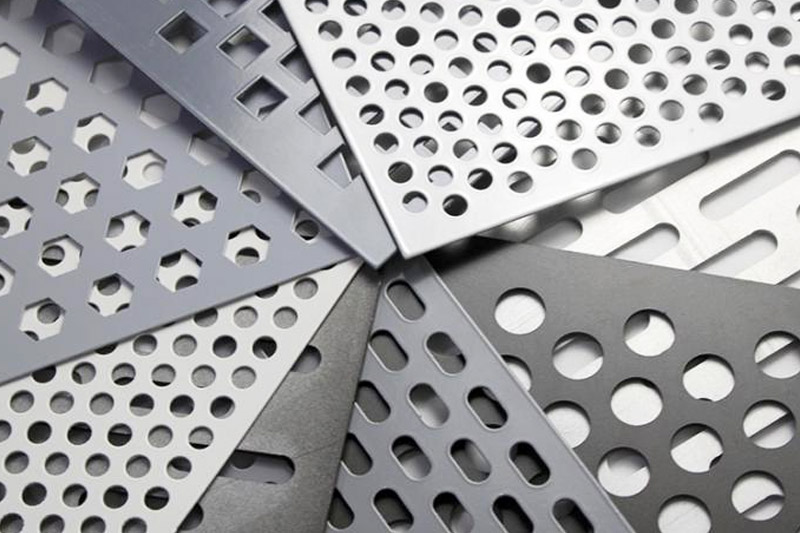
The global sheet metal fabrication market, including specialized products such as perforated or sheet metal with holes, has experienced steady growth driven by rising demand across industries like construction, automotive, HVAC, and electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global sheet metal fabrication market was valued at approximately USD 520 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.5% through 2029. A significant segment of this growth is attributed to the increasing use of perforated metal sheets for acoustic panels, architectural facades, filtration systems, and industrial screens. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that the global perforated metal market alone was valued at USD 5.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by advancements in manufacturing precision and expanding applications in green building and infrastructure. With such momentum, identifying leading manufacturers who combine innovation, scalability, and quality in producing sheet metal with holes has become critical for sourcing professionals and industrial buyers alike.
Top 10 Sheet Metal With Holes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Perforated Metal Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sss-steel.com
Key Highlights: Triple-S Steel® offers a superior range of perforated sheet metal, designed to meet various industrial, architectural, and decorative needs. Learn more!…
#2 Buy Perforated Steel Sheet Metal Online
Domain Est. 1999
Website: industrialmetalsupply.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsOrder Hole Perforated Metal Sheet Available in Southern CA, AZ & Northern Mexico. Industrial Metal Supply stocks a wide range of sizes of ……
#3 Perforated Metals Product Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2014
Website: amicoglobal.com
Key Highlights: STANDARD STOCK SHEETS. AMICO manufactures and carries a large inventory of the most common perforated metal panels in various alloys and gauges. shop now….
#4 Perforated Metal Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2015
Website: hendrickcorp.com
Key Highlights: We’re a top-rated perforated sheet metal manufacturer. We have a variety of perforation patterns and can create custom perforated sheet metal. Contact Us!…
#5 Perforated Metal Aluminum Wall Panels & Flat Sheet
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pac-clad.com
Key Highlights: PAC-CLAD perforated aluminum metal panels are available in a nearly endless combination of hole sizes & spacing to complement virtually any architectural ……
#6 Perforated Metal
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metlx.com
Key Highlights: Perforated metal is manufactured by using punches or presses to create a series of holes, slots, bars, or decorative patterns in sheet metal….
#7 Perforated Metal Sheet Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: directmetals.com
Key Highlights: We carry perforated metal in many hole shapes, sizes, and materials. Perforated sheets are versatile and can be used for metal screens, diffusers, guards, ……
#8 Perforated Metal Products & Fabrication Services
Domain Est. 1999
Website: marcospecialtysteel.com
Key Highlights: In stock – We stock & fabricate perforated metal with very different hole patterns & openings, each with its own benefits/applications. Contact us today!…
#9 Custom Perforated Metal Panels & Sheets
Domain Est. 2002
Website: remalymfg.com
Key Highlights: Contact Remaly Manufacturing Company for small to medium-sized orders of high quality custom perforated sheets and perforated metal panels….
