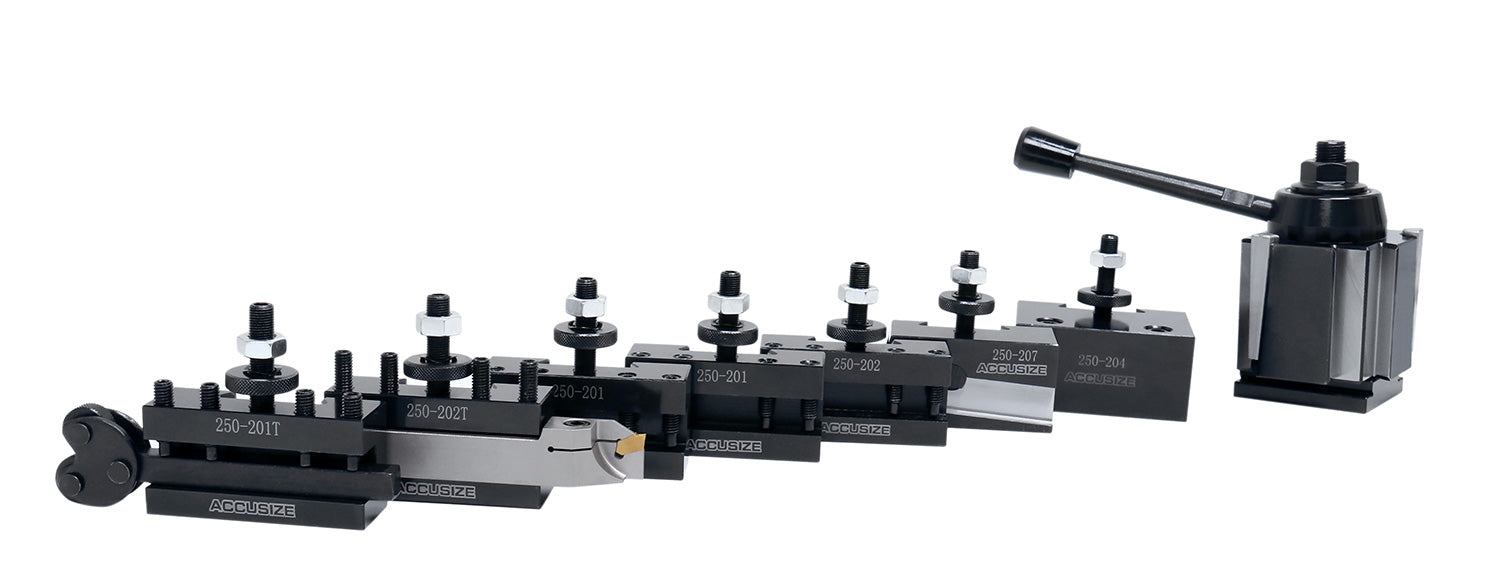
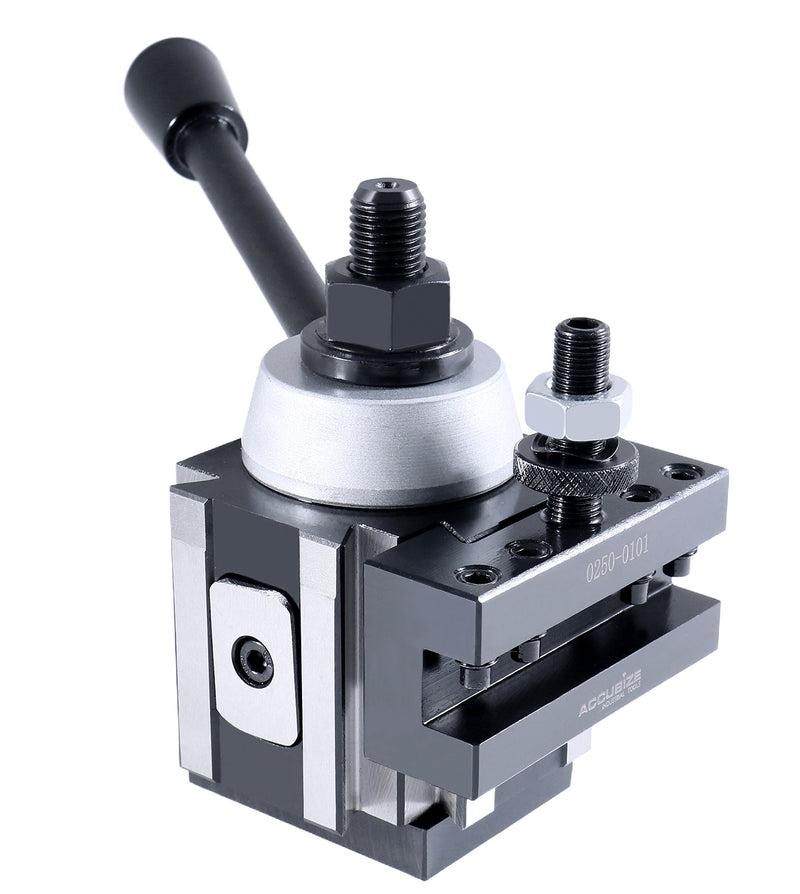
The global tooling systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes. According to Grand View Research, the global machine tools market size was valued at USD 78.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is largely attributed to the rising adoption of automation, CNC machinery, and the need for rapid tool changeover systems that minimize downtime. Quick tool change posts—critical components in stamping, press brake, and metal forming applications—are gaining prominence as manufacturers prioritize operational agility and throughput. As industries from automotive to aerospace seek faster setup times and improved repeatability, the demand for high-performance quick tool change solutions continues to climb. Based on market trends, technological innovation, and customer review analysis, here are the top 7 quick tool change post manufacturers leading this transformation.
Top 7 Quick Tool Change Post Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 High-Quality Cutting Tools
Domain Est. 1996
Website: widia.com
