The global fasteners market, encompassing screws, spacers, and related components, continues to expand driven by robust demand from automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial machinery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global fasteners market size was valued at USD 108.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This sustained growth is attributed to increasing manufacturing activities, infrastructure development, and miniaturization trends in electronics, which elevate the need for precision screws and spacers. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, noting a CAGR of approximately 4.8% through 2028, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the largest and fastest-growing region due to strong industrial output and electronics assembly hubs. Within this expanding ecosystem, a select group of manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, scale, and technical expertise—setting the standard for quality and reliability in screw and spacer production.
Top 8 Screws And Spacers Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Spacers for Industrial Bolts, Screws, and Fasteners
Domain Est. 2021
Website: gobigbolt.com
Key Highlights: Big Bolt manufactures spacers for a variety of standard and custom MRO and OEM applications. Learn more about our complete hex nut manufacturing services….
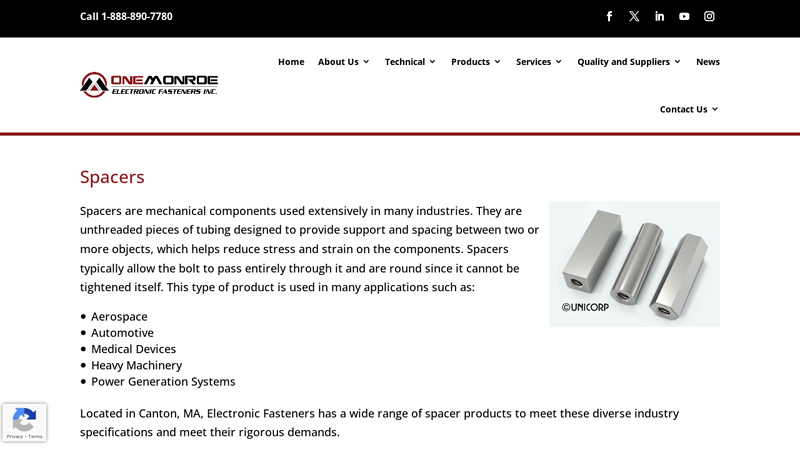
#2 Spacers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: electronicfasteners.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide selection of spacers including standard, custom, and metric sizes as well as offering options for specialty coatings or finishes….
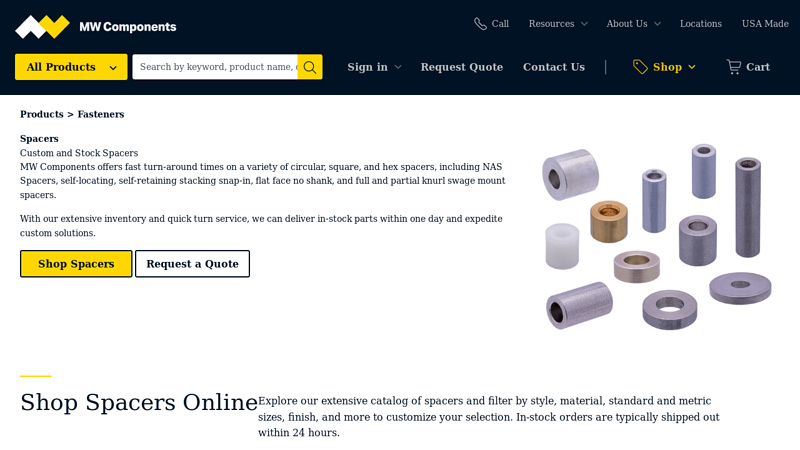
#3 Custom & Stock Spacer Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: MW Components manufacturers custom, stock, plastic, nylon & metal spacers to your specs. Shop AS9100D & ISO9001 certified spacers now or request a quote….
#4 McMaster
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mcmaster.com
Key Highlights: McMaster-Carr is the complete source for your plant with over 700000 products. 98% of products ordered ship from stock and deliver same or next day….
#5 Spacers by UNICORP Spacer Standoffs Standard/Metric
Domain Est. 1996
Website: unicorpinc.com
Key Highlights: Unicorp Spacers round-square-hex, 28 finishes, available in brass, aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, nylon, Teflon®, Phenolic, Lexan®, Delrin®, Ultem®….
