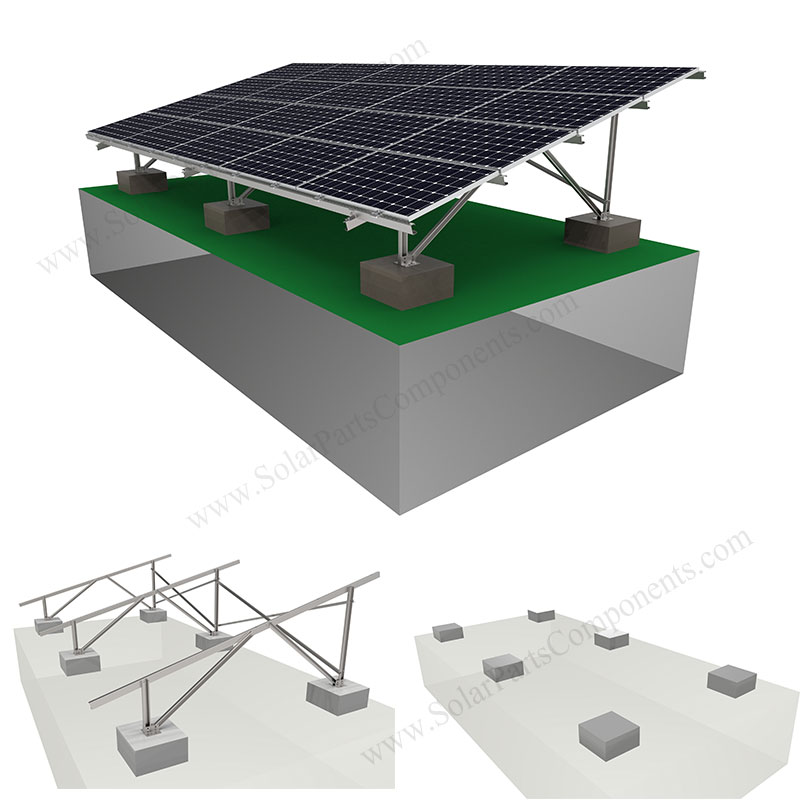
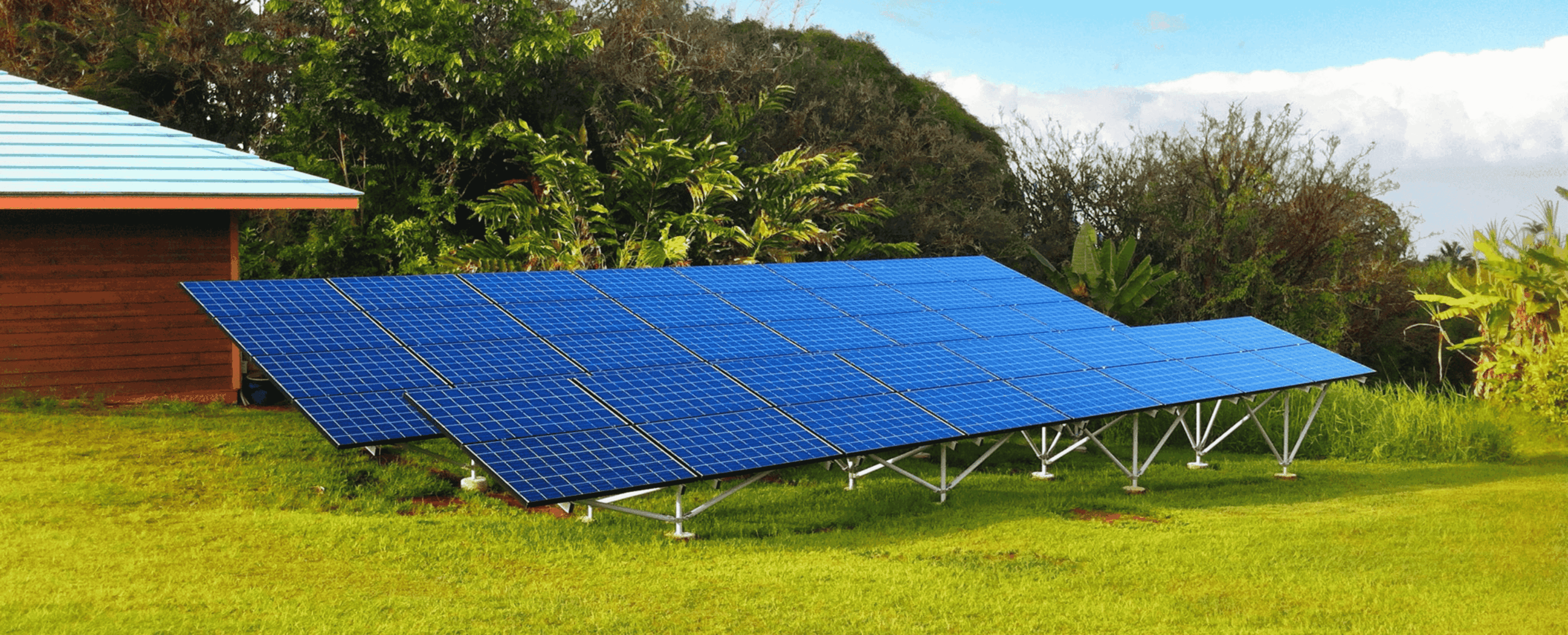
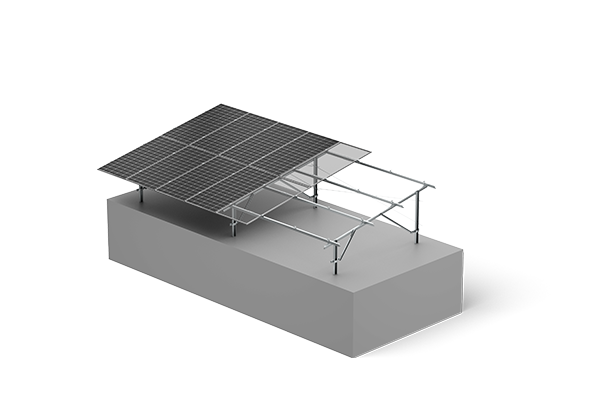
The global solar panel mounting systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the accelerating adoption of solar energy across residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the solar mounting structures market was valued at USD 22.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.5% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing demand for ground-mounted solar installations, particularly in regions with high solar irradiance and available land. Ground mount systems offer greater flexibility in panel positioning and higher energy yields compared to rooftop alternatives, making them a preferred choice for large-scale solar farms. As investments in renewable energy infrastructure surge worldwide, manufacturers specializing in durable, cost-effective, and adaptable ground mounting solutions are playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of solar deployment. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading innovation and market share in solar panel ground mounting systems.
Top 10 Solar Panel Ground Mounting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 – Ground Mount Solar
Domain Est. 2013
Website: nuanceenergy.com
