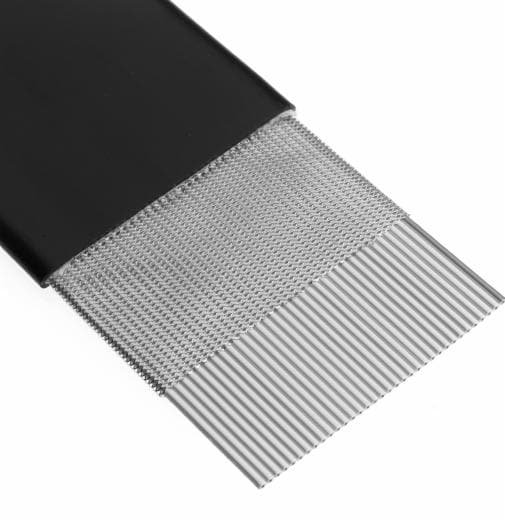
The global ribbon cables market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for compact and reliable interconnect solutions across consumer electronics, automotive, industrial automation, and healthcare sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global cable and wire market—of which ribbon cables are a key component—was valued at USD 188.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in miniaturization, increased adoption of flat flexible cables in high-speed data transmission, and the proliferation of IoT-enabled devices. Mordor Intelligence also highlights that the Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, supported by robust electronics manufacturing in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. As demand for high-performance, space-efficient wiring solutions continues to rise, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and quality. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 ribbon cables manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Ribbon Cables Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electrical and Electronic Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hirose.com
Key Highlights: Hirose Electric Co., Ltd. is a leading global supplier of innovative interconnects, employing advanced engineering services, superior customer support and ……
#2 Belden
Domain Est. 1997
Website: belden.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture and market networking, connectivity, cable products and solutions for industrial automation, smart buildings and broadcast markets….
#3 Ribbon Cable Assembly Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: datacable.ca
Key Highlights: Data Cable is a world class manufacturer of custom cable assemblies, wire harnessing, electro-mechanical assemblies and other interconnect solutions for a ……
#4 3M Flat & Ribbon Cable
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: Copper conductor bulk cable with an oblong/rectangular cross-section as opposed to a circular one. Flat cables save space and are often used to connect ……
#5 Fiber Optic Ribbon Cable
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: Ribbon cables offer higher fiber counts and fiber density than any other OSP cable. It’s becoming the easiest, fastest way to plan for future network needs….
#6 High
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: These cables are designed specifically to prevent the signal interruptions that are prevalent in harsh environments due to failures with PVC and TPE cables….
#7 IDC Cable Systems
Domain Est. 1995
Website: samtec.com
Key Highlights: Tiger Eye™ IDC cables, IDC connectors, FFC cables and connectors, & ribbon cable connectors with high reliability contacts on 1.27 mm and 2.00 mm pitch, ……
#8 Custom Ribbon Cable Assemblies
Domain Est. 2001
Website: cypressindustries.com
Key Highlights: Cypress Industries manufactures custom ribbon cable assemblies for customers in many industries. Our ribbon cable assemblies can include: Flat ribbon cable, ……
#9 Flat Ribbon Cable Assemblies
Domain Est. 2009
Website: epectec.com
Key Highlights: Save space with custom flat ribbon cables. Our assemblies feature folding, color coding, and terminations designed for complex electronic applications….
#10 IP Optical Networking and Communications
Domain Est. 2017
Website: ribboncommunications.com
Key Highlights: Ribbon offers innovative IP and optical networking solutions and cloud-to-edge communications solutions. These solutions include optical and IP systems for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ribbon Cables
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ribbon Cables
The ribbon cable market in 2026 is expected to exhibit steady growth driven by technological evolution, rising demand in key industries, and a shift toward miniaturization and high-speed data transmission. While traditional applications remain stable, emerging trends are shaping the future landscape.
