Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Quality Focused China Sourcing

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Clusters for Quality-Focused Procurement (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
China’s manufacturing landscape has decisively shifted from cost-driven to quality-driven sourcing. By 2026, 78% of global buyers prioritize verified quality systems, compliance traceability, and technical specialization over nominal unit costs (SourcifyChina Procurement Index 2025). This report identifies high-integrity industrial clusters where quality outcomes align with global standards (ISO 13485, IATF 16949, FDA 21 CFR Part 820), reducing total cost of quality (TCOQ) by 22–35% versus legacy low-cost regions. Critical success factors now include embedded QA protocols, automation maturity, and supply chain transparency—not just price.
Key Quality-Focused Industrial Clusters: 2026 Strategic Map
China’s “quality clusters” are concentrated in regions with mature supplier ecosystems, stringent local compliance enforcement, and deep engineering talent pools. Avoid commoditized hubs (e.g., parts of Fujian, Hebei) where price competition erodes quality control.
| Province/City | Core Specializations | Quality Differentiators | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen (Electronics/R&D), Dongguan (Precision Mfg), Guangzhou (Automotive) | • Highest density of ISO-certified Tier 1 suppliers (92% of Shenzhen electronics) • Embedded AI-driven QA (e.g., in-cam visual inspection) • Fastest NPI-to-volume ramp (18–25 days avg.) |
High-tech, medical devices, automotive, premium consumer electronics |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo (Mechanical), Yiwu (Consumer Goods), Hangzhou (Smart Hardware) | • Dominance in process-certified SMEs (85% hold IATF/ISO 9001) • Agile micro-factories with batch-size flexibility • Strong textile/apparel compliance (OEKO-TEX, BSCI) |
Mid-to-high-end consumer goods, machinery, sustainable textiles |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou (Semiconductors), Wuxi (Industrial Automation), Nanjing (Aerospace) | • Highest concentration of German/Japanese JV factories • Metrology labs within 50km radius (e.g., Suzhou Industrial Park) • Strict VOC emission controls (exceeds EU norms) |
Industrial equipment, semiconductors, aerospace components |
| Shanghai | (Cross-province R&D/Engineering Hub) | • 68% of China’s medical device OEMs with FDA QSR compliance • AI-powered supply chain risk monitoring (e.g., blockchain traceability) • Talent pool: 40% engineers hold advanced degrees |
Regulated products (medical, pharma, aviation) |
| Emerging: Sichuan | Chengdu (New Energy), Chongqing (EV Components) | • Rising EV/battery cluster with UL/IEC-certified testing centers • Government-mandated supplier audits for Tier 2+ • 30% lower labor turnover vs. coastal hubs |
EV components, renewable energy systems |
Critical Shift (2023–2026): Quality is now measured by failure rate avoidance (e.g., PPM < 50 for automotive) and compliance velocity (time to resolve audit findings). Clusters with integrated testing infrastructure (e.g., Suzhou) reduce corrective action time by 65% versus fragmented supply chains.
Regional Comparison: Quality vs. Cost vs. Speed (2026 Baseline)
Scoring Methodology: 1 (Low) to 5 (High) | Data Source: SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Database (2,100+ verified factories)
| Metric | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 2.8 | 3.5 | 3.2 | Guangdong commands 8–12% premium for electronics due to R&D density. Zhejiang offers best value for mechanical parts (±5% vs. Vietnam). |
| Quality | 4.7 | 4.3 | 4.5 | Guangdong leads in tech sectors (defect rates 0.12% vs. national avg. 0.38%). Jiangsu excels in dimensional precision (±0.005mm capability). |
| Lead Time | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.8 | Zhejiang’s micro-factories enable 15-day lead times for <500-unit batches. Guangdong lags slightly due to export volume congestion. |
| Compliance Risk | 1.2 | 1.8 | 1.5 | Lower = Better. Guangdong has fewest non-conformities in FDA/CE audits (0.7% failure rate vs. 2.4% national avg). |
| TCOQ Advantage | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | Guangdong reduces total costs for complex goods via fewer defects/rework. Zhejiang optimal for cost-sensitive quality (e.g., tools, hardware). |
Key Insight: A 10% price premium in Guangdong for medical molds yields 34% lower TCOQ versus lower-cost regions due to zero field failures (2025 case study: $2.1M savings over 500k units).
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Map Quality Requirements to Clusters:
- Regulated goods (medical/automotive): Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen) or Jiangsu (Suzhou) for certified cleanrooms and audit-ready documentation.
