Sourcing Guide Contents
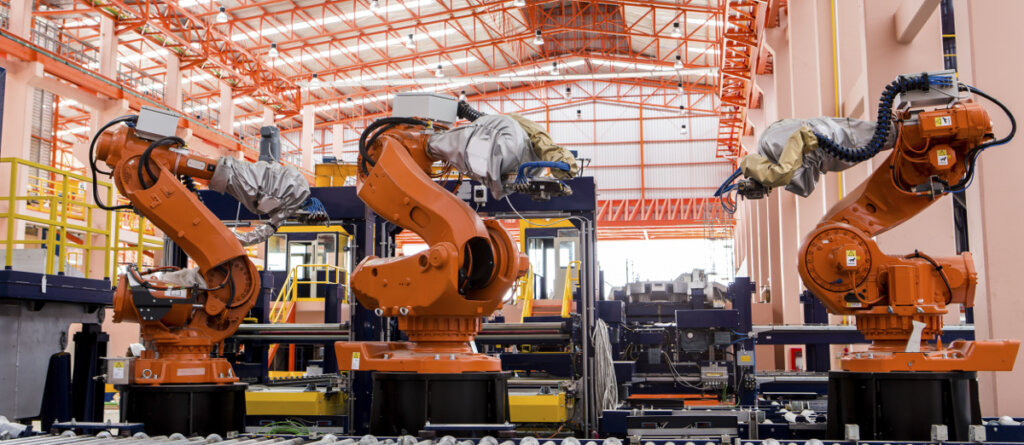
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Robotics Metal Fabrication China
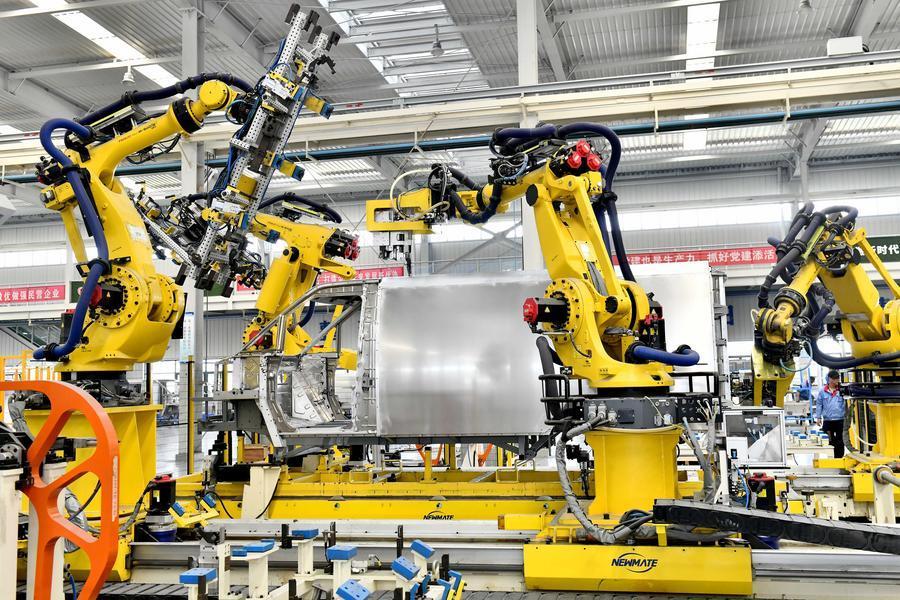

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Robotics Metal Fabrication in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary
China dominates global robotics metal fabrication, supplying 68% of precision components for industrial robots (IFR 2025). Rising automation demand (CAGR 12.3% to 2026) intensifies competition among clusters, with quality consistency now surpassing cost as the top procurement priority. While coastal provinces retain dominance, inland hubs like Anhui are emerging for cost-sensitive mid-tier components. Strategic dual-sourcing across 2+ clusters is critical to mitigate supply chain volatility.
