The global biomass fuel market, driven by rising demand for sustainable and cost-effective energy alternatives, is experiencing robust growth, with sawdust blocks emerging as a key player in the sector. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global wood pellets and biomass fuels market was valued at USD 9.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing industrial adoption of biomass as a renewable energy source, stringent government regulations on carbon emissions, and improvements in densification technology that enhance the calorific value and handling efficiency of compressed biomass products like sawdust blocks.
As industries shift toward circular economy models, sawdust blocks—compressed from wood processing by-products—offer a sustainable solution that reduces waste and lowers dependency on fossil fuels. Regions with strong timber and wood processing industries, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Southeast Asia, are leading this transformation. Against this expanding backdrop, manufacturers specializing in high-density sawdust blocks are scaling production, improving logistics, and investing in R&D to meet evolving environmental standards and global export demand. The following list highlights the top eight sawdust block manufacturers positioning themselves at the forefront of this clean energy shift.
Top 8 Sawdust Blocks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Sawdust Pallet Block Machine Manufacturer and Supplier …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: thoyu.com
Key Highlights: Sawdust Pallet Block Machine Manufacturers, Factory, Suppliers From China, With advantage of industry management, the company has always been committed to ……
#2 Manufacturing Hardwood Dimension Products Directly from Logs
Domain Est. 1997
Website: research.fs.usda.gov
Key Highlights: Many techniques have been suggested to improve the overall dimension product yield from logs, including back-gages, thin kerf saws, and computer automation….
#3 Wood Bricks & Coal
Domain Est. 2005
Website: btpellet.com
Key Highlights: Enviro-Bricks are manufactured from 100% kiln dried hardwood lumber sawdust and compressed with 24,000 lbs pressure making them twice as dense as cordwood….
#4 Bio Blocks
Domain Est. 2009
#5 The Envi & Envi8 – Wood Block
Domain Est. 2013
Website: bio-div.com
Key Highlights: Bio-Diversity Envi Blocks are an all-natural wood product made from a naturally renewable resource (hardwood sawdust and shavings). · They contain no additives, ……
#6 Enviro
Domain Est. 2014
Website: envirobrick.net
Key Highlights: Enviro-Bricks are manufactured from 100% kiln dried hardwood lumber sawdust and compressed with 24,000 lbs pressure making them twice as dense as cordwood….
#7 Sierra Energy Logs
Domain Est. 2019
Website: sierraenergylogs.com
Key Highlights: Energy Logs are made entirely of wood by-products from sawmills, and are a much cleaner burning fuel than traditional firewood….
#8 Envi 8 Blocks
Domain Est. 2024
Website: biomasfuels.com
Key Highlights: Manufactured in the USA by Bio-Diversity, these compressed wood fuel bricks are made entirely from 100% recycled hardwood sawdust and shavings—without any ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sawdust Blocks
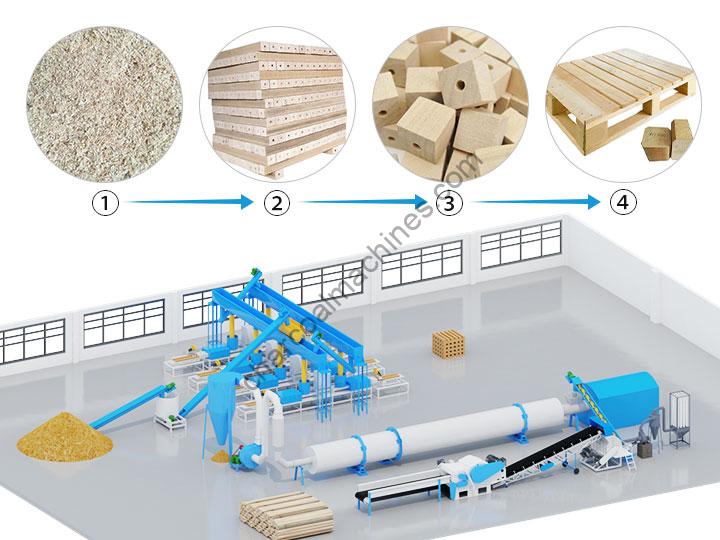
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Sawdust Blocks
The market for sawdust blocks—a sustainable building material composed primarily of compressed sawdust and a binding agent—is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by global sustainability mandates, rising demand for eco-friendly construction, and advancements in material science, several key trends are expected to shape this niche but growing sector.
1. Accelerated Demand from Green Building Initiatives
By 2026, stringent environmental regulations and certifications (such as LEED, BREEAM, and net-zero building codes) will increasingly favor low-carbon construction materials. Sawdust blocks, which utilize wood waste and have a significantly lower embodied carbon footprint compared to concrete or fired bricks, will see rising adoption in residential, commercial, and public infrastructure projects—especially in Europe and North America.
