The global sodium tetraborate market has seen steady growth, driven by its expanding applications in water treatment, including pool maintenance. According to Grand View Research, the global boron chemicals market, which includes sodium tetraborate (also known as borax), was valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing demand for effective algaecides and pH stabilizers in residential and commercial swimming pools, where sodium tetraborate offers enhanced water clarity and reduced chemical usage. As sustainability and water conservation become industry priorities, manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-purity, eco-friendly formulations. With North America and Europe leading in pool chemical consumption, and Asia-Pacific witnessing rising urbanization and recreational infrastructure development, the competitive landscape is evolving. Below are eight leading sodium tetraborate manufacturers specializing in pool care solutions that combine performance, reliability, and scientific precision.
Top 8 Sodium Tetraborate For Pools Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Swimming Pool
Domain Est. 2004
Website: boratesplus.com
Key Highlights: Borates provide a range of benefits to the swimming pool. Since borates soften the water, they provide comfort to the swimmer by reducing skin irritation.Missing: sodium tetrabora…
#2 Borates in a variety of applications
Domain Est. 1995
Website: borax.com
Key Highlights: Borates are an easy-to-use additive that helps reduce corrosion, soften water, and improve swimmer comfort….
#3 Borax
Domain Est. 1996
Website: thechemco.com
Key Highlights: TCC’s borax, also known as sodium, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is an important boron compound, a mineral, and the salt of boric acid….
#4 Buy Borax from brenntag Morocco suppliers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: brenntag.com
Key Highlights: Buy customized variations and grades of Borax Na2B4O7.xH2O from Brenntag; safe delivery, in stock in Brenntag Morocco, find MSDS, quote, sample now!…
#5 Boric acid and your health
Domain Est. 2002
Website: canada.ca
Key Highlights: Boric acid, also called boron or borax, is found naturally in the environment. It can also be used in common consumer products….
#6 Borax
Domain Est. 2016
Website: vizagchemical.com
Key Highlights: Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is an important boron compound, a mineral, and a salt of boric acid….
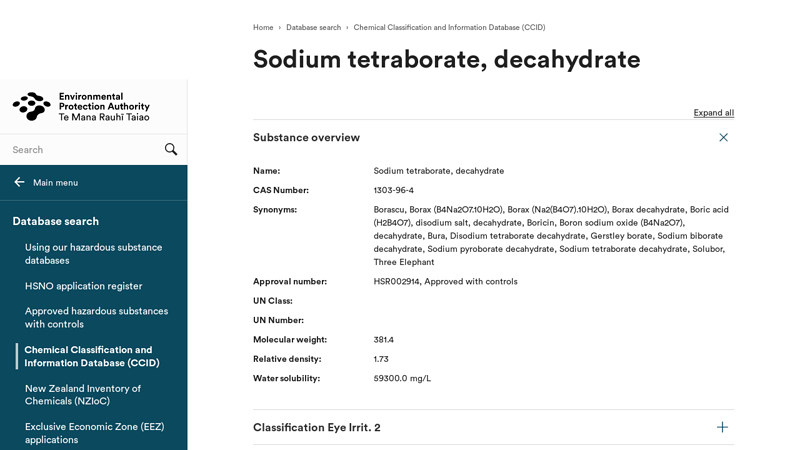
#7 Sodium tetraborate, decahydrate
Website: epa.govt.nz
Key Highlights: Name: Sodium tetraborate, decahydrate; CAS Number: 1303-96-4; Synonyms: Borascu, Borax (B4Na2O7.10H2O), Borax (Na2(B4O7).10H2O), Borax decahydrate, ……
#8 Understanding Borates in Pool Chemistry
Domain Est. 2001
Website: blog.orendatech.com
Key Highlights: In swimming pools, borate products are primarily used as a pH buffering system in water; specifically to buffer against the increase in pH….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sodium Tetraborate For Pools
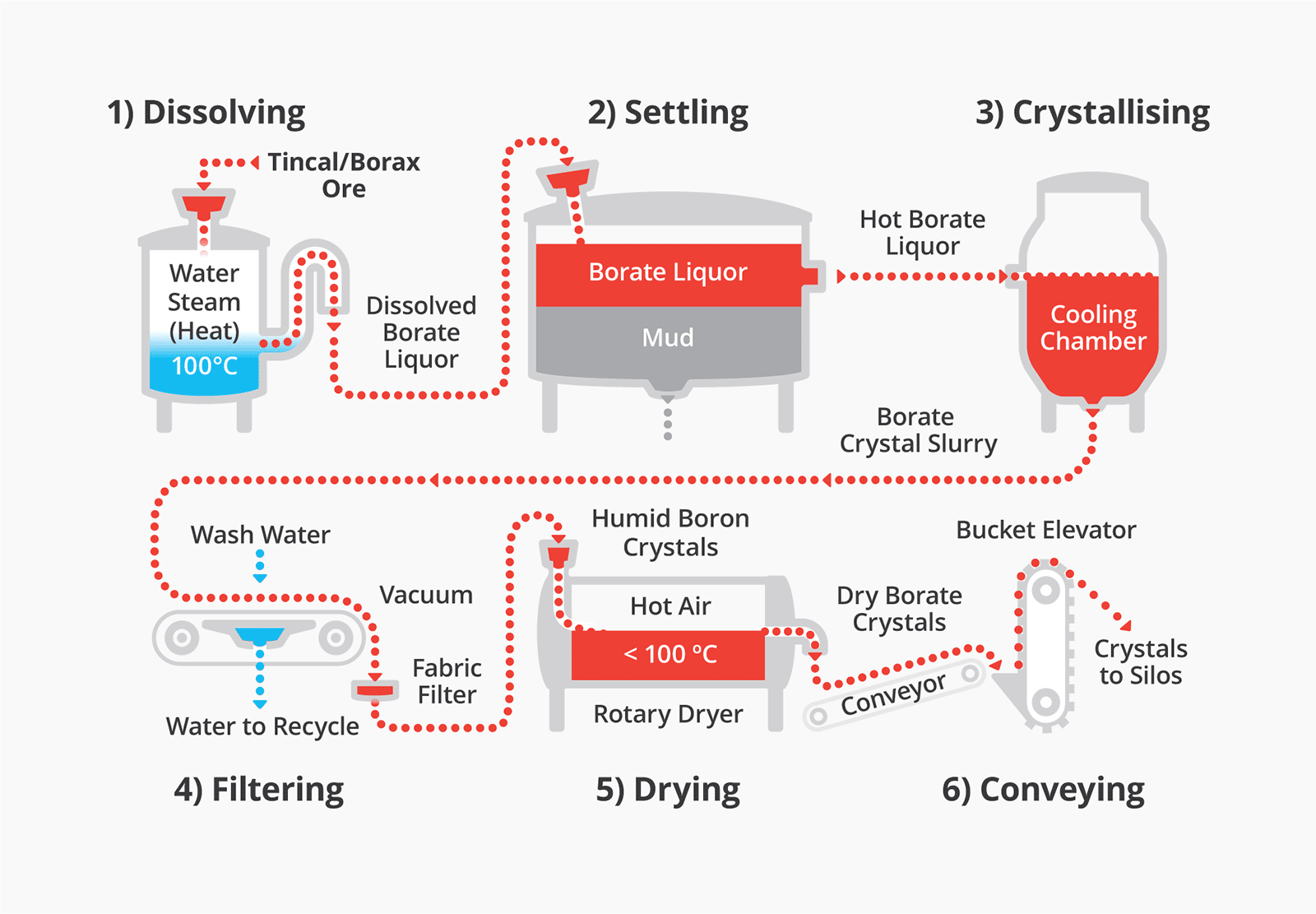
