The global slake lime market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across key industries such as construction, environmental protection, and chemical manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global lime market size was valued at USD 35.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising infrastructure development, stringent environmental regulations requiring flue gas desulfurization, and the continued use of slaked lime in wastewater treatment and soil stabilization. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in production capacity, product quality, and technological innovation. Based on market presence, geographic reach, and output volume, the following six companies represent the top slake lime producers shaping the industry’s trajectory.
Top 6 Slake Lime Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 USLM Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: uslm.com
Key Highlights: Hydrated lime is used in a variety of industrial applications, including municipal sanitation and water treatment. It is also utilized in highway construction….
#2 Shree Gannayak Lime
Domain Est. 2017
Website: shreegannayakminerals.com
Key Highlights: SHREE GANNAYAK MINERALS AND CHEMICALS (A manufacturers and suppliers of Quick Lime powder, Quick Lime, Hydrated Lime and Limestone. ) · Welcome to Shree Gannayak ……
#3 Slaked lime|Products|CALFINE
Website: calfine.co.jp
Key Highlights: Quick lime is slaked (hydration) by Chicibu-shiki slaker.All our products satisfy Japanese Industrial Standards(JIS)….
#4 Lime
Domain Est. 2019
Website: bericalce.it
Key Highlights: Lime is obtained by heating limestone, composed mostly of carbonate of lime, at high temperatures. The limestone are reduced in pieces….
#5 Shaurya Minerals
Domain Est. 2021 | Founded: 2010
Website: shauryaminerals.com
Key Highlights: Established in 2010, Shaurya Minerals is the leading company which is engaged in the manufacturing of Quick Lime and Hydrated Lime….
#6 Slaked lime
Website: kfn.ch
Key Highlights: Traditional slaked lime is made from lime guaranteed to be wood-burnt, and very finely ground. With an exact amount of water the burnt calcium oxide is slaked….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Slake Lime
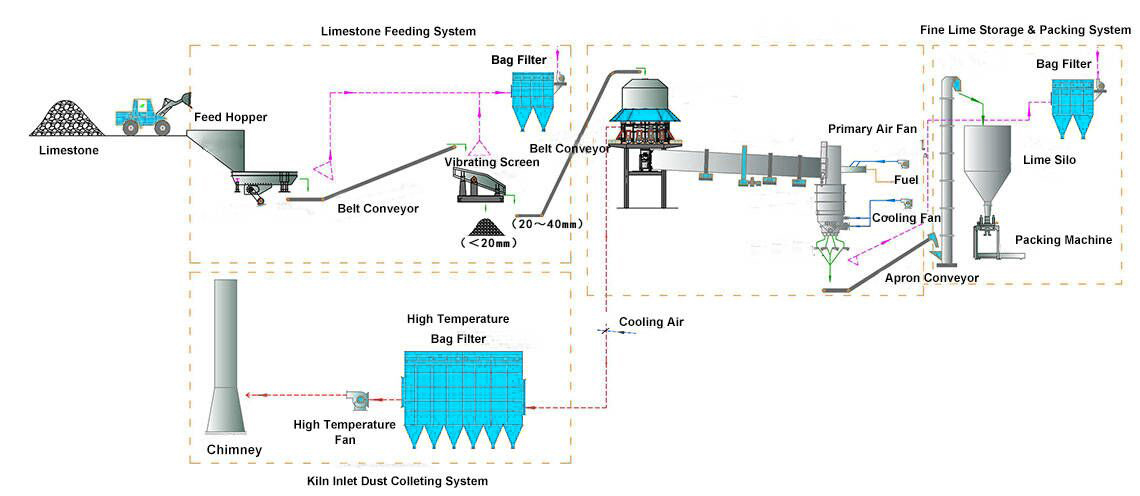
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Slaked Lime
The global slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂) market is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by sustained demand across key industrial, environmental, and construction sectors. Below is an analysis of the major market trends expected to shape the slaked lime industry in 2026:
-
Increasing Demand in Environmental Applications
A major growth driver for slaked lime is its expanding use in environmental protection. The compound is widely used in flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems in power plants to reduce sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions. With tightening global emissions regulations—especially under initiatives like the EU Green Deal and U.S. EPA Clean Air Act—utilities and industrial plants are increasingly adopting lime-based scrubbing technologies. By 2026, this trend is expected to accelerate, particularly in emerging markets investing in cleaner energy infrastructure. -
Water and Wastewater Treatment Expansion
Slaked lime plays a critical role in pH adjustment, heavy metal precipitation, and disinfection in municipal and industrial water treatment. As urbanization rises and water quality standards become more stringent, especially in Asia-Pacific and Africa, demand for lime-based treatment solutions is expected to grow. The push for sustainable water reuse and circular economy models will further boost slaked lime consumption in wastewater recycling plants. -
Growth in Construction and Building Materials
The construction sector remains a key consumer of slaked lime, particularly in mortar, plaster, and soil stabilization applications. With infrastructure development ongoing in regions such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa, the demand for high-quality, durable building materials will support stable slaked lime usage. Additionally, the resurgence of interest in traditional and eco-friendly construction methods—such as lime-based renders and plasters—is expected to provide niche but growing market opportunities. -
