The global leather goods market continues to expand, driven by rising consumer demand for premium, durable materials in fashion and accessories. According to Grand View Research, the global leather goods market size was valued at USD 433.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. A key contributor to this growth is the increasing popularity of exotic leathers, including shark hide—renowned for its distinctive texture, water resistance, and luxurious appeal. With applications spanning high-end wallets, watch straps, and designer accessories, shark hide leather has captured the attention of niche manufacturers and luxury brands alike. As sustainability and ethical sourcing become focal points, leading producers are investing in traceable supply chains and eco-conscious tanning processes. In this competitive landscape, nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining craftsmanship, innovation, and scalability to meet the rising demand for high-performance exotic leathers.
Top 9 Shark Hide Leather Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Defining Qualities of Shark Leather
Domain Est. 2000
Website: panamleathers.com
Key Highlights: The defining qualities of shark leather include water resistance, a tough (and abrasive) hide, and two-toned appearance….
#2 Shark Leather
Domain Est. 2004
Website: rojeleather.com
Key Highlights: Shark leather is world known for its rough, course texture. In the coarser developments of shark skin, it has been used like sandpaper for polishing….
#3 Shark Skin Leather
Domain Est. 2006
#4 Shark/Fish
Domain Est. 2014
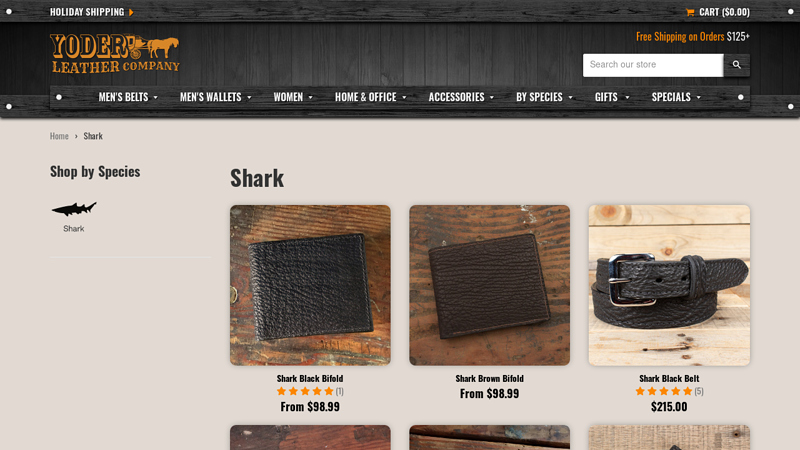
#5 Shark
Domain Est. 2015
Website: yoderleather.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $125 30-day returns…
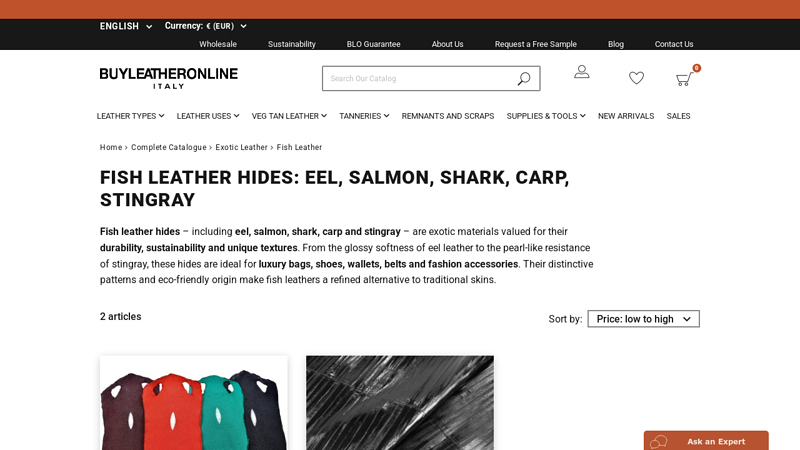
#6 Fish Leather Hides
Domain Est. 2015
#7 Japan’s first, World’s rarest shark leather ‘Atelier Shark’
Domain Est. 2019
Website: groovyjapan.com
Key Highlights: Atelier Shark, a Japanese start-up, has launched an exclusive shark leather brand, which is the first time in Japan and rare even globally….