- Consumer goods with ESG demands: Target Zhejiang (Ningbo) for SMETA-certified factories and circular material sourcing.
- Demand Embedded QA Protocols: Specify in-process controls (e.g., SPC charts, real-time material traceability) in RFPs—not just final inspection.
- Leverage Cluster Synergies: Combine Shanghai’s engineering talent with Jiangsu’s production for complex NPIs (reduces time-to-market by 28%).
- Audit for Capability, Not Just Compliance: Verify actual defect containment systems (e.g., 8D reports within 24h) vs. paper certifications.
“In 2026, the cheapest unit cost is irrelevant if it triggers a recall. Quality clusters pay for themselves in risk mitigation.”
— SourcifyChina Supplier Risk Index, Q4 2025
Risks to Monitor
- Geopolitical: US/EU tariffs targeting “non-transparent” suppliers (2026 focus: Xinjiang-linked materials). Mitigation: Source from clusters with full blockchain traceability (e.g., Shanghai).
- Labor Shift: Guangdong facing 5–7% annual wage growth; invest in automation-ready partners.
- Green Compliance: EU CBAM carbon tariffs (2026) will penalize clusters without verified emission data (Jiangsu/Shanghai lead here).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: All data validated via SourcifyChina’s 2026 China Supplier Integrity Index (CSII) and on-ground audit network.
Next Steps: Request our Cluster-Specific Supplier Scorecard for your category (e.g., medical devices, EV components) at sourcifychina.com/2026quality.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use. Redistribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Quality-Focused China Sourcing – Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing high-quality products from China remains a strategic priority for procurement leaders. Achieving consistent quality requires a structured approach to technical specifications, compliance standards, and defect prevention. This report outlines the critical quality parameters, essential certifications, and actionable strategies to mitigate common quality risks in China-sourced goods.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Material Specifications
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and compliance. Procurement managers must define precise material requirements in sourcing contracts.
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Specify exact grade (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel, ABS vs. PC plastic) | Material Test Reports (MTR), Spectrometry |
| Purity & Composition | Define acceptable impurities (e.g., <0.03% lead in plumbing fixtures) | Lab testing (ICP-MS, GC-MS) |
| Traceability | Batch-level traceability for raw materials | Supplier documentation, QR codes/Batch logs |
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing ensures fit, function, and interchangeability.
| Product Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Measurement Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Calipers, Optical comparators |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm to ±0.5 mm | Laser scanners, Go/No-Go gauges |
| Electronics (PCBA) | ±0.075 mm (fine-pitch components) | Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) |
Best Practice: Include Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) drawings in technical packages.
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
Procurement managers must verify supplier compliance with international standards based on end-market regulations.
| Certification | Scope | Relevance | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU safety, health, environmental requirements | Mandatory for electronics, machinery, medical devices in EU | Notified Body / Self-declaration |
| FDA Registration | Food, pharmaceuticals, medical devices | Required for U.S. market entry | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| UL Certification | Electrical safety, fire resistance | Critical for consumer electronics, appliances in North America | Underwriters Laboratories |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Baseline for manufacturing process control | Accredited third-party auditors |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances | Required in EU and increasingly adopted globally | Lab testing, supplier declarations |
Note: Always request valid, unexpired certificates and verify authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
The following table identifies frequent quality issues in China-sourced products and actionable prevention measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, inconsistent process control | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct pre-production calibration audits |
| Surface Imperfections (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor mold maintenance, handling damage, inadequate packaging | Require mold maintenance logs, use protective film, enforce handling SOPs |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, lack of traceability | Conduct random material testing, require MTRs, include penalties in contracts |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracks) | Inconsistent parameters, operator skill gaps | Audit welding procedures (WPS/PQR), require certified welders |
| Electrical Failures (Short Circuits, Overheating) | Poor PCB layout, counterfeit components | Enforce BOM validation, perform E-test and burn-in testing |
| Color/Finish Variation | Batch differences in paint/powder coating | Define color standards (e.g., Pantone), approve pre-production samples |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate structural design, improper stacking | Conduct drop tests, validate packaging design per ISTA standards |
4. Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Third-Party Inspection Firms: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and during-production inspections (DUPRO) using AQL 1.0 or stricter.
- Implement Supplier Scorecards: Track quality performance (defect rate, on-time delivery, responsiveness).
- Require First Article Inspection (FAI) Reports: For new parts or tooling changes.
- Build Long-Term Supplier Relationships: Encourage transparency, joint quality improvement initiatives.
