The global titanium sheets market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across aerospace, defense, medical, and industrial sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the titanium market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, with titanium sheets representing a significant segment due to their high strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and performance in extreme environments. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global titanium market at USD 23.7 billion in 2022 and forecasts continued expansion, underpinned by rising aircraft production and the adoption of lightweight materials in next-generation engineering applications. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in producing high-quality titanium sheets, combining advanced metallurgical expertise with large-scale production capabilities. Below, we highlight the top nine titanium sheet manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through innovation, global reach, and consistent material performance.
Top 9 Sheets Of Titanium Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Titanium Industries, Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: titanium.com
Key Highlights: Titanium Industries is a global leader in Specialty Metals supply. Complete inventory of Titanium Round Bar, Titanium Plate & Sheet, and more….
#2 Laube Technology
Domain Est. 1995
Website: laube.com
Key Highlights: We supply a full range of titanium mill products—including titanium bars, titanium tubes, titanium plates, titanium sheets, titanium powder, and titanium coil ……
#3 Titanium Plates/Sheets
Domain Est. 2014
Website: usa-titanium.com
Key Highlights: Suitable for applications such as Chemical industry, Electrometallurgy, Sewage treatment, Electrolytic copper, Organic electrochemical synthesis, Cathodic ……
#4 Titanium Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: twmetals.com
Key Highlights: TW Metals is a leading distributor of Aerospace titanium tubing in support of commercial and military aircraft. Complimentary products in bar, sheet and plate ……
#5 Titanium supplier, titanium bars, stainless steel, cobalt chrome bars …
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1991
Website: acnis-titanium.com
Key Highlights: Since 1991, Acnis International delivers quality products immediately available from stock of titanium and other metals in bars, sheets or powder, with a smile!…
#6 Hermith GmbH
Domain Est. 2009
Website: hermith.com
Key Highlights: We are proud to offer you a variety of titanium materials: Sheets, Plates, Bars and Billets, Tubes. All of our competitively priced material is multi ……
#7 Titanium Sheet Suppliers
Domain Est. 2012
Website: titaniummanufacturers.com
Key Highlights: Discover ISO 9001 certified titanium sheet suppliers providing top-quality, high-strength sheets at competitive prices with exceptional service….
#8 Titanium
Domain Est. 2013
Website: atimaterials.com
Key Highlights: We produce high strength commercially pure titanium and titanium alloy products in flat-rolled and long forms, net-shapes and components….
#9 TMS Titanium
Domain Est. 2014
Website: tmstitanium.com
Key Highlights: TMS Titanium is a supplier and stocking distributor of titanium mill products. We stock the highest quality products, including sheet, plate, block, bar, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sheets Of Titanium
