The global fastener market, driven by robust demand from automotive, construction, and industrial equipment sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. With screw sizes like M6 being among the most widely used metric fasteners in mechanical assemblies, the demand for high-precision, standardized components continues to rise. Asia Pacific dominates production and consumption, supported by extensive manufacturing infrastructure in China, Japan, and India. As industries prioritize reliability and compliance with ISO and DIN standards, the competitive landscape for M6 screw manufacturers has intensified. This list highlights the top six manufacturers excelling in quality, scalability, and innovation within this expanding market.
Top 6 Screw Size M6 Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 M6 Model Screw and Nut
Domain Est. 1992
Website: fs.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.9 (21) The “M” designation for metric screws indicates the nominal outer diameter of the screw. For example, an M6 screw has a nominal outer diameter of 6 milli…
#2 M6 Machine Screws
Domain Est. 1994
Website: newark.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 60-day returnsFind a huge range of M6 Machine Screws at Newark Electronics. We stock a wide range of Machine Screws, such as M4, M3, M5 & M6 Machine Scre…
#3 M6 Screws & Fasteners
Domain Est. 1995
Website: mouser.com
Key Highlights: $4.99 delivery · 30-day returnsM6 Screws & Fasteners are available at Mouser Electronics. Mouser offers inventory, pricing, & datasheets for M6 Screws & Fasteners….
#4 M6 Screw with Hex/Phillips Head (1421HPM6 Series)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hammfg.com
Key Highlights: M6 x 12mm (0.472″) length steel screws. · 10mm (25/64″) Hex Phillips head. · Zinc plated finish. · Designed for use with the HMEGS but can be used for rack mount ……
#5 M6 Carbon Steel Socket Head Cap Machine Screws (SHCS)
Domain Est. 2019
Website: us.store.bambulab.com
Key Highlights: M6 Carbon Steel Socket Head Cap Machine Screws (SHCS) ; L (mm). Bolt Length ; D (mm). Head Diameter ; H (mm). Head Thickness ; k (mm). Hexagon Across Flats ; t (mm)….
#6 Understanding M6 Screw Size: A Comprehensive Guide
Domain Est. 2024
Website: oreateai.com
Key Highlights: The number ‘6’ refers to its nominal diameter of 6 millimeters. The standard pitch for an M6 screw is 1 millimeter, which classifies it as a ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screw Size M6

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for M6 Screws
The global market for M6 screws—standard metric fasteners with a 6mm diameter—is expected to experience steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by industrial expansion, technological advancements, and shifts in manufacturing practices. Key trends shaping the M6 screw segment include:
-
Increased Demand from Automotive and Construction Sectors
The automotive industry, especially in emerging economies, continues to drive demand for M6 screws due to their widespread use in vehicle assembly, engine components, and chassis systems. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), lightweight and high-strength M6 screws made from advanced alloys or stainless steel are gaining preference. Similarly, infrastructure development in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America is fueling construction-related demand for durable M6 fasteners. -
Growth in Automation and Precision Engineering
As manufacturing processes become increasingly automated, the need for standardized, high-precision M6 screws is rising. Robotics, CNC machinery, and assembly-line automation rely on consistent fastener dimensions and quality. This trend is pushing suppliers to adopt tighter tolerances, improved thread accuracy, and enhanced surface treatments for M6 screws to meet industry specifications. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations are prompting manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production methods and recyclable materials. By 2026, a growing share of M6 screws is expected to be made from recycled steel or corrosion-resistant, low-impact coatings such as zinc-nickel or organic polymer finishes. Biodegradable lubricants used in threading processes are also gaining traction. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Optimization
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain dominant in both production and consumption of M6 screws due to robust industrial activity and cost advantages. However, nearshoring and supply chain resilience initiatives in North America and Europe are leading to localized production hubs, reducing dependency on long global supply chains. -
Digitalization and Smart Fastening Solutions
Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies is influencing the M6 screw market. Smart fasteners with embedded sensors or RFID tags—though still niche—are beginning to emerge for critical applications in aerospace and heavy machinery. While M6 screws in this category remain limited, digital inventory tracking and AI-driven quality control in M6 production are becoming standard. -
Price Volatility and Raw Material Fluctuations
The market may face challenges from fluctuating steel and alloy prices influenced by geopolitical tensions and energy costs. Producers are responding by diversifying material sources, investing in energy-efficient manufacturing, and entering long-term supply contracts to stabilize costs.