Key Highlights: TRAILBLAZING GROUND-MOUNT SOLAR RACKING Nuance Energy is transforming the solar industry with award-winning and multi-patented earth anchor foundation ……
#2 APA Solar
Domain Est. 2021
Website: apasolar.com
Key Highlights: APA Solar is a leading U.S.-based solar racking manufacturer specializing in engineered foundation and mounting solutions for commercial and utility-scale ……
#3 Unirac: World
Domain Est. 1999
Website: unirac.com
Key Highlights: Better Solar Starts Here with Unirac. We Make World-Class Solar Mounting & Racking Solutions and Provide Everything You Need to Make Solar Happen….
#4
Domain Est. 2007
Website: k2-systems.com
Key Highlights: We develop mounting systems for photovoltaic systems. Our customers benefit from our longstanding international experience and expertise….
#5 SnapNrack
Domain Est. 2008
Website: snapnrack.com
Key Highlights: Say goodbye to fumbling with T-bolts and rail hardware! With our innovative Clamp Mounts, all of our roof attachments come rail-ready right out of the box….
#6 Polar Racking
Domain Est. 2009
Website: polarracking.com
Key Highlights: s. Polar Racking is a global leader in the design, engineering and manufacturing of PV mounting systems and foundations….
#7 Antai Solar
Domain Est. 2010
Website: antaisolar.com
Key Highlights: Antai Solar designs durable solar mounting systems for residential, commercial & utility-scale projects. Custom solutions, trusted by installers worldwide….
