The global trailer mover market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient, labor-saving solutions in transportation, logistics, and recreational vehicle sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global electric vehicle market—under which trailer movers are often categorized due to their electric drivetrains—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 22.6% from 2023 to 2030. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence reports that the growing adoption of smart and automated towing technologies is further accelerating market expansion, particularly in North America and Europe. As remote-controlled and precision-maneuvering systems gain traction, manufacturers are innovating rapidly to meet the needs of commercial fleets, RV owners, and marine operators. In this evolving landscape, six key players have emerged as leaders in remote trailer mover technology, combining advanced engineering, user-centric design, and proven reliability to dominate the competitive field.
Top 6 Remote Trailer Mover Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
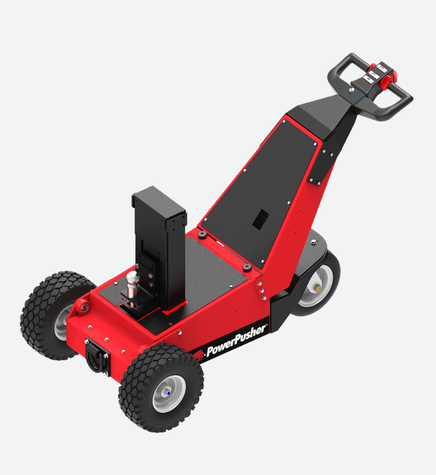
#1 Electric Trailer Movers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: powerpusher.com
Key Highlights: Our electric trailer movers and trailer dollys are the perfect way to easily and safely move and maneuver trailers, boats and more at your facility….
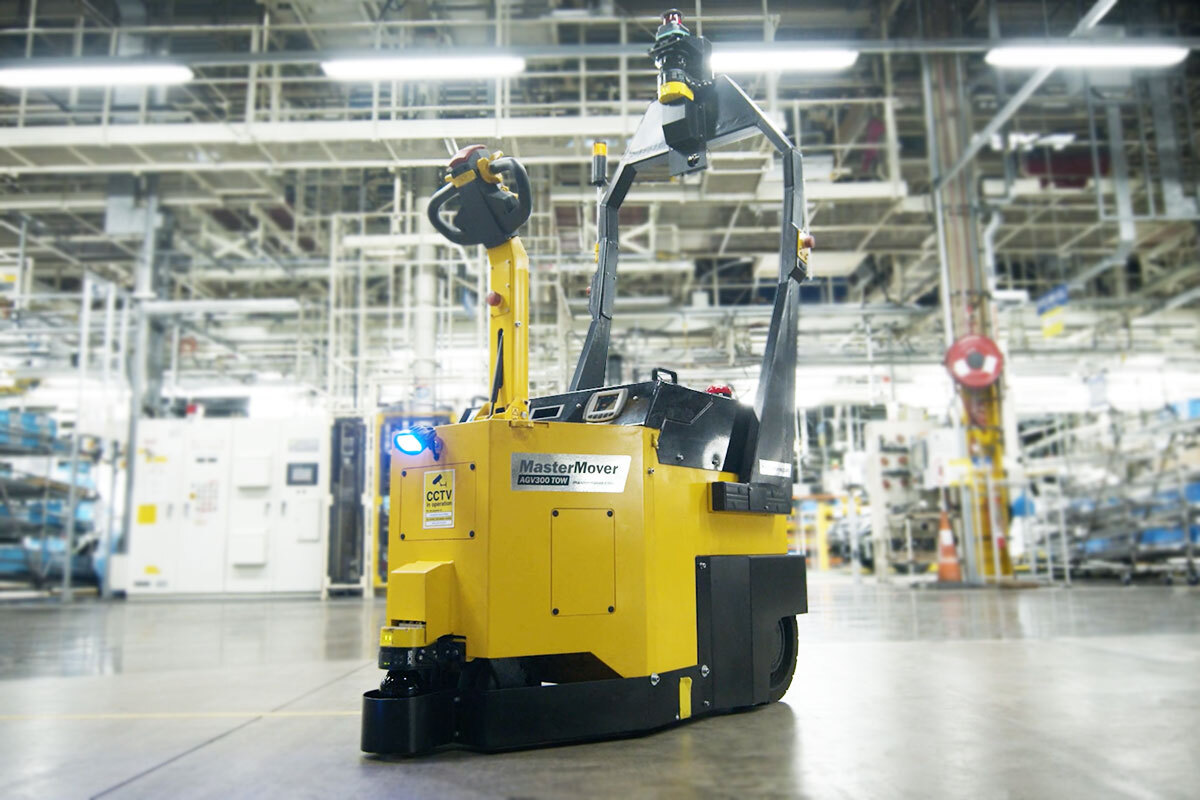
#2 Electric Trailer Mover Enables Safe Movement of …
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mastermover.com
Key Highlights: The Trailer Moving System is a versatile electric trailer dolly that is designed for moving lorry trailers through manufacturing processes and service centers….