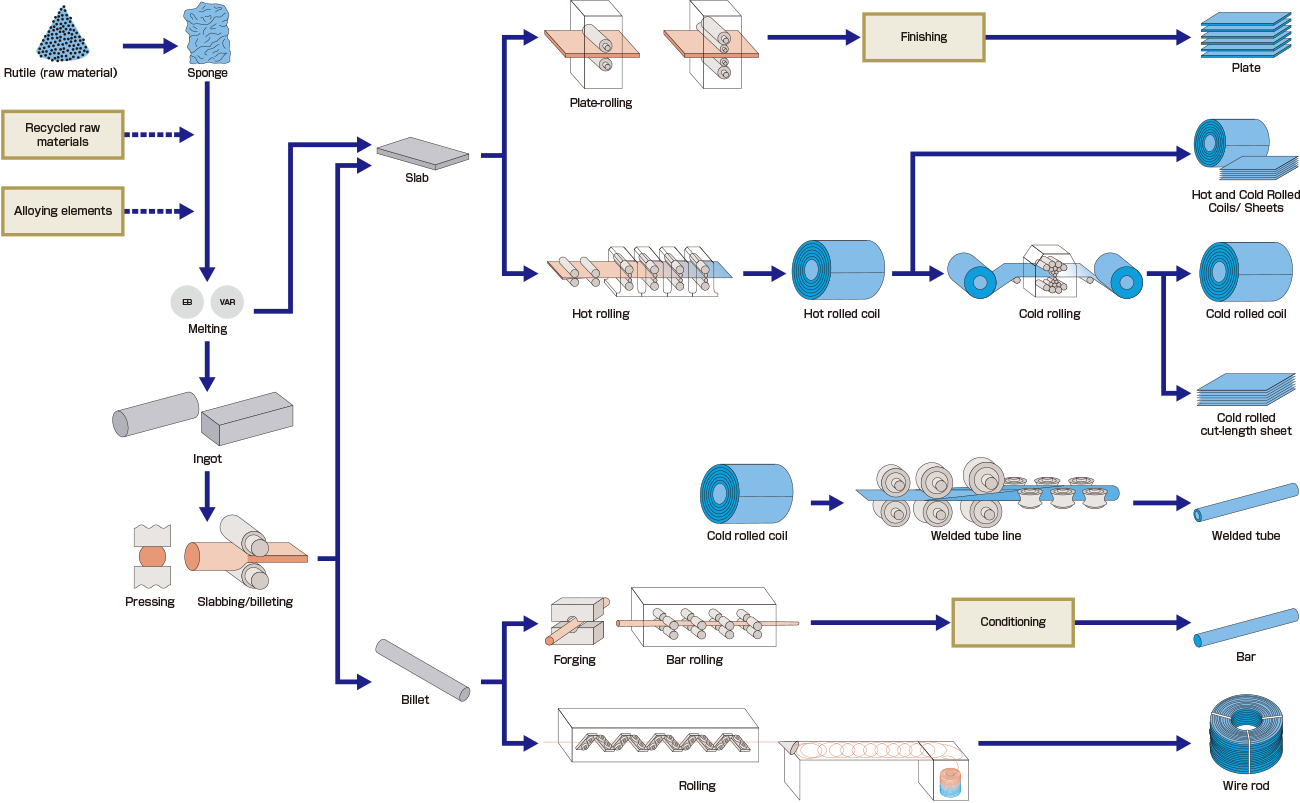
2026 Market Trends for Sheets of Titanium
The global market for titanium sheets is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving demand across key industries, technological advancements, and shifting geopolitical and environmental dynamics. Here are the primary trends expected to shape the market:
Rising Aerospace and Defense Demand
Aerospace remains the dominant consumer of titanium sheets, and this trend will intensify by 2026. The continued production ramp-up of commercial aircraft—especially next-generation fuel-efficient models like the Boeing 787 and Airbus A350—will require large volumes of high-strength, lightweight titanium sheet metal for airframes, engines, and landing gear. Simultaneously, increased global defense spending will boost demand for advanced military aircraft, drones, and naval vessels, all of which utilize titanium extensively for its corrosion resistance and performance in extreme conditions.
Expansion in Green Energy and Industrial Applications
The clean energy transition will significantly influence titanium sheet consumption. By 2026, demand is expected to grow in hydrogen economy infrastructure, particularly for electrolyzers and fuel cells where titanium’s corrosion resistance in acidic and alkaline environments is critical. Additionally, titanium sheets are increasingly used in geothermal plants, offshore wind turbine components, and desalination facilities, driven by their longevity in harsh marine and high-temperature environments.
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions experienced in recent years will push manufacturers toward regionalization of titanium production. By 2026, North America and Europe are likely to invest more in domestic titanium processing and sheet rolling capabilities to reduce reliance on single-source suppliers. This shift may lead to the development of new domestic supply chains and strategic stockpiling initiatives, particularly in defense-critical sectors.
Advancements in Manufacturing and Cost Reduction
Innovations in additive manufacturing (3D printing) and near-net-shape forming will complement traditional titanium sheet production. While sheet metal remains essential for large structural parts, hybrid manufacturing techniques could reduce waste and lower costs. Additionally, improvements in titanium extraction (e.g., FFC Cambridge process) and recycling technologies are expected to modestly reduce production costs by 2026, making titanium sheets more accessible for cost-sensitive applications.
Sustainability and Recycling Pressure
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will drive increased recycling of titanium scrap into new sheets. Titanium’s infinite recyclability without loss of properties makes it attractive, and by 2026, closed-loop recycling systems are expected to become more prevalent, especially in aerospace and medical sectors. This trend will help mitigate the environmental footprint of primary titanium production, which is energy-intensive.
Growth in Medical and High-Tech Sectors
The medical device industry will continue to adopt titanium sheets for implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment due to its biocompatibility and strength. Furthermore, emerging high-tech applications in consumer electronics, luxury goods, and advanced robotics may create niche but growing demand for precision titanium sheet products.
