The global raw cashew nut market has seen consistent expansion, driven by rising demand for healthy snacks and plant-based protein sources. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of the nutritional benefits of cashews, expanding distribution channels, and surging demand in regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. As global production remains concentrated in West Africa—with major processing hubs in India and Vietnam—the competitive landscape is shaped by manufacturers capable of ensuring high-quality, traceable, and sustainably sourced raw cashew nuts. In this context, identifying the top raw cashew nut manufacturers becomes essential for buyers seeking reliability, scale, and compliance with international food safety standards.
Top 10 Raw Cashew Nut Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Manufacturer of Cashew Nuts & Organic Cashew by Shri Adinath …
Domain Est. 2024
Website: shriadinathcashew.com
Key Highlights: Shri Adinath Cashew Private Limited – Manufacturer of Cashew Nuts, Organic Cashew & Raw Cashew Nuts from Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. … S240 Cashew Nut · Rs 800 ……
#2 Western India Cashew Company
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1932
Website: wenders.com
Key Highlights: The Western India Cashew Company is a third-generation cashew-nut processing business. We are the legacy of the Dhanalaxmi Vilas Cashew Company founded in 1932….
#3 Raw Cashew Nuts
Domain Est. 2000
Website: rawcashewnuts.com
Key Highlights: Source markets for raw cashewnuts. The cashew nut, the third widely consumed edible tree nut, often thought to be a seed is actually……
#4 CASHEW INFORMATION
Domain Est. 2002
Website: cashews.org
Key Highlights: The cashew tree grows in tropical areas with an annual rainfall ranging from 400 to 4,000 mm, and it grows from sea level to an altitude of 1,000 m….
#5 Patel Agri Exports
Domain Est. 2013
Website: patelagriexport.in
Key Highlights: We are leading Cashew Processors, Exporters & Importers in India. We import Raw Cashew nuts from several regions of Africa and we carry out, in-house production ……
#6 Alphonsa Cashew Industries
Domain Est. 2014
Website: alphonsacashew.com
Key Highlights: Alphonsa Cashew Industries is one of the leading procurer, processor and exporter of Cashew Nuts from India. We have ownership or active engagement in all ……
#7 Keshar Cashewnuts
Domain Est. 2019
Website: kesharcashewnuts.com
Key Highlights: We are trusted importers of premium-quality raw cashew nuts from leading sources across India and Africa. Our strict selection process ensures only the finest ……
#8 Premium Organic Cashew Nuts I 100% Indian Cashews I AchalOrg
Domain Est. 2021
Website: achalorg.com
Key Highlights: 1-day returnsBuy 100% Indian organic cashew nuts. Organic cashews available in flavour, cashew butter, plain & dry roasted. Great for gifting, snacking or as ……
#9 Vietnamese Cashew Nuts
Domain Est. 2024
Website: vietnamcashewnuts.com
Key Highlights: We are a large-scale cashew import and export company. With three large factories in Binh Phuoc, Binh Duong and Dong Nai, we supply + 1000 Vietnamese and ……
#10 CPT CORP
Website: cptcorp.vn
Key Highlights: Our organic raw cashew nuts are collected from VietNamese farmers, especially in Binh Phuoc that cashew quality is the best in the world. Moreover, we are ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Raw Cashew Nut
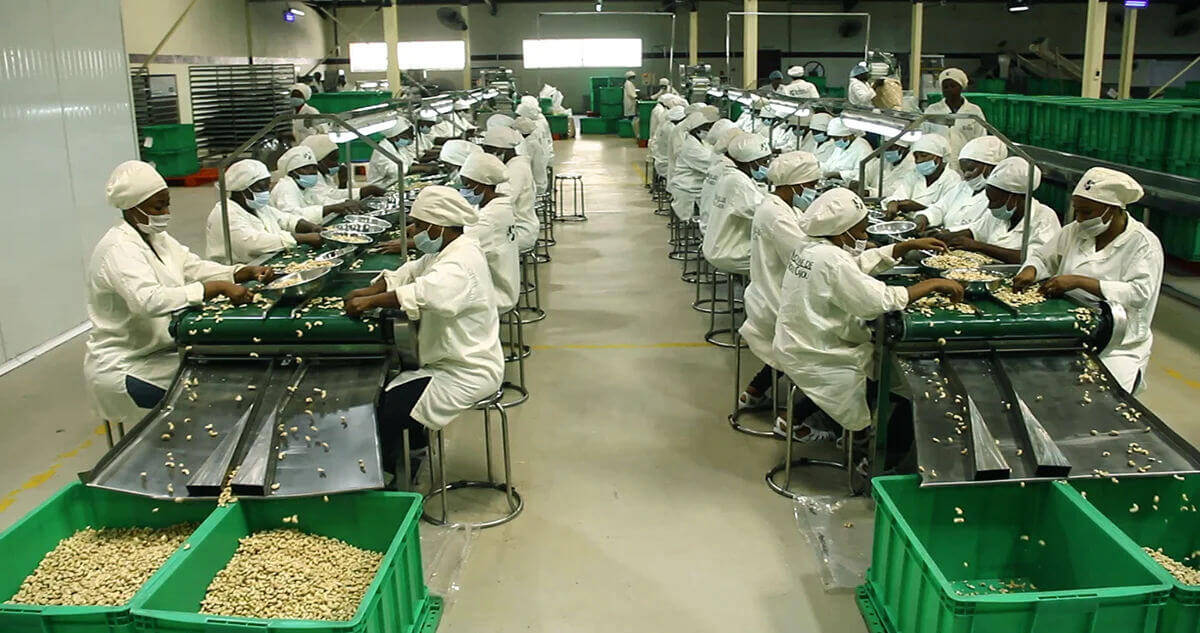

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Raw Cashew Nuts
The global raw cashew nut (RCN) market in 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of supply constraints, evolving demand dynamics, sustainability pressures, and geopolitical factors. Here’s an analysis of the key trends anticipated for that year:
-
Supply Tightness and Geopolitical Volatility:
- Ivory Coast Dominance & Weather Risks: Ivory Coast will likely remain the world’s largest producer, but its output will be highly susceptible to climate volatility (erratic rainfall, potential droughts) and logistical challenges within the country. Any significant shortfall here will ripple through the global market, tightening supply and supporting prices.
- West African Production Uncertainty: Other major producers like Guinea, Nigeria, and Benin face similar climate risks and potential political instability. Investment in orchard rejuvenation and processing is often inconsistent, limiting significant yield increases.
- India’s Shifting Role: India will continue to be a major processor but a declining producer. Its reliance on imports (primarily from Africa) will remain high, making it sensitive to global RCN price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Domestic production stagnation is expected to continue.
- Emerging Producers (Cautious Growth): Countries like Cambodia, Vietnam (though focused on processing), and parts of Latin America (e.g., Brazil, Colombia) may show incremental growth in production. However, they are unlikely to offset potential shortfalls from West Africa significantly by 2026, acting more as marginal suppliers.
-
Demand Resilience with Shifting Patterns:
- Sustained Global Appetite: Underlying demand for cashews (driven by health trends, snacking, and culinary use) is expected to remain robust globally, particularly in North America, Europe, and increasingly in Asia.
- Processing Capacity Expansion (Asia & Africa): Vietnam will likely maintain significant processing capacity, but African nations (especially Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria) are actively pushing to retain more value by expanding domestic shelling capacity. This increases competition for RCN within Africa itself, potentially diverting supply away from traditional exporters like India and Vietnam.
- Premiumization & Niche Markets: Demand for high-grade, traceable, and specialty RCN (e.g., organic, fair trade, specific origin) will grow. Buyers are increasingly willing to pay premiums for quality, sustainability, and ethical sourcing, influencing sourcing strategies.
-
Price Volatility and Cost Pressures:
- Upward Pressure: The combination of constrained supply growth, rising logistics costs (fuel, shipping), increasing labor costs in processing hubs (especially India and Vietnam), and higher input costs (fertilizers) will create persistent upward pressure on RCN prices.
- Volatility: Prices are expected to remain volatile, reacting sharply to crop reports from West Africa, weather events, and fluctuations in the cost of competing commodities or transportation. Hedging and long-term contracts may become more prevalent.
-
Sustainability and Traceability Imperatives:
- Non-Negotiable for Major Buyers: Large international buyers (retailers, food manufacturers) will demand verifiable proof of sustainable sourcing, ethical labor practices (especially concerning worker welfare in processing), and environmental stewardship (deforestation, water use). Certifications (e.g., Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance, Organic) will become increasingly important market access tools.
- Traceability Investment: Significant investment in blockchain and other traceability technologies will accelerate, allowing buyers to track RCN from farm to factory, meeting consumer and regulatory demands for transparency.
- Focus on Origin: “Origin storytelling” will gain importance, with consumers and brands valuing specific regional characteristics and supporting community development initiatives linked to the cashew trade.
