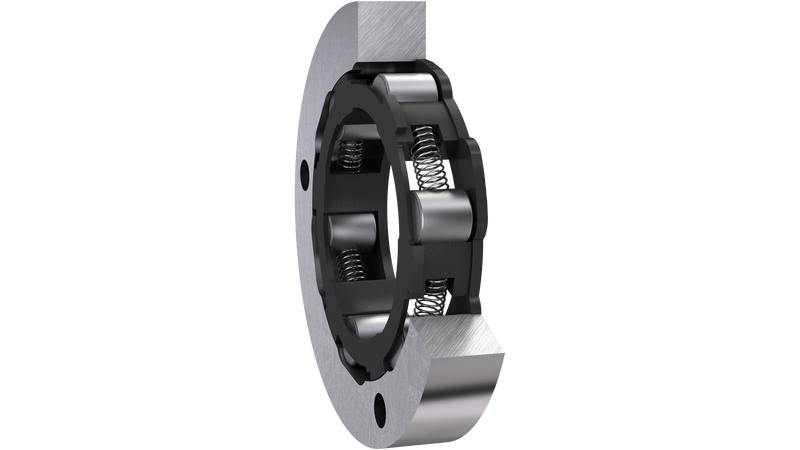
The global roller clutch market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace applications. According to Grand View Research, the global clutch market size was valued at USD 23.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. Roller clutches, known for their high torque transmission, compact design, and reliability in overrunning applications, are a critical subset of this market. Their adoption is rising particularly in electric vehicles and advanced transmission systems, where precision and efficiency are paramount. With such momentum, identifying the leading manufacturers becomes essential for OEMs and suppliers aiming to source high-performance components. Based on market presence, innovation, production capabilities, and global reach, the following seven companies stand out as the top roller clutch manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 7 Roller Clutch Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Buy KHK One-Way Clutch Bearings
Domain Est. 2020
Website: khkbearings.com
Key Highlights: Order one-way clutch bearings from KHK’s official manufacturer. High performance, reliable engagement, and long service life….
#2 Marland Clutch
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1931
Website: marland.com
Key Highlights: Marland Clutch provides world-class backstopping and overrunning clutch solutions for demanding heavy duty applications. Founded in 1931, Marland Clutch has ……
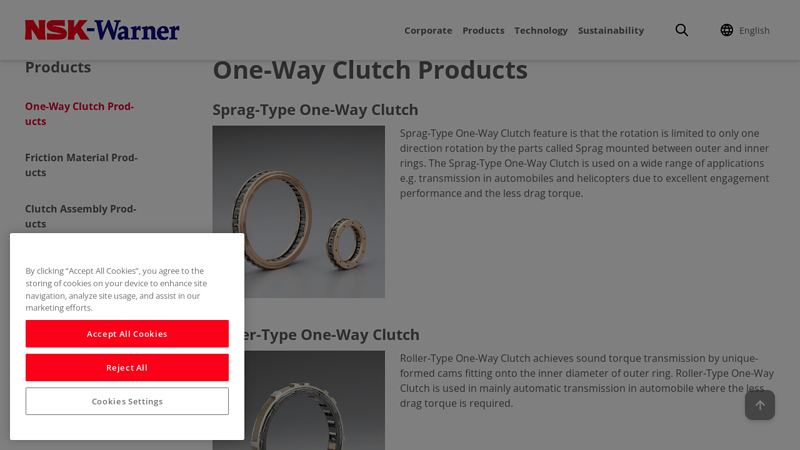
#3 One-Way Clutch Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: The Sprag-Type One-Way Clutch is used on a wide range of applications eg transmission in automobiles and helicopters due to excellent engagement performance….
#4 SKF One Way Clutch
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: SKF’s One Way Clutch is customisable as per customer need using integrated ring gear-barrel system, sheetmetal barrel and multi roller designs. Other benefits ……
#5 Roller Ramp Clutches
Domain Est. 2000
Website: gmnbt.com
Key Highlights: Our VEK series roller ramp clutch fits shafts 10-50 mm and is rust protected. This series provides perfect performance with 100% repeatability….
