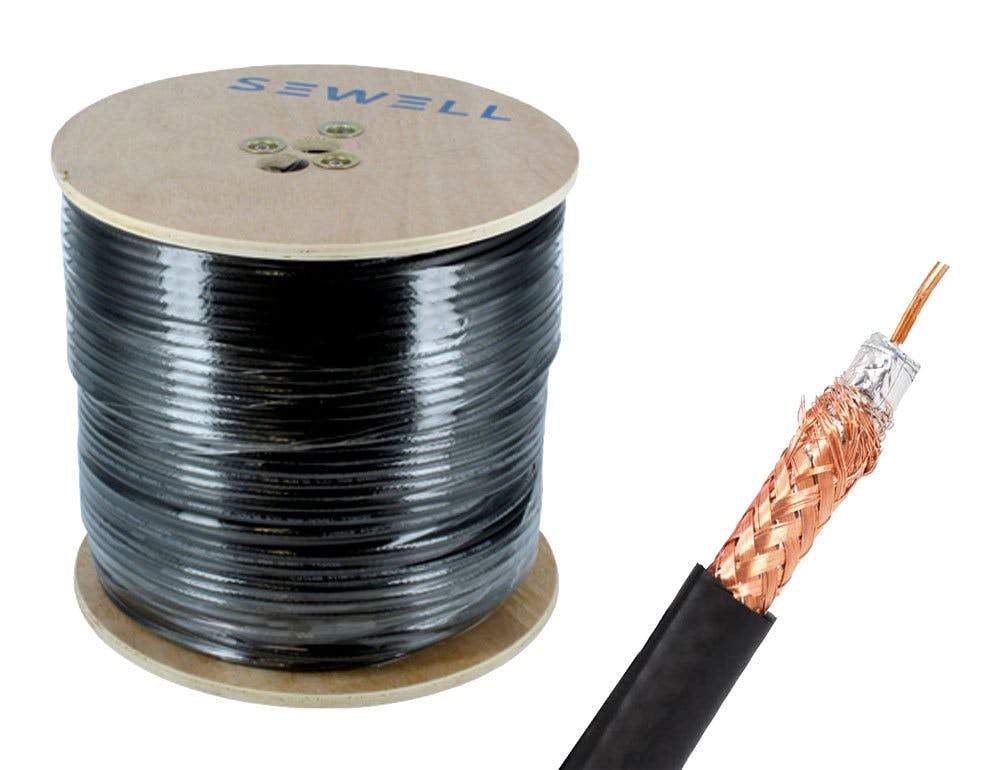
The demand for high-performance coaxial cables such as RG59 and RG6 has surged in recent years, driven by expanding applications in telecommunications, broadband internet, surveillance systems, and cable television infrastructure. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global coaxial cable market was valued at USD 8.2 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by the ongoing deployment of fiber-coaxial hybrid networks and the rising adoption of high-definition video transmission systems in both residential and commercial sectors. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that increasing investments in smart city projects and security surveillance are further accelerating demand for reliable signal transmission cables like RG6, known for its superior bandwidth and longer-distance performance, and RG59, commonly used in short-range video applications. As infrastructure modernization continues worldwide, identifying leading manufacturers who deliver quality, scalability, and innovation in coaxial cable production becomes critical. The following list profiles the top nine manufacturers shaping the RG59 and RG6 landscape based on market presence, product breadth, and technological advancement.
Top 9 Rg59 And Rg6 Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Coax Cable RG6
Domain Est. 1999
Website: windycitywire.com
Key Highlights: Ensure strong, HD surveillance with durable RG6 cables built for industrial use. Upgrade your CCTV system with dependable performance—shop now….
#2 RG59 Archives
Domain Est. 2006
Website: verticalcable.com
Key Highlights: Vertical Cable – U.S. Wire and Cable Manufacturer and Distributor. Privacy Pledge | Terms of Use | Terms of Sale….
