The global shift module market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for automated systems in automotive, industrial machinery, and electric vehicle transmissions. According to Grand View Research, the global automatic transmission market—of which shift modules are a critical component—was valued at USD 114.6 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects continued expansion in transmission and drivetrain subsystems, attributing growth to advancements in electromechanical actuation and rising adoption of dual-clutch and automated manual transmissions. As vehicles evolve toward greater efficiency and automation, shift modules have become pivotal in enabling seamless gear transitions. This data-backed momentum underscores the importance of innovation and reliability among manufacturers. Below are the top 10 shift module manufacturers leading this transformation through technological excellence, global supply chain integration, and strategic R&D investments.
Top 10 Shift Module Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
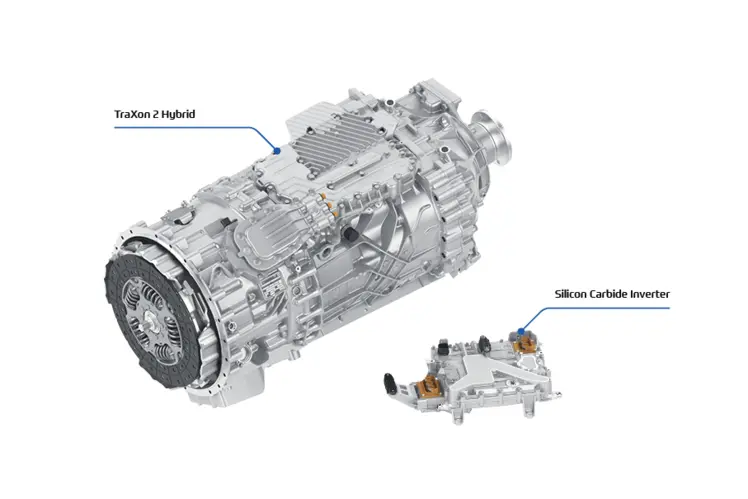
#1 TraXon 2
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zf.com
Key Highlights: The modular automated transmission system TraXon 2 for OEMs. Efficient, secure, and scalable for medium to heavy-duty mobile cranes….
#2 Sustainable technology from Germany
Domain Est. 2020
Website: shift.eco
Key Highlights: SHIFT is so much more than just a smartphone or a detachable notebook, so much more than just sustainable technology….
#3 Control Modules – toward Electrification
Domain Est. 1991
Website: magna.com
Key Highlights: Magna’s RDCM controls the torque at the rear wheels of the vehicle balancing it left to right, and shifting torque when needed. Powertrain Control Module (PCM)….
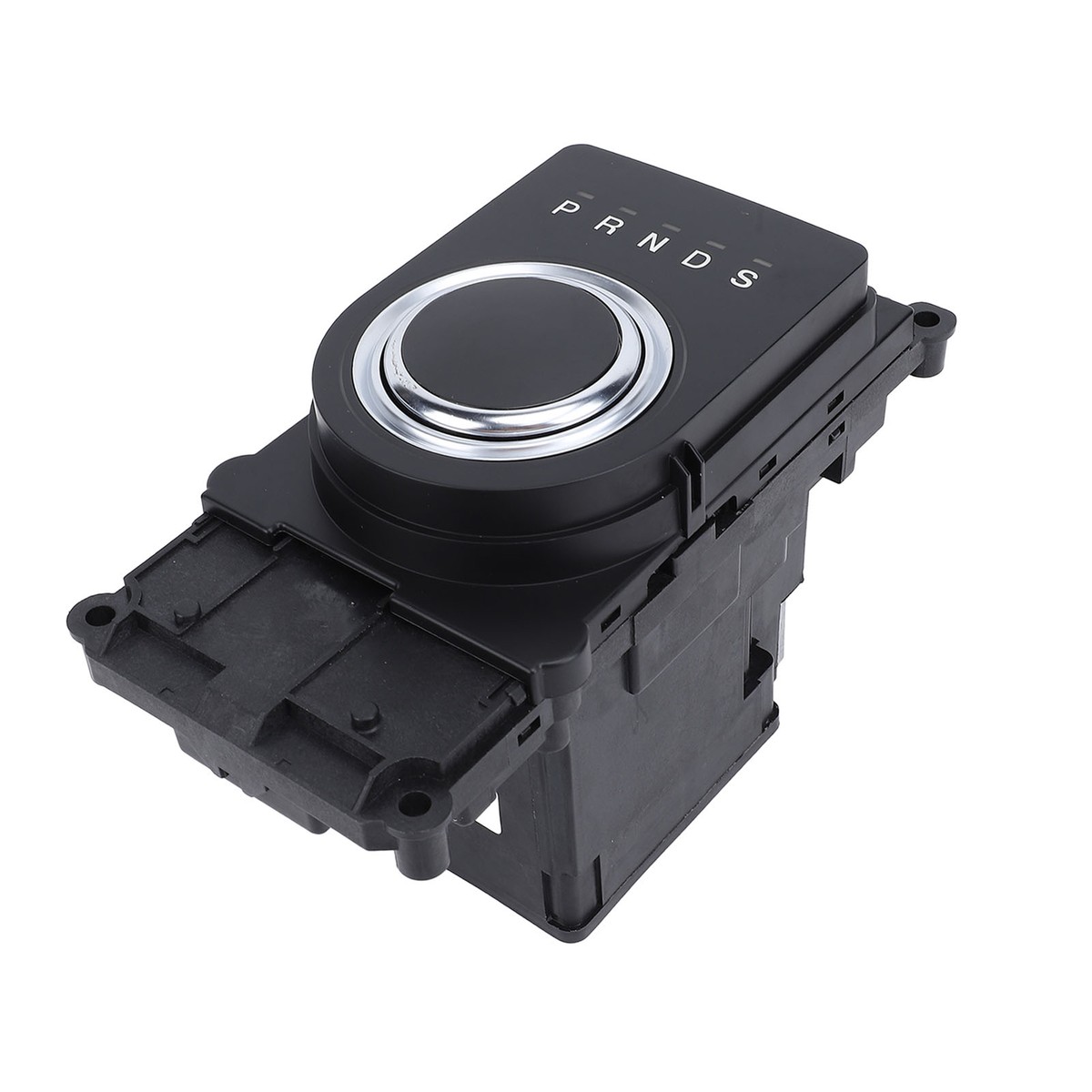
#4 Electronic Shifter Module
Domain Est. 1995
Website: strattec.com
Key Highlights: An Electronic Shifter or E-shifter is a center console switchpack that communicates changes in transmission gear modes; Park, Reverse, Neutral and Drive (PRND)….
#5 Hurst ()
Domain Est. 1995
Website: holley.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $149 · 90-day returnsShop the official site of Hurst shifters for automatic and manual vehicles. Reduce your vehicle’s shift throw by up to 35% or more at Holle…
#6 Allison Transmission
Domain Est. 1998
Website: allisontransmission.com
Key Highlights: Allison Transmission is a global leader in automatic transmissions, with locations worldwide providing hybrid propulsion solutions for commercial vehicles ……
#7 Commercial Trucks, Buses, Engines & Parts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: international.com
