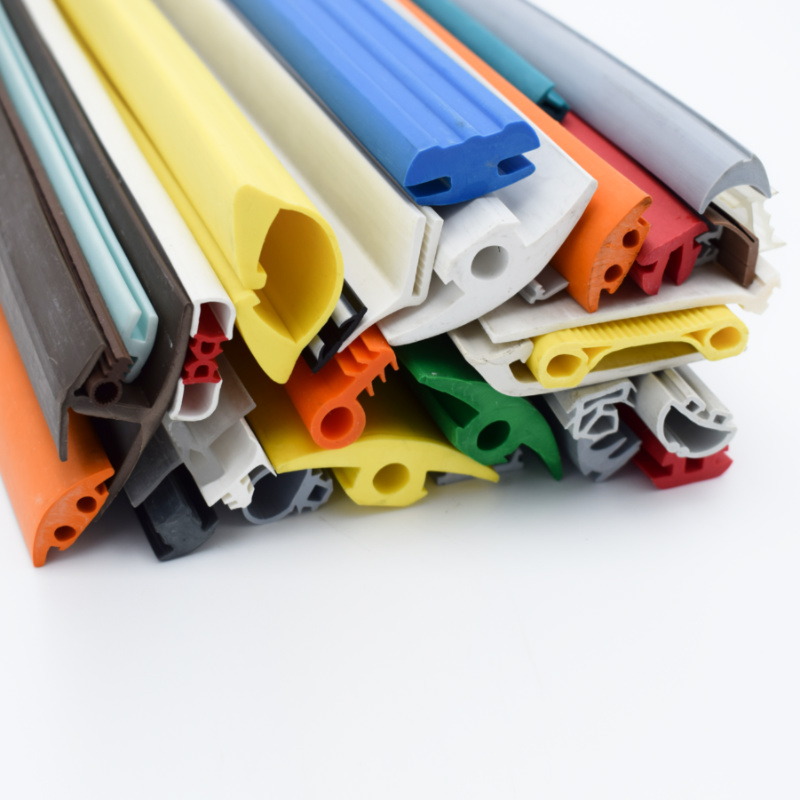
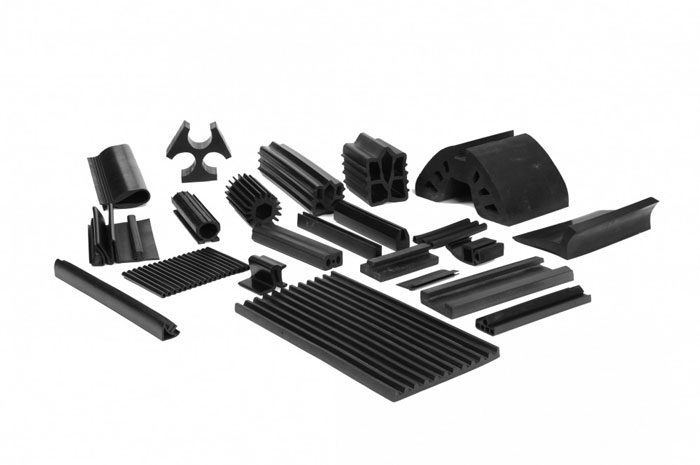
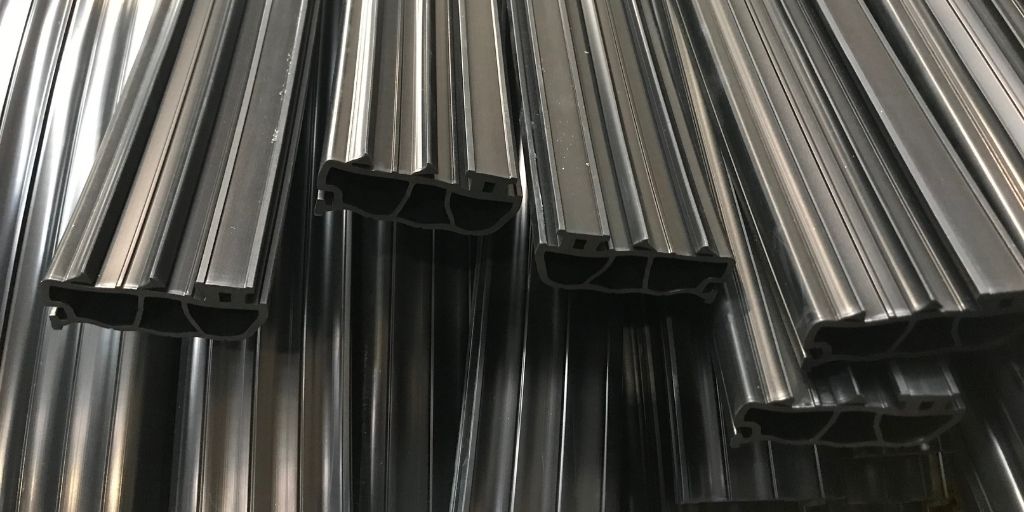
The global rubber extrusions market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, construction, industrial machinery, and healthcare sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global rubber tubing and extruded rubber products market was valued at USD 5.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 7.54 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.3% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by rising vehicle production, infrastructure development, and the need for durable sealing and insulation solutions in manufacturing. With stringent industry standards and evolving material technologies, manufacturers are focusing on advanced elastomers such as EPDM, silicone, and neoprene to meet performance demands. In this competitive landscape, a select group of rubber extrusions manufacturers are leading through innovation, precision engineering, and vertical integration—setting the benchmark in quality and scalability.
