The manufacturing industry is undergoing a transformative shift driven by automation, with robotics at the forefront of this evolution. According to Mordor Intelligence, the robotics market in manufacturing is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by increasing demand for precision, efficiency, and cost reduction in production processes. Industrial robots are no longer limited to large-scale operations—SMEs are rapidly adopting robotic solutions to remain competitive. Advances in AI, machine vision, and collaborative robotics have expanded the capabilities of automated systems, enabling faster throughput, improved quality control, and safer working environments. As global labor costs rise and supply chains demand greater resilience, manufacturers are turning to robotics to future-proof their operations. This list highlights the top 10 robots transforming the manufacturing landscape, selected based on performance metrics, integration ease, scalability, and real-world impact across industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
Top 10 Robots For Manufacturing Industry Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
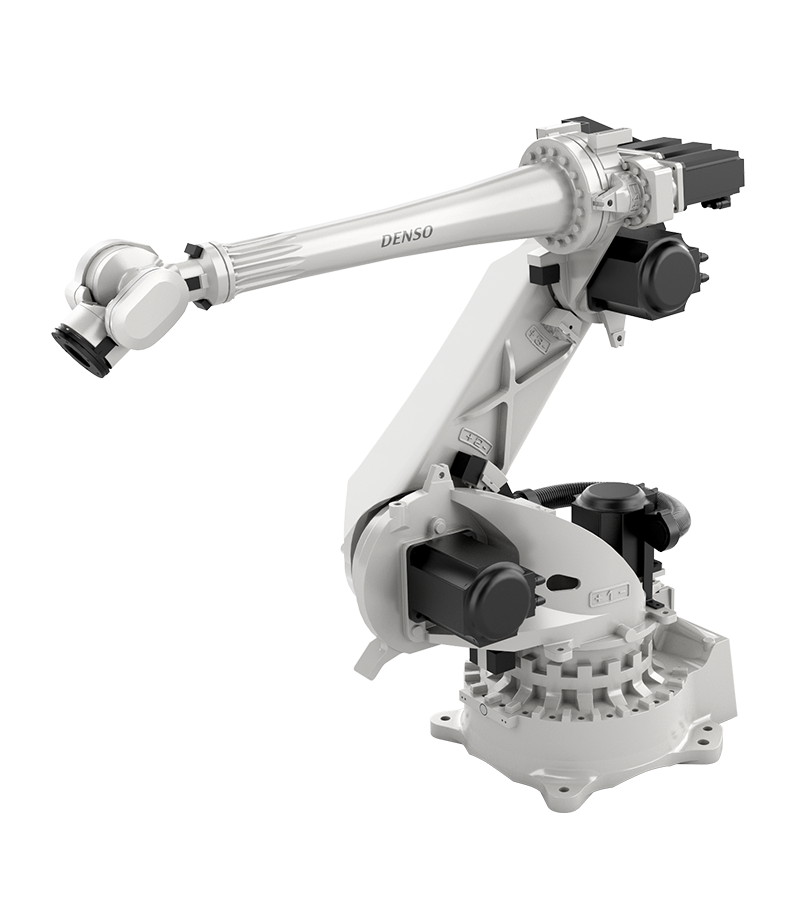
#1 DENSO Robotics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: densorobotics.com
Key Highlights: DENSO Robotics is the leading industrial robotics manufacturer. We build custom robotic automation solutions for our customers around the world….
#2 Yaskawa Motoman
Domain Est. 1995
Website: motoman.com
Key Highlights: Explore industrial robots, cobots, and turnkey automation for welding, handling, palletizing & more. Specs, integrations & lifetime support….
#3 Industrial Robots for Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fanucamerica.com
Key Highlights: FANUC has the expertise to help you succeed. With over 100 robot models and over 40 years of manufacturing experience, we’re ready for any challenge….
#4 Kawasaki Robotics – Industrial Robotics
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kawasakirobotics.com
Key Highlights: At Kawasaki Robotics, we create innovative, reliable, and downright awesome industrial robots and automation solutions that keep industries moving. From ……
#5 Collaborative robotic automation
Domain Est. 2005
Website: universal-robots.com
Key Highlights: Universal Robots combines innovative cobot engineering with industrial-grade performance: payloads up to 35 kg, reach up to 1750 mm, and deployment in minutes….
#6 Mecademic Industrial Robotics
Domain Est. 2012
Website: mecademic.com
Key Highlights: We develop and build the world’s smallest, most compact industrial robots. Our solutions are designed for maximum efficiency, even in extreme space limitations….
#7 USABotics
Domain Est. 2016
Website: usabotics.com
Key Highlights: Our robots can handle machine loading, parts transfer, sanding, polishing, finishing and multi-axis machining to help you create high-quality and low-cost wood ……
#8 The nation’s leading collaborative in robotics and workforce …
Domain Est. 2016
Website: arminstitute.org
Key Highlights: Our Robotics Manufacturing Hub program helps manufacturers of all sizes understand how robotics can enhance their competitiveness. Get started with an ……
#9 ABB Robotics
Domain Est. 1990
Website: abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB Robotics leads in robotics and automation with integrated robots, AMRs, and software, helping industries boost resilience and efficiency….