In summary, the 2026 market for M6 screws will be characterized by higher demand for quality, sustainability, and integration with modern manufacturing ecosystems. Companies that innovate in materials, embrace digital tools, and adapt to regional market dynamics are likely to gain competitive advantage in this mature yet evolving segment.
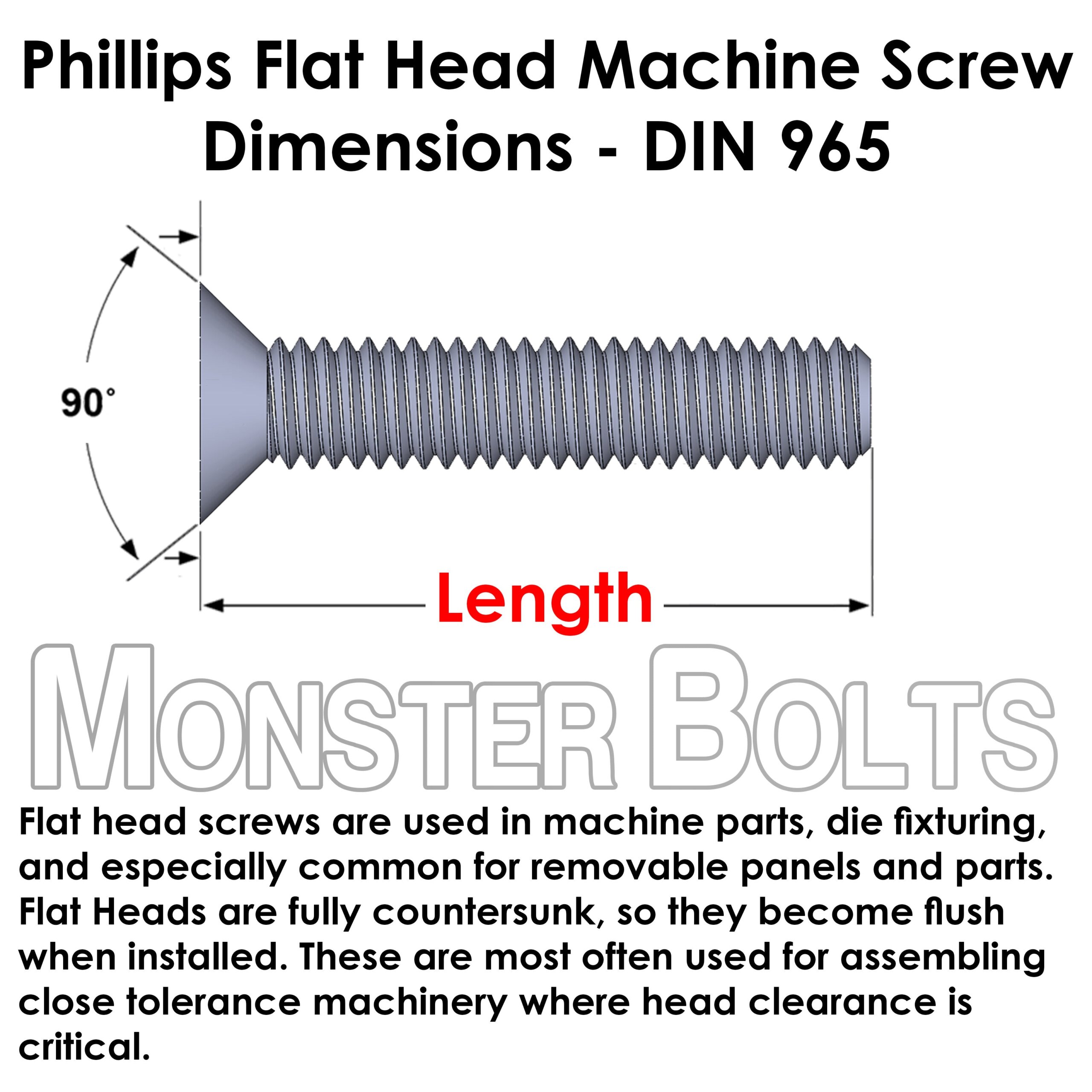
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing M6 Screws (Quality & IP)
Sourcing M6 screws seems straightforward, but overlooking critical quality and IP (Ingress Protection) factors can lead to costly failures. Avoid these common pitfalls:
1. Assuming “M6” Defines Quality
* **Pitfall:** Believing any M6 screw meets requirements. M6 only specifies the nominal diameter (6mm) and pitch (e.g., 1.0mm coarse, 0.75mm fine). It says nothing about material, strength, or finish.