Key Highlights: INTERNATIONAL® S13® INTEGRATED POWERTRAIN SHIFT WHAT’S POSSIBLE. A unified engine, transmission and aftertreatment system, the S13® Integrated is simple, easy ……
#8 TREMEC
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tremec.com
Key Highlights: Performance engineered line of transmissions and components for line haul and vocational vehicles. · Optimal durability, ease of shifting and low ownership costs ……
#9 Transmission Technologies
Domain Est. 2002
Website: borgwarner.com
Key Highlights: BorgWarner is the worldwide leader in automatic transmission clutch components and systems, BorgWarner supplies wet friction clutch modules, friction plates, ……
#10 TI Fluid Systems
Domain Est. 2016
Website: tifluidsystems.com
Key Highlights: TI Fluid Systems designs and manufactures thermal management and fluid handling systems that improve efficiency, performance and sustainability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Shift Module

H2 2026 Market Trends for Shift Modules
As we approach H2 2026, the shift module market is poised for significant transformation driven by technological convergence, evolving consumer demands, and macroeconomic shifts. While “shift module” can refer to various applications (e.g., automotive transmission systems, industrial automation components, or modular power/energy systems), this analysis focuses on the broader, high-growth interpretation: modular components enabling dynamic reconfiguration in automation, robotics, and sustainable systems. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Accelerated Adoption in Flexible Automation & Robotics:
- Demand for Agility: Manufacturers face increasing pressure for mass customization and rapid reconfiguration. Shift modules enabling quick changeovers of robotic end-effectors, workstations, or production lines will be critical.
- Plug-and-Play Standardization: H2 2026 will see wider adoption of standardized interfaces (e.g., based on IO-Link, OPC UA) for shift modules, reducing integration time and cost. Vendors offering truly interoperable “plug-and-produce” solutions will gain significant market share.
- Integration with AI/ML: Shift modules will increasingly incorporate embedded intelligence (sensors, edge processing) to enable predictive maintenance, adaptive positioning, and autonomous reconfiguration based on real-time production data.
-
Electrification & Sustainable Mobility Driving Automotive Shift Modules:
- Beyond ICE Transmissions: While traditional transmission shift modules evolve, the growth engine will be in electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains. This includes:
- Multi-Speed E-Transmissions: Shift modules enabling efficient 2-speed transmissions for high-performance or long-range EVs.
