The global rotor stator homogenizer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for high-shear mixing solutions across the pharmaceutical, food & beverage, and chemical industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.28 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in processing technology, rising emphasis on product consistency, and the need for scalable, efficient mixing systems in R&D and production environments. As industries prioritize precision and throughput, rotor stator homogenizers have become essential tools for emulsification, dispersion, and particle size reduction. In this evolving landscape, identifying leading manufacturers is critical for organizations seeking reliable, innovative, and performance-verified equipment. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and customer reach, the following ten companies represent the forefront of rotor stator homogenizer manufacturing worldwide.
Top 10 Rotor Stator Homogenizer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 OMNI
Domain Est. 1996
Website: omni-inc.com
Key Highlights: Omni International, Inc is a leading global manufacturer and distributor of laboratory homogenizers … Rotor-Stator Homogenizers. Tubes. Consumables. Front ……
#2 PRO Scientific
Domain Est. 1997
Website: proscientific.com
Key Highlights: Discover precision homogenizers trusted worldwide. PRO Scientific manufactures rotor-stator and multi-sample systems for biotech, pharma, food & cosmetic ……
#3 Homogenizer Suppliers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: industrialmixers.com
Key Highlights: Our high performance rotor/stator mixers, also sometimes called homogenizers, are available in sizes from benchtop through full-scale production, in batch and ……
#4 Benchtop to Inline Homogenizer Mixers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: silverson.com
Key Highlights: Silverson Homogenizer Mixers deliver rapid, uniform homogenization with droplet and particle sizes typically in the 2–5 micron range….
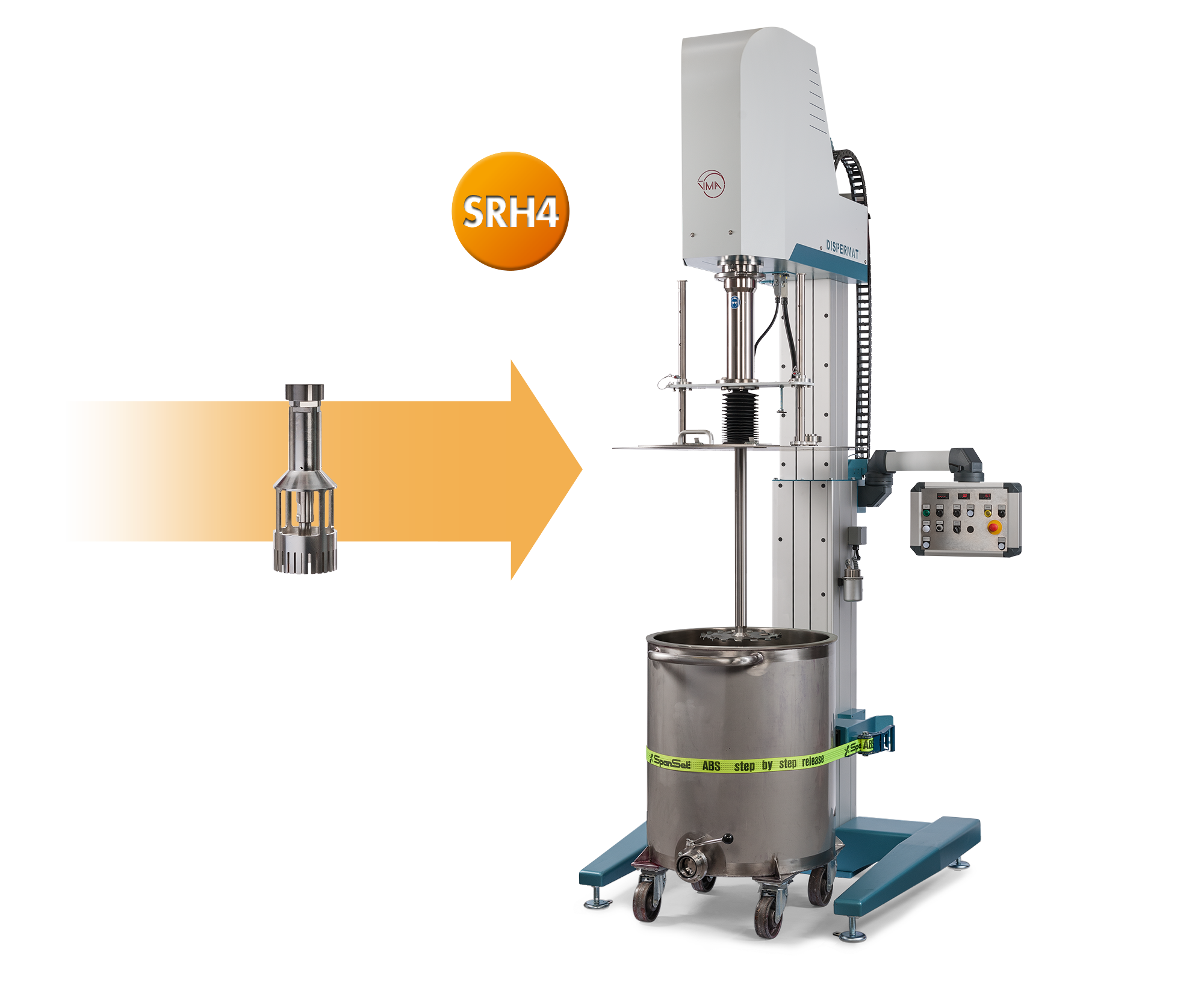
#5 SRH4 rotor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vma-getzmann.com
Key Highlights: The SRH4 rotor-stator accessory turns a DISPERMAT production dissolver into a high shear batch process homogenizer….