* **Consequence:** Using a low-strength (e.g., Class 4.8) screw instead of a high-strength (e.g., Class 8.8, 10.9, or 12.9) one leads to fastener failure under load.
* **Solution:** Specify the required **strength class** (e.g., 8.8, A2-70, A4-80) and **material** (e.g., Carbon Steel, A2/A4 Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel) explicitly. Verify certifications (e.g., ISO 898-1, ISO 3506).
2. Neglecting Surface Finish & Corrosion Protection
* **Pitfall:** Failing to define the required coating or plating for the environment (Indoor, Outdoor, Marine, Chemical).
* **Consequence:** Unprotected carbon steel screws rust rapidly. Inadequately coated screws (e.g., thin zinc) fail in harsh environments, leading to seizing, galling, or structural weakness.
* **Solution:** Specify the **exact coating** (e.g., Zinc Plating (specify thickness, e.g., 8µm), Dacromet, Geomet, Hot-Dip Galvanizing, Passivated A4 Stainless). For IP considerations, ensure the coating is compatible with the intended environment and doesn't compromise sealing.
3. Ignoring Thread Tolerance & Fit
* **Pitfall:** Assuming all M6 threads are interchangeable. Tolerance classes (6g for external threads, 6H for internal) affect fit and function.
* **Consequence:** Too tight (e.g., 4g) = difficult assembly, risk of galling/stripping. Too loose (e.g., 8g) = insufficient preload, vibration loosening, poor alignment.
* **Solution:** Specify the required **thread tolerance class** (e.g., 6g) on drawings and purchase orders. Ensure mating parts have compatible tolerance (e.g., 6H nut).
4. Overlooking Head Style, Drive Type & Geometry
* **Pitfall:** Focusing only on size, not the head design needed for the application (e.g., clearance, countersinking, torque requirements, tool access).
* **Consequence:** Wrong head style (e.g., pan head instead of countersunk) prevents proper seating. Wrong drive (e.g., Phillips instead of Torx) causes cam-out and damage. Insufficient head height limits torque.
* **Solution:** Precisely specify **head style** (e.g., Hex, Socket Cap, Pan, Flat/Countersunk), **drive type** (e.g., Hex Socket (Allen), Torx, Phillips), and critical **dimensions** (head diameter, height, underhead radius).
5. Confusing IP Rating with Screw Properties
* **Pitfall:** Believing the screw *itself* has an IP rating. **IP ratings apply to the *enclosure or assembly*, not individual fasteners.** The screw is a component affecting the seal.
* **Consequence:** Misunderstanding leads to incorrect sourcing. A screw cannot be "IP67 rated."
* **Solution:** Focus on how the screw *contributes* to the assembly's IP rating: **Thread Seal Design** (e.g., requires a gasket, O-ring, or sealant), **Head Design** (e.g., flanged head compresses gasket), **Length** (ensures full thread engagement for clamping force), and **Material/Finish** (prevents corrosion that degrades the seal).
6. Inadequate IP Contribution: Poor Sealing Design
* **Pitfall:** Sourcing a standard M6 screw for an IP67 application without considering the sealing mechanism.
* **Consequence:** Water/dust ingress through the screw hole, even if the screw is corrosion-resistant. The fastener path becomes a breach.