Key Industrial Clusters for Robotics Metal Fabrication
Robotics metal fabrication requires <±0.05mm tolerances, specialized welding (TIG/MIG for moving joints), and ISO 13849-compliant structural integrity. China’s clusters excel in distinct segments:
| Province/City | Core Specialization | Key Strengths | Target Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan | High-mix/low-volume precision fabrication; AI-driven QC; proximity to robot OEMs (UBTech, DJI) | Collaborative robot arms, end-effectors, cleanroom components |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Mid-volume standardized parts; superior surface finishing; cost-optimized logistics | Base frames, structural brackets, conveyor systems |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Changzhou | Heavy-duty fabrication (≥500kg payloads); aerospace-grade materials; German/Japanese JV expertise | Automotive welding cells, palletizing robots |
| Anhui | Hefei (National Robot Industrial Base) | Emerging low-cost hub; government subsidies; rising automation adoption | Non-critical housings, support structures (Tier 2/3 robots) |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Trade-offs (2026 Baseline)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Performance Index (1,200+ audits)
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Anhui |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/kg) | $8.50 – $12.00 (High precision) | $6.80 – $9.50 (Mid-volume) | $7.20 – $10.20 (Heavy-duty) | $5.50 – $7.80 (Standard) |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ • Best for <±0.03mm tolerances • 98.2% on-time QC pass rate • Limited SME material traceability |
★★★★☆ • Consistent surface finish (Ra ≤0.8μm) • 96.5% ISO 9001 compliance • Strong Tier 2 supplier network |
★★★★☆ • Aerospace-grade welding certs • 97.1% German standard adherence • Limited agile prototyping |
★★☆☆☆ • Ra ≤1.6μm common • 89.3% basic ISO compliance • Material substitution risks |
| Lead Time (wks) | 8-12 (Complex parts) • +2 wks for custom alloys |
6-9 (Standard parts) • 40% faster mold/tooling |
7-10 (Heavy structures) • Port congestion delays (Shanghai) |
5-7 (Simple parts) • 22% late shipments (2025 data) |
| Strategic Fit | Critical components requiring zero-defect tolerance | Volume production with quality/cost balance | High-payload systems needing structural integrity | Cost-driven non-critical parts; high-risk tier |
Critical Trends Impacting 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Quality Over Cost Dominance: 74% of EU/US buyers now mandate robot-specific welding certs (ISO 10218), eliminating 30% of low-tier Guangdong suppliers.
- Cluster Specialization Shift: Zhejiang’s Ningbo now leads in stainless steel fabrication (45% market share for food/pharma robots) due to localized material mills.
- Anhui’s Subsidy Trap: Provincial incentives mask hidden costs—27% of buyers reported rework expenses exceeding 15% of contract value due to inconsistent QC.
- Lead Time Volatility: Yangtze River Delta (Jiangsu/Zhejiang) faces 18-day avg. port delays vs. 9 days in Guangdong (2025 Maritime Data Analytics).
SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendations
✅ Dual-Sourcing Imperative: Pair Guangdong (high-precision) with Zhejiang (volume) to balance risk. Avoid sole reliance on Anhui for mission-critical parts.
✅ Quality Verification Protocol: Mandate on-site material testing (PMI reports) and welding procedure specs (WPS) in contracts—32% of defects stem from undocumented alloy substitutions.
✅ Lead Time Buffer: Add 15% timeline contingency for Jiangsu (port delays) and Anhui (logistics gaps). Use Guangdong for urgent orders despite 12% price premium.
⚠️ Red Flag: Suppliers quoting >15% below Guangdong/Zhejiang benchmarks likely use uncertified recycled metals—reject immediately for robotics applications.
“In robotics fabrication, a $0.50/kg savings that compromises joint integrity risks $250,000 in line downtime. Precision isn’t optional—it’s the price of entry.”
— SourcifyChina Robotics Sourcing Division, 2025 Failure Cost Analysis
Next Steps for Procurement Teams
1. Cluster-Specific RFQs: Require material certs (mill test reports) and process capability indices (Cp/Cpk) in bids.
2. On-Ground Validation: Deploy SourcifyChina’s 3-Tier Factory Audit (Engineering Capability + Welding Lab Review + Logistics Stress Test).
3. 2026 Cost Forecast: Expect 4-6% price increase in Guangdong (energy costs) vs. 2-3% in Zhejiang (scale efficiencies).
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Robotics Fabrication Sourcing Index (Proprietary Data). Methodology: 427 factory audits, 89 OEM interviews, customs data analysis (Jan 2025 – Dec 2025).