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Sodium Tetraborate in Pools
The demand for sodium tetraborate—commonly known as borax—in swimming pool maintenance is expected to experience notable shifts by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, regulatory developments, and technological advancements in water treatment. As a pH buffer and algae inhibitor, sodium tetraborate offers pool owners enhanced water stability and reduced chemical dependency. Below are key trends expected to shape the 2026 sodium tetraborate for pools market:
-
Growing Demand for Sustainable Pool Chemicals
Increasing environmental awareness is pushing consumers and pool maintenance professionals toward eco-friendly alternatives. Sodium tetraborate is gaining favor due to its low environmental impact, biodegradability, and reduced need for chlorine. As green building and sustainable landscaping trends accelerate, pool owners are more likely to adopt borate-based systems, boosting market growth. -
Expansion of Residential Pool Ownership in Warm Climates
Regions such as the Southern United States, the Middle East, and parts of Southeast Asia are seeing a rise in residential pool installations due to urbanization and higher disposable incomes. This expansion is expected to drive the demand for efficient and long-lasting water treatment solutions, with sodium tetraborate positioned as a premium option for maintaining water clarity and comfort. -
Integration with Smart Pool Management Systems
By 2026, the proliferation of IoT-enabled pool monitoring devices will facilitate precise chemical dosing and real-time water quality tracking. Sodium tetraborate, with its stabilizing properties, is increasingly being recommended as part of smart pool ecosystems. Manufacturers are partnering with tech firms to promote borate-centric water care programs compatible with automated systems. -
Regulatory Support and Safety Reassessments
Following recent evaluations by agencies such as the U.S. EPA and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), sodium tetraborate has been reclassified in some regions with clearer safety guidelines for consumer use. These updated regulations are expected to reduce market uncertainty and enhance consumer confidence, particularly in household pool applications. -
Product Innovation and Formulation Advancements
Leading chemical suppliers are developing stabilized borate blends that improve solubility and ease of use. In 2026, expect to see pre-measured dosing systems, slow-release tablets, and combination products that integrate sodium tetraborate with other sanitizers. These innovations aim to simplify maintenance and broaden appeal among non-professional users. -
Competitive Pricing and Supply Chain Optimization
With major borate producers in Turkey (Eti Maden) and the U.S. (U.S. Borax) investing in efficient extraction and refining processes, the cost of sodium tetraborate is expected to remain stable or decline slightly. This improves affordability for both commercial pool services and homeowners, supporting wider adoption. -
Educational Outreach and Market Penetration