Top 10 Rubber Extrusions Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rubber Extrusion Profile Suppliers & Manufactures China …
Domain Est. 2018
Website: seashoreseal.com
Key Highlights: Qingdao Seashore Industrial Co.Ltd is a prefessional manufacturer of high quality rubber extrusion profile,sponge rubber profile,co-extrusion sealing strip….
#2 Custom Rubber Products & Plastic Parts Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: viprubber.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in custom rubber extrusions, plastic extrusions, rubber sheet products, molded rubber products, plastic pipe and tubing. We have been ……
#3 Extruded Rubber Profiles & Tubing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: minorrubber.com
Key Highlights: Minor Rubber is a leading manufacturer of rubber extrusions & extruded rubber profiles & tubing, including standard styles like P-strips. Call us today!…
#4 NW Rubber Extruders – We Are The Flexible People
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nwreinc.com
Key Highlights: Full-service extrusion manufacturer of rubber, plastic, silicone, and custom-extruded elastomeric products for a variety of applications….
#5 Rubber Extrusion Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: extrudedrubber.net
Key Highlights: GSH Industries supplies rubber extrusions to a range of industries. We offer rubber in materials such as Neoprene, Viton®, Nitrile, Silicone & more. We have ……
#6 Pro
Domain Est. 2004
Website: proflex.ca
Key Highlights: Pro-Flex Rubber is an expert manufacturer of rubber products. Pro-Flex rubber has strong expertise in rubber moulding and rubber extrusion….
#7 Central Rubber Extrusions: Rubber Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2005
Website: centralrubberextrusions.com
Key Highlights: We are a specialized manufacturer of extruded rubber products produced in the United States in our facility in Highland Illinois….
#8 Custom Rubber Extrusions
Domain Est. 1999
Website: cooperstandard.com
Key Highlights: Providing custom rubber seals for diverse industries, to your specification. Our engineers design and optimize sealing solutions from start to finish….
#9 Rubber Extrusions
Domain Est. 1999
Website: warco.com
Key Highlights: WARCO specializes in custom rubber extrusions, with thousands of custom profiles on hand. Explore our Extrusion & Splicing Capabilities….
#10 Extrusions & Profiles
Domain Est. 2013
Website: therubbercompany.com
Key Highlights: At The Rubber Company, we manufacture and supply an extensive range of rubber extrusions and profiles for a whole host of applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rubber Extrusions
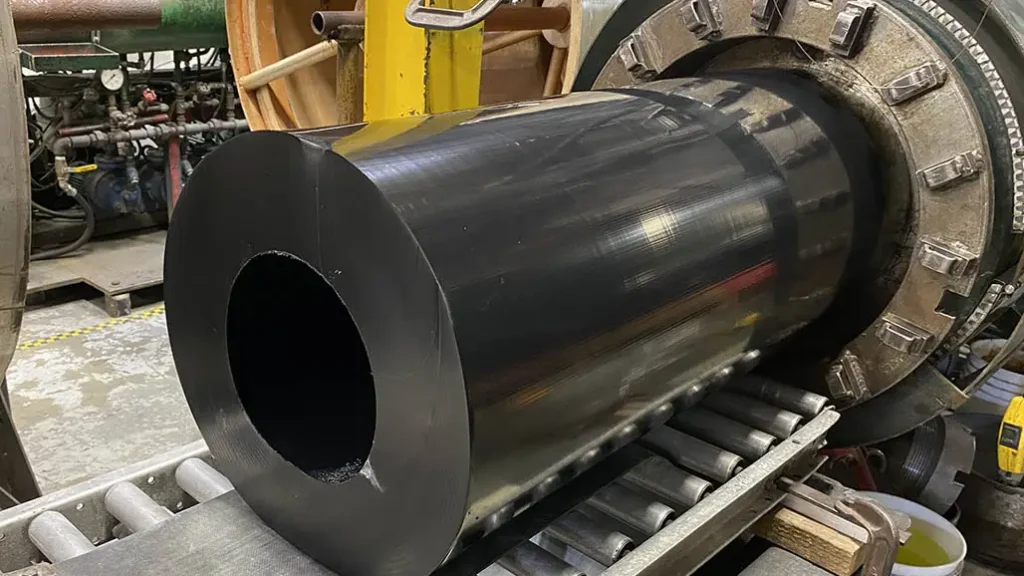

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Rubber Extrusions
The global rubber extrusions market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by rising demand across key end-use industries, technological advancements, and a shift toward sustainable materials. Several macroeconomic and sector-specific trends are shaping the trajectory of this market, positioning rubber extrusions as a critical component in automotive, construction, healthcare, and industrial manufacturing applications.
