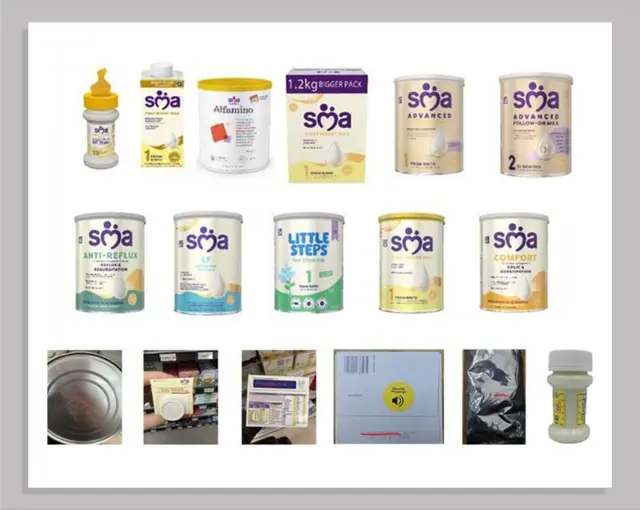
The global specialty medical infant formula (SMA) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising awareness of pediatric health, increasing prevalence of food allergies and metabolic disorders in infants, and greater healthcare expenditure. According to Grand View Research, the global infant formula market was valued at USD 78.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030, with specialty formulas—particularly for children with metabolic conditions, malabsorption, or allergies—contributing significantly to this expansion. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trend, noting a surge in demand for hypoallergenic and nutritionally tailored formulas, especially in North America and Europe, where regulatory support and maternal health initiatives bolster market development. As clinical nutrition becomes more personalized, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, quality, and market share in the SMA segment. Below are the top 5 SMA infant formula manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 5 Sma Infant Formula Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nestle issues global recall of some baby formula products over toxin …
Domain Est. 1989
Website: bbc.com
Key Highlights: The food and drink giant said specific batches of its SMA infant formula and follow-on formula were not safe to be fed to babies….
#2 Recall of specific batches of various SMA infant formula and follow …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fsai.ie
Key Highlights: Message: Nestlé is recalling the below batches of its SMA infant formula and follow-on formula products due to the possible presence of ……
#3 SMA First Infant Milk
Domain Est. 2000
Website: smahcp.co.uk
Key Highlights: SMA First Infant Milk is nutritionally complete formula milk with HMOs that’s suitable from birth for infants not breastfed or who are combination fed….
#4 SMA Baby Milk and Formula
Domain Est. 2003
#5 SMA® Nutrition
Domain Est. 2011
Website: smababy.co.uk
Key Highlights: We have been making infant formula for over 100 years. During that time, we have used our industry leading research to bring ever better products to families….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sma Infant Formula
2026 Market Trends for SMA Infant Formula: Strategic Outlook
As the infant nutrition landscape evolves, SMA (a leading infant formula brand under the Nestlé umbrella) is poised to navigate several key market dynamics in 2026. Driven by shifting consumer preferences, regulatory developments, and technological advancements, the following trends are expected to shape SMA’s market positioning and growth trajectory.
Rising Demand for Premium and Specialized Formulas
By 2026, parents are increasingly seeking premium infant formulas that offer added health benefits. SMA is capitalizing on this trend by expanding its portfolio of specialized products—including hypoallergenic, anti-reflux, and formulas enriched with prebiotics, probiotics (such as B. lactis), and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFAs) like DHA. These formulations cater to digestive health, immune support, and cognitive development, aligning with the growing consumer emphasis on preventive health and science-backed nutrition.
Emphasis on Breastfeeding Support and Hybrid Feeding Solutions
While breastfeeding remains the gold standard, hybrid feeding—combining breast milk with formula—is on the rise. SMA is positioning itself to support this trend through educational initiatives, lactation consultant partnerships, and product innovations like “follow-on” and “toddler” milks designed to complement breastfeeding. The brand’s marketing in 2026 is expected to focus on empowering parents with balanced, non-judgmental feeding choices, enhancing brand trust and loyalty.
Clean Label and Transparency Expectations
Consumers in 2026 are more informed and demand transparency in sourcing, ingredients, and manufacturing. SMA is responding by simplifying ingredient lists, reducing the use of added sugars, and highlighting non-GMO, sustainably sourced components. Traceability features—such as QR codes linking to farm origins and nutritional data—are likely to become standard, reinforcing consumer confidence and differentiating SMA in a crowded market.
Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
Global regulatory bodies are tightening standards on marketing practices, especially under the WHO International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes. SMA’s 2026 strategy will emphasize compliance, particularly in emerging markets. Additionally, sustainability is a growing concern; SMA is expected to advance its eco-initiatives by reducing plastic use, optimizing supply chain emissions, and adopting recyclable packaging—an important differentiator as environmentally conscious parenting grows.
Digital Engagement and Personalized Nutrition
The integration of digital health tools will be a major trend in 2026. SMA is likely to expand its use of AI-driven apps that offer personalized feeding recommendations, growth tracking, and expert advice. These platforms not only improve user experience but also generate valuable data for product development and targeted marketing, fostering deeper customer engagement.
Competitive Landscape and Market Expansion
SMA faces increasing competition from both established rivals (like Aptamil and Similac) and emerging clean-label or plant-based startups. To maintain its foothold, SMA is expected to focus on innovation in emerging markets—particularly in Asia and Africa—where urbanization, rising incomes, and improved healthcare access are driving formula adoption. Strategic partnerships with healthcare providers and e-commerce platforms will be crucial for market penetration.
In conclusion, SMA’s success in the 2026 infant formula market will depend on its ability to balance scientific innovation with ethical marketing, sustainability, and digital transformation—ensuring it remains a trusted partner for modern families worldwide.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing SMA Infant Formula (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing SMA (Special Medical Adapted) infant formula involves navigating a complex landscape of regulatory, quality, and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Due to the sensitive nature of infant nutrition—especially for babies with medical conditions—ensuring product safety, authenticity, and legal compliance is paramount. Below are key pitfalls to avoid when sourcing SMA infant formula.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Compromised Product Authenticity and Counterfeiting
SMA infant formulas are often high-value, medically necessary products, making them targets for counterfeiters. Sourcing from unauthorized or unverified suppliers increases the risk of receiving adulterated, expired, or fake products that can endanger infant health.
Mitigation:
– Source exclusively through authorized distributors or directly from the manufacturer.
– Verify batch numbers, packaging integrity, and expiration dates.
– Use third-party testing for critical shipments.
2. Inadequate Cold Chain and Storage Conditions
Many SMA formulas are sensitive to temperature and humidity. Breaks in the cold chain during shipping or storage can degrade nutrients and compromise sterility.
Mitigation:
– Ensure suppliers and logistics partners comply with cold chain protocols.
– Monitor temperature logs throughout the supply chain.
– Audit storage facilities for compliance with pharmaceutical-grade standards.
3. Non-Compliance with Regulatory Standards
SMA formulas are regulated as medical foods or special dietary foods, often requiring approval from health authorities (e.g., FDA, EFSA, or local equivalents). Sourcing products not compliant with destination country regulations can lead to shipment rejection, legal penalties, or patient harm.
Mitigation:
– Confirm regulatory approval in the target market.
– Review product labeling for compliance with local language and ingredient disclosure rules.
– Maintain documentation for import permits and product registrations.
4. Lack of Traceability and Batch Recall Capability
Without full traceability, identifying and recalling defective or contaminated batches becomes nearly impossible, increasing liability and health risks.
Mitigation:
– Require full batch traceability from manufacturer to delivery.
– Ensure suppliers have a documented recall process.
– Maintain records of all sourcing and distribution steps.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
5. Infringement of Trademarks and Brand Rights
SMA is a registered trademark owned by certain manufacturers (e.g., Reckitt, which markets SMA® in several countries). Unauthorized use of the brand name or packaging can lead to legal action, seizure of goods, or reputational damage.
Mitigation:
– Verify trademark ownership and licensing in the target jurisdiction.
– Avoid using “SMA” or similar branding unless authorized.
– Use generic or medically descriptive product names when appropriate.
6. Sourcing Generic or Private-Label Versions Without IP Clearance
Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” SMA formulas under private labels. However, these products may infringe on patented formulations, manufacturing processes, or packaging designs.
Mitigation:
– Obtain legal review of product formulations and branding.
– Require suppliers to warrant IP compliance.
– Avoid copying patented features (e.g., specific protein hydrolysates or nutrient blends).
7. Misuse of Marketing and Labeling Claims
Claims such as “clinically proven,” “equivalent to SMA®,” or “recommended by pediatricians” may violate advertising regulations or imply endorsement, leading to IP or regulatory issues.
Mitigation:
– Ensure all marketing claims are evidence-based and approved.
– Avoid comparative claims without authorization.