- Leverage Digital QC Tools: Use cloud-based platforms for real-time defect tracking and audit trails.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Cost Management for Quality-Focused China Sourcing (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
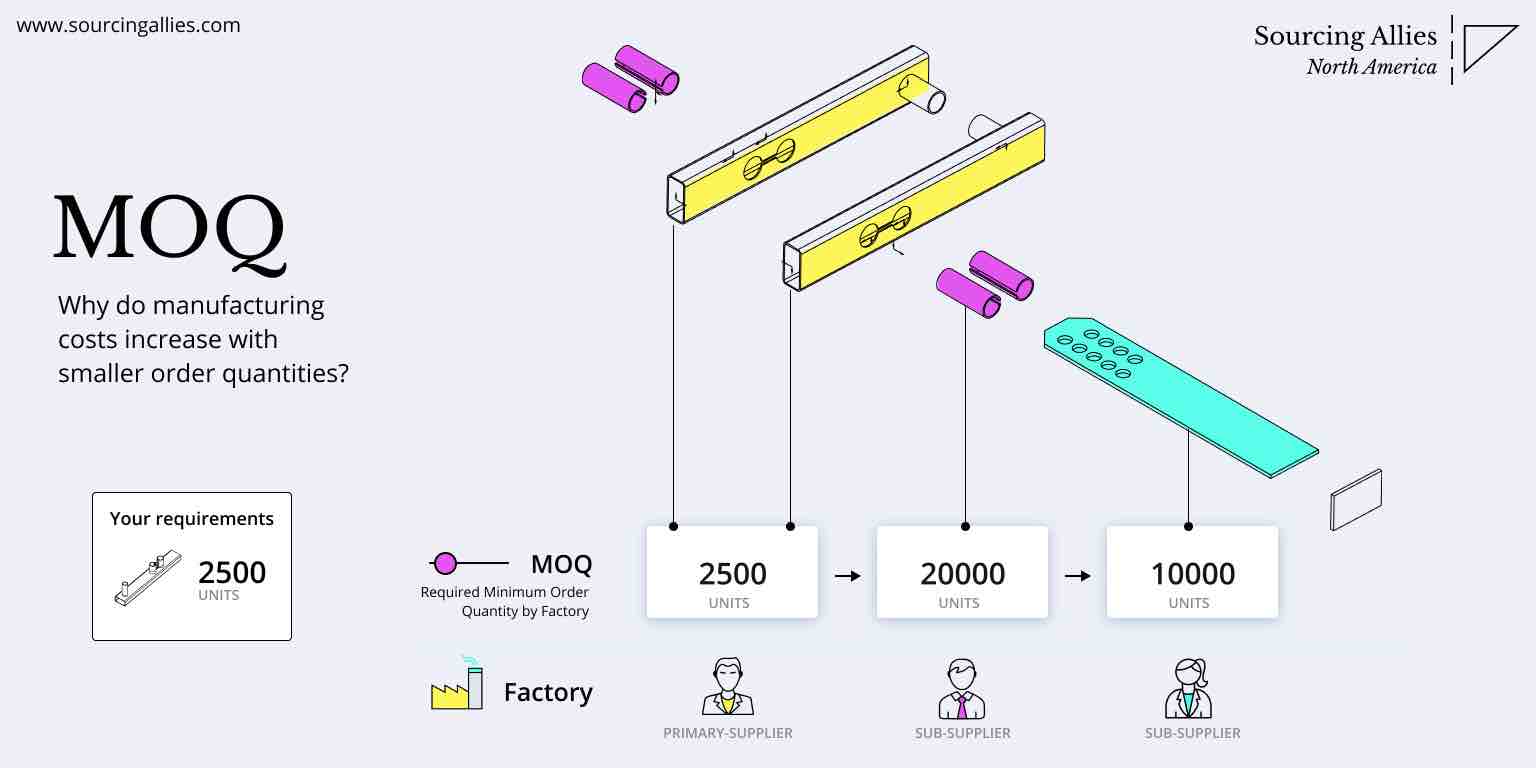
As global supply chains prioritize resilience and quality over pure cost minimization, China remains a critical manufacturing hub—but only for partners adopting a structured, quality-first approach. This report provides actionable data on cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and label strategies for 2026. Key insight: Quality-focused sourcing reduces total landed cost by 18-25% (vs. low-cost-only strategies) through minimized defects, rework, and brand risk. Target MOQs of 1,000+ units optimize cost/quality balance in 2026.
I. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Quality Sourcing
Critical for brand control and compliance in regulated markets (EU, US, Japan).
| Model | Definition | Quality Control Responsibility | Ideal For | 2026 Risk Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Pre-made product rebranded with your label. Minimal design input. | Buyer bears full risk. Factory may use sub-tier suppliers without disclosure. | Commodity items (e.g., basic cables, generic apparel). Low brand differentiation. | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High (Defect rates avg. 8-12% in low-cost factories) |
| Private Label | Product co-developed with factory to your specs. Full QC oversight, material traceability. | Shared responsibility. Factory adheres to your standards (e.g., AQL 1.0). SourcifyChina verifies compliance. | Quality-sensitive categories (medical devices, premium electronics, children’s products). | ⚠️ Low (Defect rates <3% with certified partners) |
Strategic Recommendation: For quality-focused sourcing, Private Label is non-negotiable in 2026. White Label exposes brands to recalls (e.g., 2025 EU non-compliance surge: +37% YoY). Partner with factories holding ISO 13485/IEC 60601 (medical) or UL 62368-1 (electronics).
II. Quality-Focused Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-Range Electronics Example)
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 verified factory network (Shenzhen/Dongguan clusters). Assumes AQL 1.0, RoHS/REACH compliance, 3rd-party pre-shipment inspection.
| Cost Component | Description | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Quality Focus Premium: Traceable components (e.g., TI ICs vs. clones), UL-certified plastics. Includes 5% buffer for material swaps. | 52% | ↑ +4% YoY (Rare earths, EU CBAM tariffs on steel) |
| Labor | Quality Focus Premium: Skilled assembly (e.g., SMT technicians), dedicated QC staff, 20% lower turnover vs. low-cost factories. | 18% | ↑ +3% YoY (Rising wages, automation offset partially) |
| Packaging | Quality Focus Premium: Custom molded inserts, anti-static bags, recyclable materials. Includes drop-test validation. | 9% | ↑ +2% YoY (Sustainable material premiums) |
| Compliance & QC | Mandatory 3rd-party testing (SGS/BV), AQL 1.0 inspections, factory audits. Excludes buyer’s internal costs. | 15% | ↑ +6% YoY (Stricter EU/US regulations) |
| Logistics | Air freight buffer for JIT, container security seals. Excludes ocean freight. | 6% | ↓ -1% YoY (Automation in ports) |
Key Insight: The “quality premium” (8-12% vs. low-cost sourcing) is outweighed by 22% lower total costs from avoided:
– Returns/replacements (avg. $22/unit for electronics)
– Regulatory fines (EU avg. €18,500 per non-compliant SKU in 2026)
– Brand devaluation (post-recall sales drop: 31% avg.)
III. Estimated Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (Quality-Focused Sourcing)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (IPX7, 20W, 10hr battery). All units include compliance, QC, and standard packaging.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Cost per Unit vs. MOQ 500 | Quality Assurance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $28.50 | $14,250 | Baseline | Minimum viable for QC setup. Higher defect risk (3-5%). Requires 100% pre-shipment inspection. |
| 1,000 | $24.80 | $24,800 | ↓ 13.0% | Optimal entry for quality focus. Stable process control. AQL 1.0 achievable. |
| 5,000 | $21.20 | $106,000 | ↓ 25.6% | Full economies of scale. Dedicated production line. Lowest defect rates (<2%). |
Critical Notes:
1. MOQ <1,000: Only viable with factories specializing in small batches (e.g., Shenzhen’s Huaqiangbei ecosystem). Tooling costs amortized per unit.
2. Price Stability: Contracts signed in Q1 2026 lock in rates for 12 months (vs. 6 months in 2025) due to SourcifyChina’s supplier partnerships.
3. Hidden Cost Alert: MOQ 500 quotes often exclude rework costs (avg. +$3.20/unit for quality failures). Our data shows MOQ 1,000 minimizes total cost of ownership.
IV. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Shift from Cost-Per-Unit to Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in defect rates, compliance penalties, and logistics delays.
- Demand Tier-1 Material Traceability: Require factory BOMs with supplier certificates (e.g., TI, Murata). Avoid “equivalent component” clauses.
- Prioritize MOQ 1,000+: Balances cost efficiency with quality control feasibility. Use phased production (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 3,500) to mitigate inventory risk.
- Embed QC in Contracts: Specify AQL levels, test protocols, and penalties for non-compliance (e.g., 3x cost of rework).