1. Automotive Industry Expansion and EV Adoption
The automotive sector remains the largest consumer of rubber extrusions, particularly for weatherstripping, seals, gaskets, and anti-vibration components. With the global push toward electric vehicles (EVs), demand for specialized rubber profiles designed for battery enclosures, noise insulation, and thermal management is increasing. By 2026, EV production is expected to account for over 30% of total vehicle output in major markets, amplifying the need for high-performance, lightweight, and chemically resistant rubber extrusions.
2. Growth in Construction and Infrastructure
Urbanization and infrastructure development, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are fueling demand for rubber extrusions used in window and door seals, expansion joints, and HVAC systems. Building codes emphasizing energy efficiency and weather resistance are encouraging the adoption of durable, long-lasting elastomeric profiles. Green building initiatives are also supporting the use of recyclable or bio-based rubber materials.
3. Technological Advancements in Material Science
Innovation in synthetic rubber compounds—such as EPDM, silicone, neoprene, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs)—is enabling manufacturers to produce extrusions with enhanced properties like UV resistance, ozone stability, and extreme temperature tolerance. By 2026, smart rubber extrusions embedded with sensors for structural health monitoring may begin emerging in niche industrial and aerospace applications.
4. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations, particularly in North America and Europe, are pushing manufacturers to reduce VOC emissions and increase the use of recycled rubber content. The European Green Deal and similar policies are accelerating the development of bio-based and recyclable rubber solutions. Companies investing in closed-loop production systems and sustainable sourcing are likely to gain competitive advantage by 2026.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the rubber extrusions market by 2026, driven by China, India, and Southeast Asia’s robust manufacturing base and infrastructure spending. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on product innovation and compliance with environmental standards, creating opportunities for high-value, specialty extrusions.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regionalization. Many automotive and industrial OEMs are seeking local rubber extrusion suppliers to reduce lead times and mitigate risk. This trend is fostering investment in localized production facilities and onshoring strategies, particularly in the U.S. and Germany.
Conclusion
By 2026, the rubber extrusions market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and regional diversification. Manufacturers who adapt to EV trends, invest in eco-friendly materials, and strengthen supply chain agility will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in a competitive global landscape.
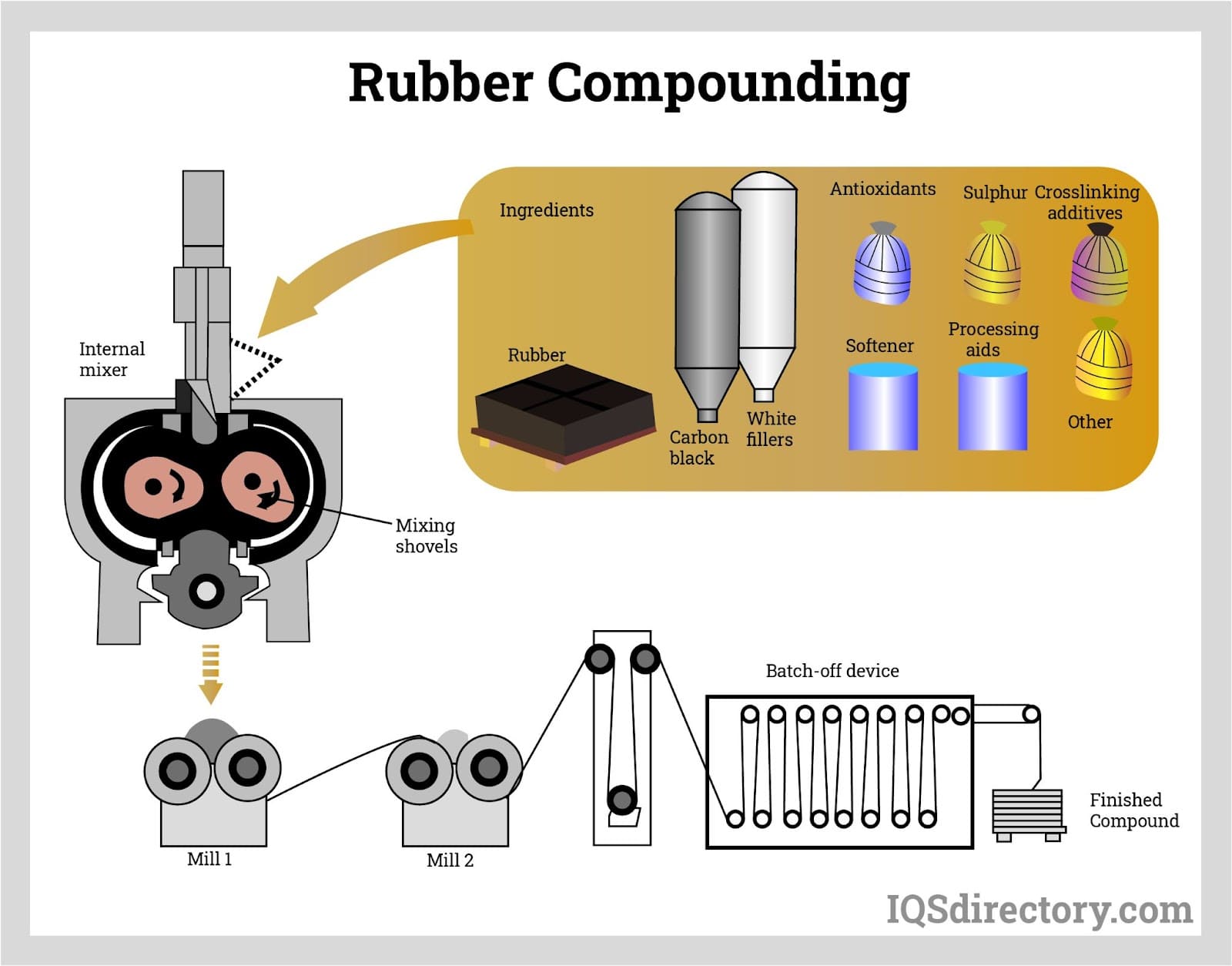