#6 Rotor Stator Homogenizers
Domain Est. 2013
Website: labsup.net
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $2,000Rotor-stator homogenizers consist of a fast-spinning inner rotor with a stationary outer sheath (stator) to homogenize samples through mechanical tearing, …
#7 Misceo homogenizer rotor stator tools for high shear
Domain Est. 2017
Website: misceo-cosmetics.com
Key Highlights: Misceo Rotor Stator homogeniser tools are the high shear accessory for emulsion formulation. Options for all motor blocks….
#8 Rotor
Domain Est. 2020
Website: revvity.com
Key Highlights: Upgrade lab homogenization with our high-shear rotor-stator homogenizers. Achieve precise results in high shear applications….
#9 In
Domain Est. 2023
Website: mgt-mixing.com
Key Highlights: Rotor-Stator Homogenizer PowerBlend® – a high shear mixer uses a high-speed rotor/stator generator to apply intense mechanical and hydraulic shear….
#10 Rotor Stator Homogenizer by MAXWELL
Domain Est. 2024
Website: maxwellmixing.com
Key Highlights: rotor stator homogenizer developed and produced by MAXWELL is widely applied to many industries and fields. It can fully meet the diversified needs of customers ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rotor Stator Homogenizer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Rotor Stator Homogenizers
The global rotor stator homogenizer market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising demand across key industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and cosmetics. These high-shear mixing devices are essential for achieving fine emulsions, dispersions, and particle size reduction, making them critical in modern processing environments.
One major trend shaping the 2026 market landscape is the increasing focus on process efficiency and scalability. Manufacturers are integrating smart technologies and automation into rotor stator systems, enabling real-time monitoring, data analytics, and remote operation. This Industry 4.0 integration improves consistency, reduces downtime, and supports compliance with regulatory standards—especially vital in cGMP environments.
Another key development is the expansion of applications in emerging sectors, particularly personalized medicine and plant-based food products. The demand for nanoemulsions and liposomal formulations in drug delivery systems is driving innovation in high-precision homogenizers capable of operating at lab, pilot, and industrial scales with minimal product loss.
Sustainability is also gaining prominence. Equipment manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient designs, reduced maintenance needs, and materials that support cleanability and longevity. This aligns with broader industry shifts toward green manufacturing and reduced environmental impact.
Regionally, North America and Europe remain dominant due to advanced R&D infrastructure and stringent quality requirements. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to register the highest growth rate by 2026, fueled by expanding pharmaceutical production, rising disposable incomes, and increased investment in food processing technologies in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
Additionally, market consolidation and strategic partnerships are on the rise, with key players expanding their product portfolios through acquisitions and collaborations. Companies are also focusing on modular and customizable rotor stator systems to meet diverse client needs across industries.
In summary, the 2026 rotor stator homogenizer market will be defined by technological innovation, sustainability, and regional diversification, positioning these systems as indispensable tools in advanced material processing and formulation development.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Rotor Stator Homogenizer (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a rotor stator homogenizer requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, legal risks, and increased long-term costs. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Choosing a homogenizer with substandard materials or imprecise manufacturing can severely impact performance and durability. Low-quality stainless steel or inadequate sealing may lead to contamination, corrosion, or mechanical failure—especially in demanding environments (e.g., pharmaceutical or food processing). Ensure suppliers use high-grade materials (e.g., 316L stainless steel) and provide documentation on tolerances and surface finishes.
Inadequate Validation and Documentation for Regulated Industries
In industries like biotech or pharmaceuticals, sourcing equipment without proper validation documentation (e.g., IQ/OQ/PQ protocols, material certifications, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance) can delay regulatory approvals. Verify that the supplier offers full documentation packages and adheres to relevant industry standards.
Lack of Scalability and Process Compatibility
A common mistake is selecting a homogenizer based solely on lab-scale needs without considering future scale-up. Units that perform poorly when scaled can disrupt process development. Ensure the rotor stator design is scalable and compatible with your specific viscosity, flow rate, and shear requirements.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Purchasing from manufacturers that infringe on patented designs or proprietary technology can expose your organization to legal liability. Always verify that the equipment does not violate third-party patents—especially in high-performance homogenizer designs where rotor geometry and stator configurations may be protected. Conduct due diligence or consult legal experts when sourcing from lesser-known suppliers or low-cost regions.