#6 Freewheel Clutches
Domain Est. 2002
Website: crossmorse.com
Key Highlights: Cross+Morse offer an extensive range of Freewheel Clutches: Sprag, roller ramp, contact free element clutches, to provide the designer with a wide selection of ……
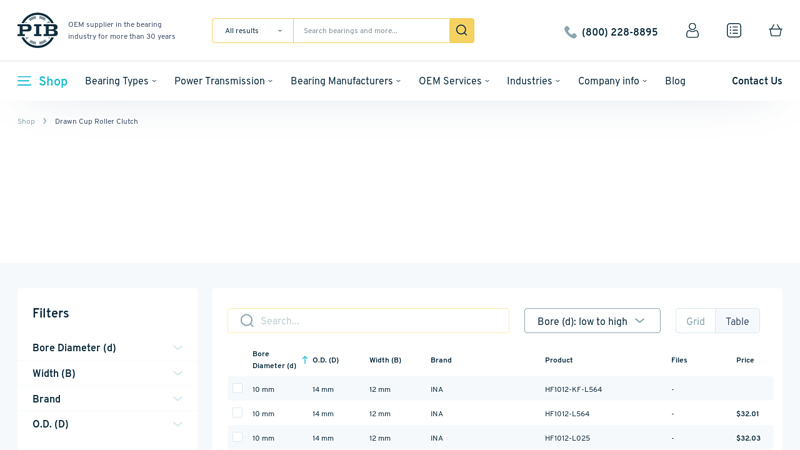
#7 Drawn Cup Roller Clutches
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pibsales.com
Key Highlights: $10 deliveryThese drawn cup roller clutches comprise thin-walled, drawn outer rings with a series of ramps on the inside diameter, plastic cages and needle rollers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Roller Clutch
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Roller Clutches
The roller clutch market in 2026 is poised for moderate but strategic growth, driven by technological advancements, evolving industrial demands, and increasing focus on efficiency and reliability. While not experiencing explosive expansion, the market is undergoing significant transformation influenced by several key trends:
1. Rising Demand in Electrified and Hybrid Powertrains (Automotive & Industrial):
A major growth catalyst for roller clutches in 2026 is their integration into electric and hybrid vehicle (EV/HEV) transmissions and auxiliary systems. Roller clutches are essential in:
* e-Axles & Transmission Disconnects: Enabling efficient decoupling of electric motors to reduce drag losses and improve EV range.
* Regenerative Braking Systems: Facilitating smooth engagement/disengagement during energy recovery.
* Hybrid Power Split Devices: Managing torque transfer between internal combustion engines and electric motors.
The global push towards electrification is directly translating into increased demand for high-precision, compact, and reliable roller clutches in automotive applications.
2. Emphasis on Miniaturization and Lightweighting:
Across industries (automotive, aerospace, robotics, medical devices), there is a strong trend towards smaller, lighter components. Roller clutches benefit from this as they are inherently more compact than some alternatives (like sprag clutches) for equivalent torque capacity. Manufacturers are focusing on:
* Advanced materials (high-strength steels, composites) to reduce weight.
* Optimized cage and roller designs to minimize size while maintaining performance.
* Integration into modular drive units.
3. Advancements in Materials and Surface Engineering:
To meet the demands of higher speeds, loads, and harsher environments (especially in EVs and industrial automation), 2026 sees significant R&D in:
* Superior Bearing Steels: Improved fatigue life and load capacity.
* Advanced Coatings: Diamond-like carbon (DLC), nitriding, and specialized lubricious coatings to enhance wear resistance, reduce friction, and extend service life.
* Lubrication Solutions: Development of specialized greases compatible with electric motor environments (resistant to electrical arcing) and for maintenance-free operation.
4. Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics:
The continued expansion of robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and precision manufacturing equipment drives demand for reliable overrunning/clutching functions. Roller clutches are favored for:
* Backstop and Indexing Applications: Preventing reverse rotation in conveyors and rotary tables.
* Torque Limiting and Load Isolation: Protecting motors and gearboxes.
* Smooth Engagement in Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Ensuring safety and precise control.
The need for precision, low noise, and long service life in these applications aligns well with roller clutch capabilities.
5. Focus on Efficiency and Sustainability:
Energy efficiency regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing industries to minimize mechanical losses. Roller clutches contribute by:
* Reducing Drag Torque: Especially critical in EVs for maximizing range.
* Enabling Predictive Maintenance: Integration of sensors (though less common than in larger components) for condition monitoring, reducing downtime and waste.
* Extending Component Life: Leading to less frequent replacements and lower resource consumption.