#10 Perforated Sheets Metal
Domain Est. 2014
Website: perforated-sheet.com
Key Highlights: Perforated sheet metal gives you a stunning effect with round, square, slot, hexagon and whatever designs you want. We can customize them for you….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sheet Metal With Holes
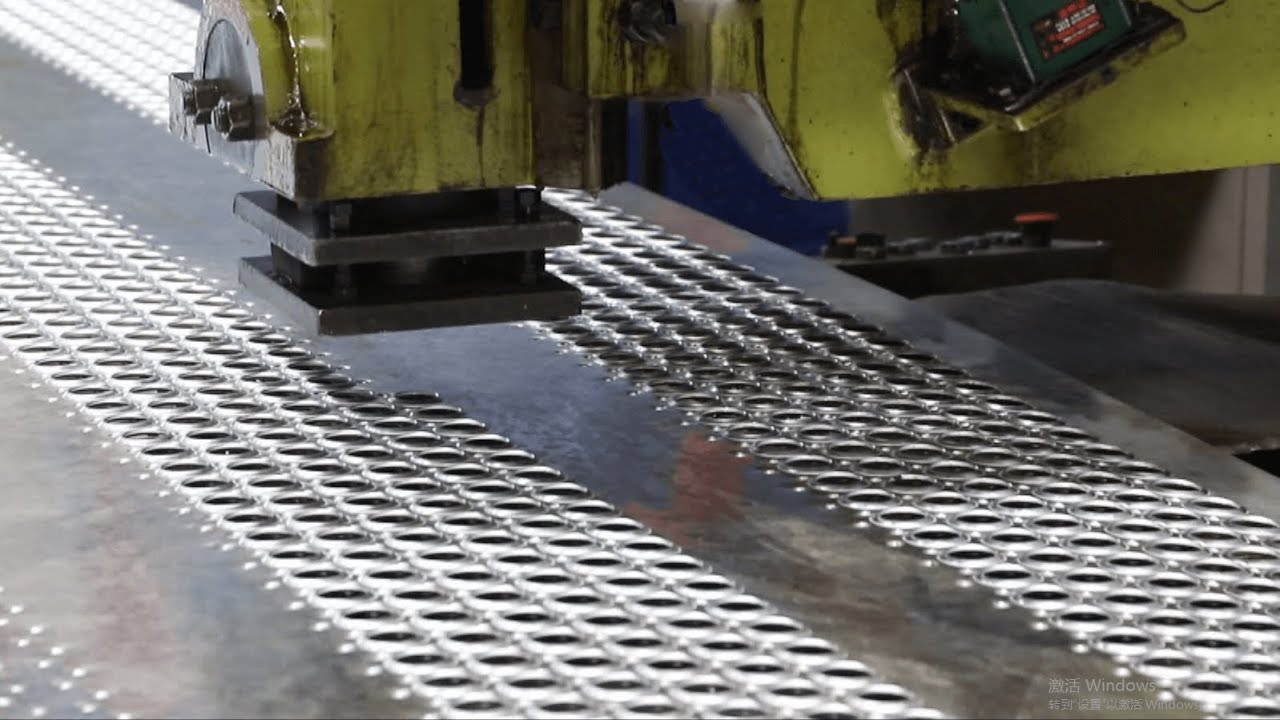

H2: Projected Market Trends for Sheet Metal With Holes in 2026
The global market for sheet metal with holes is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand across key industries, and evolving sustainability standards. This specialized form of perforated and punched metal is essential in sectors such as construction, automotive, aerospace, HVAC, electronics, and renewable energy. Below are the key trends expected to shape the market landscape in 2026:
1. Increased Demand from the Construction and Architecture Sector
Architectural applications will remain a primary growth driver. The use of perforated sheet metal in façades, sunscreens, acoustic panels, and interior design elements is expanding due to its aesthetic versatility and functional benefits like light diffusion and sound absorption. By 2026, urbanization in emerging economies and the global push for energy-efficient buildings will accelerate adoption.