– Consult legal counsel for compliance with advertising standards.
Conclusion
Sourcing SMA infant formula requires rigorous attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property rights. Failure to address these pitfalls can result in serious health risks, legal liabilities, and supply chain disruptions. Engaging reputable suppliers, conducting due diligence, and maintaining compliance with international and local regulations are essential steps in responsible sourcing.
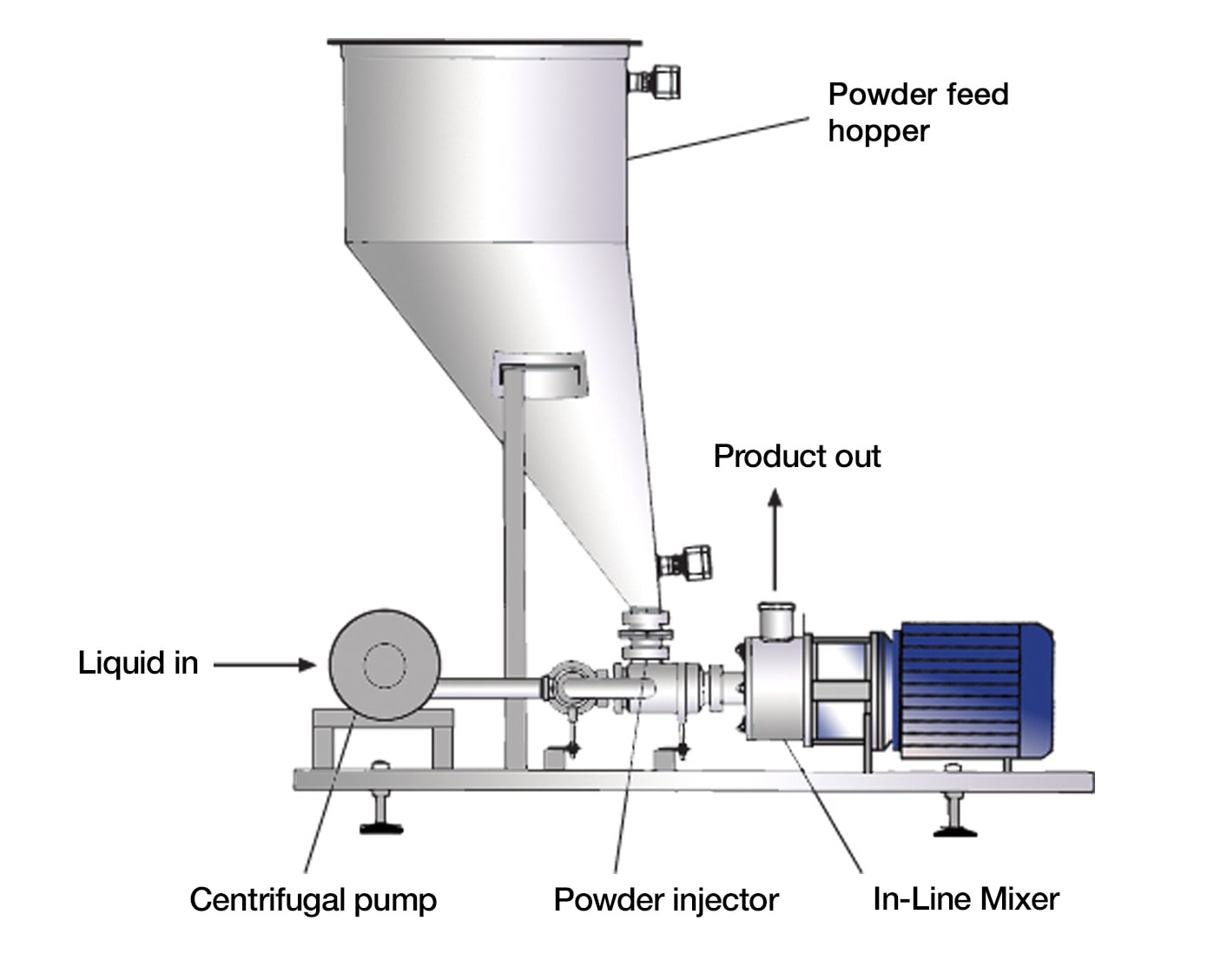
Logistics & Compliance Guide for SMA Infant Formula
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for handling, storing, transporting, and distributing SMA Infant Formula. Adherence to these protocols ensures product safety, regulatory compliance, and consumer trust.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
SMA Infant Formula must comply with Codex Alimentarius standards, particularly Codex Stan 72-1981, which sets the compositional and labeling requirements for infant formula. Manufacturers and distributors must also follow guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO), including the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes.