Key Highlights: WIDIA offers a wide range of cutting tools and solutions for industrial applications. Explore their website for high-quality tools and expert advice….
#2 Tooling Shop & Milling Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: doriantool.com
Key Highlights: Tooling shop with 8000 USA-made machine shop tools and milling supplies: tool posts & holders, tool presetters, knurling tools, angle heads, vflange, ……
#3 Workholding Equipment & Automation Tooling Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: destaco.com
Key Highlights: Camco Conveyors / Robohand Slides. DESTACO’s linear positioning solutions deliver accurate, reliable motion control for automation and manufacturing processes….
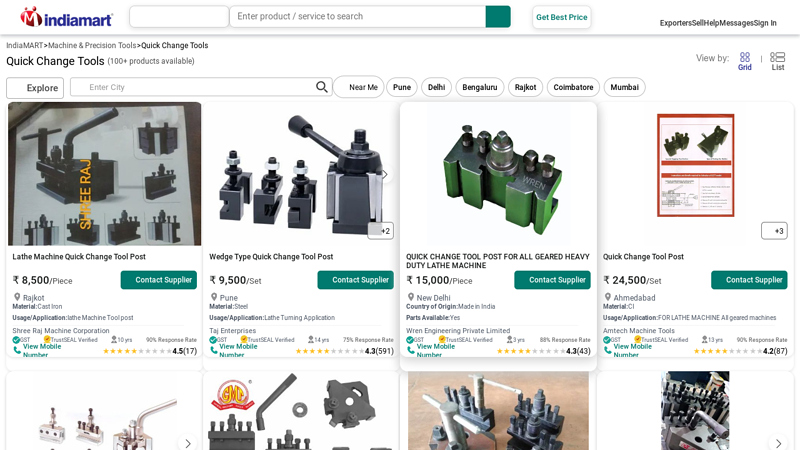
#4 Lathe Machine Quick Change Tool Post
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dir.indiamart.com
Key Highlights: WREN “Quick Change Tool Post” (QCTP) is a specialized tool holder designed for lathes, allowing for rapid and easy switching between different cutting tools ……
#5
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dmctools.com
Key Highlights: For 75 years, DMC® has manufactured tooling for mission-critical electrical systems in aerospace and defense, rail, marine, and several other industries….