#10 OMRON Robotics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: robotics.omron.com
Key Highlights: Solve manufacturing inefficiencies with OMRON Robotics’ cutting-edge robots — engineered to maximize productivity, quality, and safety….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Robots For Manufacturing Industry

2026 Market Trends for Robots in the Manufacturing Industry
As we approach 2026, the integration of robotics in the manufacturing industry continues to accelerate, driven by technological advancements, labor market dynamics, and the increasing demand for efficiency, precision, and scalability. Several key trends are shaping the landscape of industrial robotics, transforming traditional production lines into intelligent, adaptive, and highly automated ecosystems.
Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
One of the most significant trends in 2026 is the widespread adoption of collaborative robots, or cobots. Designed to work safely alongside human operators, cobots are becoming essential in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require flexible automation solutions. Enhanced safety features, intuitive programming interfaces, and reduced deployment costs are fueling their popularity. By 2026, cobots are expected to account for over 35% of new robot installations in manufacturing, particularly in assembly, packaging, and quality inspection tasks.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing robotic capabilities in manufacturing. In 2026, AI-powered robots can perform predictive maintenance, optimize production schedules, and adapt to variations in real time. Vision systems with deep learning algorithms enable robots to handle complex part recognition and defect detection with higher accuracy than traditional systems. This shift towards cognitive automation enhances decision-making and reduces downtime, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Growth of Mobile and Autonomous Robots
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are gaining momentum in factory logistics and material handling. Unlike fixed automation systems, AMRs navigate dynamic environments using advanced sensors and mapping technologies. In 2026, AMRs are increasingly used for just-in-time delivery of parts, inventory management, and inter-process transportation. Their ability to integrate seamlessly with existing workflows makes them ideal for smart factories pursuing Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability is a growing priority for manufacturers, and robotics is playing a key role in reducing environmental impact. By 2026, robot manufacturers are focusing on energy-efficient designs, recyclable components, and longer operational lifecycles. Additionally, precise robotic systems minimize material waste and optimize energy consumption during production, supporting corporate sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
Expansion of Robotics in Emerging Markets
While North America, Europe, and East Asia continue to lead in robotic adoption, emerging markets in Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America are rapidly investing in automation. Rising labor costs, government incentives, and the need to boost manufacturing competitiveness are driving this expansion. By 2026, these regions are expected to witness double-digit growth in industrial robot installations, particularly in electronics, automotive, and consumer goods sectors.
Workforce Reskilling and Human-Robot Collaboration
As robots take over repetitive and hazardous tasks, the manufacturing workforce is shifting toward roles that require technical oversight, programming, and maintenance. In 2026, companies are increasingly investing in reskilling programs to prepare workers for human-robot collaboration environments. This trend not only improves job satisfaction but also ensures a sustainable talent pipeline for advanced manufacturing operations.
Supply Chain Resilience Through Automation
Recent global disruptions have underscored the need for resilient supply chains. Robotics enables manufacturers to localize production and reduce dependency on offshore labor. In 2026, more companies are adopting robotic systems to support “nearshoring” and “reshoring” strategies, enhancing agility and responsiveness to market demands.
Conclusion
The 2026 manufacturing robotics market is defined by intelligent automation, human-robot collaboration, and a strong focus on flexibility and sustainability. As technology matures and adoption barriers decline, robots are no longer a luxury for large corporations but a strategic necessity across the manufacturing spectrum. Companies that embrace these trends will gain a competitive edge through increased productivity, improved quality, and greater operational resilience.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Robots for the Manufacturing Industry (Quality, IP)
Sourcing robots for manufacturing offers significant efficiency and productivity gains, but it also presents critical challenges—particularly in ensuring quality and protecting intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these areas can lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, and long-term competitive disadvantages. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Testing
Many manufacturers rush the procurement process without rigorously evaluating a robot’s build quality, reliability, or performance under real-world conditions. This can lead to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent output, and high maintenance costs. Always verify that the supplier adheres to recognized quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001), offers comprehensive testing protocols, and provides documented performance data from similar industrial environments.
Lack of Transparency in Component Sourcing
Robots often include critical components (e.g., motors, sensors, controllers) sourced from third-party suppliers. If the integrator or robot manufacturer is not transparent about these components, it can create hidden vulnerabilities in quality, support, and longevity. Ensure full visibility into the supply chain and confirm that all parts meet industrial-grade specifications.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Service Coverage
Even high-quality robots require maintenance, repairs, and software updates. A common pitfall is selecting a vendor based solely on upfront cost while neglecting their service infrastructure. Limited regional support or slow response times can result in extended downtime. Evaluate the vendor’s service network, spare parts availability, and technical expertise before committing.
Inadequate Protection of Intellectual Property
When customizing robotic systems or integrating them into proprietary processes, manufacturers risk exposing sensitive production data, control logic, or unique workflows. Some vendors may claim ownership of software modifications or collect operational data without clear agreements. Always establish robust contractual terms that define IP ownership, data usage rights, and confidentiality.
