The global ruby laser market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in dermatology, tattoo removal, and precision industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global solid-state laser market—of which ruby lasers are a key subset—was valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Ruby lasers, known for their 694.3 nm wavelength and high peak pulse energy, remain particularly relevant in aesthetic medicine and scientific research. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, noting increased adoption of laser-based treatments in emerging economies and ongoing advancements in optoelectronic components. With these market dynamics in play, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, product reliability, and global reach. Below are the top 7 ruby laser manufacturers shaping the industry landscape in 2024.
Top 7 Ruby Laser Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ruby Crystals
Domain Est. 2018
Website: laser-crylink.com
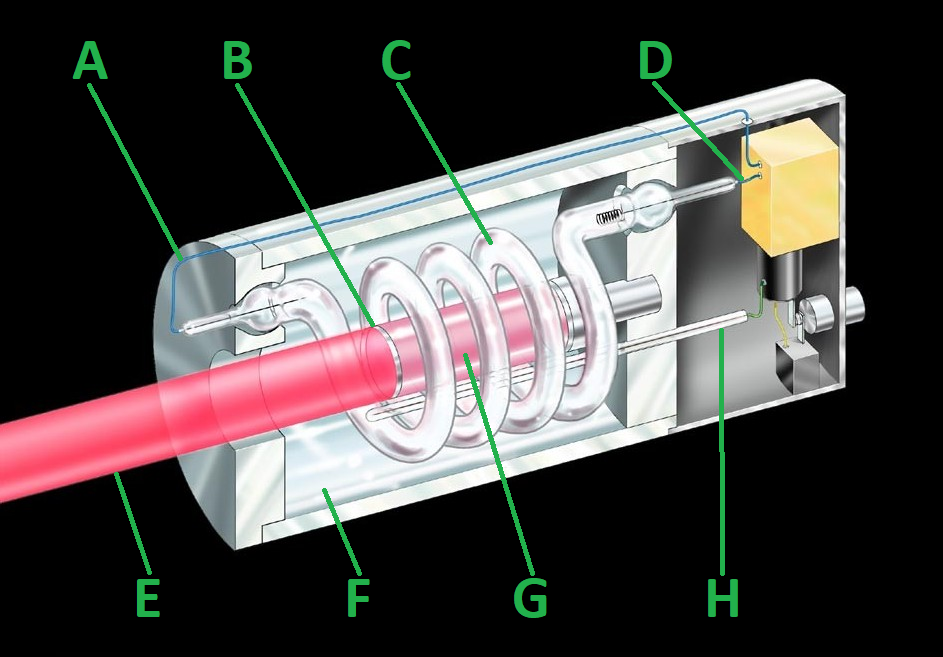
Key Highlights: Micromachining: Ruby lasers are used in precision micromachining for electronics and optical components, ensuring high resolution with minimal thermal impact….
#2 Ruby Crystal from Maiman Laser
Domain Est. 1992
Website: si.edu
Key Highlights: This is a ruby crystal from Theodore Maiman’s experiments of May 1960, and may be the first crystal to generate laser light. The synthetic crystal was ……
#3 About
Domain Est. 1994
Website: hrl.com
Key Highlights: Researchers at Hughes and now HRL Laboratories have continued to investigate and exploit the enormous advantages of optics and optoelectronics….
#4 Laser Crystals » Ruby Laser Rods
Domain Est. 1998
Website: roditi.com
Key Highlights: Roditi supplies Czochralski grown Ruby in a wide range of sizes, with consistent optical quality which makes predictable system performance possible. Ruby laser ……
#5 Ruby Lasers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: innolas.co.uk
Key Highlights: InnoLas are a major supplier of pulsed ruby lasers for a variety of applications. Based upon our revolutionary carbon fibre laser head structure….