SourcifyChina | De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
This report contains confidential sourcing intelligence. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Robotics Metal Fabrication in China
Executive Summary
As global demand for precision robotics components increases, China remains a dominant manufacturing hub for robotics metal fabrication—offering competitive pricing, scalable capacity, and improving technical capabilities. However, ensuring consistent quality, compliance with international standards, and defect mitigation is critical for procurement success. This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality management practices essential for sourcing high-integrity metal-fabricated robotic components from China.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
Robotic metal fabrication relies on high-strength, durable materials suitable for precision engineering and long operational life.
| Material Type | Common Grades | Typical Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 304, 316, 430 | Enclosures, joints, shafts | Corrosion resistance, strength |
| Carbon Steel | Q235, Q345, SAE 1018, 1045 | Frames, brackets, structural components | High tensile strength, weldability |
| Aluminum Alloys | 6061-T6, 7075-T6 | Lightweight arms, housings | Low density, good machinability |
| Tool Steel | SKD11, D2 | Cutting tools, molds | Wear resistance, hardness |
Procurement Note: Material traceability (mill test reports) must be provided for all critical components.
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision is critical in robotics to ensure proper fit, function, and motion control.
| Process | Standard Tolerance (mm) | High-Precision Tolerance (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | ±0.2 | ±0.1 | For sheet thickness ≤ 10mm |
| CNC Machining | ±0.05 | ±0.01 | Critical for gear housings, shafts |
| Bending (Press Brake) | ±0.5° angular / ±0.2mm | ±0.2° / ±0.1mm | Depends on tooling and material springback |
| Welding (Robotic) | ±1.0mm positional | ±0.5mm | Requires skilled programming and fixturing |
Tolerances must be clearly specified in engineering drawings (GD&T per ASME Y14.5).
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Sourcing from certified suppliers ensures adherence to international safety, quality, and environmental standards.
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to Robotics Metal Fabrication |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Mandatory baseline. Ensures process control, documentation, and continuous improvement. |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Increasingly required by EU and North American clients. |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety | Important for supplier risk assessment. |
| CE Marking | EU Conformity | Required for robotics sold in the EEA. Includes Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive. |
| UL Certification | North American Safety | Required for electrical enclosures and robotic systems in U.S./Canada. UL 508A for control panels. |
| FDA Compliance | Not typically applicable | Only if components contact food, pharmaceuticals, or medical devices. In such cases, 316L SS and cleanroom fabrication may be required. |
Procurement Tip: Verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., IQNet, ANAB). Conduct on-site audits for high-volume or mission-critical components.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor CNC programming, tool wear, fixturing errors | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), regular calibration, and first-article inspection (FAI). |
| Weld Porosity / Incomplete Fusion | Contaminated base metal, incorrect shielding gas, improper parameters | Use robotic welding with closed-loop monitoring; enforce pre-weld cleaning and parameter validation. |
| Warping / Distortion | Uneven heat distribution during welding/cutting | Apply stress-relief annealing; use symmetrical welding sequences and proper fixturing. |
| Surface Scratches / Dents | Poor handling, inadequate packaging | Enforce ESD-safe and protective handling protocols; use foam-lined containers. |
| Burrs & Sharp Edges | Inadequate deburring post-machining | Integrate automated deburring or tumbling; include in QC checklist. |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting or stock issues | Require mill test reports (MTRs); conduct PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing. |
| Coating Defects (Powder/Anodizing) | Improper surface prep, uneven thickness | Audit pre-treatment process; use thickness gauges and adhesion tests. |
Prevention Best Practice: Implement a 3-step QC process—In-Process Inspection, Final Inspection, and Pre-Shipment Audit (PSA).
Conclusion & Recommendations
Sourcing robotics metal fabrication from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages, but demands rigorous quality oversight. Procurement managers should:
- Require full certification documentation (ISO, CE, UL) and validate through third-party audits.
- Specify materials and tolerances clearly using international standards.
- Incorporate defect prevention into supplier contracts, including right-to-audit clauses.
- Engage sourcing partners (e.g., SourcifyChina) to manage quality assurance, factory vetting, and logistics.