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Rubber Extrusions (Quality, IP)
Sourcing rubber extrusions presents several critical challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to production delays, product failures, and legal risks.
Inconsistent Material Quality and Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving rubber extrusions that do not meet specified material properties—such as durometer (hardness), tensile strength, elongation, or compression set. Variability can arise from inconsistent raw material batches, improper curing (under- or over-vulcanization), or inadequate process controls at the supplier’s facility. This inconsistency compromises product performance, especially in demanding applications like automotive or medical devices.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Rubber extrusions often require tight tolerances to ensure proper fit and sealing. Poor tooling, worn dies, or suboptimal extrusion processes can result in dimensional inaccuracies, warping, or surface defects. These flaws may lead to assembly issues, leaks, or premature failure in the end-use application.
Lack of Traceability and Material Certification
Without proper documentation—such as Certificates of Conformance (CoC), material test reports, or lot traceability—it becomes difficult to verify that the rubber compound meets required industry standards (e.g., FDA, NSF, UL, or automotive OEM specs). This lack of traceability increases risk, particularly in regulated industries, and can hinder root cause analysis during quality investigations.
Inadequate IP Protection and Design Theft
Sharing custom profiles or proprietary rubber formulations with suppliers without proper legal safeguards exposes companies to intellectual property risks. Unscrupulous suppliers may replicate designs for competing customers or sell them to third parties. Absence of robust Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses in contracts increases vulnerability to design theft and loss of competitive advantage.
Limited Process Control and Quality Assurance
Some suppliers lack comprehensive quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 or IATF 16949), resulting in inconsistent inspection protocols, insufficient in-process checks, or inadequate corrective action processes. This increases the likelihood of defective batches reaching the customer and undermines long-term reliability.
Supply Chain and Lead Time Instability
Dependence on suppliers with poor production planning or limited capacity can result in unpredictable lead times and supply disruptions. This is exacerbated if the rubber compound requires specialty materials or long cure cycles, making just-in-time inventory strategies difficult to maintain.
Failure to Validate Supplier Capabilities
Companies often overlook on-site audits or fail to request sample production runs before full-scale ordering. Without verifying a supplier’s technical expertise, equipment condition, and quality systems upfront, there’s a higher risk of encountering performance issues post-engagement.