2. Technological Advancements in Binding and Durability
Ongoing R&D is expected to yield improved binders (e.g., bio-based resins or mineral cements) that enhance moisture resistance, compressive strength, and fire retardancy. By 2026, next-generation sawdust blocks will likely meet or exceed international building standards, overcoming historical concerns about longevity and performance in humid climates. This will expand their applicability beyond non-load-bearing walls to structural components.
3. Integration with Circular Economy and Waste Valorization
Sawdust blocks will become a key component in circular economy models within the forestry and woodworking industries. With increasing pressure to reduce industrial waste, lumber mills and furniture manufacturers will partner with block producers to convert sawdust—traditionally a disposal cost—into a revenue-generating resource. This synergy will lower production costs and improve supply chain sustainability.
4. Regional Expansion and Localization of Production
While current production is concentrated in regions with abundant wood waste (e.g., Scandinavia, Southeast Asia, and Canada), 2026 will see decentralized, small-scale manufacturing units emerging globally. Modular production systems will enable localized fabrication, reducing transportation emissions and supporting community-based construction, particularly in developing economies.
5. Competitive Pressure and Market Differentiation
As awareness grows, competition will intensify among manufacturers. Leading players will differentiate through product innovation (e.g., insulating sawdust blocks with higher thermal performance), third-party sustainability certifications, and transparent supply chains. Price parity with conventional blocks, aided by economies of scale, will become critical to mainstream adoption.
6. Policy Support and Incentives
Governments aiming to meet climate targets will likely introduce subsidies, tax breaks, or procurement preferences for bio-based construction materials. Incentive programs for retrofitting and low-income housing using sustainable materials will further boost demand for sawdust blocks by 2026.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for sawdust blocks will be defined by technological maturity, regulatory support, and integration into sustainable construction ecosystems. While challenges around standardization and perception remain, the convergence of environmental urgency and innovation positions sawdust blocks as a transformative material in the future of green building.
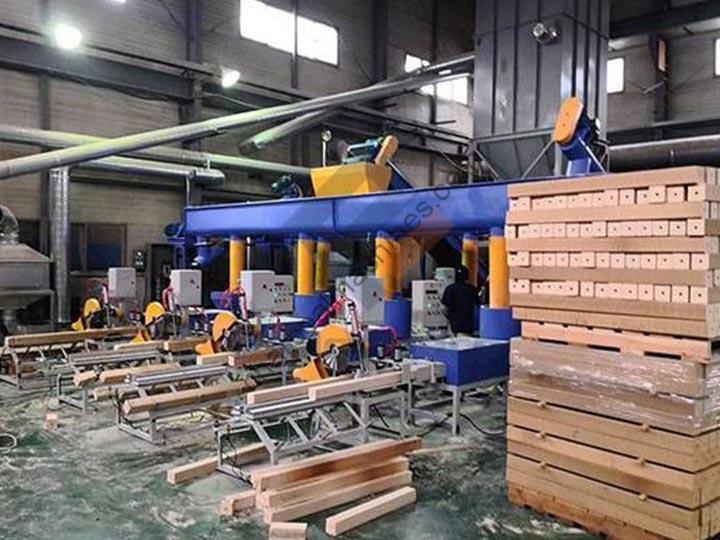

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sawdust Blocks (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing sawdust blocks—a sustainable building material made from compressed sawdust and natural binders—can offer environmental and economic benefits. However, buyers and manufacturers often encounter key challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for successful and legally sound sourcing.
Inconsistent Raw Material Quality
The quality of sawdust blocks heavily depends on the source and composition of the raw sawdust. Variations in wood species, moisture content, and contamination (e.g., paint, adhesives, or chemicals from treated wood) can lead to weak or unstable blocks. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in inconsistent product performance, such as reduced structural integrity or poor insulation properties.
Lack of Standardized Production Processes
Many small-scale or regional producers lack standardized manufacturing protocols. Without controlled compression, curing, and drying methods, the resulting blocks may vary in density, durability, and dimensional accuracy. This inconsistency compromises construction safety and can lead to project delays or rework.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Sawdust blocks may not always undergo rigorous third-party testing for fire resistance, load-bearing capacity, or environmental emissions. Sourcing blocks without proper certification (e.g., ASTM, ISO, or local building codes) can pose compliance risks and liability issues, especially in commercial or residential construction projects.
Misrepresentation of Sustainability Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate the eco-friendliness of their sawdust blocks, claiming full biodegradability or carbon neutrality without evidence. Buyers may fall into greenwashing traps if they don’t verify sourcing practices, energy use in production, or the type of binders used (e.g., synthetic vs. natural resins).
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Certain sawdust block formulations, production machinery, or design methods may be protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing from manufacturers using proprietary technology without proper licensing can expose buyers to IP litigation, especially when importing or scaling production internationally.