Agricultural Soil Amendment Usage
In agriculture, slaked lime is used to neutralize acidic soils and improve crop yield. As global food security concerns grow and sustainable farming practices gain traction, agronomic lime applications are expected to rise. Precision agriculture and government-supported soil health programs in countries like Brazil, the U.S., and several EU nations will contribute to higher lime demand by 2026. -
Supply Chain and Production Challenges
Despite growing demand, the slaked lime market may face headwinds due to energy-intensive production processes. The calcination of limestone (CaCO₃) to produce quicklime (CaO), which is then hydrated to create slaked lime, requires significant thermal energy, often from fossil fuels. Rising energy costs and carbon pricing mechanisms could pressure producers to innovate, potentially accelerating the adoption of alternative kiln technologies and renewable energy sources. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: Expected to dominate market growth due to rapid industrialization, urban development, and pollution control investments, particularly in China and India.
- North America and Europe: Mature markets with steady demand, driven by environmental compliance and infrastructure rehabilitation. Regulatory support for carbon capture (where lime can play a role) may open new avenues.
-
Latin America and Africa: Emerging markets with rising demand in mining (for pH control and metal recovery) and municipal water treatment.
-
Innovation and Sustainability Initiatives
By 2026, industry players are likely to focus on sustainability through carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) integration, energy-efficient kilns, and circular use of lime by-products (e.g., in cement production). Research into enhanced reactivity and pelletized forms of slaked lime for easier handling and transport may also influence market competitiveness.
Conclusion
The slaked lime market in 2026 is poised for moderate but consistent growth, underpinned by regulatory, environmental, and infrastructure development trends. While challenges related to energy costs and emissions persist, innovation and regional expansion will create opportunities for producers who align with sustainability and efficiency goals. Companies investing in cleaner production methods and diversified applications are likely to gain a competitive edge in the evolving market landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Slaked Lime (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂) for industrial, construction, or chemical applications requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production inefficiencies, product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Chemical Purity and Reactivity
Slaked lime varies in purity due to differences in raw limestone quality and hydration processes. Sourcing from suppliers without stringent quality control may result in inconsistent Ca(OH)₂ content, high levels of inert impurities (e.g., silica, alumina), or variable reactivity. This can negatively impact processes such as flue gas treatment, pH adjustment, or construction mortar performance.
2. Poor Particle Size Distribution
The effectiveness of slaked lime in applications like water treatment or soil stabilization depends heavily on particle size. Suppliers may provide material with broad or unsuitable particle distributions, leading to reduced dissolution rates or clogging in dosing systems. Always verify specifications for fineness (e.g., D50, sieve analysis) and ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
3. Moisture Content Variability
Excessive moisture can cause clumping, handling issues, and reduced active lime content. Some suppliers may deliver hydrated lime with higher-than-acceptable free moisture, impacting weighing accuracy and storage stability. Confirm moisture content specifications (typically <1%) and packaging conditions (e.g., moisture-resistant bags or bulk silos).