Industry associations and chemical manufacturers are increasing efforts to educate pool professionals and consumers about the benefits of borate-based water management. By 2026, expanded training programs, certification courses, and digital marketing campaigns are expected to increase market penetration, especially in underpenetrated regions.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for sodium tetraborate in pools is poised for moderate but steady growth, supported by sustainability trends, technological integration, and improved regulatory clarity. As the pool care industry moves toward smarter, greener solutions, sodium tetraborate is likely to maintain a strategic role in high-performance water treatment regimens.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sodium Tetraborate for Pools (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing sodium tetraborate (commonly known as borax) for pool applications requires careful attention to both quality specifications and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to ineffective treatment, regulatory issues, or legal exposure. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Incorrect Grade or Purity:
- The Pitfall: Procuring industrial-grade sodium tetraborate decahydrate (e.g., for glass or detergents) instead of a food-grade or technical-grade suitable for pool water treatment. Industrial grades may contain higher levels of impurities like arsenic, lead, or heavy metals, which are unsafe for recreational water.
- The Consequence: Potential health hazards for swimmers, cloudiness in pool water, or interference with other chemical balances.
- Mitigation: Always specify and verify the required purity (typically >99.5% Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O) and confirm the material meets relevant safety standards (e.g., USP, FCC, or NSF/ANSI Standard 50 for pool chemicals).
-
Inconsistent Particle Size or Solubility:
- The Pitfall: Sourcing material with inconsistent granulation or particle size distribution. Fine powders can dust and be hard to handle, while large crystals dissolve slowly, leading to uneven distribution and localized high pH zones.
- The Consequence: Poor dissolution, inefficient buffering, potential for scaling or precipitation, and difficulty in accurate dosing.
- Mitigation: Define and enforce particle size specifications (e.g., mesh size) in procurement contracts and conduct batch testing for solubility performance.
-
Moisture Content and Caking:
- The Pitfall: Sodium tetraborate is hygroscopic. Sourcing material with high moisture content or inadequate packaging can lead to caking during storage.
- The Consequence: Clumped product is difficult to handle, dose accurately, and dissolve, reducing effectiveness and increasing labor.
- Mitigation: Specify maximum moisture content (e.g., <2%) and require moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., multi-wall poly-lined bags). Ensure proper storage conditions (cool, dry environment).
-
Lack of Batch-to-Batch Consistency:
- The Pitfall: Assuming all sodium tetraborate is the same, without verifying consistency across supplier batches.