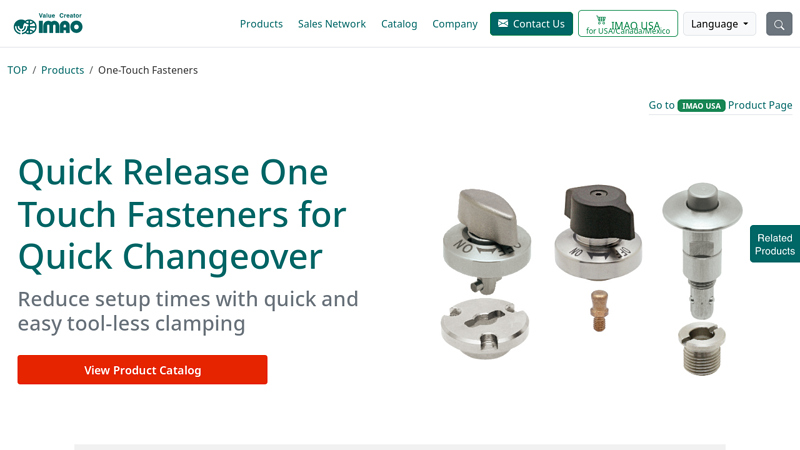
#6 Quick Release Fasteners – Quarter Turn & Ball Lock Fasteners
Domain Est. 2000
Website: imao.com
Key Highlights: One-Touch Fasteners are quick release fasteners such as quarter turn fasteners and ball lock fasteners that reduce setup time in machine changeover….
#7 Lathe Tool Accessories, Hand Tools & Woodworking Tools
Domain Est. 2002
Website: garvintools.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturing Lathe tool accessories, woodworking Tools, cutting, Vices and hand tools in India … Quick Change Tool postsQuick Change Toolposts. Quick Change ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Quick Tool Change Post
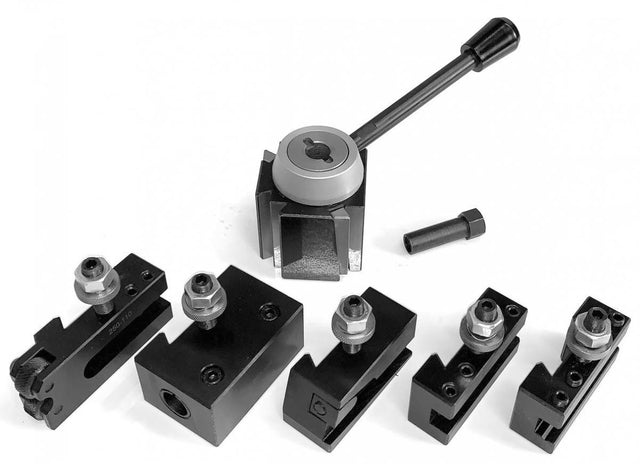

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Quick Tool Change Posts
The market for Quick Tool Change (QTC) posts is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by automation demands, precision manufacturing needs, and technological integration. Here’s a breakdown of key trends shaping this specialized segment of industrial tooling:
1. Accelerated Adoption in High-Mix, Low-Volume (HMLV) Manufacturing:
As manufacturers increasingly shift toward flexible production models, the ability to rapidly switch between jobs becomes critical. QTC posts enable swift transitions between different tools or workholding setups on CNC machines, robots, and automated cells. By 2026, sectors like aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and custom job shops will rely heavily on QTC systems to maintain profitability in HMLV environments, reducing non-cutting time and boosting machine utilization.
2. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and IIoT:
QTC posts will increasingly incorporate sensors and connectivity features, becoming part of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of “smart” QTC systems that monitor tool engagement force, position accuracy, thermal drift, and wear. These systems will feed real-time data into manufacturing execution systems (MES) and digital twins, enabling predictive maintenance, quality assurance, and process optimization.
3. Standardization and Interoperability:
To support flexible automation across multi-vendor environments, industry-wide standardization of QTC interfaces (e.g., mechanical coupling, communication protocols) will gain momentum. By 2026, modular QTC systems compliant with open standards like OPC UA or MTConnect will dominate, allowing seamless integration between machine tools, robots, and tool changers from different manufacturers.
4. Growth in Robotic and Collaborative Automation:
The rise of robotics—especially collaborative robots (cobots)—in machining and assembly applications will drive demand for compact, lightweight, and highly repeatable QTC posts. These systems allow robots to switch end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) autonomously, expanding their versatility. By 2026, expect specialized QTC solutions optimized for cobot payloads and safety requirements.
