The global screwdriver machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing automation across electronics, automotive, and precision manufacturing sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the Electric Screwdriver Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by rising demand for high-precision fastening solutions and Industry 4.0 integration. Similarly, Grand View Research reported that the global power tools market—within which screwdriver machines are a key segment—was valued at USD 53.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.1% through 2030, supported by advancements in cordless technology and smart tool systems. As manufacturers prioritize efficiency, torque accuracy, and traceability in assembly processes, the competition among screwdriver machine suppliers has intensified. In this landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation with intelligent driving systems, IoT-enabled diagnostics, and scalable automation solutions. Here are the top 10 screwdriver machine manufacturers shaping the future of precision assembly.
Top 10 Screwdriver Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MYTORQ Industrial Precision Torque Control Screwdriver
Domain Est. 2020
Website: mytorqtools.com
Key Highlights: We are an industrial electric torque control screwdriver manufacturer helping users to work correctly, efficiently, and comfortably….
#2 Screwdriving Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: weberusa.com
Key Highlights: Industry leader in designing and manufacturing automated screwdriving systems and screw feeding systems for assembly applications in industrial markets….
#3 Speciality Screwdriver Sets Made in the USA by Chapman …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chapmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Made in the USA for over 85 years, Chapman provides a variety of screwdriver sets for industrial assembly, maintenance, home repairs, and more….
#4 MCI Screwdriver Systems, Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mciscrewdriver.com
Key Highlights: Leaders in lean manufacturing for automatic screwdrivers & small part processing & assembly. Offering fixtured, insertion, handheld, & other solutions….
#5 Milwaukee® Tool
Domain Est. 2000
Website: milwaukeetool.com
Key Highlights: Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools, hand tools, instruments, and accessories….
#6 Air and Electric Screwdrivers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: powertools.ingersollrand.com
Key Highlights: Ingersoll Rand offers a full line of production fastening equipment, in a broad range of configurations for automotive and industrial applications….
#7 Corded Electric Screwdriver System
Domain Est. 1990
Website: assemblytools.na.panasonic.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 Free 30-day returns…
#8 Electric Screwdrivers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mountztorque.com
Key Highlights: Mountz electric screwdrivers simplify process control and regulatory compliance by interfacing with screw counters for automatic oversight….
#9 AT
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hakkousa.com
Key Highlights: CHP brush type electric screwdrivers feature large side windows for easy access and fast replacement of carbon brushes….
#10 Equipment
Domain Est. 2014
Website: sloky.com.tw
Key Highlights: Designed specifically for CNC machining, lathing, turning, and milling applications, it offers the perfect balance of precision, safety, and ease of use….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screwdriver Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Screwdriver Machines
The global screwdriver machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and the expansion of smart factory initiatives. Below are key trends shaping the industry landscape:
1. Rising Adoption of Automated and Smart Screwdriver Systems
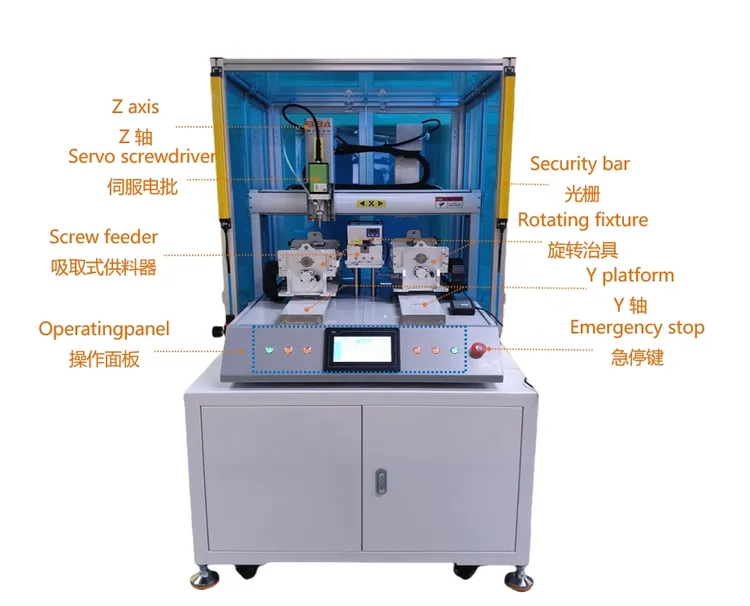
Manufacturers across electronics, automotive, and consumer goods sectors are increasingly integrating automated screwdriver machines equipped with IoT capabilities. These smart systems offer real-time torque monitoring, error proofing, and data collection, improving assembly line efficiency and product quality. By 2026, demand for programmable and network-connected screwdriver machines is expected to surge, particularly in high-mix, low-volume production environments.