6. Competitive Landscape and Regional Dynamics:
Asia-Pacific Dominance: China, Japan, and South Korea remain key manufacturing hubs and major consumers, driven by massive automotive (especially EV) and electronics production.
* Consolidation and Specialization: Larger players (like NTN, NACHI, SKF, Schaeffler) leverage scale and R&D, while niche players focus on specific high-performance or custom applications.
* Supply Chain Resilience:* Ongoing focus on securing supply chains for critical materials and components, potentially reshoring or near-shoring some production.
Conclusion:
The 2026 roller clutch market is characterized by steady growth fueled primarily by the electrification of transportation and the relentless march of industrial automation. Success hinges on innovation in materials, design for compactness and efficiency, and the ability to meet the stringent reliability requirements of next-generation applications, particularly in electric vehicles. While competition is intense, manufacturers focusing on high-performance, specialized solutions for these growing sectors are best positioned for success.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Roller Clutch: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing roller clutches, especially from international or non-traditional suppliers, involves several critical pitfalls related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these can lead to product failures, legal challenges, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
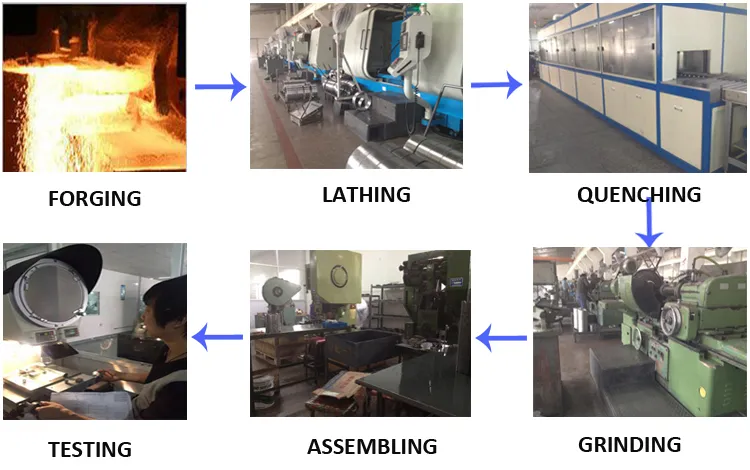
Inadequate Material Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is the use of substandard materials. Roller clutches require precise metallurgy for components like the outer race, inner race, and rollers to ensure durability and performance under load. Suppliers may use inferior steel grades or skip essential heat treatment processes to cut costs, leading to premature wear, fatigue, or sudden failure in operation.
Poor Manufacturing Tolerances
Roller clutches depend on tight dimensional tolerances and surface finishes to function correctly. Inconsistent machining or lack of precision control can result in improper engagement, increased slippage, or excessive noise. Without access to detailed inspection reports or process validation, buyers risk receiving units that fail under real-world conditions.
Lack of Testing and Certification
Reputable roller clutch manufacturers typically conduct load testing, endurance cycling, and dimensional inspection. Sourcing from suppliers who do not provide verifiable test data or certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of undetected defects. Absence of performance validation may only become evident after field failures.
Inconsistent Quality Control Processes
Suppliers with weak quality management systems often exhibit batch-to-batch variability. Without robust incoming inspection or in-process controls, even a single shipment may contain non-conforming parts, disrupting production lines or end-product reliability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication of Patented Designs
Many high-performance roller clutches are protected by patents covering unique geometries, spring mechanisms, or assembly methods. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate these designs without licensing exposes the buyer to infringement claims, even if unintentional. This is particularly common with OEM-equivalent or “compatible” parts.
Reverse-Engineered Components
Some suppliers reverse-engineer branded roller clutches and sell them as generic alternatives. While this may reduce costs, it often violates design patents or utility models. Buyers may face legal action from IP holders, especially when used in commercial products or exported to IP-enforcing jurisdictions.
Lack of IP Warranty or Indemnification
Many suppliers, especially in low-cost regions, do not provide contractual assurances that their products do not infringe third-party IP. Without a clear indemnity clause in procurement agreements, buyers assume full liability for any IP disputes, including litigation costs and product recalls.
Misrepresentation of Branding and Origin
Counterfeit or grey-market roller clutches may be falsely labeled as genuine OEM parts. This not only violates trademarks but also undermines traceability and accountability. Buyers may unknowingly integrate fake components into their systems, risking warranty voids and safety issues.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Require material certifications and third-party test reports.