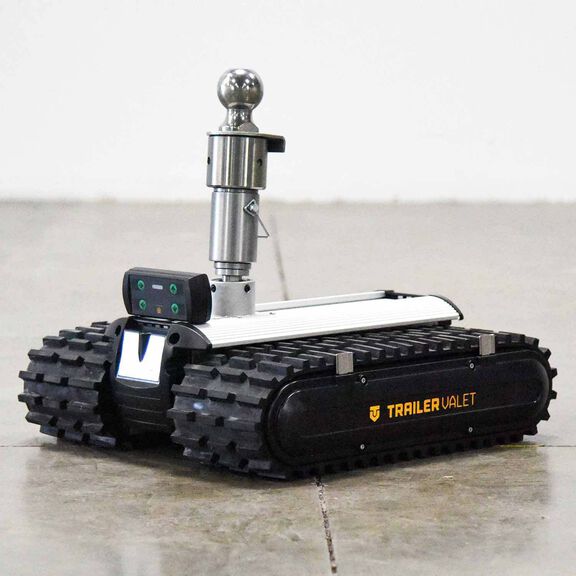
#3 9,000 lb Remote
Domain Est. 2010
Website: trailervalet.com
Key Highlights: Out of stock Rating 4.6 (29) The Trailer Valet RVR9 makes moving heavy trailers effortless with 9,000 lbs towing capacity and 450-900 lbs tongue weight. It connects via the coupl…
#4 Products
Domain Est. 2013
Website: purplelineusa.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading supplier to the RV market, offering a comprehensive range of remote trailer movers and one of the largest and most varied travel trailer ……
#5 Watch as the REMOTE TRAX Precisely Maneuvers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: remotetraxmover.com
Key Highlights: The Remote Trax is a manufactured home mover and a mobile home mover, it maneuvers manufactured homes around obstacles with precision and all by remote ……
#6 TRAX J5 Remote
Domain Est. 2020
Website: traxdolly.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsThe TRAX J5 Remote-Controlled Trailer Dolly is the ultimate trailer-moving solution, designed to handle trailers up to 15,000 lbs with precision and power….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Remote Trailer Mover

2026 Market Trends for Remote Trailer Movers
The remote trailer mover market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and expanding applications. Key trends shaping this growth include:
Increased Adoption of Smart and Connected Technology
By 2026, remote trailer movers will increasingly integrate smart features such as Bluetooth connectivity, mobile app control, GPS tracking, and diagnostic feedback. Consumers will demand real-time data on battery life, load status, and operational alerts. Integration with smart towing systems in pickup trucks and telematics platforms will enhance safety and convenience, particularly in commercial and fleet operations.
Expansion into Commercial and Industrial Applications
While initially popular in the recreational vehicle (RV) sector, remote trailer movers are gaining traction in commercial logistics, agriculture, and construction. Businesses are adopting these systems to improve yard efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance worker safety by minimizing manual trailer handling. This shift will drive demand for heavy-duty, scalable models capable of handling larger loads.
Focus on Battery Efficiency and Power Solutions
Advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state battery technology will lead to longer run times, faster charging, and lighter-weight systems. By 2026, eco-conscious consumers and businesses will prioritize energy-efficient models with sustainable components, pushing manufacturers to innovate in power management and recyclability.