2. Growth in Miniaturization and Precision Requirements
As electronic devices become smaller and more complex, there is a growing need for micro-precision screwdriver machines capable of handling tiny screws (e.g., 0.6mm or smaller). Markets in Asia-Pacific—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—are leading this trend due to their dominant role in electronics manufacturing. By 2026, screwdriver machines with advanced vision systems and force-sensing technologies will be standard in high-precision applications.
3. Expansion of Electric and Cordless Models
Driven by workplace safety and operational flexibility, cordless electric screwdriver machines are gaining popularity. Improvements in battery life, motor efficiency, and ergonomics are making them viable for continuous industrial use. The trend toward lightweight, ergonomic designs will continue to support worker productivity and reduce fatigue, especially in assembly-intensive industries.
4. Integration with Industry 4.0 and MES Platforms
Screwdriver machines are increasingly being integrated into broader Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and digital twin frameworks. By 2026, seamless data exchange between screwdriving tools and central production systems will enable predictive maintenance, traceability, and quality analytics. This integration supports compliance with standards like ISO 9001 and IATF 16949, particularly in automotive and medical device manufacturing.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
While Asia-Pacific remains the largest market due to its manufacturing base, North America and Europe are witnessing renewed growth due to reshoring and nearshoring trends. Companies are investing in localized production facilities, boosting demand for reliable screwdriver automation solutions. This shift is also encouraging regional partnerships and localized after-sales support services.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient screwdriver machines. By 2026, energy consumption metrics and recyclable components will become key differentiators in product design, with suppliers emphasizing eco-friendly manufacturing and longer product lifecycles.
Conclusion
By 2026, the screwdriver machine market will be defined by intelligence, integration, and precision. Companies that invest in smart, scalable, and sustainable solutions will gain a competitive edge. As automation becomes non-negotiable in modern manufacturing, screwdriver machines will evolve from simple tools to critical nodes in connected production ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Screwdriver Machine (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a screwdriver machine—especially for automated or high-volume production—can significantly impact product quality, operational efficiency, and legal compliance. However, several common pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks can undermine your investment if not properly addressed.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing screwdriver machines, particularly from low-cost manufacturers, is inconsistent build quality and unreliable performance. Machines may fail prematurely, deliver inaccurate torque, or exhibit poor repeatability—leading to defective assemblies and increased downtime. Buyers often assume specifications on paper reflect real-world performance, but without rigorous on-site audits or third-party testing, substandard components and lax manufacturing processes may go undetected.
Lack of Standard Compliance and Certification
Many suppliers, especially in emerging markets, may not adhere to international safety and performance standards such as CE, UL, or ISO. Sourcing a machine without proper certification can result in regulatory non-compliance, workplace safety hazards, and voided insurance coverage. Always verify that the screwdriver machine meets applicable industry standards for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and mechanical reliability.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and repair over time. A critical oversight is failing to assess the supplier’s global support network. Some manufacturers offer attractive upfront pricing but lack local service teams or readily available spare parts. This can lead to extended machine downtime, increased total cost of ownership, and production delays.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of purchasing machines that infringe on patented technologies. Some suppliers reverse-engineer or copy designs from established brands, which may expose your company to legal liability, product seizures, or forced redesigns. Always conduct due diligence on the supplier’s design origin, request proof of IP ownership or licensing, and include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
Hidden Software and Firmware Limitations
Modern screwdriver machines often rely on proprietary software for torque control, data logging, and integration with factory systems. A common pitfall is discovering post-purchase that the software is outdated, non-customizable, or locked to specific hardware. Additionally, unclear licensing terms may restrict your ability to scale or transfer the system. Ensure full transparency around software capabilities, updates, and usage rights before finalizing a purchase.