– Conduct on-site audits or use independent inspection services.
– Perform due diligence on supplier IP compliance and request indemnity clauses.
– Work with legally vetted suppliers who respect IP rights and offer traceable sourcing.
Proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns ensures reliable performance and legal safety in roller clutch procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Roller Clutch
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance of roller clutches—mechanical components commonly used in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications.
Product Classification and Identification
Ensure accurate product classification using standardized systems such as:
– HS Code (Harmonized System Code): Typically classified under 8483.60 (clutches and shaft couplings) depending on design and application. Confirm with local customs authorities.
– UN Number (if applicable): Roller clutches are generally not hazardous, but verify if packaging materials or associated lubricants require special handling.
– Part Numbers and SKUs: Maintain consistent internal identification to prevent misshipment and support traceability.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during shipping:
– Use moisture-resistant, corrugated cardboard or reusable crates with internal foam or plastic inserts to prevent movement.
– Apply protective coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to prevent rust, especially for ferrous metal components.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Part number and description
– Quantity
– “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators if applicable
– Barcodes for inventory tracking
Storage Conditions
Store roller clutches in a controlled environment to maintain performance:
– Temperature: 10°C to 30°C (50°F to 86°F)
– Humidity: Below 60% RH to prevent corrosion
– Location: Dry, clean, and well-ventilated warehouse area, off the floor on pallets or shelves
– Shelf Life: Monitor for long-term storage; inspect for corrosion or lubricant degradation after 12+ months
Transportation Logistics
Choose appropriate transportation modes based on volume, urgency, and destination:
– Domestic Shipments: Standard freight via LTL (Less Than Truckload) or FTL (Full Truckload) with secure strapping.
– International Shipments: Ocean freight (FCL/LCL) or air freight for urgent deliveries. Ensure compliance with IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) or IATA regulations if shipped with lubricants or batteries.
– Incoterms: Use clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP) to define responsibility for shipping, insurance, and customs.
Import/Export Compliance
Meet international trade requirements:
– Export Controls: Verify if roller clutches fall under dual-use or strategic goods regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S. or EU Dual-Use Regulation). Most standard roller clutches are not controlled, but verify based on technical specs.
– Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin.
– Duties and Tariffs: Calculate applicable import duties based on destination country’s tariff schedule and preferential trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN).
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Ensure product conformity with relevant standards:
– ISO Standards: ISO 14123 (safety of machinery – shaft couplings), ISO 9001 (quality management)
– SAE/ANSI: For automotive and industrial applications (e.g., SAE J626 for clutch performance)
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm that materials used (e.g., metals, lubricants) comply with chemical restrictions.
– Proposition 65 (California): Disclose if product contains chemicals listed by the state of California.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records:
– Batch/lot tracking for quality control and recalls
– Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and Material Test Reports (MTR) upon request
– Retain logistics documentation for a minimum of 5 years for audit purposes
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Follow eco-friendly logistics practices:
– Use recyclable or reusable packaging materials
– Optimize load efficiency to reduce carbon footprint
– Partner with carriers offering carbon-neutral shipping options
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Establish a clear returns process:
– Define conditions for acceptable returns (e.g., damaged in transit, wrong item shipped)
– Provide RMA (Return Merchandise Authorization) numbers
– Inspect returned units for reuse, refurbishment, or proper disposal
By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure efficient, compliant, and safe handling of roller clutches throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Roller Clutch
After a thorough evaluation of available suppliers, product specifications, cost structures, quality standards, and lead times, it is concluded that sourcing roller clutches from a combination of established manufacturers and qualified alternative suppliers offers the optimal balance between reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency. Prioritizing suppliers with proven experience in precision engineering, ISO certifications, and consistent quality control ensures product durability and compatibility with application requirements.
Engaging in long-term agreements with top-tier suppliers can provide volume-based cost savings and supply chain stability, while maintaining a secondary source mitigates risks associated with disruptions. Additionally, local or regional sourcing should be considered to reduce logistics lead times and import dependencies.
In summary, a strategic sourcing approach—rooted in technical validation, total cost analysis, and supplier reliability—will ensure the successful integration of high-performance roller clutches into our systems, supporting operational efficiency and long-term maintenance goals.