In summary, the 2026 market for sheets of titanium will be characterized by robust demand from aerospace and clean energy, regional supply chain restructuring, technological innovation, and a stronger focus on sustainability. These factors will collectively drive market growth and reshape competitive dynamics across the titanium value chain.
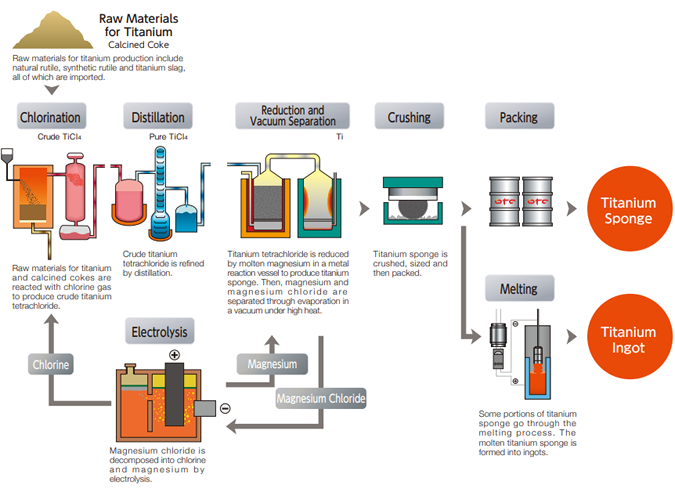
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sheets of Titanium (Quality, IP)
Sourcing titanium sheets—especially for high-performance industries like aerospace, medical, or defense—requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to supply chain disruptions, product failures, or legal issues. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
1. Assuming All Titanium Is the Same
One of the most common mistakes is treating titanium as a generic material. Titanium comes in multiple grades (e.g., Grade 1 to Grade 38), each with different mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and alloy compositions (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V, CP titanium). Using the wrong grade can compromise performance and safety.
Pitfall: Procuring Grade 2 when Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is required for high-stress applications.
Solution: Clearly define the required ASTM, AMS, or MIL specifications in procurement contracts.
2. Inadequate Quality Certification and Traceability
Titanium used in regulated industries requires full material traceability (mill test reports, heat numbers, and CoC—Certificate of Conformance). Lack of proper documentation can result in rejected shipments or non-compliance.
Pitfall: Accepting sheets without full traceability, leading to disqualification in audits or certifications.
Solution: Require certified mills or suppliers with documented quality management systems (e.g., AS9100, ISO 13485).
3. Overlooking Surface Quality and Finishing
Titanium sheets are often used in applications where surface integrity is critical (e.g., medical implants or aerospace components). Poor surface finish, scratches, or contamination can lead to premature failure.
Pitfall: Receiving sheets with surface defects that require costly rework or rejection.
Solution: Specify surface finish requirements (e.g., #4 finish, pickled, ground) and include inspection criteria in purchase orders.
4. Sourcing from Unverified or Non-Compliant Suppliers
Using suppliers without proven track records or certifications increases the risk of receiving substandard or counterfeit material. Some suppliers may misrepresent alloy composition or origin.
Pitfall: Receiving “titanium” that fails spectrographic analysis or contains unauthorized substitutions.
Solution: Audit suppliers, require third-party testing (e.g., PMI—Positive Material Identification), and prefer vendors on approved manufacturer lists (AMLs).
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Material Specifications
In high-tech sectors, titanium sheet specifications may be part of proprietary designs or patented manufacturing processes. Sourcing materials that mimic or infringe on protected IP can lead to legal disputes.
Pitfall: Using a supplier that reverse-engineers a proprietary titanium alloy or process, exposing your company to IP litigation.
Solution: Ensure sourcing agreements include IP indemnification clauses and verify that materials do not violate patents or technical data rights.
6. Ignoring Geographic and Trade Compliance
Titanium is a strategic material subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Sourcing from certain countries or using materials with restricted origins can trigger compliance violations.
Pitfall: Importing titanium from sanctioned regions or failing to meet defense trade regulations.
Solution: Confirm supplier compliance with export control laws and maintain documentation for customs and regulatory audits.
7. Failing to Validate Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
Titanium production is energy-intensive and concentrated among a few global suppliers. Relying on a single source without contingency plans risks disruption.
Pitfall: Production delays due to supplier capacity issues or geopolitical factors.