2. Growth in Automotive and Transportation Applications
Automakers are increasingly incorporating perforated metal for lightweight structural components, filtration systems, and interior design. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers, in particular, are exploring perforated metal for battery enclosures and heat dissipation solutions. As EV production scales globally, demand for precision-engineered sheet metal with holes is expected to rise significantly.
3. Advancements in Precision Manufacturing Technologies
The integration of laser cutting, CNC punching, and AI-driven design software will enhance the precision, customization, and cost-efficiency of perforated metal production. By 2026, smart manufacturing systems will enable rapid prototyping and on-demand production, reducing lead times and waste. This technological shift will particularly benefit small-batch and high-complexity orders.
4. Rising Use in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Sheet metal with holes is increasingly used in solar panel frames, wind turbine components, and heat exchangers for geothermal systems. As the global transition to clean energy accelerates, demand for durable, corrosion-resistant perforated metals—especially those made from aluminum and stainless steel—will grow.
5. Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push manufacturers toward recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods. By 2026, the market will see increased use of recycled metals and closed-loop manufacturing processes. Additionally, perforated metal’s role in green building certifications (e.g., LEED) will boost its appeal.
6. Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, will dominate market growth due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. North America and Europe will focus on high-value applications in aerospace, defense, and smart buildings, supported by strong R&D investment.
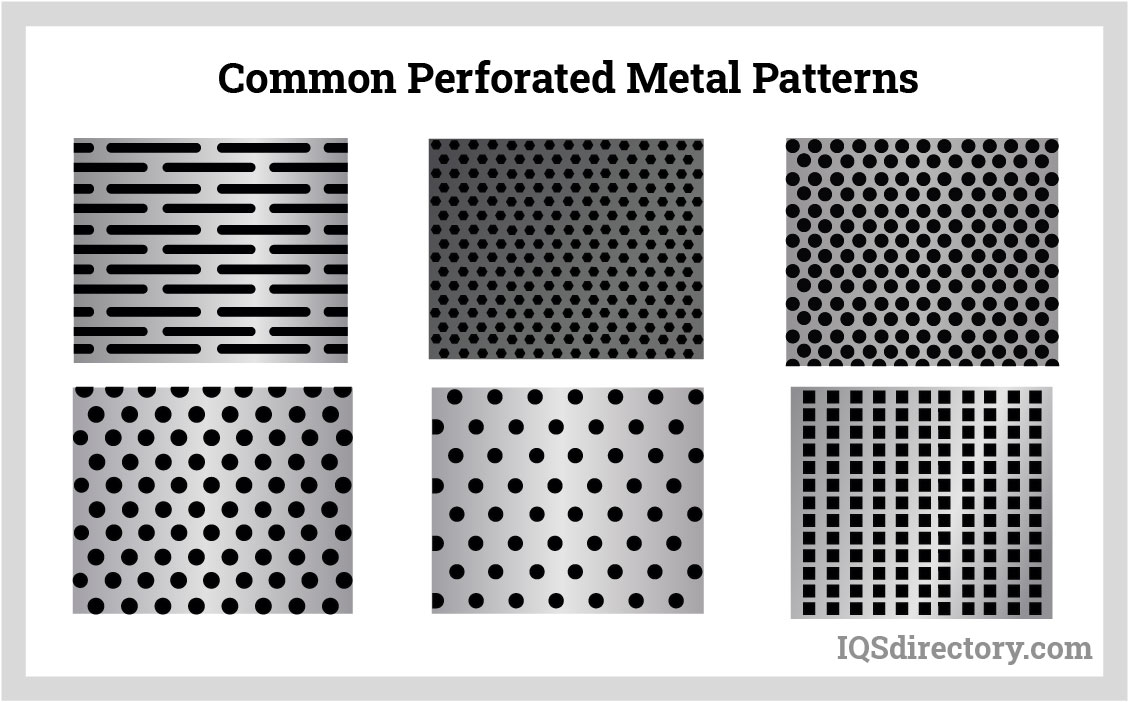
7. Customization and Design Flexibility as Competitive Advantages
End-users will demand higher levels of customization in hole patterns, sizes, and finishes. Suppliers offering digital design platforms and rapid turnaround will gain market share. The trend toward modular and prefabricated construction will further amplify the need for standardized yet adaptable perforated metal solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for sheet metal with holes will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and diversification across industries. Companies that invest in advanced manufacturing, eco-friendly materials, and application-specific solutions will be well-positioned to capture growth opportunities in this dynamic sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sheet Metal With Holes (Quality, IP)
Sourcing sheet metal with pre-punched or pre-drilled holes can streamline manufacturing, but it comes with significant risks related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to production delays, increased costs, and legal exposure.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance Control
One of the most frequent quality issues is inconsistent hole placement, diameter, or edge quality due to inadequate tooling or process control. Suppliers may use worn dies or improper alignment, resulting in parts that do not fit during assembly. This is especially problematic in high-precision applications such as electronics enclosures or structural components.