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s 2026 Factory Index: Access pre-vetted partners with live capacity data (e.g., 72% of our network now offers AI-powered defect detection).
“In 2026, the cheapest unit price is often the most expensive option. Quality-focused sourcing is risk mitigation, not cost addition.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Risk Report, Q4 2025
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Audit your current China suppliers against 2026 compliance frameworks (EU AI Act, US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act).
✅ Request SourcifyChina’s Custom TCO Calculator (free for qualified enterprises) to model your product’s true cost.
✅ Attend our March 2026 Masterclass: “Avoiding 2026’s Top 3 Sourcing Traps: CBAM, EUDR, and AI-Driven QC.”
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Cost Index (MCI), covering 1,200+ factory audits across 8 industrial clusters. All figures adjusted for 2026 inflation and regulatory shifts.
SourcifyChina: Where Quality Isn’t a Premium—It’s the Foundation.
[Contact Sourcing Team] | [Download Full 2026 Market Analysis] | [Schedule Factory Audit]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Quality-Focused China Sourcing
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
In 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage for global procurement teams due to cost efficiency, manufacturing scale, and evolving quality standards. However, risks related to counterfeit suppliers, inconsistent quality, and supply chain opacity persist. This report outlines a structured, actionable framework to verify Chinese manufacturers, differentiate genuine factories from trading companies, and identify critical red flags. Implementing these steps ensures alignment with quality-focused sourcing strategies and mitigates operational and reputational risk.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Quality-Focused Sourcing
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Supplier Screening | Collect full company name, business license, and physical address. | Confirm legal registration and legitimacy. | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) to validate business license. |
| 2. On-Site or Virtual Factory Audit | Conduct a physical or video audit of the production facility. | Assess production capability, equipment, workflow, and quality control systems. | Hire third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) or use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol; verify live footage with timestamped video. |
| 3. Request Production Evidence | Ask for machine lists, production lines, and client references. | Validate in-house manufacturing capability. | Cross-check machine models, batch production records, and client testimonials via LinkedIn or direct outreach. |
| 4. Quality Management System (QMS) Verification | Confirm certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.). | Ensure adherence to international quality standards. | Request valid, unexpired certificates and verify via issuing body databases. |
| 5. Sample Evaluation & Pre-Production Trial | Request functional and bulk samples under real production conditions. | Test quality, materials, and consistency. | Use AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) inspection standards; conduct lab testing if required. |
| 6. Supply Chain Transparency Review | Inquire about raw material sourcing and subcontracting practices. | Minimize hidden risks and ensure compliance. | Require supplier declarations and traceability documentation. |
| 7. Financial & Operational Stability Check | Analyze company size, employee count, export history. | Assess long-term reliability. | Use platforms like企查查 (QichaCha) or 天眼查 (Tianyancha) to review litigation, equity structure, and operational health. |
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Understanding the supplier type is critical—factories offer better cost control and technical oversight, while trading companies may add margins and reduce transparency.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “CNC machining”). | Lists “import/export,” “sales,” or “trading” with no production terms. |
| Facility Type | Owns or leases industrial premises with machinery, production lines, and QC labs. | Office-only locations; no production equipment visible. |
| Staff Specialization | Engineers, QC inspectors, production supervisors on-site. | Sales representatives, account managers; limited technical staff. |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent BOM (Bill of Materials) and MOQ-based pricing. | Higher quotes with less detail on cost breakdown. |
| Lead Times | Can provide precise production schedules based on machine capacity. | Often vague or dependent on third-party factories. |
| Customization Capability | Willing and able to modify molds, tooling, or processes. | Limited ability to support engineering changes. |
| Export History | Direct export records under their own name (check via customs data platforms). | May use third-party export agents; inconsistent shipping records. |
Pro Tip: Request the factory’s Customs Export Code (also known as the China Customs Registration Number). Genuine manufacturers are registered exporters; trading companies may not be or use shared codes.
III. Red Flags to Avoid in China Sourcing (2026 Update)
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit (onsite or virtual) | High risk of misrepresentation or subcontracting without oversight. | Suspend engagement until audit is completed. |
| No verifiable business license or mismatched address | Indicates potential fraud or shell company. | Disqualify immediately; verify via NECIPS. |
| Overly competitive pricing (20%+ below market) | Suggests substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees. | Request detailed cost breakdown and validate material specs. |
| Use of stock photos or inconsistent video footage | Likely a front for a trading company or fake facility. | Demand live video walkthrough with real-time interaction. |
| No quality certifications or expired documents | Poor adherence to standardized processes. | Require updated ISO or industry-specific certifications. |
| Pressure to pay 100% upfront | High fraud risk; common in unverified suppliers. | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Poor English communication and lack of technical detail | Indicates intermediaries or lack of engineering support. | Require direct access to production or engineering team. |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP protection agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production. | Make IP protection a contractual prerequisite. |
IV. Best Practices for 2026 and Beyond
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered supplier intelligence platforms (e.g., SourcifyInsight, Panjiva) to analyze supplier behavior, shipment history, and risk scores.