* **Solution:** Source screws designed for sealing:
* **Sealing Screws:** Incorporate integrated O-rings or gaskets under the head.
* **Flanged Screws:** Provide a larger sealing surface to compress a separate gasket.
* **Specify Sealant:** Require thread sealant (e.g., liquid gasket, PTFE tape) application during assembly.
* **Correct Length:** Ensure sufficient thread engagement to achieve the clamping force needed to compress the seal.
7. Ignoring Sourcing & Supply Chain Risks
* **Pitfall:** Choosing the cheapest supplier without vetting quality systems or relying on a single source.
* **Consequence:** Receiving substandard screws (wrong material, poor heat treatment, inconsistent coating) or facing supply disruptions. Counterfeit fasteners are a risk.
* **Solution:** **Qualify suppliers** rigorously (audits, material certs, test reports). Require **traceability** (batch/lot numbers). Consider **dual sourcing** for critical applications. Inspect incoming stock.
Key Takeaways for Reliable Sourcing
- M6 is just the start. Define Strength, Material, Finish, Tolerance, Head, Drive, and Length.
- IP Rating is for the assembly. Specify how the screw enables the required IP (sealing design, gasket compression, corrosion resistance).
- Demand Documentation: Require material certs (e.g., MTRs), test reports, and compliance with standards (ISO, DIN, ASTM).
- Inspect: Perform incoming quality checks on critical parameters (dimensions, coating thickness, strength spot checks).
By addressing these pitfalls, you ensure M6 screws perform reliably, contribute to the required environmental protection, and prevent costly failures in the final product.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screw Size M6 – Using H2 Clearance Hole
Version: H2 Standard | Applicable Industries: Mechanical Assembly, Automotive, Aerospace, Construction, Electronics
1. Overview
This guide provides comprehensive logistics and compliance information for the use of M6 screws in conjunction with H2 clearance holes, ensuring dimensional accuracy, interchangeability, and adherence to international standards. H2 refers to a standardized tolerance class for clearance holes defined in ISO 286-1 and commonly applied in mechanical design.
2. Screw Specification – M6
| Parameter | Value |
|———|——-|
| Nominal Diameter | 6 mm |
| Thread Standard | ISO Metric Thread (ISO 68-1) |
| Common Lengths | 10 mm to 100+ mm (customizable) |
| Thread Pitch (Standard) | 1.0 mm (coarse), 0.75 mm (fine) |
| Strength Class (Typical) | 8.8, 10.9, or A2-70 (stainless) |
| Head Types | Hex, Socket Cap, Pan, Flat, etc. |
| Drive Type | Hex key, Slotted, Phillips, Torx |
| Material Options | Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel (A2/A4), brass |
| Surface Finish | Zinc plating, galvanization, passivation, black oxide |
3. H2 Clearance Hole Specification
The H2 tolerance class specifies the minimum and maximum hole diameters to allow a free fit for M6 screws.
| Parameter | Value |
|———|——-|
| Nominal Hole Diameter | 6.6 mm |
| Tolerance Class | H2 (ISO 286-1) |
| Lower Deviation (min) | +0.030 mm |
| Upper Deviation (max) | +0.060 mm |
| Hole Diameter Range | 6.63 mm – 6.66 mm |
| Purpose | Ensures free insertion of M6 screw with minimal friction; ideal for alignment and vibration-prone assemblies |
✅ Design Tip: Use H2 holes when precise alignment is required but no force fit is desired. H2 is tighter than H13 or H14, offering better positional accuracy.
4. Compliance Standards
Ensure all components meet the following international standards:
| Standard | Description |
|——–|————-|
| ISO 273 | Clearance holes for bolts and screws |
| ISO 286-1 | Geometrical product specifications (GPS) – ISO system of limits and fits |
| ISO 4014 / ISO 4017 | Hex head screws and socket head cap screws |
| DIN 912 | Metric socket head cap screws (common alternative reference) |
| ASTM A325 / A490 | Structural bolts (if used in construction) |
| RoHS / REACH | Material compliance (especially for electronics and EU markets) |
| DIN EN ISO 898-1 | Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel |
5. Logistics Considerations
A. Packaging
- Pack screws in anti-corrosive bags or trays (especially for stainless or plated variants).