Enhanced Safety and Automation Features
Safety will remain a core selling point. Future models will incorporate obstacle detection sensors, automatic braking, and precision control algorithms to prevent accidents during tight maneuvers. Some high-end systems may offer semi-autonomous docking capabilities, especially for large RVs and trailers, reducing user error and stress.
Growing DIY and Aftermarket Installation Demand
As awareness spreads and costs stabilize, the aftermarket segment will expand. Consumers will favor user-friendly, plug-and-play systems that can be easily installed on existing trailers. Online tutorials, modular designs, and broader compatibility with trailer types will fuel DIY adoption.
Market Consolidation and Competitive Differentiation
The market is expected to see consolidation, with larger players acquiring niche innovators. To stand out, brands will focus on differentiation through superior design, customer support, app ecosystems, and bundling with towing accessories. Price segmentation will broaden, offering options from budget-friendly models to premium, feature-rich systems.
Regulatory and Standardization Developments
As remote trailer movers become more prevalent, regulatory bodies may introduce safety and performance standards. Industry-wide certifications could emerge by 2026, increasing consumer confidence and streamlining product comparisons.
In summary, the 2026 remote trailer mover market will be defined by smarter, safer, and more versatile solutions catering to both recreational and commercial users. Innovation in connectivity, power, and automation will drive growth, making remote trailer movers a standard feature in modern towing ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Remote Trailer Mover (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a remote trailer mover—especially from overseas or lesser-known suppliers—can present significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate potential legal, operational, and financial issues.
Poor Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many low-cost remote trailer movers use substandard materials and components to reduce manufacturing costs. This often results in reduced durability, inconsistent performance, and premature mechanical or electrical failures. Motors may overheat, gearboxes can strip under load, and wireless remotes may suffer from signal interference or short range. Without rigorous third-party testing or certifications (e.g., IP ratings for water/dust resistance), buyers risk purchasing a product that fails under real-world conditions.
Lack of Safety Features and Compliance
Inferior models often lack essential safety mechanisms such as overload protection, emergency stop functions, or fail-safes during signal loss. Additionally, these products may not meet regional safety standards (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS), exposing buyers to liability and compliance issues. Non-compliant products can be seized at customs or banned from sale, leading to costly delays and reputational damage.
Inadequate Waterproofing and Environmental Resistance
Remote trailer movers operate in harsh environments—exposed to rain, mud, and temperature extremes. Many budget units boast “waterproof” claims without legitimate IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. A common pitfall is misrepresentation of IP67 or IP68 ratings without independent verification. Without proper sealing, moisture ingress can damage motors and electronics, leading to early failure.
Weak or Unreliable Wireless Remote Systems
The remote control system is critical for safety and usability. Low-quality units may use unstable frequencies, lack encryption, or have very limited range (often under 30 feet in real-world conditions). Some remotes are prone to signal dropouts or interference from other devices, increasing the risk of accidents during trailer movement.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that copy patented designs or use unauthorized technology puts buyers at serious legal risk. Many affordable remote trailer movers replicate features or外观 (appearance) protected by IP held by established brands. Purchasing such products—even unknowingly—can result in customs seizures, lawsuits, or injunctions, particularly in markets with strict IP enforcement (e.g., the U.S., EU).
Lack of Technical Documentation and Support
Suppliers of low-quality units often provide incomplete or inaccurate technical specifications, user manuals, or firmware details. This absence of documentation complicates installation, troubleshooting, and warranty claims. Additionally, poor after-sales support makes it difficult to resolve defects or obtain spare parts, increasing long-term ownership costs.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Certifications
Some suppliers falsely claim certifications (e.g., CE, FCC, IP ratings) by using forged documents or self-declaration without testing. Buyers who rely on these claims may discover too late that the product does not meet required standards. Always request verifiable test reports from accredited laboratories.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request product samples, verify certifications with independent labs, audit supplier facilities if possible, and consult legal counsel regarding IP risks. Prioritizing quality and compliance over initial cost can prevent costly failures and legal exposure in the long run.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Remote Trailer Mover
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements when using a Remote Trailer Mover (RTM) in industrial, warehouse, or distribution environments. RTMs enhance safety and efficiency but must be operated and maintained in accordance with regulatory and operational standards.