#8 What Should You Know About Shark Leather
Domain Est. 2021
Website: leatherav.com
Key Highlights: Shark pelts are similar to stingray and eel ones, as they’re impervious to water. Even though shark leather itself doesn’t pass water, it can adversely impact ……
#9 Wholesale Leather Hides and Cowhide Rugs
Domain Est. 2000
Expert Sourcing Insights for Shark Hide Leather
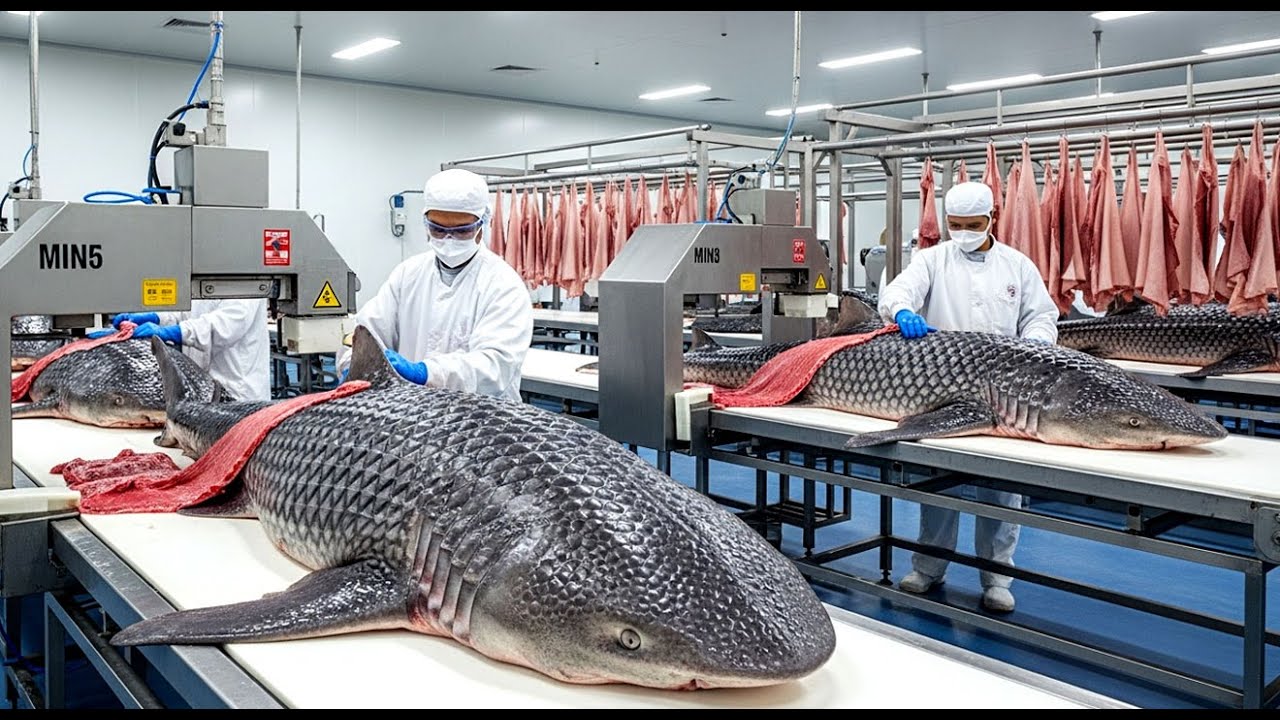

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Shark Hide Leather
As global markets evolve in response to sustainability concerns, shifting consumer preferences, and regulatory developments, the niche luxury materials sector—including shark hide leather—is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026. Shark hide leather, known for its durability, unique texture, and premium aesthetic, has historically been used in high-end fashion, accessories, and luxury goods. However, its market trajectory in 2026 will be shaped by several interrelated factors.
