider Fittings: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing spider fittings—critical structural components used in glass façades and curtain wall systems—presents several challenges, particularly related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for ensuring project safety, compliance, and long-term performance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material and Manufacturing Standards
One of the most common issues is the variation in material quality among suppliers, especially from regions with less stringent manufacturing oversight. Substandard stainless steel (e.g., using 201-grade instead of 316-grade) can lead to corrosion, reduced load capacity, and premature failure. Always verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A354 or ISO 3506.
2. Lack of Independent Testing and Certification
Many suppliers claim their fittings meet load and safety requirements without providing third-party test reports. Without certified structural testing (e.g., proof load, fatigue, and ultimate strength tests), there is a significant risk of using underperforming components. Demand up-to-date test certificates from accredited laboratories.
3. Poor Welding and Surface Finishes
Spider fittings often require precision welding and high-quality surface finishes to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. Poor craftsmanship—such as incomplete welds or inconsistent polishing—can lead to stress concentrations, corrosion initiation, and visual defects. Conduct site audits or request sample inspections before bulk orders.
4. Inadequate Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability for each batch, including heat numbers, inspection records, and compliance documentation. Lack of traceability increases the risk of using counterfeit or non-conforming parts, making it difficult to address issues during or after installation.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Risk of Sourcing Counterfeit or Copycat Designs
Many high-performance spider fittings are patented or protected by design rights. Sourcing from unlicensed manufacturers can result in the use of IP-infringing products, leading to legal disputes, project delays, or forced replacement of components. Always verify that the supplier holds proper licensing for branded designs (e.g., from companies like Sapa, Gartner, or Seele).
2. Ambiguity in Design Ownership
When working with OEMs or custom manufacturers, unclear contracts may result in disputes over design ownership. Ensure agreements explicitly define IP rights, especially if custom modifications are made to standard fittings.
3. Use of “Generic” Versions with Unverified Performance
Suppliers may offer “compatible” or “generic” versions of patented fittings at lower costs. These often lack the rigorous engineering and testing of original designs, posing safety risks and potential liability. Even if they resemble legitimate products, performance cannot be assumed without validation.
4. Limited Recourse in Case of IP Infringement
If a project is found to use IP-infringing components, the end user or specifier—not just the supplier—may face legal and financial consequences. Conduct due diligence by requesting proof of IP compliance and including indemnity clauses in procurement contracts.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Pre-qualify suppliers through audits, reference checks, and review of quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Require full documentation, including material test reports, third-party certifications, and IP licensing proof.
- Engage independent testing labs for sample validation, especially for large or critical projects.
- Work with reputable distributors or authorized partners of established brands to mitigate IP and quality risks.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP concerns, project stakeholders can ensure the structural integrity, longevity, and legal compliance of their façade systems.
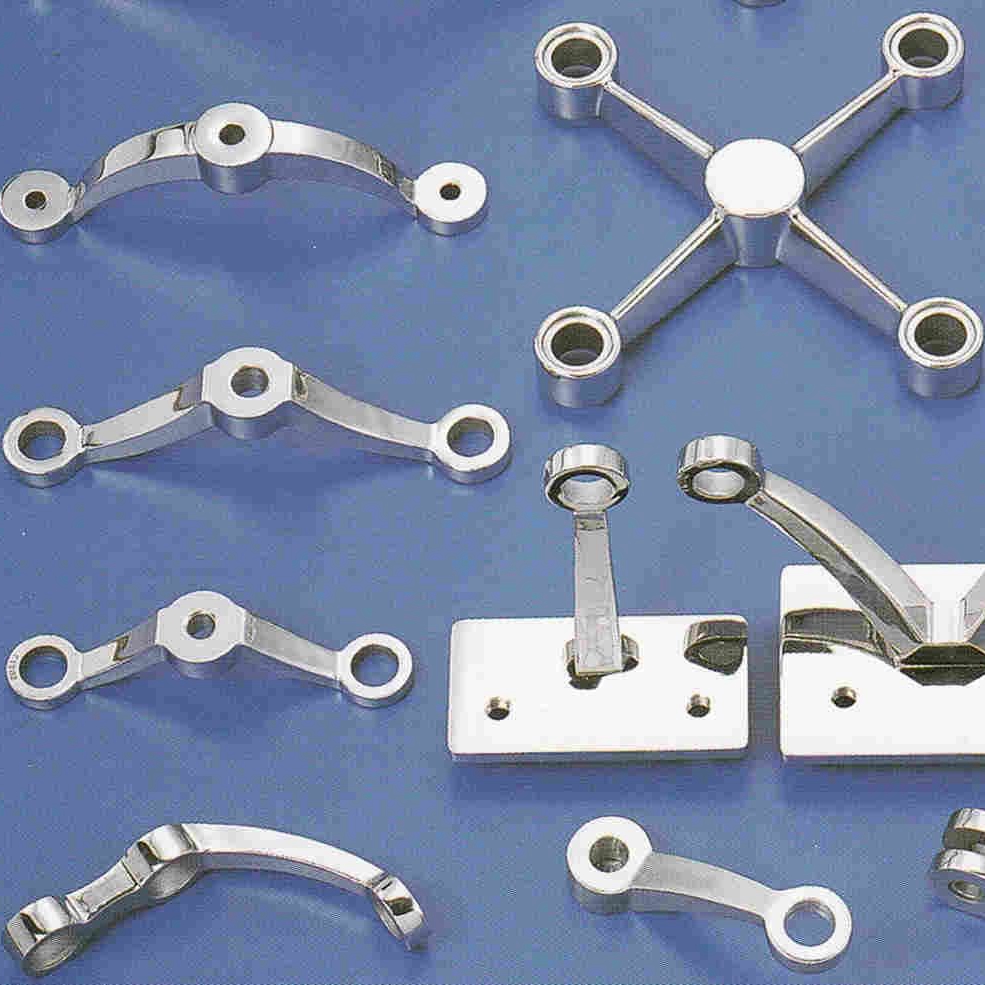
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Spider Fitting
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, and installation of Spider Fittings—structural hardware used in glass façade systems to support and connect glass panels to building frameworks.