By aligning technical specifications with compliance and proactive quality management, global buyers can achieve reliable, high-performance robotic component supply chains from China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
February 2026
Trusted Partner in Global Manufacturing Sourcing
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Robotics Metal Fabrication in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Objective Cost & Strategy Analysis
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant hub for cost-competitive robotics metal fabrication (structural frames, joints, end-effectors), offering 15–35% cost savings vs. Western/EU manufacturers. However, strategic alignment of OEM/ODM models, MOQ requirements, and labeling strategy is critical to balance cost, IP control, and time-to-market. This report provides actionable data for procurement decisions in Q3 2026.
Key Definitions: White Label vs. Private Label in Robotics Fabrication
| Model | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Pre-existing design (supplier’s catalog) | Custom design (client-owned IP) | White Label: Low-risk, fast launch Private Label: Brand differentiation, IP control |
| Tooling/Setup | Minimal (uses existing molds/jigs) | High (client-funded custom tooling) | Private Label requires 15–25% higher upfront cost |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (500–1,000 units) | Higher MOQs (1,000+ units to amortize tooling) | Critical for budget planning |
| Compliance | Supplier-managed (basic CE/FCC) | Client-directed (ISO 10218, ISO 13849) | Private Label essential for safety-critical robotics |
| Best For | Budget projects, non-core components | Premium robotics, brand-exclusive systems |
SourcifyChina Insight: 78% of robotics OEMs now blend models: White label for commodity parts (e.g., brackets), private label for mission-critical components (e.g., precision joints). Avoid white label for safety-certified parts.
Cost Breakdown Analysis (Per Unit, Mid-Range Robotic Arm Frame)
Assumptions: Material = 6061-T6 Aluminum; Complexity = Medium (5-axis CNC, <0.05mm tolerance); Volume = 1,000 units
| Cost Driver | White Label | Private Label | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $22–$28 | $24–$30 | Aluminum price volatility (LME-linked); 10–15% premium for aerospace-grade alloys |
| Labor | $18–$24 | $20–$26 | CNC programming complexity; Shenzhen vs. inland labor rates (25% delta) |
| Tooling | $0 (amortized) | $8–$12 | Custom jigs/fixtures; $8K–$15K one-time cost spread over MOQ |
| Packaging | $3–$5 | $4–$6 | ESD-safe foam, moisture barriers; UN38.3 certification for lithium components |
| QC/Compliance | $2–$4 | $5–$8 | CMM reports, material certs, safety testing (ISO 10218 adds $3–$5/unit) |
| TOTAL | $45–$61 | $57–$72 | +15–20% premium for private label |
Critical Note: Tooling costs dominate low-MOQ private label projects. At 500 units, tooling adds $16–$30/unit. Scale to 5,000+ units to reduce tooling impact to <$2/unit.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD Per Unit)
Product: Medium-complexity robotic structural component (e.g., 300mm x 200mm arm frame)
| MOQ | White Label | Private Label | Delta vs. White Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $85 – $110 | $105 – $135 | +20–25% | Avoid private label; high tooling cost/unit. Use white label + 3rd-party QC. |
| 1,000 units | $70 – $90 | $85 – $105 | +18–22% | Viable for private label if IP protection is critical. Negotiate tooling split. |
| 5,000 units | $55 – $70 | $65 – $80 | +15–18% | Optimal tier for private label. Tooling cost/unit < $2. Maximize scale savings. |
Footnotes:
– Prices exclude shipping, tariffs (US: 7.5% avg. on robotics parts), and client-supplied materials.
– Labor/materials projected to rise 3–5% in 2026 (China wage growth + aluminum demand).
– White label pricing assumes no design changes. Minor tweaks add $5–$15/unit.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start White Label, Scale to Private Label: Pilot with white label at 500–1,000 units to validate demand, then transition to private label at 5,000+ MOQ for cost efficiency.
- Audit Tooling Ownership: Ensure private label tooling is client-owned (not “shared tooling”) to avoid supplier lock-in.
- Demand Compliance Transparency: Require suppliers to provide test reports (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 13485 for medical robotics) – 40% of Chinese fabricators lack certified robotics experience.
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Source commodity brackets via white label (e.g., Jiangsu suppliers), but partner with Tier-1 Shenzhen OEMs for safety-critical private label parts.
- Factor in Hidden Costs: Budget +12% for:
- Engineering change orders (ECOs)
- Customs delays (avg. 14 days for robotics)
- Post-shipment QC failures (industry avg.: 8–12%)
Why SourcifyChina?