4. Inadequate Testing and Certification
Relying on suppliers that do not provide regular certificates of analysis (CoA) or third-party testing increases the risk of receiving substandard material. Ensure suppliers conduct routine testing for key parameters such as calcium hydroxide content, reactivity (e.g., temperature rise test), and heavy metal contaminants.
5. Incorrect Grade or Form Selection
Slaked lime comes in various forms—powder, slurry, or putty—each suited to specific applications. Sourcing the wrong form (e.g., dry powder for a slurry-based process) can lead to operational inefficiencies. Clearly define required physical form and handling specifications during procurement.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Use of Proprietary Processes Without Licensing
Some suppliers or end-users employ patented methods for producing or applying slaked lime (e.g., specialized hydration techniques or formulations for enhanced performance). Sourcing or using materials derived from such processes without proper licensing can expose your organization to IP infringement claims, especially in niche applications like advanced construction materials or specialty chemicals.
2. Reverse Engineering or Misappropriation Risks
Attempting to replicate a competitor’s lime-based product formulation or process based on publicly available slaked lime may inadvertently violate trade secrets or patented methods. Conduct thorough IP due diligence before adopting new sourcing or application strategies.
3. Ambiguous Supplier Agreements on IP Ownership
When co-developing lime-based formulations or processes with a supplier, failing to clarify IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Ensure agreements explicitly state who owns improvements, formulations, or process innovations resulting from collaborations.
4. Sourcing from Unverified or Informal Channels
Procuring slaked lime from non-reputable or informal suppliers increases the risk of inadvertently using materials produced via infringing processes. Stick to vetted suppliers with transparent manufacturing practices and compliance documentation.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require detailed technical data sheets and CoAs with every shipment.
- Audit suppliers regularly for quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and process controls.
- Conduct pilot testing before full-scale adoption.
- Engage legal counsel to review contracts and assess IP risks, especially for custom formulations or new applications.
- Monitor patent landscapes relevant to lime utilization in your industry.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and freedom to operate when sourcing slaked lime.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Slaked Lime
Overview of Slaked Lime
Slaked lime, also known as calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂), is a white, powdery or slurry chemical compound produced by adding water to quicklime (calcium oxide). It is widely used in water treatment, construction, agriculture, chemical manufacturing, and environmental remediation. Due to its caustic nature and reactivity, strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed during handling, storage, transportation, and disposal.
Regulatory Classification
Slaked lime is classified under various regulatory frameworks based on physical state and concentration:
– GHS Classification: Skin corrosion/irritation (Category 1B), serious eye damage/eye irritation (Category 1), specific target organ toxicity (single exposure, Category 3 – respiratory irritation).
– UN Number: UN 3262 (Calcium hydroxide, solid) or UN 1824 (Calcium hydroxide solution), depending on form.
– Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive Substances) under the UN Model Regulations.
– EPA/OSHA/REACH: Subject to reporting requirements under EPCRA (Section 311/312), OSHA HAZCOM, and REACH in the EU if quantities exceed thresholds.
Packaging Requirements
Appropriate packaging is essential to prevent moisture absorption, contamination, and exposure:
– Dry Powder: Use multi-wall paper bags with polyethylene liner, fiber drums, or super sacks (FIBCs) rated for hazardous materials. Ensure closures are secure and moisture-resistant.
– Slurry/Solution: Transport in corrosion-resistant tanks or containers made of polyethylene, fiberglass, or stainless steel. Avoid carbon steel due to potential corrosion.
– Labeling: All packages must display GHS-compliant labels with hazard pictograms (corrosion, exclamation mark), signal word (Warning or Danger), hazard statements (H315, H318, H335), and precautionary statements.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage minimizes risks of degradation and exposure:
– Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from acids, moisture, and incompatible materials (e.g., ammonium salts, aluminum).