1. Growth in High-Speed and Miniaturized Designs:
Demand is shifting toward high-speed ribbon cables capable of supporting data rates essential for modern electronics, including USB 3.0/3.1, PCIe, and internal high-bandwidth interconnects. Flat flexible cables (FFCs) — a subset of ribbon cables — are increasingly replacing traditional round cables in consumer electronics, wearables, and compact medical devices due to their slim profile and flexibility. This trend is accelerating as devices become smaller and more integrated.
2. Rising Adoption in Automotive and Industrial Automation:
The automotive sector, particularly electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), is a growing market for ribbon cables. These cables are used in infotainment systems, sensor arrays, and internal control units where reliability and space efficiency are critical. Similarly, industrial automation and robotics are leveraging ribbon cables for compact internal wiring in control panels and machinery, boosting demand in the industrial segment.
3. Shift Toward High-Performance Materials:
To meet the demands of harsh environments and high-frequency signals, manufacturers are adopting advanced materials such as fluoropolymers and high-temperature plastics. These materials enhance signal integrity, reduce crosstalk, and improve resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion—critical for automotive, aerospace, and medical applications.
4. Regional Manufacturing and Supply Chain Adjustments:
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, remains the dominant production hub. However, trade dynamics and supply chain resilience concerns are encouraging regional diversification. North America and Europe are seeing renewed interest in localized production, particularly for high-reliability applications in defense and medical technology.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Compliance:
Environmental regulations, such as RoHS and REACH, continue to influence material selection. The industry is moving toward lead-free, halogen-free, and recyclable cable solutions. While not a primary driver, sustainability is becoming a differentiating factor among competitive suppliers.
6. Competitive Landscape and Innovation:
The market remains fragmented with key players like Molex, TE Connectivity, Fujikura, and 3M investing in R&D to develop ultra-thin, high-density, and high-speed ribbon interconnects. Customization and integration with connectors (e.g., ZIF – Zero Insertion Force) are key value propositions.
Outlook:
The global ribbon cable market is projected to grow at a moderate CAGR of 3–5% through 2026. While traditional parallel data applications are declining due to serial communication dominance, the adaptability of ribbon cables—especially FFCs—in space-constrained, high-reliability environments ensures sustained relevance. Innovation in materials, design, and application-specific solutions will be critical for market participants to capture emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ribbon Cables: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing ribbon cables may seem straightforward, but overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to product failures, compliance issues, and legal risks. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure reliability and protect your business.
Poor Material Quality and Construction
One of the most frequent issues is receiving ribbon cables made with substandard materials. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior-grade PVC insulation that becomes brittle over time, or conductors with inconsistent copper purity, leading to higher resistance and signal loss. Poorly bonded conductors can separate easily during installation or use, especially in high-flex applications. Always verify material specifications and request samples for mechanical and electrical testing before mass procurement.
Inconsistent Dimensions and Tolerances
Ribbon cables require precise pitch (typically 0.05″, 0.025″, etc.) and thickness to fit connectors properly. Inconsistent manufacturing can result in cables that don’t seat correctly in IDC (Insulation Displacement Connectors), causing intermittent connections or complete assembly failure. Verify dimensional tolerances with the supplier and inspect incoming goods with calipers or gauge fixtures.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Many ribbon cables on the market lack proper certifications such as UL, CSA, or RoHS. Using non-compliant cables in commercial or industrial products can lead to regulatory rejection, safety hazards, or voided insurance. Ensure suppliers provide documentation proving compliance with relevant standards and traceability of materials.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Components
Some suppliers may falsely claim that their cables meet specific performance grades (e.g., high-speed data transmission, high-temperature resistance) without proper testing. This misrepresentation can be a form of IP infringement if the product mimics branded, patented designs. Always source from reputable distributors or directly from manufacturers with verifiable credentials.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Copying proprietary cable designs, shielding configurations, or connector interfaces without authorization can expose your company to IP litigation. Some suppliers may offer “compatible” cables that closely mimic patented products, crossing into infringement territory. Conduct due diligence on supplier designs and ensure they offer legally distinct alternatives or proper licensing.