Lack of Material Certification and Traceability
Many suppliers fail to provide material test reports (MTRs) or certificates of conformance (CoC), making it difficult to verify that the metal meets required specifications (e.g., grade, thickness, corrosion resistance). Without traceability, identifying the root cause of failures becomes nearly impossible.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Burrs
Holes often exhibit sharp burrs or rough edges that require secondary deburring operations. Poor surface finishes can also affect coating adhesion or cause safety hazards. Suppliers may overlook these details unless explicitly specified and inspected.
Failure to Protect Intellectual Property (IP)
Sharing CAD files or detailed drawings with suppliers exposes proprietary designs. Unscrupulous vendors may replicate the part for competitors, reverse engineer your product, or sell excess inventory on the gray market. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are often ignored or unenforced, especially with overseas manufacturers.
Inconsistent Quality Inspection and Lack of Reporting
Some suppliers perform minimal or no in-process quality checks, relying solely on visual inspection. Without standardized measurement plans (e.g., first article inspection, SPC data), defects may go undetected until parts reach final assembly—leading to costly rework or recalls.
Tooling Ownership and Long-Term Supply Risk
When custom dies are used, unclear ownership agreements can create dependency on a single supplier. If the supplier goes out of business or raises prices, retooling elsewhere becomes expensive and time-consuming. Ensure tooling ownership and replication rights are clearly defined in contracts.
Insufficient Packaging and Handling Practices
Sheet metal parts with holes are prone to scratching, warping, or contamination during shipping. Poor packaging—such as inadequate interleaving or stacking—can damage edges and hole features, especially in delicate alloys or coated materials.
Geographic and Communication Challenges
Overseas sourcing introduces language barriers, time zone differences, and cultural gaps in quality expectations. Miscommunication about specifications or inspection criteria can result in non-conforming shipments and extended lead times for corrections.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, establish rigorous supplier qualification processes, require detailed quality documentation, enforce IP protection agreements, and conduct regular audits. Clear technical specifications and strong contractual terms are essential for ensuring both quality and IP security when sourcing sheet metal with holes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sheet Metal With Holes
When transporting, storing, and handling sheet metal with holes, specific logistical and compliance considerations must be addressed to ensure safety, product integrity, and regulatory adherence. This guide outlines best practices and key compliance requirements.
Material Handling and Packaging
Proper packaging and handling are essential to prevent damage during transit and storage. Sheet metal with holes is prone to deformation, edge damage, and contamination due to its perforated structure.
- Edge Protection: Use edge protectors or corner guards to prevent bending or chipping.