#8 All Products
Domain Est. 2010
#9
Domain Est. 2015
Website: tamaracksolar.com
Key Highlights: Tamarack Solar Products manufactures innovative solar module mounting structures that are designed to install quickly and provide a secure mounting….
#10 HQ MOUNT
Domain Est. 2017
Website: hqmount.com
Key Highlights: HQ MOUNT specializes in researching and developing,manufacturing,selling solar mounting system solutions.Roof mount,ground mount,solar carport,solar farm ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Panel Ground Mounting

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Solar Panel Ground Mounting Systems
The global market for solar panel ground mounting systems is poised for substantial growth by 2026, driven by accelerating renewable energy adoption, declining solar technology costs, and supportive government policies. As countries intensify efforts to meet climate targets under international agreements such as the Paris Accord, utility-scale and commercial solar installations—predominantly reliant on ground-mounted systems—are expected to dominate solar capacity additions.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the rising demand for dual-use or agrivoltaic installations, where ground-mounted solar panels are integrated with agricultural activities. This approach optimizes land use, particularly in regions with space constraints, and enhances economic returns for landowners. Innovations in mounting height, panel spacing, and tracking systems are enabling better sunlight penetration and crop yields, making agrivoltaics a growing niche within the ground mount segment.
Additionally, single-axis and dual-axis solar tracking systems are gaining prominence due to their ability to increase energy yield by up to 25–35% compared to fixed-tilt structures. By 2026, trackers are projected to capture a larger market share, especially in high-irradiance regions like the southwestern United States, the Middle East, and parts of Australia and India. The integration of AI and IoT in tracker controls for real-time performance optimization will further enhance system efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Material innovation is another emerging trend, with manufacturers shifting toward lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials such as anodized aluminum and advanced composites. These materials reduce shipping and installation costs while improving durability in harsh environments—critical for remote or desert-based solar farms.
Geopolitically, supply chain resilience is becoming a focal point. In response to trade uncertainties and logistical disruptions, regional manufacturing hubs for mounting structures are expanding in North America, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe. This localization trend is expected to reduce lead times and dependency on imports, particularly from China.
Finally, regulatory incentives and renewable energy mandates, such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and the EU’s Green Deal, are accelerating project pipelines. By 2026, the ground mount segment is forecasted to account for over 60% of new solar installations globally, with the market value exceeding $18 billion, according to industry analysts.
In summary, the 2026 solar panel ground mounting market will be characterized by technological innovation, increased deployment of tracking systems, sustainable land-use practices, and strong policy support—positioning it as a cornerstone of the global energy transition.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Solar Panel Ground Mounting Systems (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing solar panel ground mounting systems involves critical considerations beyond price and availability. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to long-term performance issues, legal risks, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Corrosion Resistance
Many suppliers use substandard materials—such as low-grade steel or inadequate galvanization—to cut costs. This leads to premature rusting and structural failure, especially in harsh environments. Ensure the mounting systems use hot-dip galvanized steel (minimum G90 or AZ35 coating) or aluminum with proper corrosion resistance certifications. Avoid systems lacking third-party testing or compliance with ASTM or ISO standards.
Lack of Structural Engineering Validation
Some suppliers offer “one-size-fits-all” mounting solutions without site-specific engineering. This can result in system failure under wind or snow loads. Always require certified engineering documentation, including structural calculations and stamped drawings by a licensed professional, tailored to your project’s geographic and environmental conditions.
Inadequate Certifications and Compliance
Mounting systems should meet international standards such as UL 2703, IEC 62282, or AS/NZS 1170. Sourcing from manufacturers without these certifications can void insurance, fail permitting, or lead to non-compliance penalties. Verify that products have up-to-date test reports from accredited labs.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Some low-cost suppliers replicate patented designs from leading manufacturers (e.g., mounting profiles, clamps, or foundations). Using such systems exposes developers and EPC contractors to legal action for IP infringement, including cease-and-desist orders or damages. Always confirm the manufacturer holds legitimate IP rights or licenses for their designs and request documentation to validate originality.
Insufficient Warranty and After-Sales Support
A long warranty (e.g., 10–25 years) means little if the supplier lacks the financial stability or technical support to honor it. Evaluate the manufacturer’s track record, global presence, and customer service responsiveness. Avoid suppliers who offer vague or non-transferable warranties.