Insufficient Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality homogenizers require maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers with poor technical support or limited spare parts availability can lead to extended downtime. Confirm post-purchase service agreements, lead times for critical components (e.g., rotors, bearings), and availability of trained field engineers.
Hidden Costs from Poor Energy Efficiency or Maintenance Needs
Some low-cost units may have higher energy consumption or frequent maintenance demands, increasing total cost of ownership. Evaluate power efficiency, ease of cleaning (especially for CIP/SIP systems), and expected service intervals before finalizing procurement.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, technical evaluation, and attention to both engineering quality and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rotor Stator Homogenizer
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
The Rotor Stator Homogenizer is classified as a laboratory or industrial mixing and homogenizing device, primarily used for cell disruption, emulsification, and sample preparation. Depending on its application, it may fall under various regulatory frameworks including medical device, laboratory equipment, or industrial machinery standards. It is essential to determine the intended use (e.g., research-only, clinical, pharmaceutical, or food processing) to identify applicable regulations.
International Shipping and Import/Export Compliance
When shipping a Rotor Stator Homogenizer internationally, ensure compliance with export control regulations such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) in the U.S. or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Most homogenizers are classified under Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) 2B999 or similar, indicating they may be subject to licensing requirements depending on destination country. Verify sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, EU sanctions) and obtain necessary export licenses if shipping to restricted regions.
Electrical and Safety Standards
The homogenizer must comply with regional electrical safety standards prior to import or use:
– CE Marking (Europe): Comply with the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (2014/30/EU).
– UL/ETL Listing (North America): Meet UL 61010-1 (Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Use).
– Other Regions: Adhere to local standards such as CCC (China), KC (Korea), or RCM (Australia/New Zealand).
Ensure power supply specifications (voltage, frequency) match the destination country’s grid requirements. Include appropriate power cords or adapters when shipping.
Packaging and Transportation Requirements
Use robust, shock-resistant packaging to protect the homogenizer during transit. Include anti-static materials if sensitive electronic components are present. Clearly label packages with:
– Fragile and upright handling indicators
– Product name and model number
– Weight and dimensions
– Manufacturer and recipient contact information
For air freight, verify compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations—note that homogenizers generally do not contain hazardous materials unless accessories (e.g., chemical probes) are included.
Documentation for Customs Clearance
Prepare the following documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice (with item description, value, quantity, and harmonized system (HS) code)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Compliance Certificates (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS)
– Export License (if required)
The recommended HS code for rotor stator homogenizers is 8479.89 (Machines of a kind used in laboratories; other). Confirm with local customs authorities as classifications may vary.
Environmental and Chemical Compliance
Ensure compliance with environmental directives such as:
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical equipment.
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals—particularly relevant if the device includes replaceable parts with chemical components.
– WEEE (EU): Proper labeling and end-of-life take-back obligations for electrical equipment.
If the homogenizer is used with biological or hazardous materials, additional biosafety or chemical handling regulations may apply at the user’s facility.
Installation, Training, and User Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure end-users receive:
– Installation instructions
– Operator training (if required by safety regulations)
– Safety data sheets (SDS) for any consumables or accessories
– Maintenance and calibration guidelines
Maintain records of user compliance, especially in regulated industries (e.g., GLP, GMP, or ISO 17025 environments).
Warranty, Service, and Post-Market Compliance
Adhere to regional warranty and consumer protection laws. For devices used in regulated applications, maintain post-market surveillance records and report malfunctions or adverse events as required (e.g., under EU MDR if classified as a medical device). Provide accessible technical support and service networks in the target market.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management ensures safe, legal, and efficient distribution of Rotor Stator Homogenizers across global markets. Always verify local regulations and consult with regulatory experts when entering new jurisdictions.
Conclusion for Sourcing Rotor-Stator Homogenizer:
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, performance requirements, supplier credibility, cost-effectiveness, and after-sales support, sourcing a rotor-stator homogenizer should prioritize a balance between quality, reliability, and long-term operational efficiency. The selected equipment must align with the application-specific demands, such as viscosity range, throughput, particle size reduction goals, and material compatibility, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, cosmetics, or biotechnology.
Key considerations in the final decision include the robustness of the rotor-stator design, ease of maintenance and cleaning (especially for hygienic applications), scalability for future production needs, and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., CE, FDA, or GMP). Additionally, partnering with a supplier that offers technical support, spare parts availability, and training enhances operational continuity and reduces downtime.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy involves selecting a high-performance rotor-stator homogenizer from a reputable manufacturer, ensuring consistent processing results, durability, and integration capability within the existing workflow—ultimately contributing to improved product quality and operational efficiency.