#3 RG6 cable products Catalog
Domain Est. 2015
Website: zion-communication.com
Key Highlights: RG 6 cable is most famous for TV. ○ RG-59 cable is similar to the RG-6 but has an even thinner center conductor (20AWG=0.81mm). This makes it a good choice ……
#4 Coaxial Cables
Domain Est. 1994
Website: commscope.com
Key Highlights: Diverse Types: CommScope provides various coaxial cable sizes and types, such as RG6, RG11, and RG59, catering to specific needs. Impedance ……
#5 RG6 Cable
Domain Est. 1997
Website: belden.com
Key Highlights: Belden’s low-loss RG6 Cable is small in diameter (18 AWG) and easy to bend. It features excellent bandwidth capabilities, low capacitance and double-sided foil ……
#6 RG6 vs. RG58 vs. RG59 vs. RG11 Coaxial Cables
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conwire.com
Key Highlights: The most common types of coaxial cable include RG6, RG58, RG59, and RG11. Here, we’ll look at how coax cable is constructed and used, as well as how the types ……
#7 High
Domain Est. 1998
Website: remee.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.4/4.5 (300) Upgrade your connectivity with top-quality RG coax cables! Choose from RG6, RG11, RG59, & more for crystal-clear TV, internet, and CCTV signals….
#8 ABA Elite Coax Cable
Domain Est. 2007
Website: abacable.com
Key Highlights: COAX Cable These coaxial cables are for signal transmission in electronic applications and data communications. Coaxial cables now can accommodate faster…
#9 RG59/RG6/RG174/RG11
Domain Est. 2015
Website: ghtcable.com
Key Highlights: Our Coaxial Cable Rj59 is ideal for applications requiring lower frequency work below 50 MHz, such as Plasma TVs, component video, video projectors, and CCTV ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rg59 And Rg6

H2: 2026 Market Trends for RG59 and RG6 Coaxial Cables
As we approach 2026, the market for coaxial cables—specifically RG59 and RG6—is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving infrastructure demands, and competition from alternative connectivity solutions. While both cable types have historically played critical roles in video transmission, surveillance, and broadband delivery, their trajectories are diverging due to differences in performance and application suitability.
Declining Demand for RG59
By 2026, the RG59 coaxial cable is expected to continue its decline in mainstream applications. Primarily used in older analog video systems and short-distance CCTV installations, RG59’s smaller center conductor and higher signal attenuation limit its effectiveness for high-frequency and long-distance signal transmission. As industries shift toward high-definition (HD), 4K, and IP-based surveillance systems, RG59’s bandwidth limitations make it increasingly obsolete. Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of -3.2% for RG59 through 2026, with demand largely confined to legacy system maintenance and low-cost residential installations.
Sustained Relevance of RG6
In contrast, RG6 is anticipated to maintain steady market relevance, particularly in broadband internet, satellite/cable TV, and modern security systems. Its thicker center conductor, improved shielding, and lower signal loss at higher frequencies make it well-suited for digital signal transmission up to 3 GHz. With the continued rollout of DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber-deep network architectures, RG6 remains a vital component in hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) networks. Additionally, the expansion of 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and smart home ecosystems supports demand for reliable in-building cabling, where RG6 is often the preferred choice. The global RG6 market is projected to grow at a modest CAGR of 2.1% through 2026.
Emerging Influences
Several factors will shape the 2026 landscape:
– Fiber Optic Competition: The increasing deployment of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) may reduce reliance on coaxial cables, but RG6 will remain essential for last-mile distribution within buildings.
– Smart Infrastructure: Growth in smart cities and IoT devices sustains demand for reliable, cost-effective cabling, benefiting RG6 in particular.
– Regulatory and Standards Shifts: Updated building codes and telecommunications standards may favor higher-performance cables, further marginalizing RG59.
In summary, while RG59 continues to fade from prominence, RG6 is adapting to modern connectivity needs and is expected to retain a strategic role in telecommunications infrastructure through 2026.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing RG59 and RG6 Cables (Quality and IP Considerations)
Inconsistent Cable Quality and Material Substitution
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing RG59 and RG6 coaxial cables is inconsistent manufacturing quality. Many low-cost suppliers use inferior materials such as copper-clad steel (CCS) instead of pure copper conductors, or employ undersized center conductors and inadequate shielding. These substitutions significantly degrade signal performance, increase attenuation, and reduce long-term reliability—especially over longer runs or in high-frequency applications like HD video or broadband internet. Buyers may receive cables that meet nominal specifications on paper but fail in real-world installations.
Misleading or Inaccurate IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
RG59 and RG6 cables are often marketed with IP66, IP67, or even IP68 ratings, suggesting resistance to dust and water immersion. However, these ratings typically apply only to the connectors and enclosures, not the cable itself. The coaxial cable along its length lacks true IP protection unless specifically designed with water-blocking gel, foil barriers, or robust outer jackets. Relying solely on IP claims without verifying the full system (cable + connector + installation method) can lead to moisture ingress, corrosion, and signal loss in outdoor or high-humidity environments.