#6 Ruby® laser software
Domain Est. 2002
Website: troteclaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser software and graphic design software combined ✓ Smooth workflow ✓ Web-based platform for networked tasks ✓ Mac compatible. Get more information now!…
#7 Ruby Lasers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: photonics.com
Key Highlights: A ruby laser is an optically pumped, solid-state laser that uses sapphire as the host lattice and chromium as the active ion. The emission takes place in the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ruby Laser
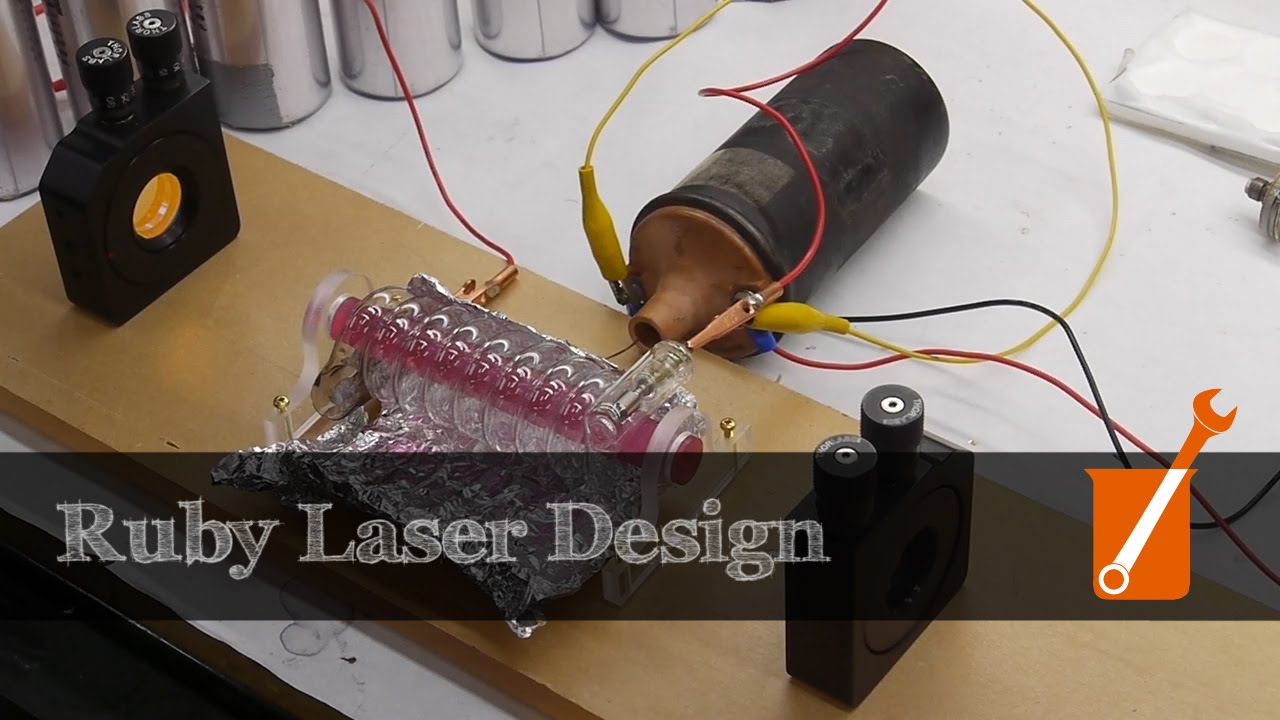
2026 Market Trends for Ruby Lasers
The ruby laser, the first working laser demonstrated in 1960, holds a significant place in history but occupies a highly specialized and diminishing role in the modern laser market. By 2026, its market presence will continue to reflect this niche status, shaped by technological advancements and shifting industry demands.
Decline in Mainstream Industrial and Medical Applications
Ruby lasers, operating at a 694.3 nm wavelength in the deep red visible spectrum, have been largely superseded by more efficient, reliable, and versatile solid-state lasers like Nd:YAG, fiber lasers, and diode-pumped systems. In industrial settings—cutting, welding, and marking—ruby lasers are practically obsolete due to their low efficiency, high thermal load, and pulsed-only operation. Similarly, in dermatology and aesthetic medicine, where ruby lasers were once used for tattoo removal and pigmented lesion treatment, they are increasingly replaced by Q-switched Nd:YAG and Alexandrite lasers, which offer better depth control, faster repetition rates, and broader clinical applicability. By 2026, demand in these sectors will remain minimal, confined to legacy systems or specific research protocols.