Solution: Diversify sourcing, establish long-term agreements, and assess supplier financial and operational health.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable access to high-integrity titanium sheets while minimizing risk and maintaining compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sheets of Titanium
Titanium sheets are high-value, regulated materials used across aerospace, medical, industrial, and defense sectors. Proper logistics and compliance procedures are essential to ensure safe handling, legal transport, and adherence to international standards. This guide outlines key considerations for managing the shipment and regulatory compliance of titanium sheets.
Material Classification & Regulatory Overview
Titanium sheets are generally classified as strategic or dual-use materials due to their application in defense and aerospace industries. Depending on the alloy composition (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V), form, and intended use, they may fall under export control regulations such as:
- ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) – If used in defense articles, certain titanium products require ITAR licensing.
- EAR (Export Administration Regulations) – Most commercial titanium sheets fall under the Commerce Control List (CCL), typically ECCN 1C006 or 1C997, depending on purity, strength, and form.
- Customs Tariff Classification – HS Code 8108.20 (Titanium waste and scrap; unwrought titanium; powder) or 8108.90 (Other) may apply depending on form and finish.
Verify the specific alloy, dimensions, and end-use to determine correct classification.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage and contamination:
- Protective Wrapping: Use moisture-resistant, anti-corrosion wrap (e.g., VCI paper) to prevent oxidation and surface damage.
- Palletization: Secure sheets on wooden or metal skids using strapping or banding. Use edge protectors to prevent bending or chipping.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), material grade, heat number, dimensions, weight, and regulatory markings if applicable.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent moisture exposure and corrosion.
Transportation Logistics
Domestic Transport (e.g., U.S.)
- Use flatbed or enclosed trailers depending on environmental exposure risk.
- Secure loads with straps or chains to prevent shifting.
- Comply with DOT regulations for load securement (49 CFR Part 393).
- Maintain documentation including bill of lading, material test reports (MTRs), and chain of custody.
International Shipping
- Mode Selection: Air freight for urgent, high-value shipments; ocean freight for bulk orders.
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibility using Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP).
- Export Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and export license (if required).
- Customs Clearance: Provide accurate HS codes, ECCN, and End-User Statements where necessary.
Export & Import Compliance
- License Requirements: Determine if an export license is needed based on destination country and end-use. Countries under embargo or with military end-use may require additional scrutiny.
- Sanctions Screening: Screen all parties (consignee, end-user, freight forwarder) against OFAC, BIS Denied Persons List, and other global watchlists.
- Recordkeeping: Retain export documentation for a minimum of five years (per EAR) or longer under ITAR (five years post-shipment or license expiration).
- Re-Exports: Be aware that re-export of titanium sheets from one foreign country to another may also require authorization.
Quality & Traceability Documentation
Ensure full traceability with:
– Material Test Reports (MTRs) – Certify chemical composition and mechanical properties per ASTM B265 or AMS 4911.
– Heat/Lot Numbers – Each sheet should be traceable to its production batch.
– Certificates of Conformance (CoC) – Required for aerospace and defense contracts.
– NDT Reports – If applicable, include ultrasonic or eddy current testing results.
Special Considerations
- Dual-Use Risk: Even commercial-grade titanium can be subject to controls if exported to high-risk regions or for sensitive applications.
- Insurance: Obtain cargo insurance covering full replacement value, including risks like theft, damage, and delay.
- Carrier Vetting: Use carriers experienced in handling high-value metals and compliant with CTPAT (Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism) if shipping to the U.S.
Conclusion
Shipping titanium sheets requires careful coordination of logistics, regulatory compliance, and documentation. By classifying materials correctly, securing proper licenses, using appropriate packaging, and maintaining traceability, companies can ensure timely, legal, and safe delivery of titanium products worldwide. Always consult with legal or compliance experts when navigating export controls and international trade regulations.
In conclusion, sourcing sheets of titanium requires careful consideration of material grade, specifications, supplier reliability, cost, and lead times. Titanium’s exceptional strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and performance at elevated temperatures make it ideal for aerospace, medical, marine, and industrial applications. However, its high cost and processing challenges necessitate working with reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ASTM or AMS. Establishing long-term relationships with certified vendors, conducting thorough quality inspections, and considering factors like mill certifications and traceability will ensure consistent material quality and supply chain efficiency. Additionally, evaluating alternative sourcing options—such as local distributors versus direct mill orders—can help balance cost, delivery speed, and technical support. Ultimately, a strategic and well-informed approach to sourcing titanium sheets is essential to meet performance requirements while maintaining project timelines and budgets.