-
Regulatory and Ethical Pressures
By 2026, stricter international regulations on wildlife trade are anticipated to impact the availability and legality of shark-derived products. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) continues to expand protections for vulnerable shark species, limiting sourcing options. Countries like the EU and the U.S. are expected to enforce tighter import controls, increasing compliance costs for manufacturers using shark hide. Ethical consumerism is also rising, with buyers favoring cruelty-free and sustainable alternatives, which could reduce demand for genuine shark leather. -
Shift Toward Sustainable Alternatives
Innovations in bioengineered and plant-based leathers are gaining momentum. By 2026, synthetic alternatives that mimic the texture and resilience of shark hide—such as lab-grown collagen or pineapple-based materials—are projected to capture market share. Luxury brands aiming for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance may shift toward these substitutes, branding them as “eco-luxury” options. This transition could relegate genuine shark hide leather to a shrinking, ultra-niche segment. -
Market Concentration and Premium Positioning
The shark hide leather market is expected to become increasingly concentrated among a few high-end specialty producers, primarily in Japan, Italy, and parts of Southeast Asia where traditional craftsmanship remains valued. These producers may emphasize artisanal heritage and rarity to justify premium pricing, targeting collectors and luxury connoisseurs. However, overall market volume is projected to decline due to restricted supply and reputational risks. -
Consumer Awareness and Transparency Demand
By 2026, consumers will demand greater supply chain transparency. Blockchain-enabled traceability and certification systems will likely become standard for any remaining shark hide products, ensuring they are sourced from non-endangered species and sustainable fisheries. Brands unable to provide verifiable provenance may face public backlash or retailer delisting. -
Regional Market Divergence
While Western markets are expected to see declining demand due to ethical and regulatory barriers, some Asian markets—particularly in China and Japan—may sustain modest demand among affluent consumers who value the material’s status symbolism. However, even in these regions, younger, environmentally conscious consumers could drive a long-term decline.
Conclusion
The 2026 outlook for shark hide leather points toward a shrinking but highly specialized market. Growth will be constrained by environmental regulations, ethical scrutiny, and competition from advanced sustainable materials. While the material may persist in ultra-luxury segments, its broader commercial relevance is expected to diminish. Companies involved in this space must adapt by investing in transparency, exploring hybrid materials, or repositioning products to align with evolving values.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Shark Hide Leather (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing shark hide leather presents unique challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to supply chain disruptions, legal risks, and reputational damage.
Inconsistent Quality and Material Authenticity
One of the primary concerns when sourcing shark hide leather is the variability in quality. Factors such as the species of shark, tanning methods, and geographical origin significantly affect texture, durability, and appearance. Suppliers may offer hides with inconsistent grain patterns, thickness, or coloration, leading to production issues and customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, due to the premium nature of shark hide, there’s a risk of adulteration or substitution with lower-quality leathers misrepresented as authentic shark hide.
Lack of Traceability and Ethical Sourcing Risks
Shark hide sourcing raises environmental and ethical concerns, especially when species are not sustainably harvested or come from protected populations. Without proper traceability systems, buyers risk supporting illegal fishing practices or violating international regulations such as CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species). This not only poses compliance risks but can also damage brand reputation if linked to unsustainable or unethical practices.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Brand Confusion
Shark hide leather is often associated with specific brands or proprietary tanning processes that are protected under intellectual property laws. Sourcing from unauthorized suppliers may lead to the unintentional use of patented techniques or trademarked finishes. Furthermore, some suppliers may falsely claim affiliation with well-known luxury brands, leading to IP infringement if the finished product mimics protected designs or branding. Buyers must conduct due diligence to ensure all processes and materials are legally licensed or developed independently.
Limited Supplier Transparency and Certification Gaps
Many shark hide suppliers operate in regions with weak regulatory oversight, making it difficult to verify claims about quality, sustainability, or IP compliance. Lack of third-party certifications (e.g., ISO standards, CITES permits, or sustainability audits) increases the risk of receiving substandard or illegally sourced materials. Relying on suppliers without transparent documentation can expose businesses to legal and operational vulnerabilities.
Supply Chain Volatility and Scalability Challenges
Shark hide is a niche material with limited availability. Relying on it for large-scale production can lead to supply shortages or price volatility. Sudden changes in fishing regulations or conservation policies may abruptly restrict access to raw materials. This unpredictability makes long-term planning difficult and increases dependency on a small number of suppliers, reducing negotiation power and increasing risk.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Shark Hide Leather
Overview
Shark hide leather is a distinctive, high-value material prized for its unique texture and durability. However, its sourcing, transportation, and use are subject to strict international, national, and regional regulations due to conservation concerns and ethical trade practices. This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for businesses involved in the procurement, processing, or sale of shark hide leather.