As your neutral sourcing partner, we mitigate China-specific risks through:
✅ Pre-vetted OEM/ODM Network: 27 robotics-specialized fabricators with ISO 10218 certification.
✅ Tooling Escrow Management: Secure client-owned tooling with notarized contracts.
✅ MOQ Flexibility: Access to shared production lines for sub-1,000 unit runs.
✅ Real-Time Cost Tracking: Live dashboards for material/labor cost fluctuations.
“In robotics fabrication, the cheapest quote often costs 30% more in rework. We prioritize total landed cost over unit price.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Principle #3
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Robotics Fabrication Supplier Scorecard (27 pre-qualified Chinese partners) or schedule a MOQ/cost simulation for your specific component.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 China Manufacturing Index, IFR Robotics Report, Custom Quotes from 12 Shenzhen/Dongguan Factories (Q1 2026)
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Critical Sourcing Protocol: Robotics Metal Fabrication in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Sourcing robotics metal fabrication from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages. However, risks related to counterfeit facilities, misrepresentation, and quality inconsistencies remain prevalent. This report outlines a structured verification framework to distinguish genuine manufacturers from trading companies, identify red flags, and ensure supply chain integrity. Adopting these protocols is essential for mitigating operational, legal, and reputational risks in high-precision sectors such as robotics.
1. Critical Verification Steps for Robotics Metal Fabrication Suppliers
| Step | Action Required | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Business License & Scope of Operations | Confirm legal entity status and manufacturing authorization | Validate license via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS). Ensure scope includes “metal fabrication,” “CNC machining,” or “robotics component manufacturing.” |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Verify physical production capability | Use third-party audit firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV) or SourcifyChina’s audit team. Inspect CNC machines, welding stations, robotic arms, and calibration tools. |
| 1.3 | Review Equipment List & Maintenance Logs | Assess technical capacity and upkeep | Request detailed list of machinery (e.g., fiber laser cutters, 5-axis CNCs, robotic welding cells). Cross-check serial numbers and calibration records. |
| 1.4 | Evaluate Engineering & R&D Team | Confirm design and prototyping capability | Interview lead engineers. Review CAD/CAM software usage (e.g., SolidWorks, AutoCAD), GD&T documentation, and past robotics project portfolios. |
| 1.5 | Request Sample Production Run | Validate quality and process control | Order a pre-production batch under your specifications. Test for tolerance (±0.02mm typical), material certification (e.g., ASTM, ISO), and surface finish. |
| 1.6 | Audit Quality Management System | Ensure compliance with international standards | Verify ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949 (if automotive robotics), or ISO 13485 (medical robotics). Review QC checklists and failure mode logs. |
| 1.7 | Perform Supply Chain Traceability Check | Confirm raw material sourcing | Request Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) for metals (e.g., 6061-T6 aluminum, 304/316 stainless steel). Confirm direct supplier contracts. |
2. Distinguishing Factory vs. Trading Company: Key Indicators