Niche Hold in Scientific and Educational Use
One of the few stable areas for ruby lasers in 2026 will be in academic and research environments. Their historical significance and straightforward design make them valuable teaching tools for demonstrating laser physics principles. Universities and physics labs may continue to use ruby lasers for pedagogical demonstrations and foundational optics experiments. Additionally, some specialized research in holography and nonlinear optics may still employ ruby lasers due to their coherent, high-peak-power pulses, although even here, modern alternatives are often preferred.
Limited Role in Heritage and Museum Applications
Ruby lasers may see marginal demand in science museums and historical technology exhibits. As the first working laser, original or replica ruby laser units serve as educational artifacts. By 2026, vendors specializing in historical scientific instruments may sustain a small market catering to museums and collectors, but this does not constitute a significant commercial segment.
No Significant Technological Advancements Expected
Unlike fiber or semiconductor lasers, there are no major R&D initiatives aimed at improving ruby laser technology. The material limitations—such as poor thermal conductivity of ruby (Cr³⁺:Al₂O₃) and low quantum efficiency—make it unlikely that ruby lasers will see performance upgrades that would revive broader interest. Consequently, no substantial market growth or innovation is expected by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the ruby laser market will remain extremely limited, sustained only by educational, historical, and niche research applications. Its role in commercial and medical fields will continue to diminish due to superior alternatives. While ruby lasers retain symbolic importance in the history of photonics, their practical market impact will be negligible, reflecting a legacy technology preserved more for its historical value than its utility.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ruby Lasers: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing ruby lasers—particularly for specialized applications in research, dermatology, or legacy systems—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is critical to ensuring reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal safety.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Crystal Quality
Ruby laser performance heavily depends on the quality of the synthetic ruby crystal (chromium-doped aluminum oxide). Poorly manufactured crystals may have impurities, inclusions, or non-uniform doping, leading to reduced efficiency, beam instability, or premature failure. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases the risk of receiving substandard materials.
Lack of Performance Verification
Many suppliers, especially those in unregulated markets, may provide exaggerated or unverified specifications (e.g., output energy, pulse duration, beam quality). Without independent testing or third-party certifications, buyers risk receiving lasers that fail to meet application requirements.
Inadequate Cooling and Optics
Ruby lasers generate significant heat and require robust thermal management. Low-cost or poorly designed systems may lack proper cooling mechanisms, leading to thermal lensing or crystal damage. Similarly, low-quality mirrors and optical coatings reduce output efficiency and longevity.
Absence of Calibration and Traceability
High-quality ruby lasers should come with calibration data and traceable documentation. Sourcing from vendors without proper metrology support can result in unreliable operation and difficulties in maintaining regulatory compliance, especially in medical or aerospace applications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Risk of Infringing Patented Technologies
Although ruby lasers are an older technology, certain modern implementations—such as Q-switching mechanisms, cooling designs, or integration into medical devices—may still be protected by active patents. Sourcing from manufacturers that do not respect IP rights could expose the buyer to infringement claims, especially in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement.
Counterfeit or Clone Devices
Some suppliers offer ruby lasers that closely mimic branded or patented models without proper licensing. These clones may appear cost-effective but carry legal risks and often lack reliability. Buyers may inadvertently support or become liable for IP violations.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When commissioning custom ruby laser systems, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Suppliers may retain rights to design improvements, limiting the buyer’s ability to modify, reproduce, or service the equipment independently.
Export and Regulatory Compliance Gaps
Ruby lasers may be subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR or EAR in the U.S.) depending on their specifications. Sourcing from vendors unfamiliar with these regulations can result in shipment delays, seizures, or legal penalties—especially if the technology incorporates protected components or designs.
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from reputable, established manufacturers with verifiable quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Request independent test reports and perform incoming inspections.
- Conduct IP due diligence, including patent landscape reviews, especially for custom or high-power systems.
- Use clear contracts that specify performance standards, IP ownership, and compliance obligations.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures not only technical success but also legal and operational integrity when integrating ruby lasers into critical applications.