5. Focus on Ultra-High Precision and Repeatability:
Advancements in micromachining and additive manufacturing post-processing will demand QTC systems with micron-level repeatability. Innovations in materials (e.g., ceramic bearings, composite housings) and locking mechanisms (e.g., hydraulic expansion, magnetic clamping) will push performance boundaries, ensuring consistent accuracy across thousands of change cycles.
6. Sustainability and Lifecycle Efficiency:
As sustainability becomes a competitive differentiator, manufacturers will favor QTC systems designed for longevity, repairability, and energy efficiency. By 2026, lifecycle analysis and total cost of ownership (TCO) will influence procurement decisions, favoring modular designs that allow easy part replacement and reduce waste.
7. Regional Market Expansion:
While North America and Western Europe remain strong markets due to advanced manufacturing infrastructure, rapid industrial automation in Asia-Pacific—particularly India, Vietnam, and Thailand—will drive new demand. Localized production of QTC components and partnerships with regional automation integrators will be key growth strategies by 2026.
In summary, the 2026 market for Quick Tool Change posts will be defined by intelligence, interoperability, and flexibility, positioning QTC technology as a cornerstone of agile, data-driven manufacturing ecosystems.
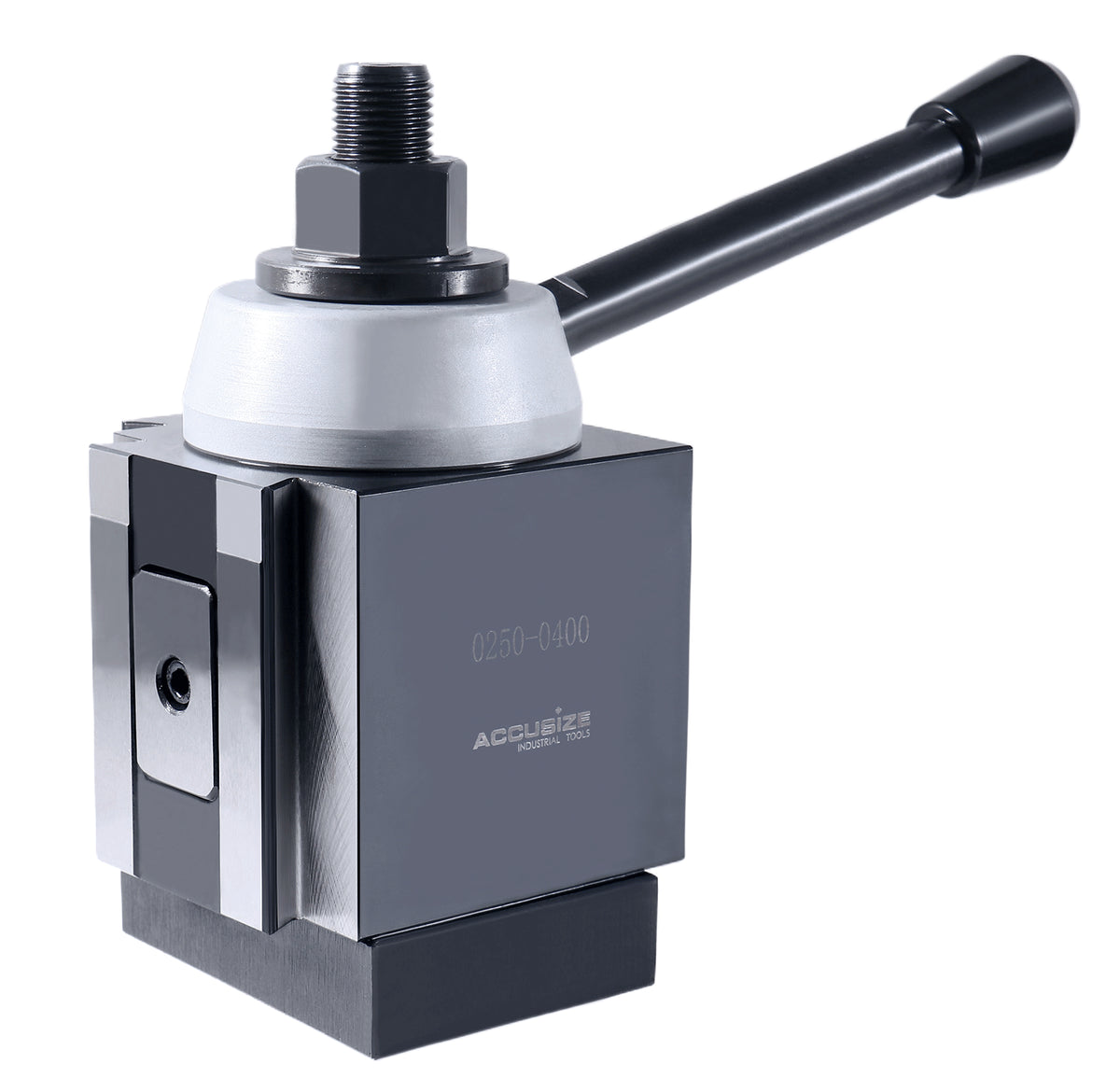

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Quick Tool Change Post (Quality & IP Concerns)
Sourcing a Quick Tool Change Post (QTCP) — a critical component in automated manufacturing and CNC systems — requires careful evaluation to avoid compromising performance, safety, and intellectual property (IP). Below are common pitfalls related to quality and IP that buyers should be aware of.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues is sourcing QTCPs made from substandard materials or with inadequate manufacturing tolerances. Low-quality posts may use inferior steel alloys or fail to undergo proper heat treatment, leading to premature wear, deformation, or catastrophic failure under operational stress. Poor machining precision can result in misalignment, leakage in hydraulic/pneumatic systems, or inconsistent tool engagement, directly impacting production accuracy and machine uptime.