Confusing RG59 and RG6 for Inappropriate Applications
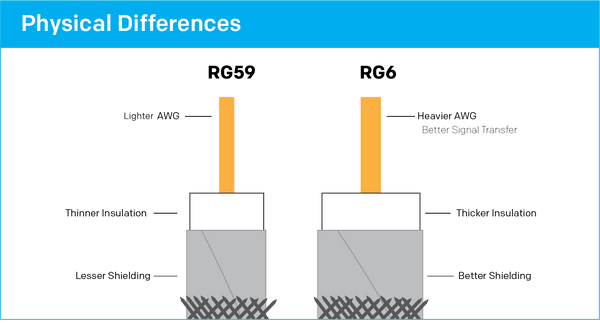
Sourcing the wrong cable type—RG59 vs. RG6—is a common error driven by cost-cutting or misunderstanding technical needs. RG59 has higher signal loss, especially at higher frequencies (above 50 MHz), making it unsuitable for modern digital video, satellite, or broadband applications. RG6, with its larger conductor and better shielding, is designed for these uses. Using RG59 in place of RG6 to save money can result in poor performance, pixelation, or complete signal failure, particularly over distances greater than 50 feet.
Lack of Shielding and Interference Susceptibility
Many budget RG59 and RG6 cables feature insufficient shielding (e.g., single-shield instead of quad-shield), making them vulnerable to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This is a critical oversight in environments with heavy electrical noise, such as industrial facilities or urban installations. Poor shielding compromises signal integrity and can lead to intermittent issues that are difficult to diagnose, ultimately increasing maintenance costs.
Non-Compliance with Industry Standards and Certifications
Reputable RG6 cables should comply with standards such as CL2/CL3 (fire safety), CMR (riser-rated), or even plenum-rated (CMP) for indoor use. RG59 often lacks these ratings altogether. Sourcing cables without proper certification poses safety risks and may violate local building codes. Additionally, absence of performance certifications (e.g., from SMPTE for broadcast video) can indicate subpar quality, especially for professional AV or security systems.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Products
The market is rife with counterfeit cables falsely labeled as RG6 or branded with fake certifications. These cables may look identical to genuine products but underperform drastically. Without proper testing or supplier vetting, organizations risk deploying unreliable infrastructure. Always source from reputable suppliers and request test reports or samples before bulk purchasing.
Overlooking Environmental and Installation Factors
Even with high-quality RG6 and proper IP-rated connectors, poor installation practices—such as sharp bends, improper grounding, or lack of drip loops—can negate performance benefits. Failing to account for UV exposure, temperature extremes, or rodent activity during sourcing can also lead to premature cable failure. Choose cables with UV-resistant jackets and direct-burial ratings when needed, and ensure compatibility with the full installation environment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for RG59 and RG6 Coaxial Cables
Overview of RG59 and RG6 Cables
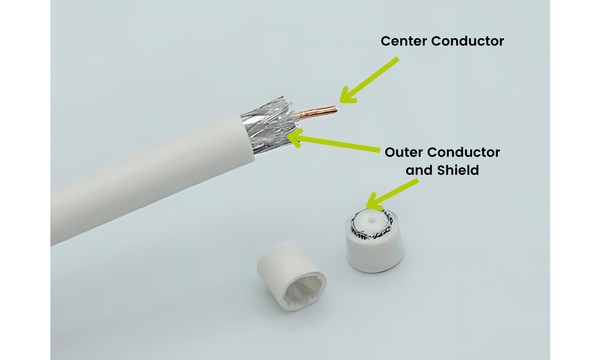
RG59 and RG6 are standardized coaxial cables widely used in video transmission, cable television (CATV), satellite systems, and surveillance networks. RG59 is typically used for shorter-distance analog video signals, while RG6 offers higher bandwidth and better shielding, making it ideal for digital TV, broadband internet, and long-distance signal runs. Understanding their logistics and compliance requirements is essential for procurement, transportation, and installation.
Regulatory and Industry Standards Compliance
Both RG59 and RG6 must comply with national and international standards to ensure performance, safety, and interoperability. Key standards include:
– UL (Underwriters Laboratories) – Ensures fire resistance, electrical safety, and material durability. Look for UL 13, UL 1581, or UL 444 certifications.