- Separation: Place protective layers (e.g., cardboard, foam, or plastic sheets) between stacked metal sheets to avoid surface scratching and burr formation.
- Palletization: Secure sheets on sturdy, clean pallets using strapping or shrink wrap. Ensure weight distribution prevents sagging or warping.
- Orientation: Store and transport sheets vertically when possible to minimize pressure and reduce the risk of denting.
Transportation Requirements
Compliance with transportation regulations ensures safe and legal shipment of sheet metal with holes, whether domestically or internationally.
- Load Securing: Follow FMCSA (U.S.) or ADR (Europe) guidelines for securing cargo. Use dunnage, braces, and straps to prevent shifting.
- Hazard Classification: While sheet metal with holes is typically non-hazardous, sharp edges may require labeling per carrier policies (e.g., “Sharp Edges” warning labels).
- Documentation: Maintain accurate shipping manifests, bills of lading, and material certifications (e.g., mill test reports, RoHS/REACH compliance).
- Carrier Coordination: Notify carriers of material dimensions, weight, and fragility to ensure appropriate handling and equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes).
Storage Conditions
Improper storage can lead to corrosion, warping, or contamination—especially in perforated metal where moisture can accumulate.
- Environment: Store in a dry, climate-controlled area to prevent rust (particularly for carbon steel). Relative humidity should be kept below 60%.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow to reduce condensation risks, especially in stacked configurations.
- Elevation: Keep sheets off the ground using pallets or racks to avoid moisture absorption and floor contaminants.
- Stack Height: Limit stack height to prevent bottom sheets from deforming under load. Follow manufacturer recommendations.
Regulatory Compliance
Sheet metal with holes must comply with regional and industry-specific standards depending on its application.
- Material Standards: Ensure compliance with ASTM, ISO, or EN standards (e.g., ASTM A653 for galvanized steel).
- Environmental Regulations:
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm absence of restricted substances, especially if used in electronics or consumer goods.
- TSCA (U.S.): Verify compliance with EPA chemical substance rules.
- Safety Standards: Adhere to OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent workplace safety regulations for handling sharp materials.
- Customs & Import/Export: Provide Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 7326.20 for other articles of steel) and origin documentation for international shipments.
Quality Control and Traceability
Maintain rigorous quality checks and traceability to meet customer and regulatory expectations.
- Inspection: Verify hole size, spacing, and edge quality per engineering drawings or specifications.
- Marking: Clearly label sheets with batch numbers, material grade, coating type, and compliance marks.
- Documentation Retention: Keep records of inspections, test results, and certifications for a minimum of 5–10 years, depending on industry requirements.
Disposal and Recycling
End-of-life management must follow environmental regulations.
- Recycling Compliance: Follow local recycling codes (e.g., ISRI standards in the U.S.) for scrap metal.
- Hazardous Waste: If coated or treated (e.g., with chromates), classify and dispose of in accordance with EPA or EU WEEE directives.
- Documentation: Retain waste transfer manifests and recycling certificates.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient handling of sheet metal with holes throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sheet Metal with Holes:
Sourcing sheet metal with pre-punched or pre-drilled holes requires a careful balance between precision, cost, lead time, and supplier capability. After evaluating various options—including custom fabrication, off-the-shelf perforated sheets, and OEM manufacturing services—the most effective approach depends on the specific application, volume requirements, and dimensional tolerances.
For high-volume or standardized needs, purchasing perforated sheet metal from established suppliers offers cost efficiency and consistency. For custom hole patterns or tight tolerances, partnering with a CNC machining or laser cutting service ensures accuracy and flexibility. Additionally, considering material type, hole size, spacing, and finishing requirements during the sourcing phase helps avoid delays and rework.
In summary, successful sourcing involves clear specifications, early supplier engagement, and a thorough assessment of total cost of ownership. By selecting the right method and supplier based on project demands, organizations can achieve high-quality results while optimizing time and budget.