Dependency on Vendor-Specific Software and Ecosystems
Many robot manufacturers lock customers into proprietary programming environments, limiting flexibility and creating long-term dependency. This can hinder future upgrades, integration with other systems, and in-house innovation. Prioritize open-architecture platforms that support standard programming languages and interfaces to maintain control over your automation ecosystem.
Underestimating Cybersecurity Risks
Connected robots are vulnerable to cyber threats, especially if they transmit operational data or integrate with enterprise networks. A major pitfall is assuming the vendor handles all security by default. Demand clear information on encryption, access controls, firmware update policies, and compliance with industrial cybersecurity standards (e.g., IEC 62443).
Failure to Verify Compliance and Certification
Robots used in manufacturing must meet safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and industry-specific regulations (e.g., FDA for food production, ATEX for explosive environments). Overlooking compliance can lead to legal issues, insurance complications, or workplace hazards. Confirm that the robot carries all necessary certifications for your region and application.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—particularly around quality assurance and IP protection—manufacturers can make smarter sourcing decisions, reduce risks, and fully realize the benefits of robotic automation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Robots in the Manufacturing Industry
Introduction to Industrial Robotics Logistics
Understanding the logistics of deploying robots in manufacturing is crucial for ensuring seamless integration, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines best practices and compliance considerations for the transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance of industrial robots.
Regulatory Compliance Standards
Industrial robots must comply with local and international safety and operational standards. Key regulations include:
– ISO 10218: Safety requirements for industrial robots (Parts 1 and 2).
– ANSI/RIA R15.06: U.S. standard for industrial robot safety.
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and related harmonized standards.
– OSHA Regulations (USA): Workplace safety standards applicable to robotic systems.
Ensure all robotic systems meet region-specific requirements before deployment.
Transportation and Handling
Proper logistics during robot shipment and receiving prevent damage and ensure safety:
– Use manufacturer-recommended packaging and handling procedures.
– Secure robots on pallets with adequate bracing during transit.
– Verify environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) during transport to protect sensitive electronics.
– Train logistics personnel on safe handling of robotic components, especially robotic arms and controllers.
Site Preparation and Installation
Successful installation begins with thorough site planning:
– Confirm floor load capacity supports robot base and auxiliary equipment.
– Ensure adequate power supply (voltage, phase, grounding) per manufacturer specifications.
– Maintain clear workspace zones to comply with safety fencing and emergency stop access.
– Plan cable routing and integration with existing production lines to avoid interference.
Risk Assessment and Safety Integration
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment prior to commissioning:
– Identify potential hazards (crushing, shearing, unexpected movements).
– Install safeguarding measures such as light curtains, safety gates, and emergency stop systems.
– Implement safe robot programming zones and lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures.
– Document safety measures and train all personnel on emergency protocols.
Operational Compliance and Maintenance
Maintain compliance throughout the robot’s lifecycle:
– Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
– Keep logs of inspections, repairs, and software updates.
– Regularly review and update risk assessments, especially after process changes.
– Ensure software complies with cybersecurity standards if connected to networked systems (e.g., Industry 4.0 environments).
Training and Personnel Certification
Personnel involved with robots must be properly trained:
– Operators and technicians should complete safety and operational training per ISO 13849 and relevant standards.
– Maintain training records and recertify staff periodically.
– Restrict programming and maintenance access to authorized personnel only.
Documentation and Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive documentation for compliance audits:
– Robot manuals, risk assessments, and conformity declarations.
– Installation records, maintenance logs, and incident reports.
– Certificates of compliance for electrical, mechanical, and safety systems.
Ensure documents are up-to-date and readily accessible.
End-of-Life and Decommissioning
Plan for responsible retirement of robotic systems:
– Follow environmental regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU) for disposal or recycling.
– Safely disconnect and de-energize all components.
– Remove sensitive data from controllers and backup systems.
– Document decommissioning procedures for audit purposes.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict adherence to compliance standards are essential for maximizing the benefits of industrial robots while ensuring workplace safety and regulatory conformity. By following this guide, manufacturing facilities can deploy robotic systems efficiently, sustainably, and in full compliance with global standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing Robots for the Manufacturing Industry
Sourcing robots for the manufacturing industry is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance productivity, precision, and operational efficiency. As automation continues to reshape modern manufacturing, selecting the right robotic solutions tailored to specific production needs—such as welding, assembly, material handling, or quality inspection—has become crucial for maintaining competitiveness. A successful sourcing strategy involves evaluating factors such as scalability, integration capabilities with existing systems, total cost of ownership, and vendor reliability.
Additionally, advancements in collaborative robots (cobots), artificial intelligence, and Industry 4.0 connectivity are expanding the possibilities for flexible and adaptive automation. Manufacturers must also consider workforce training, safety standards, and long-term maintenance support when implementing robotic systems.
Ultimately, thoughtful sourcing of robotics not only optimizes manufacturing processes but also positions companies for sustainable growth, improved product quality, and resilience in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape. By aligning robotic investments with business objectives, manufacturers can achieve a strong return on investment and secure a strategic advantage in the global market.