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Many off-brand or generic QTCPs do not conform to recognized industry standards such as ISO, DIN, or ANSI. This lack of compliance can lead to incompatibility with existing tooling systems, safety risks, and voided warranties on the host machine. Buyers may also face difficulties in obtaining certifications required for regulated industries like aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
Inadequate Testing and Quality Control
Reputable manufacturers subject QTCPs to rigorous performance testing, including cycle testing, load testing, and leak testing. However, low-cost suppliers often skip or minimize these processes. Without proper validation, the long-term reliability of the QTCP cannot be guaranteed, increasing the risk of unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
A significant IP risk arises when suppliers offer QTCPs that closely mimic patented designs from leading brands (e.g., Staudt, SBS, or Hainbuch). These products may be reverse-engineered without licensing, infringing on intellectual property rights. Purchasing such components can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement. Additionally, counterfeit parts often lack documentation, traceability, and technical support.
Absence of Technical Documentation and IP Transparency
Reliable suppliers provide detailed specifications, installation guides, and compliance documentation. When sourcing QTCPs, the absence of these materials — or vague claims about design origins — can indicate IP infringement or poor engineering practices. Buyers should request proof of design ownership or licensing agreements, particularly when the product appears to replicate a well-known proprietary system.
Hidden Costs from Downtime and Replacement
While low-cost QTCPs may appear economical upfront, poor quality often results in frequent failures, increased maintenance, and production delays. The total cost of ownership can far exceed that of a higher-quality, legally compliant alternative. Furthermore, IP-related disputes can lead to product recalls, legal fees, and reputational damage.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), transparent design processes, and clear IP compliance. Conducting supplier audits, requesting test reports, and consulting legal counsel when considering close replicas of patented designs are essential steps in responsible sourcing.