Regulatory Framework
Shark hide leather falls under the purview of several key regulatory bodies and agreements:
– CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora): Many shark species are listed in CITES Appendices, requiring export permits and import certifications. Species such as the great white shark, hammerheads, and whale sharks are strictly protected.
– IUCN Red List: Guides risk assessment for sourcing; avoid species classified as endangered or critically endangered.
– National Wildlife Protection Laws: Countries like the U.S. (Endangered Species Act), EU (Wildlife Trade Regulations), and Australia (EPBC Act) enforce strict import/export controls.
– FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) Guidelines: Promote responsible fisheries management, including shark bycatch and finning bans.
Species Restrictions and Permitted Trade
- Verify the exact species of shark used. Only species not listed under CITES Appendix I or II may be traded legally without special permits.
- Commonly used species such as the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) may be allowable under CITES Appendix II, but require non-detriment findings and valid CITES permits.
- Prohibited species include great white, basking, and whale sharks—trade in hides from these species is illegal in most jurisdictions.
Required Documentation
For legal international trade, the following documentation is typically required:
– CITES Export and Re-export Permits: Issued by the Management Authority of the exporting country.
– CITES Import Permit: Required for Appendix I species; recommended for Appendix II in some jurisdictions.
– Certificate of Origin: Specifies the country where the shark was caught or the leather was processed.
– Catch Certificate or Fisheries Compliance Documentation: Proves legal harvest in accordance with national and international laws.
– Customs Declarations: Accurate HS code classification (e.g., 4107.00 for tanned hides of reptiles or fish).
Sustainable Sourcing and Traceability
- Source from fisheries with Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) certification or equivalent sustainability credentials.
- Implement a traceability system from point of catch to final product, including vessel logs, processing records, and chain-of-custody documentation.
- Avoid suppliers involved in shark finning; ensure full utilization of the animal is practiced where legal and ethical.
Import and Export Logistics
- Pre-clearance with customs authorities is recommended due to the high scrutiny of wildlife products.
- Use freight forwarders experienced in handling CITES-regulated goods.
- Be prepared for inspections, delays, or additional documentation requests at borders.
- Label shipments clearly as “Shark Hide Leather – CITES-Regulated Material” with permit numbers visible.
Labeling and Marketing Compliance
- Product labeling must not misrepresent the species or origin.
- Avoid marketing terms that could imply endangered species (e.g., “rare shark skin” without qualification).
- In the EU and U.S., consumer protection laws require truthful advertising; false claims may result in fines or recalls.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with regulations may result in:
– Seizure of goods
– Fines or criminal charges
– Loss of import/export licenses
– Reputational damage and loss of market access
Best Practices
- Conduct regular compliance audits.
- Train procurement and logistics teams on CITES and wildlife trade regulations.
- Maintain detailed records for at least five years.
- Consult with legal experts or CITES authorities when in doubt.
Conclusion
Trading in shark hide leather demands rigorous attention to legal and environmental standards. By adhering to international regulations, ensuring traceability, and prioritizing sustainability, businesses can operate responsibly while minimizing risks. Always verify the latest CITES listings and national regulations before engaging in any transaction involving shark-derived products.
In conclusion, sourcing shark hide leather presents both unique opportunities and significant ethical, environmental, and regulatory challenges. While the material is valued for its durability, exotic texture, and luxury appeal in high-end fashion and accessories, its production raises serious concerns regarding marine biodiversity, shark conservation, and sustainable fishing practices. Many shark species are threatened or endangered, and the demand for their skins can contribute to overfishing and bycatch, undermining global conservation efforts.
Moreover, consumer awareness and increasing demand for ethical and sustainable products are pushing brands to reconsider the use of animal-derived exotic materials. Legal frameworks such as CITES regulations restrict the trade of certain shark species, making compliance essential for responsible sourcing.
Therefore, while shark hide leather may offer aesthetic and commercial value, its sourcing should be approached with extreme caution. Transparency, traceability, and adherence to conservation laws are critical. Ultimately, the future of such materials may lie in innovation—such as the development of high-quality, sustainable alternatives—that allow for luxury and responsibility to coexist. For ethical and ecological sustainability, businesses are encouraged to explore and invest in alternative materials rather than rely on wildlife-derived products.