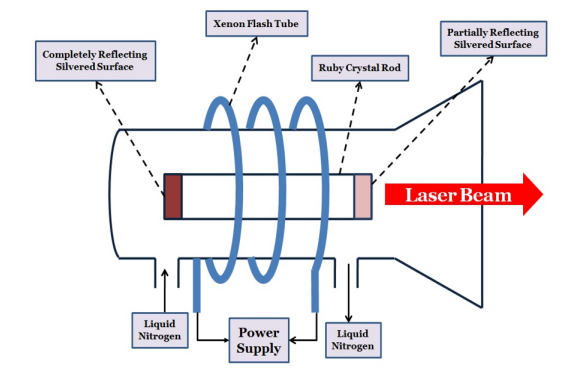
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ruby Laser
This guide outlines essential logistics and regulatory compliance considerations for the shipment, handling, and use of Ruby Lasers, which are Class 3B or Class 4 laser devices and subject to strict national and international regulations.
Regulatory Classification & Standards
Ruby lasers typically operate in the visible red spectrum (694.3 nm) and are classified as Class 3B or Class 4 lasers under the IEC 60825-1 standard. This classification determines safety requirements for manufacturing, transportation, and operation. Compliance with FDA/CDRH (U.S. Code of Federal Regulations 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11), EU Directive 2014/35/EU (CE marking), and other regional safety standards is mandatory.
Export and Import Compliance
Ruby lasers may be subject to export controls due to their potential dual-use (civilian and military applications). In the United States, verify if the laser is listed under the Commerce Control List (CCL) in the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), particularly under ECCN 6A003 or 6A005. Exporting may require a license from the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS). Similar controls may apply under the Wassenaar Arrangement in other countries. Importers must ensure compliance with local customs regulations and obtain necessary permits.
Packaging and Transportation Requirements
Ship ruby lasers in robust, shock-resistant packaging with internal cushioning to prevent damage. Include clear labeling indicating “Laser Radiation – Avoid Direct Exposure to Beam” and the applicable laser class. If batteries (e.g., for portable units) are included, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for air transport or IMDG Code for sea freight. Use certified shippers for hazardous materials when applicable, and ensure temperature-controlled logistics if components are sensitive.
Safety Documentation and Labeling
Provide all units with required safety labels per IEC 60825-1, including warning labels, aperture labels, and manufacturer information. Include in the shipment: a user manual with safety instructions, service manual, Declaration of Conformity (DoC), and FDA accession number (for U.S. market). For international shipments, documentation must be in the local language(s) as required by destination country.
End-User Verification and Recordkeeping
Maintain records of end-user information and perform due diligence to prevent diversion to unauthorized or restricted parties. Use End-User Undertakings (EUUs) or Statements of Understanding (SOU) where required. Retain export documentation, including licenses, shipping records, and compliance certifications, for a minimum of five years (or as required by jurisdiction).
On-Site Installation and Regulatory Notification
In some countries (e.g., the U.S.), facilities using Class 3B and Class 4 lasers must register with national or state regulatory bodies and appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO). Ensure customers are informed of their compliance responsibilities, including facility audits, safety training, and use of protective equipment (e.g., laser safety goggles rated for 694 nm).
Disposal and End-of-Life Management
Dispose of ruby laser systems in accordance with local electronic waste (WEEE) directives and hazardous materials regulations. Ruby rods and power supplies may contain materials requiring special handling. Provide customers with disposal guidelines and support take-back programs where applicable.
Adherence to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient logistics operations while minimizing regulatory risk throughout the lifecycle of ruby laser systems.
In conclusion, sourcing a ruby laser requires careful consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and regulatory compliance. Ruby lasers, being one of the earliest types of lasers, are primarily used in specialized applications such as dermatology, holography, and certain industrial processes due to their unique red light output at 694.3 nm. When sourcing, it is essential to verify the laser’s pulse energy, repetition rate, beam quality, and cooling requirements to ensure compatibility with the intended use. Additionally, choosing a reputable supplier that provides proper certifications, technical support, and after-sales service is crucial for long-term performance and safety. While newer laser technologies have surpassed ruby lasers in efficiency and versatility, they remain valuable in niche fields—making informed sourcing decisions key to achieving optimal results.