Regional Regulations
- European Union: Products must comply with EU Regulation (EU) 2016/127, which establishes compositional and information requirements for infant formula and follow-on formula. All products require notification to the European Commission before market placement.
- United States: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates infant formula under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Compliance includes adherence to 21 CFR Part 107, with mandatory registration of manufacturing facilities and adherence to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs).
- Other Markets: Countries such as Canada, Australia, and those in ASEAN have specific national regulations. Local labeling, nutrient profiles, and marketing restrictions must be strictly followed.
Labeling Requirements
- Labels must include product name, list of ingredients, nutritional information, batch number, expiration date, preparation instructions, and manufacturer details.
- Warning statements such as “Consult your healthcare professional before use” must be clearly visible.
- Labels must be in the official language(s) of the destination country.
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store in a cool, dry place at temperatures between 10°C and 25°C (50°F to 77°F). Avoid exposure to extreme heat or freezing.
- Humidity: Relative humidity should not exceed 65% to prevent clumping and degradation.
- Shelf Life: Typically 18–24 months from manufacture. Monitor expiration dates and implement a First-Expired, First-Out (FEFO) inventory system.
- Packaging Integrity: Ensure cans or containers remain sealed and undamaged. Store off the floor and away from walls to allow airflow and prevent contamination.
Transportation & Distribution
Domestic and International Shipping
- Use temperature-controlled vehicles where necessary to maintain product integrity.
- Ensure packaging is shock-resistant and designed to prevent tampering or moisture ingress.
- All shipments must be accompanied by documentation including Certificate of Analysis (CoA), Certificate of Conformity (CoC), and shipping manifests.
Cold Chain Considerations
While SMA Infant Formula is typically shelf-stable, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can compromise nutrient stability. Monitor transport conditions, especially in tropical climates or during summer months.
Import & Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Health Certificate (if required by importing country)
- Certificate of Free Sale
- Import Permits (e.g., from FDA, EFSA, or local authorities)
Ensure all documentation is accurate and submitted in advance to avoid customs delays.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
- Implement a full traceability system using batch/lot numbers to track products from manufacturing to point of sale.
- Conduct regular quality audits of storage facilities and logistics partners.
- Maintain records of storage conditions, transport logs, and quality inspections for a minimum of 3 years.
Handling Recalls & Non-Conformities
- Establish a recall procedure in line with local regulatory requirements.
- Notify relevant authorities within 24–48 hours of identifying a non-conforming batch.
- Clearly communicate recall information to distributors and retailers, including batch numbers, reasons, and return instructions.
Training & Personnel
- Train all logistics and warehouse staff on infant formula handling protocols, hygiene standards, and regulatory requirements.
- Ensure personnel involved in import/export understand customs procedures and documentation requirements.
Conclusion
Strict adherence to logistics and compliance standards is critical when managing SMA Infant Formula. Ensuring product safety, regulatory alignment, and efficient distribution protects public health and supports brand integrity across global markets. Regular review of evolving regulations and supply chain best practices is strongly recommended.
Conclusion for Sourcing SMA Infant Formula
Sourcing SMA (Special Medical Adaptation) infant formula requires a meticulous, compliance-driven approach due to its critical role in supporting infants with specific medical conditions such as metabolic disorders, allergies, or digestive issues. Given that SMA formulas are classified as specialist or medical foods, their procurement must adhere to strict regulatory standards, medical oversight, and quality assurance protocols.
Key considerations in sourcing SMA infant formula include ensuring authenticity and safety by purchasing from certified suppliers or healthcare-approved distributors, verifying product compliance with regional health regulations (e.g., FDA, EFSA, or local health authorities), and maintaining cold chain integrity where applicable. Collaboration with healthcare professionals—including pediatricians and dietitians—is essential to confirm medical necessity and appropriate product selection.
Additionally, supply chain reliability, traceability, and responsiveness are vital to prevent shortages, which could pose serious health risks to vulnerable infants. In emergency situations or scarcity, alternative sourcing through national health programs or authorized import channels may be necessary, always under medical guidance.
In conclusion, sourcing SMA infant formula must prioritize infant safety, regulatory compliance, and collaboration with healthcare providers. Establishing strong partnerships with reputable suppliers and maintaining transparent, auditable procurement processes ensures that infants receive the specialized nutrition they require without compromise.