Equipment Specifications and Compatibility
Ensure the RTM is compatible with the trailers and vehicles in use. Verify:
– Weight capacity (GVWR compatibility)
– Hitch type (e.g., 2″ ball, pintle hook, or specialized coupling)
– Tire size and ground clearance
– Surface type suitability (concrete, asphalt, gravel, etc.)
Mismatched equipment can lead to operational failure or safety hazards.
Operator Training and Authorization
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate an RTM. Training must include:
– Proper startup and shutdown procedures
– Remote control operation (forward, reverse, turning, emergency stop)
– Load stability awareness
– Obstacle detection and collision avoidance
– Emergency response protocols
Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher sessions.
Workplace Safety Standards
Comply with OSHA and local safety regulations:
– Maintain clear paths free of personnel during operation
– Use warning signage in RTM operating zones
– Implement a “spotter” system if visibility is obstructed
– Prohibit unauthorized personnel from approaching moving trailers
Ensure the RTM is equipped with safety features such as:
– Emergency stop (E-stop) button
– Automatic braking on signal loss
– Obstacle detection sensors (if available)
Charging and Battery Management
Follow manufacturer guidelines for battery maintenance:
– Charge in designated, ventilated areas
– Use only approved chargers
– Inspect batteries for damage or leaks regularly
– Store charged batteries safely when not in use
Lithium-ion batteries must comply with transportation and fire safety codes (e.g., NFPA 855).
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
Conduct routine inspections and preventive maintenance:
– Daily: Check tires, lights, control responsiveness, and structural integrity
– Weekly: Inspect battery connections, hydraulic systems (if applicable), and remote control function
– Monthly: Perform full system diagnostics and lubrication
Keep a maintenance log for audit and compliance purposes.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to relevant standards, including:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (General Industry Standards)
– ANSI/ITSDF B56.1 (Safety Standard for Low Lift and High Lift Trucks)
– Local fire codes for battery storage
– Environmental regulations for battery disposal (e.g., EPA, local e-waste rules)
Verify that the RTM meets CE, UL, or other applicable product safety certifications.
Operational Procedures
Establish clear protocols for RTM use:
– Pre-operation safety checklists
– Designated operating zones and speed limits (typically ≤ 3 mph)
– Communication procedures between operators and spotters
– Weather restrictions (avoid use in rain or ice unless rated for such conditions)
Document procedures and ensure accessibility to all relevant staff.
Incident Reporting and Investigation
Implement a system to report and investigate any accidents, near misses, or equipment malfunctions. Actions include:
– Immediate cessation of operations after an incident
– Documentation of events, photos, and witness statements
– Root cause analysis and corrective actions
– Reporting to management and regulatory bodies if required
Storage and Security
When not in use:
– Store RTMs in a secure, dry, and locked area
– Remove batteries if storing long-term
– Protect remote controls from damage or unauthorized access
– Prevent exposure to extreme temperatures or moisture
Secure storage reduces theft risk and prolongs equipment life.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain organized records of:
– Operator certifications
– Training logs
– Maintenance and repair history
– Safety inspections
– Incident reports
These documents support compliance audits and insurance requirements.
By following this guide, organizations can safely integrate Remote Trailer Movers into their logistics operations while meeting legal, safety, and efficiency standards. Regular review and updates to policies ensure continued compliance as technology and regulations evolve.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Remote Trailer Mover
After evaluating various options, the decision to source a remote trailer mover should be guided by specific operational needs, budget considerations, and desired features such as control range, load capacity, maneuverability, and ease of installation. High-quality remote trailer movers enhance safety, reduce physical strain, and improve efficiency—especially in tight or challenging docking environments.
Brands like Fobo, Pro Series, and PullRite offer reliable models with advanced features such as app integration, precision controls, and robust motors. When sourcing, it is essential to prioritize durability, customer support, and warranty terms. Additionally, considering both budget-friendly and premium options allows for a balanced decision based on long-term value rather than upfront cost alone.
In conclusion, investing in a well-reviewed, properly matched remote trailer mover significantly improves trailer handling and user experience. Careful sourcing—factoring in compatibility with your trailer, user requirements, and reliability—will ensure optimal performance and satisfaction.