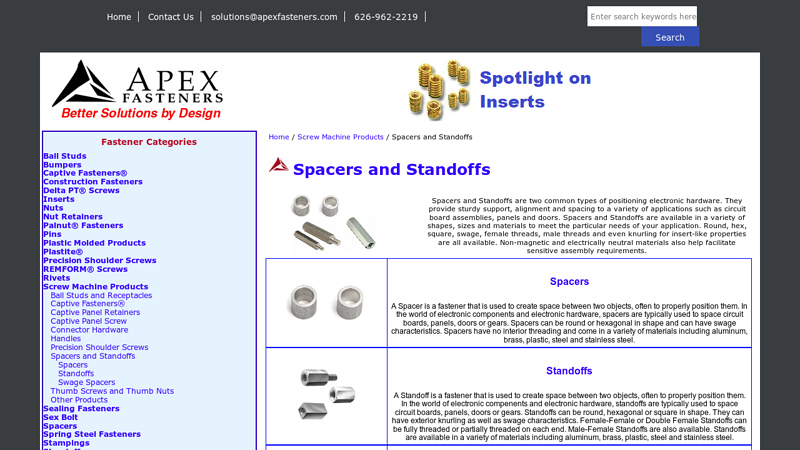
#6 Spacers and Standoffs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: apexfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Spacers and Standoffs are two common types of positioning electronic hardware. They provide sturdy support, alignment and spacing to a variety of ……
#7 MISUMI Screws & Spacers
Domain Est. 2007
#8 Spacers
Domain Est. 2010
Website: classicfastenersllc.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of spacers to meet your specific needs. Plating done per request. We are your one-stop source for all your spacer and fastener needs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screws And Spacers

2026 Market Trends for Screws and Spacers
Industry Overview and Market Growth
The global market for screws and spacers is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key industrial sectors such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and construction. As manufacturing processes become more advanced and miniaturization trends accelerate—especially in electronics—precision-engineered fasteners like screws and spacers are becoming more critical. According to market research forecasts, the global mechanical fasteners market, which includes screws and spacers, is expected to exceed $100 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.2% from 2021 to 2026.
Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
One of the defining trends shaping the 2026 landscape for screws and spacers is the shift towards high-performance materials. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials such as titanium, stainless steel, and engineered polymers (e.g., PEEK and nylon). These materials meet the demands of industries requiring durability under extreme conditions, such as aerospace and medical devices. Additionally, self-drilling, self-tapping, and thread-forming screws with enhanced coatings (e.g., zinc-nickel or black oxide) are gaining traction for improved efficiency and longevity.
In electronics, miniaturization is pushing innovation in micro screws and insulating spacers. Ultra-precision components, some as small as 0.3mm in diameter, are being developed to support compact consumer devices like wearables and foldable smartphones. These advancements are expected to elevate demand for high-tolerance, anti-magnetic, and electrically insulating spacers made from materials like ceramic or specialty plastics.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to dominate the screws and spacers market by 2026, driven by robust industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. China remains the largest producer and consumer, supported by its expansive electronics manufacturing and infrastructure development. Meanwhile, India is emerging as a key hub due to government initiatives like “Make in India” and rising investments in automotive and renewable energy sectors.
North America and Europe are witnessing growth fueled by the aerospace and defense industries, electric vehicle (EV) production, and smart manufacturing. The push for sustainability is also influencing material sourcing and production processes, with increased emphasis on recyclable fasteners and energy-efficient manufacturing.
Sustainability and Regulatory Influences
Environmental regulations are becoming a significant factor in the screws and spacers market. By 2026, compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH standards will be mandatory in many regions, pushing manufacturers to eliminate harmful coatings and adopt eco-friendly alternatives. Additionally, circular economy principles are encouraging the reuse and recycling of metal fasteners, particularly in automotive and construction sectors.
Companies are investing in green manufacturing technologies such as cold forging and precision machining to reduce material waste and energy consumption. Some are also exploring biodegradable polymers for non-structural spacers in low-load applications, although this segment remains niche.
Supply Chain and Automation Trends
The global supply chain for screws and spacers is evolving toward greater resilience and localization. Following disruptions caused by the pandemic and geopolitical tensions, many OEMs are diversifying suppliers and reshoring production. Automation is playing a pivotal role in this shift, with increased use of robotics and AI-driven quality control systems in fastener manufacturing. Smart factories are enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and customized production runs—especially beneficial for high-mix, low-volume orders.
Furthermore, digital platforms and e-procurement systems are streamlining distribution. B2B e-commerce marketplaces are allowing easier access to standardized and custom fasteners, reducing lead times and inventory costs for end users.
Conclusion
By 2026, the screws and spacers market will be shaped by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and shifting regional dynamics. Demand will continue to grow, particularly for high-precision, high-performance fasteners in advanced industries. Companies that invest in material science, automation, and sustainable practices will be best positioned to capture value in this evolving market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Screws and Spacers (Quality and IP)
Sourcing screws and spacers may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to significant downstream issues, including product failure, compliance risks, and legal exposure. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Material and Finish Specifications
Choosing the wrong material (e.g., stainless steel vs. zinc-plated steel) or inadequate surface finish can lead to corrosion, reduced strength, or incompatibility with the application environment. Always verify that the supplier adheres to international standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ASTM) and provides material certifications.
Assuming Dimensional Accuracy Without Verification
Low-cost suppliers may provide screws or spacers that deviate from specified dimensions, thread pitch, or tolerances. These discrepancies can cause assembly issues or mechanical failure. Request samples and conduct dimensional inspections before large-scale procurement.
Ignoring Mechanical Performance Requirements
Not all screws and spacers meet the required tensile strength, torque resistance, or load-bearing capabilities. Failing to validate mechanical specs (e.g., grade for screws, load capacity for spacers) can compromise product reliability and safety.
Sourcing from Unqualified or Non-Certified Suppliers
Working with suppliers lacking quality management certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of inconsistent quality and non-compliance. Always audit suppliers and verify their manufacturing and testing processes.