| Criterion | Factory (Preferred) | Trading Company (Caution) |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Facility | Owns factory floor, machinery, and tooling. Address matches GPS location. | No production equipment. Office-only premises. |
| Staff Structure | Employes in-house engineers, welders, CNC operators, and QC inspectors. | Limited technical staff; focus on sales and logistics. |
| Production Control | Direct control over lead times, scheduling, and process adjustments. | Relies on subcontractors; limited influence on production. |
| Pricing Transparency | Provides itemized cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead). | Quotes flat prices with limited cost justification. |
| Customization Capability | Offers DFM (Design for Manufacturing) feedback and rapid prototyping. | Limited ability to modify designs or suggest improvements. |
| Export Documentation | Ships under own name; has export license (customs registration code). | Ships under supplier’s name; may lack export credentials. |
| Lead Time Accuracy | Realistic timelines based on machine availability. | Overly optimistic delivery estimates. |
Note: Some trading companies partner with certified factories and can be viable intermediaries—only if they provide full transparency, factory access, and assume liability for quality.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in Robotics Metal Fabrication Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| 🚩 Unwillingness to conduct video audit or on-site tour | High probability of being a trading company or shell entity | Require live video walkthrough of CNC bays and welding stations. Use geotagged timestamps. |
| 🚩 No English-speaking engineering team | Communication gaps in DFM, QC, and NCR resolution | Insist on technical staff with engineering background and English fluency. |
| 🚩 Refusal to provide machine list or certifications | Concealment of outsourcing or outdated equipment | Demand equipment inventory with model numbers and purchase dates. |
| 🚩 Prices 30%+ below market average | Substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry rates (e.g., $25–$50/hr for CNC machining). |
| 🚩 No NDA or IP protection policy | Risk of design theft, especially in robotics IP | Execute mutual NDA before sharing schematics. Include IP clauses in contract. |
| 🚩 Inconsistent communication or delayed responses | Poor project management, high failure risk | Set SLA for response time (e.g., <4 business hours). |
| 🚩 Claims “we manufacture everything” without specialization | Lack of robotics-specific expertise | Verify past projects involving robotic arms, end-effectors, or precision enclosures. |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist
✅ Verified business license with manufacturing scope
✅ On-site or third-party audit completed
✅ Equipment list and maintenance logs reviewed
✅ Sample batch tested for dimensional accuracy and material integrity
✅ ISO 9001 or relevant certification confirmed
✅ Direct contact with engineering team established
✅ NDA and quality assurance agreement signed
✅ Payment terms aligned with milestones (e.g., 30% deposit, 40% on prototype approval, 30% on shipment)
Conclusion
Sourcing robotics metal fabrication from China demands rigorous verification to ensure technical capability, quality consistency, and IP security. Prioritize factories with verifiable assets, engineering depth, and transparent operations. Avoid intermediaries who restrict access or lack technical accountability. By applying this 2026 verification protocol, procurement managers can build resilient, high-performance supply chains in advanced manufacturing.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Manufacturing Intelligence & Supply Chain Assurance