- Use ESD-safe packaging if used in electronics.
- Label packages with:
- Part number
- Quantity
- Material & finish
- ISO/DIN standard
- Lot traceability
B. Storage
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C, RH < 60%).
- Avoid exposure to salt, acids, or chlorides.
- Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system.
C. Shipping
- Secure small parts in sealed containers to prevent loss.
- Use shock-absorbing materials for fragile or precision components.
- Comply with IATA/IMDG regulations if transporting hazardous-coated materials (e.g., cadmium-plated).
D. Inventory Coding (Example)
Part No: M6x20-H2-8.8-ZN
- M6: Diameter
- x20: Length
- H2: Clearance hole reference
- 8.8: Strength class
- ZN: Zinc plated
6. Assembly & Quality Control
A. Installation Guidelines
- Pre-drill holes to 6.63–6.66 mm for H2 fit.
- Use correct torque values (e.g., 10–12 Nm for M6 8.8 steel, depending on lubrication).
- Use thread-locking compounds if vibration resistance is needed.
B. Inspection Criteria
- Verify hole diameter with go/no-go gauge calibrated to H2 tolerance.
- Check screw thread conformity using thread gauges (ISO 1502).
- Audit material certification (e.g., mill test reports for stainless steel).
7. Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
| Requirement | Action |
|———-|——–|
| REACH (EU) | Confirm no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) in plating or materials |
| RoHS (EU) | Ensure compliance for electrical/electronic assemblies |
| Conflict Minerals (US Dodd-Frank) | Source from certified conflict-free suppliers if applicable |
| Export Controls (e.g., EAR) | Check if fasteners are ITAR or dual-use controlled (rare, but possible in aerospace) |
8. Common Applications
- Automotive: Engine mounts, chassis components
- Aerospace: Non-primary structural brackets (secondary systems)
- Electronics: Enclosure fastening, heat sink attachment
- Industrial Machinery: Motor mounts, frame assembly
- Construction: Steel framing, modular systems
9. Troubleshooting & Best Practices
| Issue | Solution |
|——|———|
| Screw binds in hole | Verify hole is within H2 tolerance (≥6.63 mm); deburr edges |
| Misalignment during assembly | Use H2 holes for precision; check hole pattern accuracy (±0.1 mm) |
| Corrosion | Use A4 stainless in marine environments; avoid dissimilar metal contact |
| Loosening under vibration | Apply thread locker or use lock washers/prevailing torque nuts |
10. References
- ISO 273:1979 – Clearance holes for bolts and screws
- ISO 286-1:2010 – Geometrical product specifications (GPS) – ISO system of limits and fits
- DIN 912:2021 – Socket head cap screws
- Machinery’s Handbook (30th Ed.) – Industrial fastener data
✅ Conclusion:
Using M6 screws with H2 clearance holes ensures precision fit, ease of assembly, and compliance with international standards. Proper logistics, quality control, and regulatory adherence are essential for reliability across industries.
For custom applications, consult a mechanical design engineer or fastener specialist.
Document Prepared By: [Your Company Name] – Engineering & Compliance Team
Date: 2024-04-05
Use authorized under H2 design protocol.
Conclusion for Sourcing M6 Screw Size:
Sourcing M6 screws requires careful consideration of specifications such as thread pitch, length, material, strength class, drive type, and coating to ensure compatibility with the intended application. Common materials include stainless steel, zinc-plated steel, and aluminum, each offering trade-offs in corrosion resistance, strength, and cost. Standard thread pitches are typically 1.0 mm (fine) or 1.0/1.25 mm (coarse), with coarse threads being more common in general applications.
Reliable suppliers, clear technical documentation, and adherence to international standards (e.g., ISO 4017, ISO 4032) are essential for consistent quality and performance. Bulk purchasing from certified vendors can reduce costs while maintaining reliability. Ultimately, selecting the correct M6 screw variant ensures structural integrity, ease of assembly, and long-term durability in the final product. Proper sourcing minimizes maintenance issues and enhances overall manufacturing efficiency.