Failing to Address Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Using proprietary designs (e.g., specialized thread profiles, patented spacer geometries) without proper licensing can result in IP infringement claims. Ensure that sourced components do not violate patents, trademarks, or design rights—especially when reverse engineering or copying existing parts.
Relying on Incomplete or Inaccurate Documentation
Lack of traceability, test reports, RoHS/REACH compliance data, or material declarations can hinder regulatory compliance and quality assurance. Demand full documentation as part of the sourcing agreement.
Prioritizing Cost Over Long-Term Reliability
Choosing the cheapest option often leads to higher total cost of ownership due to failures, recalls, or rework. Balance cost with proven quality, supplier reputation, and lifecycle performance.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, businesses can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally safe sourcing of screws and spacers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screws and Spacers
Overview
Screws and spacers are essential hardware components used across industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and construction. While small in size, their global movement involves critical logistics and compliance considerations. This guide outlines key steps for ensuring efficient and compliant international shipping, handling, and documentation.
Material and Product Classification
- Material Types: Screws and spacers are commonly made from stainless steel, aluminum, brass, plastic, or titanium.
- HTS/HS Code Determination: Accurately classify products using the Harmonized System (HS) code to determine import duties and regulations. Typical codes may fall under:
- 7318.15 (Stainless steel screws)
- 7318.29 (Other metal screws and bolts)
- 3926.30 (Plastic spacers or fasteners)
- Customs Authorities: Work with customs brokers to verify correct classification based on material, dimensions, thread type, and intended use.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Required for electronic applications in the EU. Ensure screws and spacers do not contain restricted substances such as lead, cadmium, or hexavalent chromium.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Applies to products entering the EU. Declare Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if present above thresholds.
- Conflict Minerals (Dodd-Frank Act): If sourced from certain regions (e.g., DRC), report use of tantalum, tin, tungsten, or gold.
- ITAR/EAR (U.S. Export Regulations): Check if components are used in military or aerospace applications and whether they require export licenses.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Packaging: Use anti-corrosion materials (e.g., VCI paper) for metal fasteners. Ensure moisture resistance and secure containment to prevent damage during transit.
- Labeling:
- Include product description, material type, quantity, lot/batch number, and country of origin.
- For exports, ensure multilingual labeling if required (e.g., French in Canada, Spanish in Latin America).
- Mark packages with handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”).
Shipping and Transportation
- Mode of Transport: Choose air freight for urgent, low-weight shipments; ocean freight for bulk orders.
- Incoterms®: Clearly define responsibilities using standard terms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP) in contracts.
- Weight and Volume Optimization: Use bulk packaging or tape-and-reel formats to minimize shipping costs and storage space.
- Hazardous Materials: Most screws and spacers are non-hazardous, but verify coatings or platings (e.g., zinc chromate) that may require special handling.
Import and Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed product description, HS code, value, currency, Incoterms®, and buyer/seller information.
- Packing List: Specify itemized contents, net/gross weights, and packaging types.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by many countries for tariff determination; may need chamber of commerce certification.
- Export Declaration (e.g., AES in the U.S.): File Electronic Export Information (EEI) for shipments above de minimis value.
- Import Licenses: Rarely required for standard fasteners, but verify based on destination country and end-use.
Quality and Traceability
- Batch Traceability: Maintain records linking production batches to shipments for recalls or compliance audits.
- Certifications: Provide mill test reports (MTRs) for metal components or ISO certification documentation upon request.
- Inspection and Testing: Conduct dimensional checks, torque testing, and material verification to meet industry standards (e.g., ISO 898, ASTM F568).
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recycling and Waste: Metal fasteners are recyclable; provide disposal guidance for coated or composite materials.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize logistics routes and consolidate shipments to reduce emissions.
- Supplier Audits: Ensure raw material suppliers comply with environmental and labor standards.
Risk Mitigation and Best Practices
- Inventory Management: Use just-in-time (JIT) or vendor-managed inventory (VMI) to reduce holding costs.
- Force Majeure Planning: Account for supply chain disruptions (e.g., port delays, trade disputes).
- Insurance: Cover cargo for loss, damage, or theft during transit.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to ensure adherence to international trade laws.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for screws and spacers minimizes delays, reduces costs, and ensures market access. By focusing on accurate classification, regulatory adherence, proper documentation, and sustainable practices, businesses can maintain reliable global supply chains for these critical components.
In conclusion, the sourcing of screws and spacers requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, lead time, and supplier reliability. By clearly defining technical specifications—such as material, size, thread type, tolerance, and finish—organizations can ensure compatibility and performance in their applications. Evaluating suppliers based on quality certifications, production capabilities, and track record helps mitigate risks related to defects or supply chain disruptions.
Additionally, considering factors like volume requirements, geographic location, and potential for long-term partnerships can lead to cost efficiencies and improved logistics. Whether sourcing domestically or internationally, conducting thorough supplier audits and requesting samples prior to large orders is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of screws and spacers supports overall product reliability, reduces assembly issues, and contributes to operational efficiency. A well-managed procurement process ensures that these small but critical components meet necessary standards and support the success of larger manufacturing or assembly operations.