-
Logistics and Trade Dynamics:
- Supply Chain Resilience: The industry will continue efforts to build more resilient supply chains after recent global disruptions. Diversification of sourcing origins and shipping routes will be a key strategy.
- African Export Competition: As African processing capacity grows, governments may implement policies (e.g., higher export taxes on RCN, incentives for domestic processing) to encourage local value addition. This could reduce the volume of RCN available for export from key producing nations, further tightening the global market.
- Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility, particularly for West African Franc (XOF) and Indian Rupee (INR), will impact the competitiveness of RCN exports and import costs for processors.
Conclusion:
The 2026 raw cashew nut market will likely be characterized by persistent supply tightness, driven by climate vulnerability in West Africa and limited production growth elsewhere, colliding with resilient global demand. This fundamental imbalance, combined with rising costs and logistics complexities, will support elevated and volatile prices. The most significant trend will be the intensifying focus on sustainability, traceability, and ethical sourcing, becoming critical differentiators and requirements for market access. Simultaneously, the geopolitical shift towards African value addition will reshape trade flows, reducing exportable RCN surplus and increasing competition within the continent. Success for stakeholders will depend on securing reliable, traceable supply chains, managing cost and price volatility, investing in sustainability, and adapting to the evolving landscape of African production and processing policies.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Raw Cashew Nuts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing raw cashew nuts (RCN) involves navigating several challenges related to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) considerations—especially when dealing with proprietary processing methods or branded varieties. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate risks and ensure reliable supply chains.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Nut Size and Grading
Raw cashew nuts vary significantly in size (e.g., W180, W240, W320), and suppliers may misrepresent grades or provide mixed batches. Inconsistent sizing affects processing efficiency and final product value, especially for premium markets.
2. Poor Shell Quality and High Breakage
Damaged or broken kernels due to poor harvesting, drying, or handling reduce yield and quality. High levels of splits, shrivels, or insect damage indicate inadequate post-harvest practices, impacting both appearance and shelf life.
3. Moisture Content Variability
Excessive moisture (>8%) can lead to mold growth and aflatoxin contamination, while too little moisture causes brittleness and breakage during shelling. Inadequate moisture control during storage or transport compromises food safety and quality.
4. Contamination Risks (Aflatoxins, Pesticides, Residues)
RCNs are prone to aflatoxin contamination if stored in humid conditions. Sourcing from regions with poor agricultural practices may also expose buyers to pesticide residues or chemical contaminants, leading to failed import inspections.
5. Adulteration and Mislabeling
Some suppliers may mix lower-grade nuts with higher grades, or include foreign materials (stones, husks). This not only affects quality but can damage processing equipment and erode buyer trust.
6. Seasonal Availability and Supply Gaps
Cashew harvesting is seasonal (peak varies by region: e.g., Jan–Apr in West Africa, Apr–Jul in India/Vietnam). Poor planning can lead to supply shortages or price volatility when demand exceeds seasonal output.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Varieties
Some high-yield or disease-resistant cashew cultivars (e.g., hybrid clones developed by research institutes) are protected. Sourcing from unauthorized growers may infringe on plant breeder rights or violate licensing agreements.
2. Misuse of Geographical Indications (GIs)
Certain cashew origins (e.g., “Kollam Cashews” in India) may have GI tags. Sourcing nuts labeled with such indications without proper certification misleads consumers and risks legal action for false branding.
3. Replication of Processing Techniques
Buyers developing unique shelling, peeling, or roasting methods may face IP leakage if suppliers reverse-engineer processes or share trade secrets with competitors—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement.
4. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Without blockchain or certified traceability systems, verifying the origin and authenticity of RCN becomes difficult. This opens doors to IP fraud, such as passing off generic nuts as specialty or organic-certified products.
5. Contractual Gaps in IP Ownership
When working with contract processors or co-packers, failure to define IP ownership in agreements can result in disputes over formulas, packaging designs, or process innovations developed during collaboration.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP risks—through rigorous supplier vetting, third-party testing, clear contracts, and certification compliance—buyers can build more resilient and ethical raw cashew nut supply chains.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Raw Cashew Nut
Overview of Raw Cashew Nut Trade
Raw Cashew Nuts (RCN) are a globally traded agricultural commodity primarily sourced from Africa and Southeast Asia, with India, Vietnam, and the United States as major processing and re-export hubs. Efficient logistics and strict compliance with international standards are essential due to the perishable nature, quality sensitivity, and regulatory requirements associated with RCN shipments.