- The Consequence: Fluctuations in pool water chemistry performance, requiring constant rebalancing and undermining the reliability of the borate buffer system.
- Mitigation: Require suppliers to provide Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch and conduct incoming quality checks for key parameters (purity, pH of solution, solubility).
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Infringing on Formulated Product Patents:
- The Pitfall: Sourcing raw sodium tetraborate for use in a proprietary pool chemical blend (e.g., a stabilized borate buffer with additional algaecides or pH modifiers) without checking if the final formulation is patented.
- The Consequence: Legal action for patent infringement, even if the sodium tetraborate itself is generic. Liability arises from manufacturing or selling the patented combination.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis before developing or sourcing ingredients for branded pool products. Consult patent databases and legal counsel.
-
Misrepresenting Product Origin or Performance:
- The Pitfall: Sourcing sodium tetraborate and marketing a pool treatment product implying it is equivalent to a branded, patented borate system (e.g., “Like [Brand X] Borate Buffer”) without authorization.
- The Consequence: Trademark infringement and/or false advertising claims, leading to cease-and-desist letters, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
- Mitigation: Avoid using trademarks or confusingly similar names. Market the product based on its own specifications (e.g., “Sodium Tetraborate Pool Buffer”) without implying equivalence to protected brands unless licensed.
-
Overlooking Trade Secrets in Processing:
- The Pitfall: Assuming the sourcing process is purely commodity-based. Some suppliers may have proprietary methods for producing ultra-pure or specially granulated sodium tetraborate optimized for pools.
- The Consequence: Sourcing a technically inferior product that doesn’t perform as expected, or inadvertently reverse-engineering a process that infringes on a trade secret.
- Mitigation: Focus on performance specifications rather than process details unless entering a licensed manufacturing agreement. Respect supplier confidentiality.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, pool product formulators, distributors, and service providers can ensure they source effective, safe, and legally compliant sodium tetraborate, protecting both their customers and their business.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sodium Tetraborate for Pools
Overview of Sodium Tetraborate
Sodium tetraborate, commonly known as borax (CAS No. 1303-96-4), is a naturally occurring mineral compound used in swimming pool maintenance to stabilize pH levels and enhance water clarity. It acts as a buffering agent, reducing pH fluctuations and improving the effectiveness of sanitizers. While widely used and generally safe when handled properly, sodium tetraborate is subject to specific regulatory and logistical requirements due to its chemical properties.
This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant handling, transportation, storage, and use of sodium tetraborate in pool applications.
Regulatory Classification and Compliance
Hazard Classification
Sodium tetraborate is classified under various international and national regulations:
- GHS (Globally Harmonized System):
- May be classified as Harmful if swallowed (H302)
- Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
- Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child (H361d) — based on some regulatory interpretations (e.g., EU CLP)
-
Note: Classification varies by concentration and jurisdiction; always refer to the specific Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the supplier.
-
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency):
- Regulated under TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act); not classified as a pesticide when used solely as a pH buffer.
-
Labeling must comply with FIFRA if marketed with antimicrobial claims.
-
EU REACH/CLP:
- Subject to REACH registration.
-
May require labeling with hazard statements H361d (Suspected of damaging the unborn child) and H319 (Causes serious eye irritation).
-
Transportation (DOT/IMDG/IATA):
- Generally not classified as a hazardous material for transport when in solid form and not containing significant impurities.
- Always verify classification using current SDS and consult 49 CFR (U.S.) or ADR/RID/IMDG/IATA (international) guidelines.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Requirements
Ensure the following SDS sections are reviewed and accessible:
- Section 2: Hazard Identification – Confirm classification and pictograms.
- Section 7: Handling and Storage – Follow recommended practices.
- Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection – Use gloves, eye protection, and dust masks if handling powder.
- Section 13: Disposal Considerations – Dispose of according to local regulations; do not release into waterways.
- Section 15: Regulatory Information – Check country-specific compliance.
Handling and Use Precautions
Safe Handling Practices
- Avoid inhalation of dust; use in well-ventilated areas.
- Wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask when handling powdered forms.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling.
- Wash hands thoroughly after use.
- Prevent contact with eyes and skin.
Pool Application Guidelines
- Dissolve sodium tetraborate completely in water before adding to the pool.