Hidden Costs from Design Incompatibility
Mounting systems not designed for specific panel models or inverters may require costly custom brackets or labor-intensive installation. Ensure compatibility with your BOS components and verify ease of installation to avoid delays and unexpected labor expenses.
By rigorously evaluating material quality, engineering rigor, compliance, and IP integrity, stakeholders can mitigate risks and ensure long-term reliability and legal safety in solar ground mount projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Panel Ground Mounting
Site Assessment and Permitting
Prior to initiating any ground-mounted solar project, a comprehensive site assessment is essential. This includes evaluating topography, soil composition, drainage patterns, and proximity to existing infrastructure. A land survey and geotechnical analysis help determine foundation requirements and ensure long-term structural stability. Environmental assessments must be conducted to identify protected species, wetlands, or cultural resources that could impact siting. Once the site is evaluated, engage with local authorities to secure necessary permits, including zoning clearance, building permits, and grading permits. Submit detailed site plans, engineering drawings, and environmental reports as required by municipal, county, and state agencies.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Ground-mounted solar installations must comply with a range of environmental regulations. Projects may require review under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) for federal involvement or state-level equivalents. Compliance with the Clean Water Act involves implementing a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) and obtaining a National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit if stormwater runoff is expected. Endangered Species Act (ESA) and Migratory Bird Treaty Act (MBTA) considerations may necessitate habitat assessments and mitigation plans. Additionally, projects on agricultural land may need approval under state farmland protection programs. Maintain documentation of all compliance efforts for audits and inspections.
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Efficient logistics planning is critical for transporting solar panels, mounting structures, inverters, and other components to the site. Coordinate with suppliers and freight carriers to ensure timely delivery, considering road access, bridge weight limits, and seasonal access restrictions. Use specialized equipment such as cranes and forklifts for unloading and handling delicate solar panels to prevent damage. Store materials in a secure, dry area with proper elevation to avoid moisture exposure. Implement an inventory management system to track materials and reduce loss or theft. Schedule deliveries to align with construction phases to minimize on-site storage needs.
Construction and Installation Standards
Installation must adhere to engineering specifications and national safety standards, including the National Electrical Code (NEC), particularly Article 690 for solar photovoltaic systems. Foundations—whether driven piles, helical piers, or concrete footings—must be installed according to geotechnical recommendations to ensure structural integrity. Mounting structures should be properly leveled and anchored to withstand wind and snow loads per local building codes. Electrical work must be performed by licensed personnel, with proper grounding, wiring, and overcurrent protection. All work should follow OSHA safety protocols to protect workers during excavation, assembly, and electrical integration.
Interconnection and Utility Coordination
Prior to commissioning, coordinate with the local utility for interconnection approval. Submit a formal interconnection application that includes single-line diagrams, equipment specifications, and protection settings. The utility will review the system’s impact on grid stability and may require additional equipment such as smart inverters or isolation devices. Install a dedicated metering setup as specified—either net metering or production metering depending on the tariff structure. Ensure all communication systems for remote monitoring are configured and tested. Final inspection by the utility and local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) is required before system energization.
Post-Installation Compliance and Monitoring
After installation, conduct a final commissioning process that includes performance testing, insulation resistance checks, and verification of grounding systems. Submit as-built drawings and operation & maintenance (O&M) manuals to stakeholders and regulatory bodies. Register the system with relevant incentive programs such as the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), ensuring all documentation meets IRS requirements. Implement ongoing monitoring to track energy production and detect faults. Schedule periodic inspections to maintain compliance with fire codes, vegetation management regulations, and environmental mitigation commitments. Keep detailed records of maintenance, inspections, and any modifications for audit purposes.
In conclusion, sourcing solar panel ground mounting systems requires a comprehensive approach that balances cost, quality, durability, and local site conditions. Key factors such as soil type, climate, system scalability, and compliance with local regulations must be carefully evaluated to ensure long-term performance and return on investment. By prioritizing reputable suppliers, engineering-certified designs, and corrosion-resistant materials, project developers can secure reliable mounting solutions that support optimal panel alignment and structural integrity. Additionally, considering logistics, installation support, and future maintenance access contributes to overall project efficiency. Ultimately, a well-sourced ground mount system not only enhances energy output and system lifespan but also strengthens the viability and sustainability of large-scale solar installations.