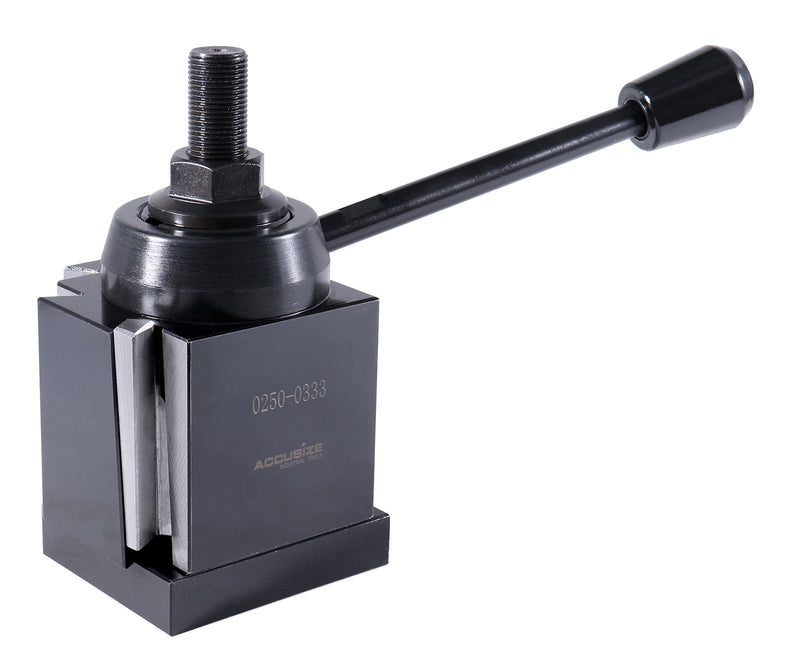

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Quick Tool Change Post
Proper logistics and compliance management are essential for the safe, efficient, and legally sound operation of Quick Tool Change (QTC) systems in industrial environments. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure smooth integration, regulatory adherence, and operational reliability.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Ensure QTC components are transported using appropriate methods to prevent damage. Use protective packaging for electrical connectors, hydraulic lines, and precision alignment features. During shipping and on-site movement, secure all parts to avoid shifting or impact. Follow manufacturer-recommended lifting guidelines and use certified rigging equipment when handling heavy tool changers or end-of-arm tooling.
Installation and Integration Procedures
Install QTC systems according to the manufacturer’s specifications and site safety standards. Verify compatibility with existing robotic arms, control systems, and power sources. All hydraulic, pneumatic, and electrical connections must be made by qualified personnel following local codes (e.g., NEC, IEC). Perform post-installation alignment checks and functional tests before commissioning.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Adhere to all applicable regulations, including but not limited to:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 – General industry safety standards, particularly machine guarding and lockout/tagout (LOTO)
– ANSI/RIA R15.06 – Safety requirements for industrial robots and robot systems
– ISO 10218 – International standards for robot safety
– ATEX/IECEx (if applicable) – For operations in explosive environments
– Local electrical and pressure system codes
Ensure all QTC components carry required certifications (e.g., CE, UL) and maintain documentation for audit purposes.
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
Implement a preventive maintenance program tailored to the QTC system’s usage frequency and operating environment. Key tasks include:
– Weekly inspection of coupling mechanisms for wear or contamination
– Monthly verification of alignment pins, seals, and fluid connections
– Quarterly calibration of sensors and communication signals
– Annual full system review and replacement of consumable parts
Document all inspections and repairs in a centralized maintenance log.
Personnel Training and Safety Protocols
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate or service QTC systems. Training must cover:
– Safe tool change procedures
– Emergency stop functions
– LOTO protocols during maintenance
– Hazard recognition (pinch points, high pressure, electrical risks)
Provide refresher training annually or after system modifications.
Environmental and Waste Management
For QTC systems using hydraulic fluids or coolants, implement spill containment and proper disposal procedures in accordance with EPA and local environmental regulations. Use drip trays during tool changes and recycle used fluids through certified vendors. Monitor for leaks and address immediately to prevent environmental contamination.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain up-to-date records including:
– Equipment manuals and schematics
– Risk assessments and safety certifications
– Maintenance logs and repair history
– Operator training records
– Incident reports (if applicable)
Store documentation digitally with secure backups and ensure easy access for audits or compliance checks.
Emergency Response Preparedness
Develop and post emergency procedures specific to QTC failures, such as:
– Tool detachment during operation
– Hydraulic/pneumatic line rupture
– Communication failure between robot and tool
Ensure emergency shutoff valves and lockout points are clearly marked and accessible. Conduct drills annually to verify response readiness.
By following this guide, facilities can maximize the efficiency of Quick Tool Change systems while ensuring full compliance with safety, environmental, and operational standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a quick tool change system is a strategic investment that enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves overall productivity in manufacturing and production environments. By carefully evaluating key factors such as compatibility with existing machinery, reliability, ease of maintenance, and total cost of ownership, businesses can select a solution that meets their specific needs. Partnering with reputable suppliers and leveraging industry expertise ensures access to high-quality components and ongoing support. Ultimately, implementing an effective quick tool change system streamlines processes, increases flexibility, and contributes to a more agile and competitive operation.