Unclear Ownership of Formulation Rights
When working with custom formulations or co-developing products, ambiguity in contractual agreements can lead to disputes over who owns the rights to the final product. Without clear IP clauses, buyers may lose control over manufacturing rights or be restricted from replicating the blocks elsewhere.
Dependence on Proprietary Equipment
Some sawdust block technologies require specialized machinery that is patented or sold under exclusive agreements. Relying on such equipment without assessing IP restrictions can limit scalability and create vendor lock-in, increasing long-term costs and operational risks.
Failure to Conduct IP Due Diligence
Buyers often overlook the need to perform IP audits before finalizing supplier agreements. This includes checking patent databases, reviewing supplier claims, and consulting legal experts to ensure that the sourced blocks or production methods do not infringe existing intellectual property rights.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls early, stakeholders can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal safety in their sawdust block sourcing strategy.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sawdust Blocks
Overview
Sawdust blocks, also known as biomass briquettes or fuel blocks, are compressed blocks made from sawdust and other organic biomass materials. They are used as a renewable energy source for heating and industrial applications. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure safe transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence.
Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Sawdust blocks are typically classified as a solid biofuel. Depending on the region, they may fall under specific environmental, agricultural, or energy regulations.
– UN Classification: Generally not classified as hazardous (UN3220 applies to compressed sawdust only if treated with flammable binders).
– REACH/CLP (EU): Ensure no hazardous chemicals are used in binders; compliance with REACH regulations for chemical safety.
– EPA (USA): Comply with EPA air quality standards if used in combustion; check state-level biomass fuel regulations.
– Customs and Import/Export: Declare under HS Code 4401 (Fuel wood, in logs, in billets, in branches, in chips or particles, etc.) or 6805 (Other articles of stone or of agglomerated minerals). Verify country-specific import requirements.
Packaging and Handling
- Packaging: Use moisture-resistant polypropylene or woven poly bags (25–50 kg per bag). Bulk shipments in big bags (1,000 kg) are also common.
- Palletization: Stack on standard wooden or plastic pallets (1.2m x 1.0m); secure with stretch wrap.
- Handling: Use forklifts or pallet jacks. Avoid dropping or piercing packages to prevent dust release and structural damage.
- Labeling: Include product name, net weight, batch number, manufacturer details, and handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Fragile”).
Storage Requirements
- Location: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse off the ground.
- Moisture Control: Relative humidity should be below 60%; moisture content of blocks must remain under 10% to ensure combustion efficiency.
- Fire Safety: Keep away from open flames and ignition sources. Maintain a minimum 1-meter clearance from walls and other stored materials. Install smoke detectors and fire extinguishers (Class A).
- Stacking: Limit stack height to 3–4 pallets to prevent collapse. Avoid outdoor storage unless covered with waterproof tarps.
Transportation Guidelines
- Domestic Transport:
- Use enclosed trucks or containers to prevent moisture absorption and dust emissions.
- Secure loads with straps or nets to prevent shifting.
- Comply with local road weight and dimension regulations.
- International Shipping:
- Use dry, ventilated containers (20’ or 40’).
- Include desiccants if shipping through humid climates.
- Provide phytosanitary certificate if required (especially for raw, untreated biomass).
- Follow IMDG Code if shipped by sea (though generally not classified as dangerous goods).
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Dust Control: Sawdust blocks can generate combustible dust. Use dust masks during handling and ensure proper ventilation.
- Spills: Sweep up spilled material promptly; avoid water (can cause clumping).
- Sustainability Certification: For premium markets, consider certifications such as ENplus, DINplus, or FSC to verify sustainable sourcing and production.
Documentation Checklist
Ensure the following documents accompany shipments:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Phytosanitary Certificate (if required)
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – even if not hazardous, recommended for transparency
– Sustainability or Quality Certification (optional but recommended)
Compliance Monitoring and Audits
- Conduct regular internal audits of storage, handling, and labeling practices.
- Stay updated on changes in national and international biofuel regulations.
- Maintain records of supplier compliance, test reports (moisture, calorific value), and shipment documentation for at least 5 years.
By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure efficient, safe, and compliant logistics operations for sawdust blocks across domestic and international markets.
In conclusion, sourcing sawdust blocks presents a sustainable and cost-effective solution for energy production, especially in regions with abundant wood processing by-products. These biomass fuel blocks offer a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and supporting waste-to-energy initiatives. When sourcing sawdust blocks, key considerations include the quality and moisture content of the raw material, the reliability of suppliers, production standards, and transportation logistics. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers and ensuring consistent quality control are essential for maximizing efficiency and performance. With growing demand for clean, renewable energy, sawdust blocks represent a viable option for industrial, commercial, and domestic heating applications, aligning environmental responsibility with economic practicality.