Insufficient Documentation and Training Materials
Poorly documented machines—lacking clear manuals, schematics, or programming guides—can hinder integration and troubleshooting. This is especially problematic when staff turnover occurs or third-party technicians are needed. Confirm that comprehensive technical documentation and operator training are included in the sourcing agreement.
By carefully evaluating these quality and IP-related risks during the sourcing process, businesses can avoid costly setbacks and ensure reliable, compliant, and legally secure automation solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screwdriver Machine
This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant transportation, handling, and operation of screwdriver machines, including both manual and automated (e.g., electric, pneumatic, or robotic) types.
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the screwdriver machine for international and domestic shipping. Determine the correct Harmonized System (HS) Code based on machine type, power source, and function. Prepare essential documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and any required export licenses. For automated or industrial systems, include technical specifications and CE or UL certification documents.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package screwdriver machines securely to prevent damage during transit. Use sturdy, moisture-resistant packaging with adequate cushioning (e.g., foam inserts or molded trays) to protect sensitive components. Clearly label packages with orientation arrows, fragile indicators, and handling instructions. For heavy or large automated screwdriving units, use skids or pallets and secure with strapping. Avoid stacking heavy items on top.
Transportation and Shipping
Use reliable carriers experienced in handling industrial equipment. For air freight, comply with IATA regulations—ensure batteries (if present) meet UN38.3 testing standards and are properly installed or packed. For sea freight, protect against moisture and salt corrosion using desiccants or vacuum sealing where appropriate. Maintain stable temperatures during transit, especially for machines with electronic controls or sensors.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify compliance with import regulations in the destination country. This may include conformity assessment procedures, local safety certifications (e.g., UKCA, CCC, PSE), and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements. Declare any restricted materials, such as certain plastics or electronic components, under relevant environmental regulations like RoHS or REACH. Obtain necessary import permits or approvals prior to shipment.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
Ensure the screwdriver machine meets applicable safety standards such as IEC 60745 (hand-held motor-operated tools) or ISO 12100 (safety of machinery). Machines intended for industrial automation must comply with machinery directives (e.g., EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC). Provide user manuals in the local language and include safety warnings, maintenance instructions, and emergency procedures.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery, inspect the machine for shipping damage before installation. Follow manufacturer guidelines for assembly, grounding, and power supply connection. Verify that electrical inputs (voltage, frequency) match local infrastructure. For robotic screwdriving systems, conduct risk assessments and install appropriate guarding and emergency stops per OSHA or equivalent standards. Document all commissioning steps.
Maintenance and Traceability
Establish a maintenance schedule in accordance with manufacturer recommendations to ensure ongoing compliance and performance. Keep records of inspections, repairs, and component replacements. For regulated industries (e.g., automotive, aerospace), maintain traceability of torque calibration and tool usage data. Use only approved spare parts and accessories.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Dispose of packaging materials in compliance with local waste regulations. At end-of-life, recycle the screwdriver machine through certified e-waste channels. Adhere to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions. Avoid landfill disposal of electronic components or motors.
Training and Operator Certification
Provide comprehensive training for operators and maintenance personnel. Cover safe operation, torque control, changeover procedures, and lockout/tagout (LOTO) protocols. In automated environments, ensure staff are trained on programming interfaces and safety interlocks. Maintain training records to demonstrate compliance during audits.
In conclusion, sourcing a screwdriver machine requires a thorough evaluation of production needs, machine specifications, budget constraints, and supplier reliability. Automated screwdriver machines can significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in assembly processes, making them a valuable investment for manufacturing operations. It is essential to consider factors such as torque control, speed, compatibility with screw types, integration capabilities with existing production lines, and after-sales support. By carefully assessing these aspects and selecting a reputable supplier, businesses can ensure long-term reliability, reduced downtime, and improved product quality. Ultimately, the right screwdriver machine not only optimizes operational performance but also contributes to overall cost savings and competitiveness in the market.