Overview of Spider Fittings
Spider Fittings, also known as glass spider connectors or structural spiders, are precision-engineered metal components (typically stainless steel) that anchor and stabilize glass panels in curtain wall and structural glazing systems. They come in various configurations (e.g., 2-arm, 4-arm, 6-arm) and must comply with structural, safety, and material standards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Spider Fittings must adhere to regional and international standards to ensure structural integrity and safety. Key compliance standards include:
- EN 1090-1: Execution of steel structures – Mandatory CE marking for construction products in the European Economic Area (EEA).
- ASTM A370/A370M: Standard test methods for mechanical testing of steel products (applicable in the U.S.).
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems – Ensures consistent manufacturing and traceability.
- Local Building Codes: Must comply with jurisdiction-specific regulations (e.g., IBC in the U.S., Building Regulations in the UK).
- Fire Safety and Load Ratings: Fittings must be rated for expected wind, seismic, and dead loads as per project engineering specifications.
Material and Manufacturing Standards
- Material: Typically ASTM A316L or EN 1.4404 (marine-grade stainless steel) for corrosion resistance.
- Surface Finish: Must be free of burrs, cracks, or surface defects; passivation and polishing may be required.
- Certifications: Suppliers must provide Material Test Reports (MTRs), mill certificates, and compliance declarations.
Packaging and Handling Guidelines
Proper packaging and handling prevent damage and maintain finish integrity:
- Individual Protection: Each fitting should be wrapped in anti-corrosive VCI paper or plastic.
- Cushioned Packaging: Use foam inserts or corrugated dividers in sturdy cardboard or wooden crates.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with part number, quantity, batch/lot number, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”).
- Handling: Use non-marring tools; avoid dragging or dropping; wear gloves to prevent fingerprints and corrosion.
Transportation and Shipping Protocols
Ensure safe and compliant transit from manufacturer to project site:
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, sea, or air freight depending on destination and urgency.
- Securement: Crates must be palletized and strapped to prevent shifting during transit.
- Environmental Protection: Protect from moisture, salt spray, and extreme temperatures; use desiccants if needed.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of conformity, and any required export/import documentation.
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
For international shipments:
- HS Code Classification: Typically under 7326.90 (other articles of iron or steel).
- Customs Declarations: Accurate valuation, country of origin, and end-use declarations required.
- Duties and Tariffs: Verify based on trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU trade policies).
- Restricted Substances: Confirm compliance with RoHS, REACH, and CA Prop 65 if applicable.
On-Site Receiving and Inspection
Upon delivery:
- Verification: Cross-check delivery note against purchase order and packing list.
- Visual Inspection: Check for physical damage, corrosion, or packaging breaches.
- Documentation Review: Ensure all compliance certificates and test reports are present.
- Quarantine if Non-Conforming: Isolate and report any discrepancies to the supplier immediately.
Storage Recommendations
- Location: Dry, covered, and ventilated indoor area; elevated off the floor.
- Segregation: Store by type and size; avoid mixing with carbon steel to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Duration: Minimize long-term outdoor storage; use protective covers if unavoidable.
Installation and Safety Compliance
- Qualified Personnel: Only certified installers should handle and install Spider Fittings.
- Torque Specifications: Follow manufacturer’s torque values using calibrated tools.
- Alignment and Tolerance: Ensure precise alignment per architectural and engineering drawings.
- Safety Gear: Use PPE including gloves, eye protection, and fall arrest systems when working at height.
Traceability and Documentation Retention
- Batch Tracking: Maintain records of batch numbers, certifications, and inspection reports.
- As-Built Documentation: Include fitting locations and installation dates in project closeout files.
- Retention Period: Keep records for minimum 10 years or as required by local regulations.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recyclability: Stainless steel fittings are 100% recyclable; promote responsible end-of-life handling.
- Carbon Footprint: Source from manufacturers with certified environmental management systems (ISO 14001).
- Sustainable Packaging: Use recyclable or reusable packaging materials where possible.
Conclusion
Compliance and logistics planning for Spider Fittings are critical to project success, safety, and regulatory approval. Adhering to this guide ensures that all aspects—from manufacturing to installation—are executed to the highest standards, minimizing risk and supporting long-term structural performance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Spider Fittings:
After a comprehensive evaluation of suppliers, product quality, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability, the sourcing of spider fittings has been determined to be most effectively achieved through a strategic combination of certified manufacturers with proven expertise in structural glass hardware. The selected suppliers demonstrate compliance with international standards (such as ISO 9001 and EN 14351-1), offer competitive pricing, and provide consistent product performance critical for architectural applications.
Key factors influencing the final decision include material quality (stainless steel 316/304), precision in manufacturing, timely delivery, and responsive technical support. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options and full documentation (including test reports and load calculations) further ensures safety and compatibility with project specifications.
In conclusion, establishing long-term partnerships with pre-qualified suppliers will enhance project efficiency, reduce lead times, and maintain high structural and aesthetic standards in glass facade systems. Continuous performance monitoring and periodic supplier reviews are recommended to sustain quality and innovation in future sourcing efforts.