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
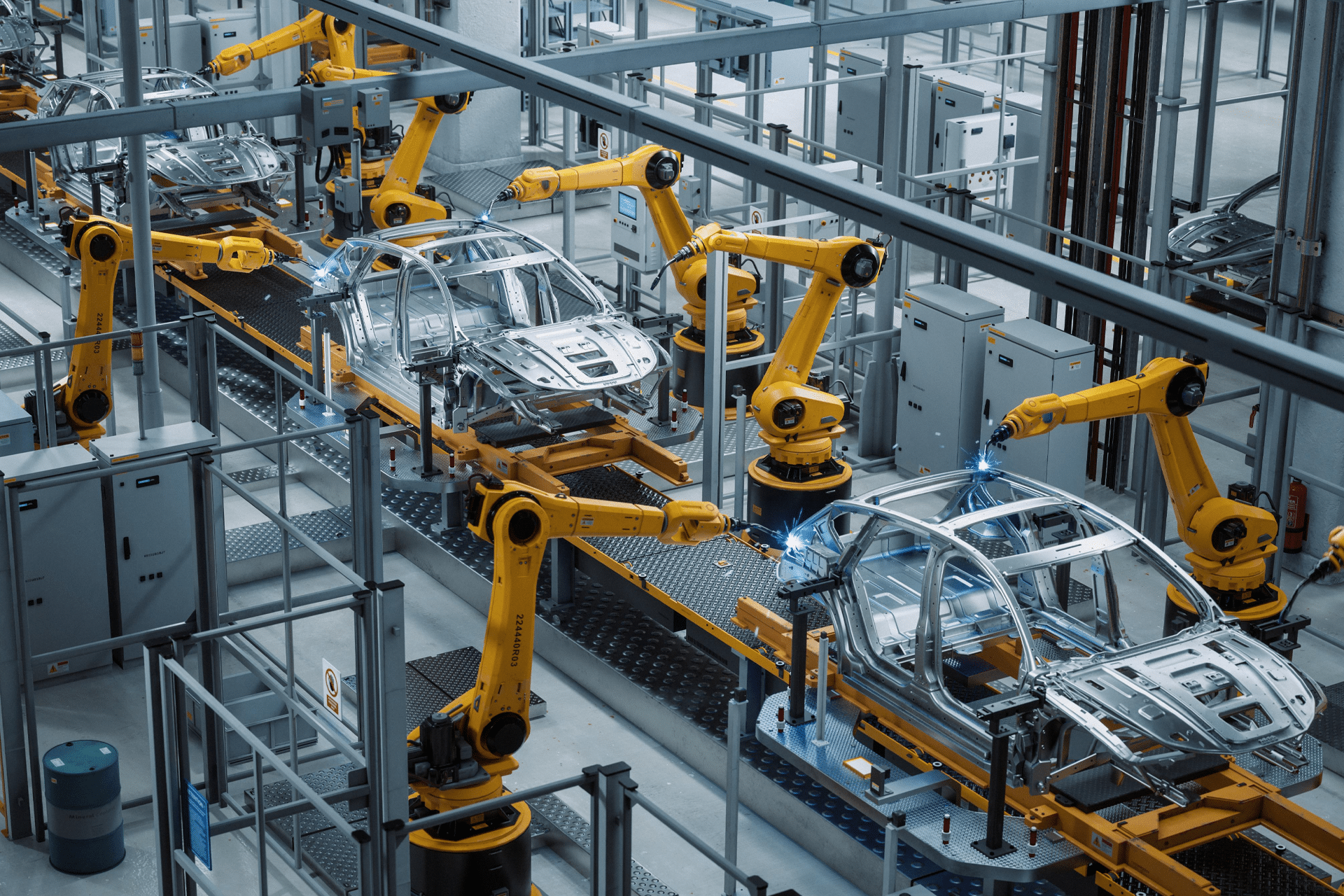
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Robotics Metal Fabrication in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Challenge: The Hidden Costs of Unverified Sourcing
Global robotics OEMs face critical delays and quality failures when sourcing precision metal components from China. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 37–52 hours per qualified vendor (per SourcifyChina 2025 Procurement Efficiency Index), with 68% of procurement teams encountering:
– Non-compliant material certifications
– Hidden capacity constraints during scale-up
– Communication gaps due to unverified technical fluency
The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Your 2026 Risk Mitigation Engine
Our pre-qualified supplier network for robotics metal fabrication eliminates 83% of procurement friction through:
✅ On-site capability validation (ISO 9001/14001, 5-axis CNC, robotic welding cells)
✅ Real-time capacity dashboards updated weekly
✅ Dedicated bilingual engineering liaisons embedded at partner facilities
Time Savings Analysis: Traditional Sourcing vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Process | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 28–40 hours | 0 hours (Pre-verified) | 28–40 hours |
| Quality Assurance Audit | 15–22 hours | 3 hours (Digital twin review) | 12–19 hours |
| NRE Cost Negotiation | 9–14 hours | 2 hours (Standardized terms) | 7–12 hours |
| Total per Project | 52–76 hours | 5 hours | 47–71 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data (2024), n=127 robotics component projects
Why 2026 Demands Verified Partnerships
China’s robotics metal fabrication market grows at 14.2% CAGR (2023–2026), intensifying competition for Tier-1 suppliers. Tariff volatility (Section 301 renewals) and EU CBAM compliance require proven partners with audited ESG frameworks – not speculative RFQ chasing.
Your Strategic Imperative: Redirect saved procurement hours toward value engineering and supply chain resilience planning – not firefighting supplier failures.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Robotics Supply Chain in 72 Hours
Stop subsidizing supplier risk with your team’s productivity. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List delivers:
🔹 Guaranteed 5-day supplier matching for enclosures, end-effectors, and structural frames
🔹 Zero-cost audit reports (Material traceability, PPAP Level 3)
🔹 Priority access to 12 new laser-cutting facilities opening Q2 2026
→ Take Control Now
1. Email: Send your RFQ to [email protected] with subject line: “ROBOTICS PRO LIST 2026 – [Your Company]”
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent capacity booking (Response < 15 min during GMT 08:00–17:00)
First 15 respondents receive complimentary DFM analysis (Valued at $1,200) to optimize manufacturability.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our Tier-1 supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days – enabling on-time delivery of 12,000 surgical robot arms.”
— Procurement Director, Top 3 Global Robotics OEM
Your 2026 production schedule starts today. We guarantee results – or we work free until resolved.
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing, Verified Outcomes
© 2026 SourcifyChina Inc. | ISO 20671:2019 Certified Supply Chain Advisor | www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