Harvesting and Initial Handling
RCNs must be harvested at peak maturity and processed promptly to prevent spoilage. After extraction from the cashew apple, nuts are typically sun-dried or mechanically dried to reduce moisture content to 6–8%. Proper handling at the farm level—including sorting to remove damaged or moldy nuts—ensures compliance with quality standards and prevents contamination during transport.
Packaging Requirements
RCNs are commonly packed in jute or polypropylene bags (50–60 kg per bag) for international shipping. Vacuum-sealed or moisture-barrier liners may be used to protect against humidity. For premium shipments, bulk containers with controlled atmosphere or food-grade liners are employed. Packaging must comply with International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPM-15) if wooden pallets are used.
Storage Conditions
RCNs should be stored in cool, dry, and well-ventilated facilities to prevent rancidity, insect infestation, and mold growth. Ideal storage conditions include temperatures below 25°C and relative humidity under 70%. Warehouses must be pest-controlled and free from contaminants. Stock rotation (FIFO—First In, First Out) is critical to maintain freshness.
Transportation Logistics
RCNs are typically transported via sea freight in 20’ or 40’ dry container loads. Refrigerated (reefer) containers are used only if required by destination regulations or prolonged transit times. Containers must be clean, dry, and free of异味 (odors). Desiccants are often placed inside to manage internal humidity. Overland transport from farms to ports requires covered trucks to protect against rain and contamination.
Export Documentation
Key export documents for RCN include:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading (or Air Waybill)
– Certificate of Origin
– Phytosanitary Certificate (issued by national plant protection organization)
– Fumigation Certificate (if required)
– Certificate of Analysis (for moisture, aflatoxin, and purity levels)
Phytosanitary and Food Safety Compliance
RCNs must comply with the importing country’s phytosanitary regulations. Most countries require a phytosanitary certificate confirming the absence of pests and diseases. Additionally, RCNs are subject to food safety standards:
– EU: Must meet aflatoxin limits (max 10 µg/kg for total aflatoxins, 5 µg/kg for B1)
– USA (FDA): Monitors for aflatoxins under the Import Alert 16-128
– GCC countries: Require halal certification and aflatoxin testing
Regular laboratory testing for aflatoxins, moisture, and foreign matter is mandatory.
Import Regulations by Key Markets
- European Union: Requires prior notification via TRACES NT, compliance with EC 1698/2005, and registration of non-EU processors.
- United States: Subject to FDA food facility registration, Prior Notice submission, and potential CBP inspection.
- India: Requires registration under the Cashew Export Promotion Council (CEPC) and adherence to Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) standards.
- China: Needs GACC registration for foreign producers and a health certificate from the exporting country.
Quality Standards and Grading
RCNs are graded based on nut size (e.g., W180, W210, W240, WP), shell color, and defect levels. The ISO 9560:2019 standard provides international grading guidelines. Buyers often specify exact size and quality requirements in contracts. Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Intertek) is common before shipment.
Risk Management
Key risks include:
– Aflatoxin contamination due to poor drying or storage
– Moisture damage during transit
– Delays at ports due to non-compliant documentation
– Price volatility in global markets
Mitigation includes pre-shipment inspection, proper drying, insurance coverage, and adherence to Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, CIF).
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Increasing demand for responsibly sourced RCNs has led to certifications such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, and Organic (EU, USDA). Traceability systems—from farm to export—are encouraged to ensure compliance with ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) standards and meet retailer requirements.
Conclusion
Successful RCN logistics and compliance require coordination across production, quality control, documentation, and regulatory adherence. Staying updated on international standards and investing in proper infrastructure ensures market access and reduces trade barriers. Regular audits and partnerships with certified suppliers enhance reliability and competitiveness in the global cashew market.
Conclusion on Sourcing Raw Cashew Nuts
Sourcing raw cashew nuts requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. As global demand for cashews continues to rise, establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers in key producing countries—such as Côte d’Ivoire, India, Vietnam, and Tanzania—is crucial. Buyers must prioritize traceability, food safety standards, and ethical sourcing practices to meet consumer and regulatory expectations.
Furthermore, understanding market fluctuations, seasonal availability, and geopolitical factors affecting production and export can help mitigate risks and ensure consistent supply. Investing in long-term partnerships, direct sourcing models, and possibly vertical integration can enhance control over quality and sustainability. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for raw cashew nuts not only supports business growth but also contributes to the empowerment of farming communities and the long-term viability of the cashew industry.