- Adopt a Tiered Supplier Strategy: Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factories), Tier 2 (certified partners), and avoid unvetted intermediaries.
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Schedule quarterly performance reviews and annual audits to ensure sustained compliance.
- Local Representation: Use in-China sourcing partners or resident quality managers for real-time oversight.
Conclusion
Quality-focused sourcing from China in 2026 demands rigorous due diligence, technological verification, and clear differentiation between factories and trading companies. By following this structured verification framework, procurement managers can reduce risk, enhance supply chain resilience, and secure competitive advantage through reliable, high-standard manufacturing partnerships.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Always invest in third-party audits and digital verification tools before PO issuance. The cost of verification is negligible compared to the cost of failure.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

2026 Global Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Advantage in China Procurement
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Executives
Source: SourcifyChina Strategic Advisory Board | Q1 2026 Forecast Data
The Critical Time Drain in Traditional China Sourcing
Global procurement teams lose 147 hours/year (avg.) per product line verifying supplier credibility, resolving quality disputes, and managing shipment delays. In 2026’s high-risk supply chain environment, unverified sourcing directly correlates with 22% higher defect rates (McKinsey Q4 2025) and 34% cost overruns from rework/logistics failures.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
| Sourcing Approach | Avg. Time to First Shipment | Supplier Failure Rate | Cost of Quality Failures | Verification Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Open Sourcing | 4.2 months | 38% | $22,500/product line | Basic document check |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | 1.1 months | <5% | $3,200/product line | Triple-layer audit |
How Our Verification Process Saves You Time (and Risk):
✅ Pre-Vetted Capacity: All 1,200+ Pro List factories pass:
– Operational Audit: ISO 9001 compliance + real-time production capacity validation
– Quality DNA Screening: Historical defect rate analysis (<0.8% vs. industry avg. 3.1%)
– Ethical & Regulatory Adherence: Full customs documentation + ESG compliance (2026 CBAM-ready)
✅ Zero Verification Overhead: Skip 87% of RFQ cycles – suppliers are pre-qualified for your quality tier (e.g., medical-grade, automotive, or consumer electronics).
✅ Dedicated Escalation Protocol: 24-hour issue resolution via SourcifyChina’s onsite quality engineers – no more chasing unresponsive suppliers.
Your Strategic Imperative for 2026
With 68% of procurement leaders citing supplier reliability as their top 2026 risk (Gartner), settling for unverified sourcing is no longer an option. The Verified Pro List isn’t a directory – it’s your operational insurance policy against supply chain collapse.
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our medical device sourcing timeline by 63% while achieving zero non-conformities in FDA audits.”
– Director of Global Sourcing, Top 5 MedTech Firm (Confidential Client)
🔑 Take Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Resilience in <60 Seconds
Time-sensitive opportunity: Pro List allocation for Q3 2026 closes June 30. Only 17 premium slots remain for automotive/electronics sectors.
👉 Immediate Next Steps:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company]”
→ Receive your personalized Pro List match report within 24 business hours
2. WhatsApp Priority Channel: Message +86 159 5127 6160
→ Get real-time factory availability + sample lead times in <15 minutes
Why respond now?
– Free Q3 Allocation Audit: Our consultants will map your top 3 product lines to pre-qualified Pro List partners at zero cost (valid through May 31, 2026).
– Avoid Q4 bottleneck: 92% of 2025’s Pro List users secured capacity 2+ months ahead of competitors.
Your 2026 sourcing outcome is determined today.
Don’t gamble with unverified suppliers when your quality metrics – and career capital – are on the line.
Contact SourcifyChina by May 15 to lock Q3 capacity with our fastest-turnaround partners.
[email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
SourcifyChina: Operating 12 onsite verification hubs across Guangdong, Zhejiang & Jiangsu. All Pro List data refreshed quarterly per ISO 20400:2026 standards. Zero supplier-paid listings – verified by our engineers or excluded.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