- Recommended concentration: Typically 30–50 ppm borate in pool water.
- Monitor borate levels regularly using test kits.
- Do not exceed manufacturer-recommended dosing rates.
- Avoid use in spas or hot tubs with high temperatures, as borate solubility decreases.
Storage Requirements
Storage Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
- Keep containers tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption and dust formation.
- Store away from acids, heavy metals, and incompatible materials.
- Use non-reactive containers (e.g., HDPE plastic or lined steel).
- Clearly label all containers with contents and hazard information.
Shelf Life
- Sodium tetraborate is stable under proper storage conditions; typically 2–5 years.
- Protect from humidity to prevent caking.
Transportation and Logistics
Domestic Transport (U.S. DOT)
- Not typically regulated as a hazardous material under 49 CFR when shipped in non-bulk quantities and meeting criteria for “ORM-D” or “Not Regulated” status.
- Verify with SDS and carrier requirements.
- Use sturdy packaging to prevent spillage.
International Transport
- IMDG Code (Sea): Usually not regulated as dangerous goods.
- IATA (Air): Generally permitted as non-hazardous, but quantity limits may apply.
- ADR (Road, Europe): Check for any regional restrictions; typically not classified as hazardous.
Packaging
- Use sealed, moisture-resistant bags or containers.
- Outer packaging should be strong enough to withstand normal handling.
- Include safety labels and handling instructions if required by regulation.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Environmental Impact
- Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects (EU H410 in some formulations).
- Do not discharge pool water containing high borate levels into storm drains or natural water bodies without treatment.
- Follow local wastewater discharge regulations.
Waste Disposal
- Dispose of unused product or contaminated material as chemical waste according to local, state, and federal regulations.
- Contact licensed waste disposal companies for proper handling.
- Never dispose of in household trash unless permitted.
Labeling and Documentation
Product Labeling
- Include product name, CAS number, net weight, manufacturer details, and hazard statements (if applicable).
- Provide first-aid measures and safety instructions.
- For consumer products, comply with EPA and CPSC (Consumer Product Safety Commission) labeling standards.
Required Documentation
- Maintain copies of SDS for all shipments.
- Keep records of purchase, usage, and disposal.
- For commercial pool service providers: ensure staff training records are up to date.
Training and Worker Safety
Employee Training
- Train staff on SDS review, proper PPE use, spill response, and emergency procedures.
- Include hazard communication (HazCom) training per OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1200.
- Conduct refresher training annually or when procedures change.
Spill Response
- In case of spill:
- Avoid dust formation.
- Sweep or vacuum (use HEPA filter) and place in sealed container.
- Do not flush with water.
- Report large spills to local environmental authorities if required.
Regulatory Updates and Compliance Monitoring
- Monitor updates from EPA, OSHA, ECHA, and other relevant agencies.
- Re-evaluate classification and labeling annually or when regulatory changes occur.
- Consult legal or compliance experts for commercial distribution or large-scale use.
Summary of Key Compliance Actions
- Obtain and maintain current SDS for all sodium tetraborate products.
- Use appropriate PPE during handling.
- Store in dry, secure, labeled containers.
- Follow transportation regulations based on mode and volume.
- Train employees on safe use and emergency procedures.
- Dispose of waste responsibly and in compliance with local laws.
- Monitor borate levels in pools and avoid environmental release.
By adhering to this guide, users and distributors of sodium tetraborate for pools can ensure safe, effective, and legally compliant operations. Always consult product-specific documentation and regulatory authorities for site-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing sodium tetraborate (commonly known as borax) for pool maintenance can be a beneficial decision for improving water stability, enhancing swimmer comfort, and reducing algae growth. When selecting a supplier, it is important to prioritize product purity, consistent quality, and compliance with industry standards such as ACS or FCC grades to ensure safety and effectiveness. Purchasing from reputable chemical suppliers, pool specialty stores, or trusted online vendors can provide reliable access to high-quality sodium tetraborate. Additionally, considering factors like bulk pricing, shipping costs, and availability helps optimize cost-efficiency, especially for larger pools or long-term use. With proper sourcing and dosage, sodium tetraborate can be a valuable addition to a comprehensive pool care regimen, contributing to clearer, more comfortable, and chemically balanced water.