- e-Axle Integration: Compact, high-torque shift mechanisms within integrated e-axle units for torque vectoring and efficiency optimization.
- Hybrid System Complexity: Sophisticated shift modules managing seamless transitions between ICE and electric power sources in complex hybrid architectures.
- Focus on Efficiency & NVH: Intense competition will drive demand for shift modules offering smoother, faster shifts with lower energy loss and reduced noise/vibration, directly impacting EV range and user experience.
- Beyond ICE Transmissions: While traditional transmission shift modules evolve, the growth engine will be in electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains. This includes:
-
Convergence with Energy Transition & Grid Flexibility:
- Modular Energy Storage: “Shift” concepts apply to rapidly reconfigurable energy storage solutions. H2 2026 will see growth in modular battery systems for grid support (frequency regulation, peak shaving) where capacity can be dynamically “shifted” or allocated.
- Smart Grid & Prosumer Integration: Shift modules (control systems) enabling dynamic load shifting and energy flow management between homes, EVs, and the grid (V2G, V2H) will become more sophisticated and commercially viable as grid congestion and renewable intermittency increase.
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Localization:
- Geopolitical Pressures: Ongoing supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions will push manufacturers (especially in automotive and industrial automation) to source shift modules locally or regionally.
- Reshoring/Nearshoring: H2 2026 may see increased investment in manufacturing capacity within key markets (North America, Europe, parts of Asia) for critical shift module components, impacting global sourcing strategies and potentially favoring regional suppliers.
-
Advanced Materials & Miniaturization:
- Performance Demands: Need for higher power density, efficiency, and reliability in smaller footprints will drive adoption of advanced materials (high-strength alloys, composites, specialized ceramics) and innovative manufacturing techniques (additive manufacturing, precision machining).
- Weight Reduction: Critical in automotive and aerospace applications, leading to lighter shift modules without sacrificing durability.
-
Cybersecurity & Functional Safety:
- Increased Connectivity: As shift modules become smarter and more connected (IIoT), they become potential cyberattack vectors. H2 2026 will see heightened focus on embedded security features (hardware security modules, secure boot) and compliance with standards like ISO/SAE 21434 (cybersecurity) and ISO 13849/IEC 62061 (safety).
- Safety-Critical Applications: In robotics and automotive, failure of a shift module can have severe consequences, driving demand for redundant systems and rigorous safety certification.
Summary & Outlook for H2 2026:
The shift module market in H2 2026 will be characterized by integration, intelligence, and sustainability. Success will depend on vendors offering:
* Modular, standardized solutions for easy integration into flexible systems.
* Embedded intelligence for predictive and adaptive operation.
* High efficiency and reliability in compact, durable designs.
* Strong cybersecurity and safety certifications.
* Resilient supply chains with regional capabilities.
Industries like advanced manufacturing, electric mobility, and renewable energy integration will be primary growth drivers. Companies that proactively address these converging trends will be best positioned to capture market share in the latter half of 2026.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Shift Module (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a shift module—whether for automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, or electronic control systems—can be complex. Two critical areas where organizations often encounter challenges are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production delays, increased costs, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and track record can result in substandard shift modules. Suppliers without ISO/TS 16949 (or IATF 16949) certification in automotive applications, for example, may not meet required quality standards. -
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Assuming that off-the-shelf or pre-certified modules will perform reliably in your specific application without rigorous in-house testing can lead to field failures. Environmental stress, durability, and integration testing are often overlooked during sourcing. -
Component Traceability Issues
Poor traceability of sub-components within the shift module makes it difficult to identify the source of defects or conduct effective root cause analysis during failure events. -
Lack of Long-Term Reliability Data
New or low-cost suppliers may offer competitive pricing but lack proven performance history. Without access to long-term reliability data (e.g., MTBF—Mean Time Between Failures), the risk of premature failure increases. -
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Suppliers with inconsistent production processes—especially those relying on manual assembly or outdated equipment—can introduce variability that affects module performance and lifespan.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Unclear IP Ownership
Failure to define IP ownership in sourcing agreements can lead to disputes. For example, if a shift module is co-developed or customized, it may be unclear whether the design, firmware, or software belongs to the supplier, buyer, or both. -
Use of Infringing Technology
Sourcing from suppliers who use third-party patented technologies (e.g., in gear actuation mechanisms or control algorithms) without proper licensing exposes the buyer to infringement claims, even if unintentional. -
Lack of IP Due Diligence
Not conducting IP audits or freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before finalizing a supplier can result in legal vulnerabilities. This is especially critical in highly regulated or competitive industries like automotive or aerospace. -
Inadequate Protection of Custom Designs
When providing custom specifications or designs to a supplier, failing to include non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP protection clauses may allow the supplier to reuse or resell your design to competitors. -
Embedded Software and Licensing Risks
Shift modules often include firmware or software with open-source components. Sourcing without reviewing software licenses (e.g., GPL, LGPL) can result in unintended obligations to disclose source code or pay royalties.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits and request quality certifications.