– ETL Listed – Equivalent to UL certification, verifying compliance with North American safety standards.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – Mandates that cables contain no lead, mercury, cadmium, or other restricted materials, especially for EU markets.
– REACH (EU Regulation) – Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) used in cable materials.
– NEC (National Electrical Code), Article 820 – Governs installation practices, including fire ratings (e.g., CM, CMR, CMP) for plenum and riser spaces.
– CE Marking – For distribution in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Cable Jacket Ratings and Applications
Selecting the correct jacket rating is crucial for compliance with fire safety regulations:
– CM (Communications Multipurpose) – General indoor use, non-plenum areas. Suitable for most RG59 and RG6 installations.
– CMR (Riser-rated) – For vertical runs between floors. Resists fire propagation in riser shafts. Required by NEC for multi-story buildings.
– CMP (Plenum-rated) – For air-handling spaces (plenums). Must pass stringent fire and smoke tests (e.g., NFPA 262). Mandatory in commercial HVAC environments.
Ensure packaging and product labels clearly indicate the fire rating to meet inspection and code requirements.
Packaging and Shipping Considerations
Proper packaging ensures cable integrity during transport:
– Coaxial cables are typically shipped on reels or in pull-boxes (e.g., 500 ft, 1000 ft).
– Reels must be secured to prevent unspooling during transit. Use stretch wrap and edge protectors.
– Label reels with product type (RG59 or RG6), length, jacket rating, and compliance markings (e.g., “UL CMR”).
– Avoid extreme temperatures in storage and shipping; prolonged exposure can degrade jacket materials.
– Use palletized freight for bulk orders to prevent damage and ensure traceability.
Import and Export Compliance
When moving RG59 and RG6 cables across borders:
– Verify country-specific certifications (e.g., CSA in Canada, CCC in China).
– Maintain documentation for RoHS, REACH, and other environmental directives.
– Include Harmonized System (HS) codes on shipping manifests—typically under 8544.49 (insulated wire, not elsewhere specified).
– Be aware of import duties and customs clearance procedures, especially for bulk shipments.
– Ensure supplier-provided test reports and certificates of compliance are available upon request.
Installation and Environmental Compliance
During installation, adhere to local building and electrical codes:
– Follow NEC guidelines for grounding and bonding coaxial systems.
– Use only listed connectors and tools to maintain system integrity.
– Avoid sharp bends; minimum bend radius for RG6 is typically 6 inches.
– For outdoor use, ensure cables are UV-resistant and waterproof (e.g., flooded or gel-filled variants).
– Document installations for compliance audits and future maintenance.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain accurate records to support compliance and logistics:
– Keep product datasheets, compliance certificates, and test reports on file.
– Ensure batch/lot numbers are traceable for quality control and recalls.
– Provide end-users with installation manuals and compliance statements.
– Use inventory management systems to track cable types, quantities, and certifications.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for RG59 and RG6 cables ensure safety, performance, and regulatory adherence. From procurement to installation, attention to standards, labeling, packaging, and documentation minimizes risk and supports efficient deployment in diverse environments. Always source cables from reputable suppliers with verifiable compliance credentials.
Conclusion for Sourcing RG59 and RG6 Cables:
When sourcing RG59 and RG6 coaxial cables, it is essential to consider the specific application requirements, performance needs, and long-term reliability. RG59 cables are suitable for shorter-distance video transmissions, such as analog CCTV systems or low-frequency signals, due to their smaller conductor and higher signal loss over distance. In contrast, RG6 cables, with their larger conductor and better shielding, are ideal for high-frequency applications including digital video, satellite/cable TV, broadband internet, and long-distance signal transmission, offering superior signal integrity and reduced attenuation.
In sourcing decisions, prioritize quality from reputable suppliers to ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., CL2/CL3 ratings for fire safety, triple or quad shielding for interference resistance). Consider factors such as cable length, installation environment (indoor vs. outdoor, exposed vs. concealed), and future scalability. While RG59 may offer cost advantages for basic analog setups, RG6 is increasingly becoming the standard for modern surveillance, networking, and multimedia systems due to its enhanced performance.
Ultimately, proper evaluation of project needs will guide the optimal choice between RG59 and RG6. In most new installations, especially those involving HD video or data-intensive applications, RG6 is recommended to ensure reliability, performance, and future-proofing. Effective sourcing involves balancing cost, quality, and technical specifications to achieve the best long-term value.