Addressing these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, clear technical specifications, enforceable IP agreements, and ongoing quality monitoring to ensure reliable and secure sourcing of rubber extrusions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rubber Extrusions
Product Classification and HS Code
Rubber extrusions are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) for international trade. Common HS codes include:
– 4008: Vulcanized rubber tubing
– 4009: Conveyor or transmission belts of vulcanized rubber
– 4016: Other articles of vulcanized rubber (non-hardened), including extruded profiles and seals
Accurate classification is essential for proper customs declarations, duty assessment, and regulatory compliance. Always confirm the specific HS code based on material composition (e.g., EPDM, Nitrile, Silicone) and end use.
Material Compliance and Certifications
Rubber extrusions must comply with relevant international and regional regulations depending on application:
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Ensure no banned SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) are present.
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical/electronic equipment. Applies if rubber parts are used in such products.
– FDA 21 CFR 177.2600: Required for rubber components in food-contact applications (e.g., seals in food processing equipment).
– NSF/ANSI Standard 61: For rubber products used in drinking water systems.
– USP Class VI: For medical-grade rubber extrusions.
– UL Certification: If used in electrical applications requiring fire resistance or insulation properties.
Request material test reports (MTRs) and compliance documentation from suppliers to verify adherence.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transport and supports regulatory compliance:
– Protective Packaging: Use moisture-resistant wrapping, anti-corrosion paper, or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) materials when necessary.
– Labeling: Include:
– Part number and description
– Material type (e.g., EPDM 70 Shore A)
– Batch/lot number for traceability
– Manufacturer name and location
– Compliance markings (e.g., FDA, RoHS, REACH)
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Do Not Stack”)
Labels must be durable and legible throughout the supply chain.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Rubber extrusions are sensitive to environmental conditions:
– Temperature: Store and transport between 5°C and 35°C. Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme heat or cold.
– Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 70% to prevent mold or degradation.
– Light Exposure: Protect from direct sunlight and UV radiation, which can cause premature aging.
– Ozone: Keep away from electric motors, high-voltage equipment, and other ozone-generating sources.
– Deformation: Coiled or cut-length extrusions should be stored flat or on reels to prevent kinking or permanent set.
Use climate-controlled containers for long-distance or international shipments when necessary.
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation is critical for customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (preferential or non-preferential, depending on trade agreements)
– Material Compliance Certificates (e.g., RoHS, REACH, FDA)
– Test Reports (e.g., hardness, tensile strength)
Ensure all documents reflect consistent product descriptions and HS codes to avoid delays.
Special Handling for Hazardous Materials
Most rubber extrusions are non-hazardous. However, if compounded with certain additives (e.g., halogenated flame retardants), they may require:
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS) per GHS (Globally Harmonized System)
– Hazardous materials labeling and shipping procedures (e.g., IMDG for sea, IATA for air)
Verify SDS classification before shipping to determine if special handling applies.
Traceability and Recall Preparedness
Maintain a traceability system that links:
– Raw material batches
– Production dates and shifts
– Finished goods inventory
– Customer shipments
This enables rapid response in case of quality issues or regulatory recalls. Barcode or QR code systems are recommended for efficient tracking.
Sustainability and End-of-Life Compliance
Consider environmental obligations:
– WEEE (EU): If extrusions are part of electronic equipment, ensure recyclability.
– ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles): Automotive rubber parts may need to comply with material declaration requirements (e.g., IMDS submission).
– Recycling: Provide guidance on proper disposal or recycling options for end users.
Partner with suppliers committed to sustainable practices and recyclable or bio-based rubber materials where feasible.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for rubber extrusions require attention to material specifications, regulatory standards, proper handling, and accurate documentation. Proactive management ensures smooth global distribution, minimizes customs delays, and supports product safety and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion for Sourcing Rubber Extrusions:
Sourcing rubber extrusions requires a strategic approach that balances material specifications, manufacturing expertise, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability. It is essential to partner with suppliers who demonstrate technical proficiency in rubber compounding, extrusion processes, and quality control to ensure consistent performance and durability of the final product. Key considerations such as material compatibility (e.g., EPDM, silicone, neoprene), tolerances, environmental resistance, and regulatory compliance must be carefully evaluated. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with experienced and flexible manufacturers enables improved lead times, customization capabilities, and scalability. Ultimately, successful sourcing hinges on a thorough vetting process, clear communication of requirements, and ongoing quality assurance to meet application-specific demands across industries such as automotive, construction, HVAC, and manufacturing.