- Include detailed quality requirements and testing protocols in contracts.
- Perform independent reliability and compatibility testing.
- Clearly define IP ownership and usage rights in legal agreements.
- Require suppliers to warrant that their products do not infringe third-party IP.
- Audit software components for compliance with licensing terms.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires proactive due diligence, clear contractual terms, and ongoing supplier management to ensure both quality integrity and IP security.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Shift Module
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations when implementing and operating the Shift Module in your organization. Adhering to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and efficient workforce management.
Module Overview and Purpose
The Shift Module is designed to streamline shift scheduling, time tracking, and workforce allocation across departments and locations. It supports workforce planning, labor law compliance, attendance monitoring, and payroll integration. Understanding its purpose is critical for effective deployment and adherence to operational standards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Ensure the Shift Module complies with all applicable labor laws and industry regulations, including:
- Working Hours Regulations: Adhere to maximum working hours, rest periods, and overtime rules as defined by local and national labor laws (e.g., FLSA in the U.S., Working Time Directive in the EU).
- Break and Rest Periods: Automatically enforce mandatory break times based on shift length and jurisdiction.
- Overtime Management: Track and approve overtime in accordance with legal thresholds and company policy.
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO): Avoid scheduling biases related to gender, age, religion, or protected classes.
- Data Privacy Laws: Comply with GDPR, CCPA, or other data protection regulations when storing and processing employee shift data.
Data Security and Employee Privacy
Protect sensitive employee information through:
- Access Controls: Restrict module access to authorized personnel only, using role-based permissions.
- Encryption: Ensure data is encrypted in transit and at rest.
- Audit Logs: Maintain logs of all schedule changes, approvals, and user activities for transparency and accountability.
- Data Retention Policies: Define and enforce policies for how long shift records are stored, aligned with legal requirements.
Scheduling Best Practices
To optimize efficiency and fairness:
- Advance Notice: Provide employees with shift schedules within the timeframe required by local law (e.g., 7–14 days in advance).
- Shift Bidding & Preferences: Allow employees to express availability and shift preferences to improve satisfaction and retention.
- Shift Swaps & Time-Off Requests: Enable approved peer-to-peer shift swaps and formal time-off requests with manager oversight.
- Consistency: Maintain predictable scheduling patterns where possible, especially for part-time and hourly workers.
Integration with Payroll and HR Systems
Ensure seamless data flow between the Shift Module and other systems:
- Time & Attendance Sync: Accurately transfer worked hours, absences, and overtime to payroll systems.
- HRIS Integration: Connect with Human Resource Information Systems for employee status, roles, and contract details.
- Error Handling: Establish procedures to resolve discrepancies between scheduled and recorded hours.
Training and Change Management
Successful adoption requires:
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training for managers and employees on using the Shift Module.
- Documentation: Maintain up-to-date user guides, FAQs, and troubleshooting resources.
- Support Channels: Designate internal support staff or helpdesk for module-related inquiries.
Audit and Compliance Monitoring
Regularly assess compliance and performance:
- Compliance Audits: Conduct periodic audits to verify adherence to labor laws and internal policies.
- Reporting: Generate compliance reports (e.g., overtime trends, schedule adherence) for management and legal review.
- Continuous Improvement: Use audit findings and user feedback to improve scheduling practices and system configuration.
Incident Response and Escalation
Prepare for scheduling disruptions or compliance issues:
- Contingency Planning: Define procedures for last-minute shift changes, no-shows, or system outages.
- Escalation Paths: Establish clear protocols for reporting and resolving compliance violations or scheduling errors.
- Communication Plan: Notify employees promptly of schedule changes via preferred channels (email, app alerts, SMS).
By following this guide, organizations can leverage the Shift Module to enhance operational efficiency while maintaining full compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing Shift Module
In conclusion, the sourcing of the shift module has been thoroughly evaluated considering technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost efficiency, quality standards, and delivery timelines. The selected supplier demonstrates a strong alignment with our operational requirements, offering a reliable, high-performance shift module that meets both current and anticipated future needs. Strategic sourcing practices, including risk assessment and long-term partnership considerations, have ensured a balanced decision that supports supply chain resilience and cost optimization. Moving forward, continuous performance monitoring and supplier collaboration will be essential to maintain quality, ensure on-time delivery, and support ongoing improvements. This sourcing decision positions the organization for greater efficiency and competitiveness in its product offerings.