– Use sealed containers to prevent carbonation (reaction with CO₂ in air forming calcium carbonate).
– Elevate bags or drums off concrete floors using pallets to avoid moisture uptake.
– Implement secondary containment for bulk storage to capture spills or leaks.
– Limit storage duration to prevent quality degradation; rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) principle.
Transportation Requirements
Compliance with national and international transport regulations is mandatory:
– Road (DOT 49 CFR): Use placarded vehicles for bulk shipments (Placard: CORROSIVE, UN 3262). Secure loads to prevent shifting. Drivers must have hazardous materials endorsement (if required).
– Rail (DOT/AAR): Follow AAR Manual of Standards for packaging, labeling, and documentation.
– Marine (IMDG Code): Classify under Class 8, Packing Group III (low danger). Use approved containers with proper documentation, including Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and Dangerous Goods Declaration.
– Air (IATA DGR): Generally permitted with restrictions; verify current regulations as some formulations may be forbidden or limited.
Handling Procedures
Safe handling practices protect personnel and ensure product integrity:
– Use engineering controls such as local exhaust ventilation in enclosed spaces.
– Require personal protective equipment (PPE): chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile or neoprene), safety goggles or face shield, long-sleeve clothing, and respiratory protection (N95 or half-face respirator with P100 filter) in dusty environments.
– Avoid generating dust; use wet methods or dust collection systems during transfer.
– Prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in handling areas.
Emergency Response
Prepare for spills, exposure, and fires:
– Spill Response: Contain spill using inert absorbents (e.g., sand, vermiculite). Do not use combustible materials. Neutralize with weak acid (e.g., vinegar) if appropriate. Collect material in labeled, compatible containers for disposal.
– First Aid:
– Skin contact: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes; remove contaminated clothing.
– Eye contact: Rinse immediately with water for 15–20 minutes; seek medical attention.
– Inhalation: Move to fresh air; provide oxygen if breathing is difficult.
– Ingestion: Rinse mouth; do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical help.
– Fire Response: Slaked lime is non-flammable, but may release irritating fumes when heated. Use water spray to cool containers and disperse dust clouds.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
Manage environmental impact and follow disposal regulations:
– Prevent release into waterways or soil; it can increase pH and harm aquatic life.
– Spills must be reported per local environmental regulations (e.g., CERCLA in the U.S. if quantity exceeds reportable quantities).
– Dispose of waste slaked lime or contaminated materials as hazardous waste according to RCRA (U.S.) or equivalent local regulations.
– Neutralization and stabilization may be required before landfill disposal.
Documentation & Training
Maintain compliance through proper documentation and personnel training:
– Provide up-to-date Safety Data Sheet (SDS) to all handlers and emergency responders.
– Maintain shipping papers, manifests, and permits as required by jurisdiction.
– Train employees annually on hazard communication, spill response, PPE use, and emergency procedures per OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1200 and DOT 49 CFR 172.700.
Conclusion
Slaked lime is a valuable industrial material but requires careful handling due to its corrosive properties. Adhering to logistics and compliance guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection throughout its supply chain. Regular audits, employee training, and emergency preparedness are key to maintaining a safe and compliant operation.
Conclusion for Sourcing Slake Lime
In conclusion, sourcing slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) requires a careful evaluation of quality, reliability, cost, and sustainability. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards and can provide consistent product specifications, particularly for applications in water treatment, construction, agriculture, or chemical manufacturing. Factors such as transportation logistics, storage requirements, and environmental compliance also play a significant role in the decision-making process. By conducting thorough supplier assessments, ensuring proper safety and handling protocols, and considering long-term supply agreements, organizations can secure a dependable and efficient supply of slaked lime that meets both operational and regulatory requirements. Ultimately, strategic sourcing of slaked lime supports process efficiency, product quality, and environmental responsibility.