Inadequate Traceability and Documentation
A lack of batch traceability, material certifications, or test reports makes it difficult to address quality issues or perform root cause analysis during field failures. Reliable suppliers should provide full documentation, including lot numbers and compliance data sheets (COCs), to support quality assurance and audit requirements.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires careful supplier vetting, sample testing, and attention to both technical specifications and legal compliance. Investing time upfront ensures long-term reliability and protects your product’s integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ribbon Cables
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, and use of ribbon cables across various industries.
Product Classification & HS Codes
Ribbon cables are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to electrical conductors and wiring harnesses. Common classifications include:
– HS 8544.42: Insulated electric conductors fitted with connectors, for a voltage ≤ 80 V.
– HS 8544.49: Other insulated electric conductors fitted with connectors.
Verify country-specific tariff schedules, as classifications may vary based on insulation material, voltage rating, or application.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transit:
– Use anti-static packaging for shielded or sensitive ribbon cables to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
– Coiled or flat-pack formats must avoid tight bending to prevent conductor deformation.
– Clearly label packages with ESD warnings, directional arrows, and handling instructions.
– For international shipping, use moisture-resistant packaging to avoid damage during long voyages.
Transportation & Storage Conditions
- Temperature Range: Store and transport between -10°C to +50°C unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer.
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 70% to prevent insulation degradation.
- Shelf Life: Most ribbon cables have a shelf life of 12–24 months; check manufacturer data sheets for exact durations.
- Avoid direct sunlight and contact with oils, solvents, or corrosive materials.
Regulatory Compliance Standards
Ribbon cables must meet various regional and international standards depending on application:
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances – limits lead, cadmium, mercury, and other harmful materials.
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals – requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– UL/CSA (North America): Safety certification for flammability, insulation, and electrical performance (e.g., UL 2651 for flat flexible cables).
– IPC/WHMA-A-620: Acceptability of electronic cable and wire harness assemblies (common in defense and industrial sectors).
– REACH SVHC & Conflict Minerals: Required disclosures for products sold in the EU or U.S. (Dodd-Frank Act).
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
- WEEE (EU): Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment – mandates proper recycling and disposal.
- End-of-Life Handling: Treat used ribbon cables as electronic waste; do not dispose in regular landfill.
- Recycling facilities must be certified to handle insulated copper/aluminum conductors and plastic jackets.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice (with full product description, HS code, value)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– RoHS/REACH Compliance Declaration
– UL or other safety certification (if applicable)
– Material Declarations (e.g., conflict minerals reporting for U.S. imports)
Labeling & Traceability
- Each batch or reel must include:
- Manufacturer/part number
- Date of manufacture
- Length and gauge specifications
- Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, UL)
- Use serialized or batch-coded labeling to support traceability in case of recalls or audits.
Industry-Specific Requirements
- Medical Devices: Must comply with ISO 13485 and may require biocompatible materials.
- Aerospace & Defense: Often require MIL-DTL-27500 or equivalent specs and full chain-of-custody documentation.
- Automotive: May need compliance with AEC-Q200 or LV214 standards for durability and temperature resistance.
Supplier & Quality Assurance
- Audit suppliers for adherence to ISO 9001 and relevant compliance frameworks.
- Request test reports (e.g., dielectric strength, conductor resistance) with each shipment.
- Maintain records of compliance certificates for at least five years.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient handling of ribbon cables across global supply chains. Always consult the manufacturer’s datasheets and local regulatory authorities for application-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing ribbon cables requires careful consideration of several key factors including cable type, pitch size, conductor count, length, material quality, and application requirements. It is essential to partner with reliable suppliers who offer consistent quality, compliance with industry standards (such as UL, RoHS), and responsive customer support. Evaluating options based on durability, flexibility, and compatibility with connected devices ensures optimal performance and longevity in the intended system. Whether for consumer electronics, industrial equipment, or PCB interconnects, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing cost, lead times, and technical specifications—will help achieve reliable and efficient integration of ribbon cables into your projects. Conducting periodic supplier assessments and staying updated on emerging technologies will further support continuous improvement in your supply chain.